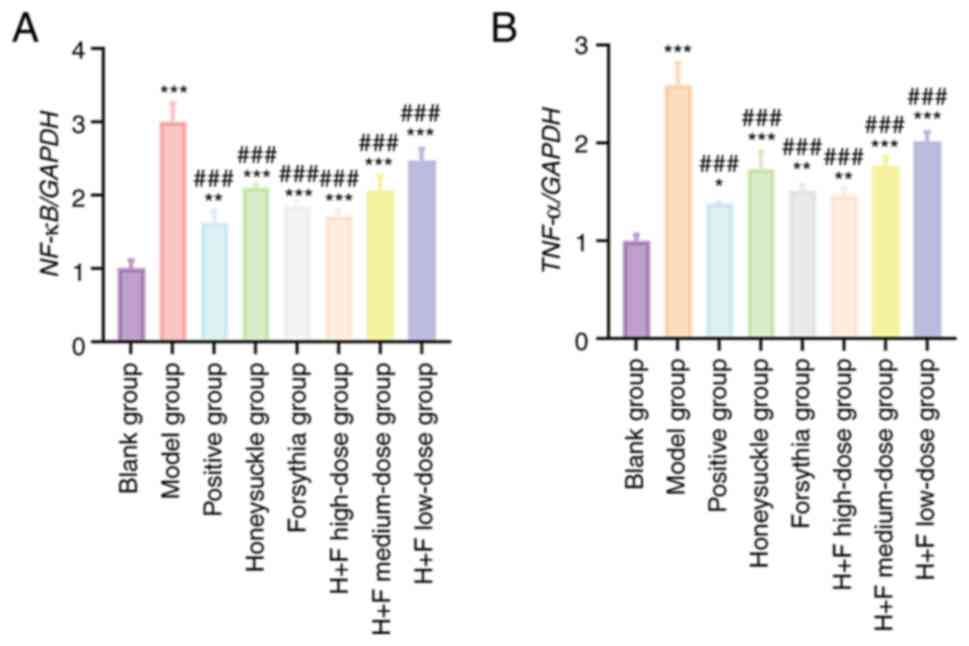
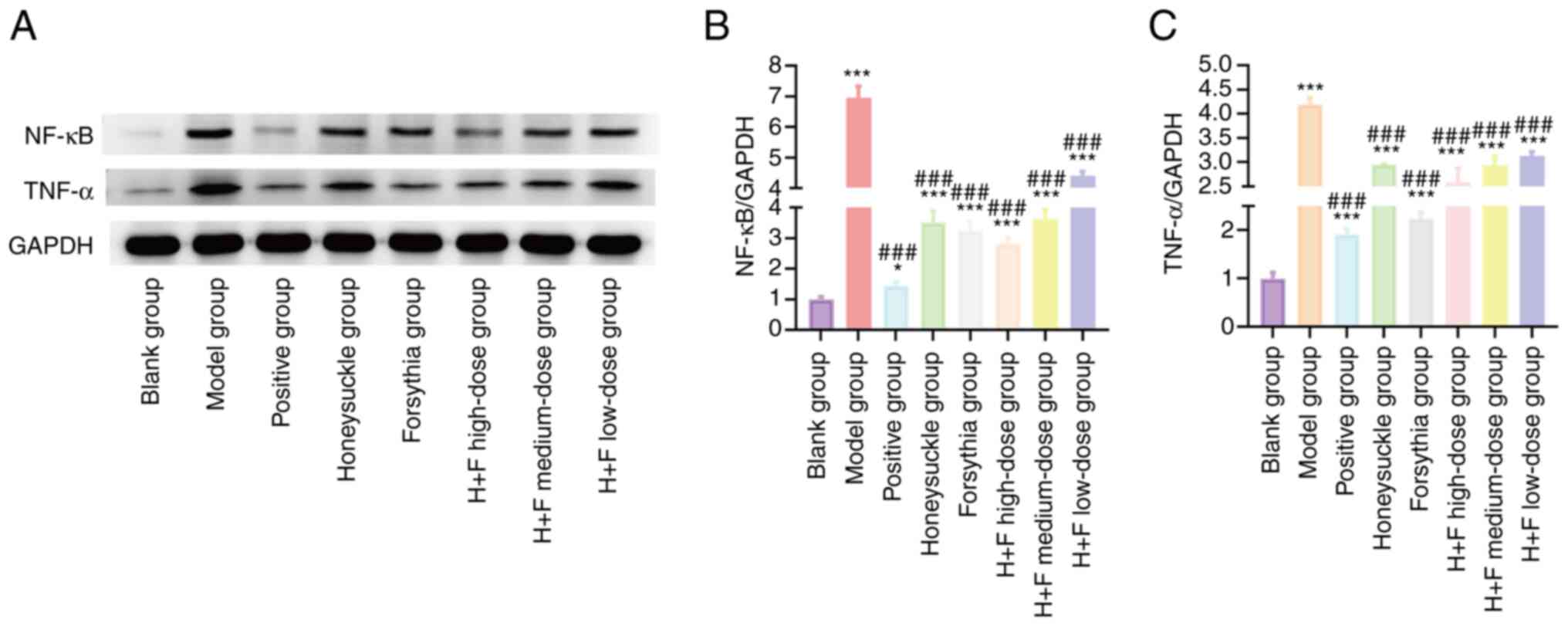
|
1
|
Shen Tao-Ye, Guo Jian-Hao and Wang
Xiao-Juan: Research progress in the treatment of acute lung injury.
Chin Mod Applied Pharm. 38:366–370. 2021.
|
|
2
|
Messer MP, Kellermann P, Weber SJ, Hohmann
C, Denk S, Klohs B, Schultze A, Braumüller S, Huber-Lang MS and
Perl M: Silencing of fas, fas associated via death domain, or
caspase 3 differentially affects lung inflammation, apoptosis, and
development of trauma-induced septic acute lung injury. Shock.
39:19–27. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jia Xuemei and Yang Guangfu: Research
progress on pathogenesis of acute lung injury/acute respiratory
distress syndrome. Chin Pract Med. 6(242)2011.
|
|
4
|
Yuan Wei, Yang Hui, Xie Yong, et al:
Effect of Forsythiaside A on regulatory T cells in mice with
systemic endotoxemia. Chin Patent Med. 36:1584–1588. 2014.
|
|
5
|
Bakowitz M, Bruns B and McCunn M: Acute
lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in the
injured patient. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med.
20(54)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bellani G, Laffey JG, Pham T, Fan E,
Brochard L, Esteban A, Gattinoni L, van Haren F, Larsson A, McAuley
DF, et al: Epidemiology, patterns of care, and mortality for
patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care
units in 50 countries. JAMA. 315:788–800. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ma Xiaolong, Chen Yueru and Shen Feiyan:
Research progress on therapeutic effect and mechanism of
traditional Chinese medicine in acute lung injury. CJMAP.
39:269–276. 2022.
|
|
8
|
Xue Bingquan, Zhu Yanhui and Yu Haiyan:
Study on the mechanism of Fructus Forsythiae in the treatmen to
facute lung injury basedon UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and network
pharmacology. Chin J Hosp Pharm. 42:2208–2215. 2022.
|
|
9
|
Yang R, Lu Y, Hao H, Zhang MD, Xuan J and
Zhang YQ: Research progress on the chemical constituents and
pharmacological activities of iridoid glycosides in Lonicera
japonica. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 46:2746–2752. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Xiao Xie Mengzhou and Gan Long:
Determination of chlorogenic acid and total flavonoids in Lonicera
japonica thunb and Lonicera japonica thunb. Chin Herb Med.
50:210–216. 2019.
|
|
11
|
Ji Hua, Wang Lin and Zhang Haixin:
Forsythia the Taoist traditional Chinese medicine in Hebei
province. Mod Rural Sci Technol. 2021(125)2021.
|
|
12
|
Gong L, Wang C, Zhou H, Ma C, Zhang Y,
Peng C and Li Y: A review of pharmacological and pharmacokinetic
properties of Forsythiaside A. Pharmacol Res.
169(105690)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang HX, Liu QP, Zhou YX, Chen YY, An P,
Xing YZ, Zhang L, Jia M and Zhang H: Forsythiasides: A review of
the pharmacological effects. Front Cardiovasc Med.
9(971491)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ding Z, Zhong R, Yang Y, Xia T, Wang W,
Wang Y, Xing N, Luo Y, Li S, Shang L and Shu Z: Systems
pharmacology reveals the mechanism of activity of Ge-Gen-Qin-Lian
decoction against LPS-induced acute lung injury: A novel strategy
for exploring active components and effective mechanism of TCM
formulae. Pharmacol Res. 156(104759)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ding Z, Zhong R, Xia T, Yang Y, Xing N,
Wang W, Wang Y, Yang B, Sun X and Shu Z: Advances in research into
the mechanisms of Chinese Materia Medica against acute lung injury.
Biomed Pharmacother. 122(109706)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liang C, Hui N, Liu Y, Qiao G, Li J, Tian
L, Ju X, Jia M, Liu H, Cao W, et al: Insights into forsythia
honeysuckle (Lianhuaqingwen) capsules: A Chinese herbal medicine
repurposed for COVID-19 pandemic. Phytomed Plus.
1(100027)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang H, Xu L, Song J, Zhang A, Zhang X,
Li Q, Qu X and Wang P: Establishment of quality evaluation method
for Yinqiao powder: A herbal formula against COVID-19 in China. J
Anal Methods Chem. 2022(1748324)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ding X, Lin Z and Wang D: Research
progress on constituents and pharmacological actions of Lonicerae
Japonicae Flos, Forsythiae Fructus and their combination. Shandong
science. 32:36–41. 2019.
|
|
19
|
Huang H: [The inheritance and development
of Shang han lun (Treatise on cold pathogenic diseases) in the
perspective of Wu Jutong's Wen bing tiao bian (Treatise on
differentiation and treatment of seasonal warm diseases)]. Zhonghua
Yi Shi Za Zhi. 32:36–38. 2002.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Kong Yurong, Li Yan, Chen Yifan, et al:
Analysing Wu Jutong's experience of using honeysuckle-forsythia
from the theory of disposition and flavour matching. Modern Chinese
Medicine Clinic. 29(52-54-67)2022.
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Cai W, Weng X, Li Q, Wang Y, Chen Y,
Zhang W, Yang Q, Guo Y, Zhu X and Wang H: Lonicerae Japonicae Flos
and Lonicerae Flos: A systematic pharmacology review. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2015(905063)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen Y, Zhang C, Wang N and Feng Y:
Deciphering suppressive effects of Lianhua Qingwen Capsule on
COVID-19 and synergistic effects of its major botanical drug pairs.
Chin J Nat Med. 21:383–400. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu H, Huang L and Xu Y: [Simultaneous
determination of five effective components in Qingrejiedu oral
liquid using high performance liquid chromatography-mass
spectrometry]. Se Pu. 26:599–602. 2008.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Li R, Zhu Y, Yu M, Liu T, Zhao Y and Yu Z:
Study on the mechanism of anti-acute lung injury of Shuanghuanglian
oral liquid based on identification of transitional components in
blood and network pharmacology. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol
Biomed Life Sci. 1212(123498)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lin L: [Application of differential
derivative spectrophotometry to the determination of total
chlorogenic acid in Lonicera japonica Thunb. and yinqiao jiedu
pian]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 16:282–284 and 318.
1991.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Ye J, Li L and Hu Z: Exploring the
molecular mechanism of action of Yinchen Wuling powder for the
treatment of hyperlipidemia, using network pharmacology, molecular
docking, and molecular dynamics simulation. Biomed Res Int.
2021(9965906)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US), Washington (DC), 2011.
|
|
28
|
Xu X, Zhang W, Huang C, Li Y, Yu H, Wang
Y, Duan J and Ling Y: A novel chemometric method for the prediction
of human oral bioavailability. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6964–6982.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ru J, Li P, Wang J, Zhou W, Li B, Huang C,
Li P, Guo Z, Tao W, Yang Y, et al: TCMSP: A database of systems
pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J
Cheminform. 6(13)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, Gindulyte A, He J,
He S, Li Q, Shoemaker BA, Thiessen PA, Yu B, et al: PubChem in
2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids
Res. 49:D1388–D1395. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen X, Ji ZL and Chen YZ: TTD:
Therapeutic target database. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:412–415.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Gorodkin J and
Jensen LJ: Cytoscape StringApp: Network analysis and visualization
of proteomics data. J Proteome Res. 18:623–632. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: A cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Huang JH, Huang XH, Chen ZY, Zheng QS and
Sun RY: Dose conversion among different animals and healthy
volunteers in pharmacological study. Chinese Clinical Pharmacology
and Therapeutics. 9:1069–1072. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Zhou L, Yang H, Ai Y, Xie Y and Fu Y:
Protective effect of Forsythiaside A on acute lung injury induced
by lipopolysaccharide in mice. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
30:151–154. 2014.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Arocho A, Chen B, Ladanyi M and Pan Q:
Validation of the 2-deltadeltaCt calculation as an alternate method
of data analysis for quantitative PCR of BCR-ABL P210 transcripts.
Diagn Mol Pathol. 15:56–61. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang Z, Yu T, Hou Y, Zhou W, Ding Y and
Nie H: Nie H: Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for ALI/ARDS:
Therapeutic potential and challenges. Curr Pharm Des. 28:2234–2240.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Nova Z, Skovierova H and Calkovska A:
Alveolar-Capillary membrane-related pulmonary cells as a target in
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Int J Mol Sci.
20(831)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Geng Q, Liu B, Zhao PC, Xiong YB, Li L, Yi
JF and Lyu C: Molecular mechanism of Fagopyri Dibotryis Rhizoma in
treatment of acute lung injury based on network pharmacology and in
vitro experiments. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 46:4816–4823.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Wu J, Zhang F, Li Z, Jin W and Shi Y:
Integration strategy of network pharmacology in Traditional Chinese
Medicine: A narrative review. J Tradit Chin Med. 42:479–486.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
D'Alessio FR: Mouse models of acute lung
injury and ARDS. Methods Mol Biol. 1809:341–350. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Huang CY, Deng JS, Huang WC, Jiang WP and
Huang GJ: Attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by hispolon in mice, through regulating the
TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways, and suppressing
oxidative stress-mediated er stress-induced apoptosis and
autophagy. Nutrients. 12(1742)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li WW, Wang TY, Cao B, Liu B, Rong YM,
Wang JJ, Wei F, Wei LQ, Chen H and Liu YX: Synergistic protection
of matrine and lycopene against lipopolysaccharide-inducedacute
lung injury in mice. Mol Med Rep. 20:455–462. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang J, Luo L, Zhao X, Xue X, Liao L, Deng
Y, Zhou M, Peng C and Li Y: Forsythiae Fructuse extracts alleviates
LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice by regulating PPAR-γ/RXR-α in
lungs and colons. J Ethnopharmacol: 293:115322,2022. doi:
10.1016/j.jep.2022.115322.
|
|
45
|
Liu C, Xiao K and Xie L: Progress in
preclinical studies of macrophage autophagy in the regulation of
ALI/ARDS. Front Immunol. 13(922702)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Li Q, Yin J, Ran QS, Yang Q, Liu L, Zhao
Z, Li YJ, Chen Y, Sun LD, Wang YJ, et al: [Efficacy and mechanism
of Lianhua Qingwen Capsules(LHQW) on chemotaxis of macrophages in
acute lung injury (ALI) animal model]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
44:2317–2323. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
47
|
Wang Y, Yuan Y, Wang W, He Y, Zhong H,
Zhou X, Chen Y, Cai XJ and Liu LQ: Mechanisms underlying the
therapeutic effects of Qingfeiyin in treating acute lung injury
based on GEO datasets, network pharmacology and molecular docking.
Comput Biol Med. 145(105454)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liu Jiao and Li Mingchun: The relationship
between PI3K/ATK pathway and EGFR tyrosine-kinase inhibitor
resistance. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology. 29:1648–1650.
2013.
|
|
49
|
Liu B, Yu H, Baiyun R, Lu J, Li S, Bing Q,
Zhang X and Zhang Z: Protective effects of dietary luteolin against
mercuric chloride-induced lung injury in mice: Involvement of
AKT/Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 113:296–302.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhan Q, Ma X and He Z: PEAR1 suppresses
the proliferation of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via
PI3K/AKT pathway in ALI model. Microvasc Res.
128(103941)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lai WY, Wang JW, Huang BT, Lin EP and Yang
PC: A novel TNF-α-targeting aptamer for TNF-α-mediated acute lung
injury and acute liver failure. Theranostics. 9:1741–1751.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yang Z, Zhang XR, Zhao Q, Wang SL, Xiong
LL, Zhang P, Yuan B, Zhang ZB, Fan SY, Wang TH and Zhang YH:
Knockdown of TNF-α alleviates acute lung injury in rats with
intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury by upregulating IL-10
expression. Int J Mol Med. 42:926–934. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Peng LY, Yuan M, Song K, Yu JL, Li JH,
Huang JN, Yi PF, Fu BD and Shen HQ: Baicalin alleviated
APEC-induced acute lung injury in chicken by inhibiting NF-κB
pathway activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 72:467–472.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Millar MW, Fazal F and Rahman A:
Therapeutic targeting of NF-κB in acute lung injury: A double-edged
sword. Cells. 11(3317)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zhang JB, Jin HL, Feng XY, Feng SL, Zhu
WT, Nan HM and Yuan ZW: The combination of Lonicerae Japonicae
Flos and Forsythiae Fructus herb-pair alleviated
inflammation in liver fibrosis. Front Pharmacol.
13(984611)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Shen F, Zou LS, Wen HM, Cui XB, Yu S, Zhu
HX, Li C, Tian G and Shao JG: Qualitative evaluation of Forsythia
suspensa by HPLC-PDA fingerprint combined with UFLC-QTOF-MS
qualitative identification. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
44:4495–4603. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
57
|
Landelle C, Nocquet Boyer V, Abbas M,
Genevois E, Abidi N, Naimo S, Raulais R, Bouchoud L, Boroli F,
Terrisse H, et al: Impact of a multifaceted prevention program on
ventilator-associated pneumonia including selective oropharyngeal
decontamination. Intensive Care Med. 44:1777–1786. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Yang B, Meng QY, Chen H, Gao YL, Shen J,
Mu YY and Xia YB: Clinical effect of acupuncture combined with
traditional Chinese medicine in treatment of
oligozoospermia/asthenozoospermia: A meta-analysis. Zhen Ci Yan
Jiu. 45:243–250. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
59
|
Gaweł S, Wardas M, Niedworok E and Wardas
P: Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker. Wiad Lek.
57:453–455. 2004.PubMed/NCBI(In Polish).
|
|
60
|
Miao L and St Clair DK: Regulation of
superoxide dismutase genes: Implications in disease. Free Radic
Biol Med. 47:344–356. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Yang L, Bi L, Jin L, Wang Y, Li Y, Li Z,
He W, Cui H, Miao J and Wang L: Geniposide ameliorates liver
fibrosis through reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory
respose, inhibiting apoptosis and modulating overall metabolism.
Front Pharmacol. 12(772635)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Xu W, Wang M, Cui G, Li L, Jiao D, Yao B,
Xu K, Chen Y, Long M, Yang S and He J: Astaxanthin protects
OTA-Induced lung injury in mice through the Nrf2/NF-κB pathway.
Toxins (BaseL). 11(540)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhu S, Wei X, Yang X, Huang Z, Chang Z,
Xie F, Yang Q, Ding C, Xiang W, Yang H, et al: Plasma
lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 and superoxide dismutase
are independent predicators of cognitive impairment in cerebral
small vessel disease patients: Diagnosis and assessment. Aging Dis.
10:834–846. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Mauad T, Duarte-Neto AN, da Silva LFF, de
Oliveira EP, de Brito JM, do Nascimento ECT, de Almeida Monteiro
RA, Ferreira JC, de Carvalho CRR, do Nascimento Saldiva PH and
Dolhnikoff M: Tracking the time course of pathological patterns of
lung injury in severe COVID-19. Respir Res. 22(32)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Tang J, Xu L, Zeng Y and Gong F: Effect of
gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the
TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol: 91:107272,2021.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107272.
|