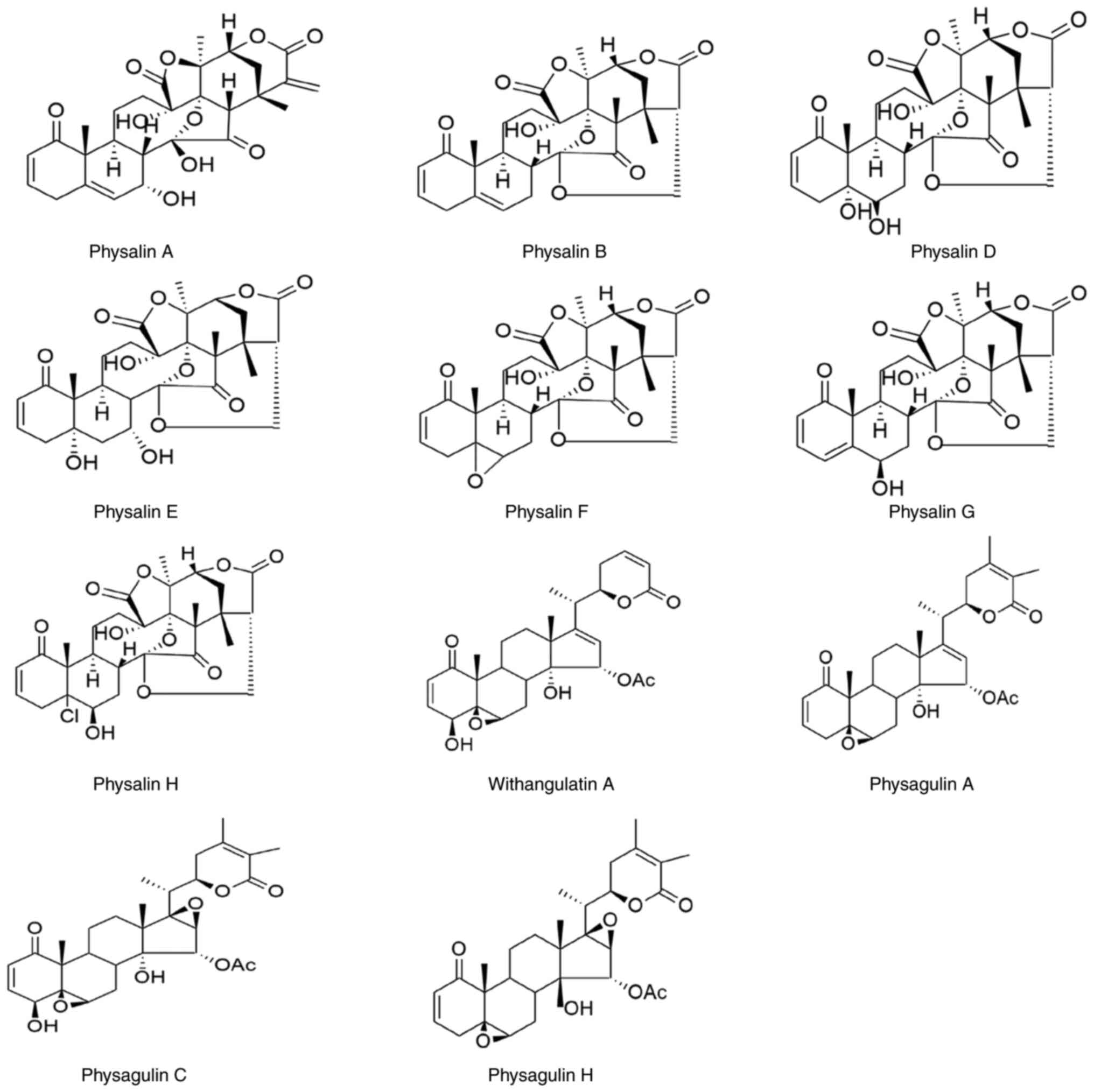
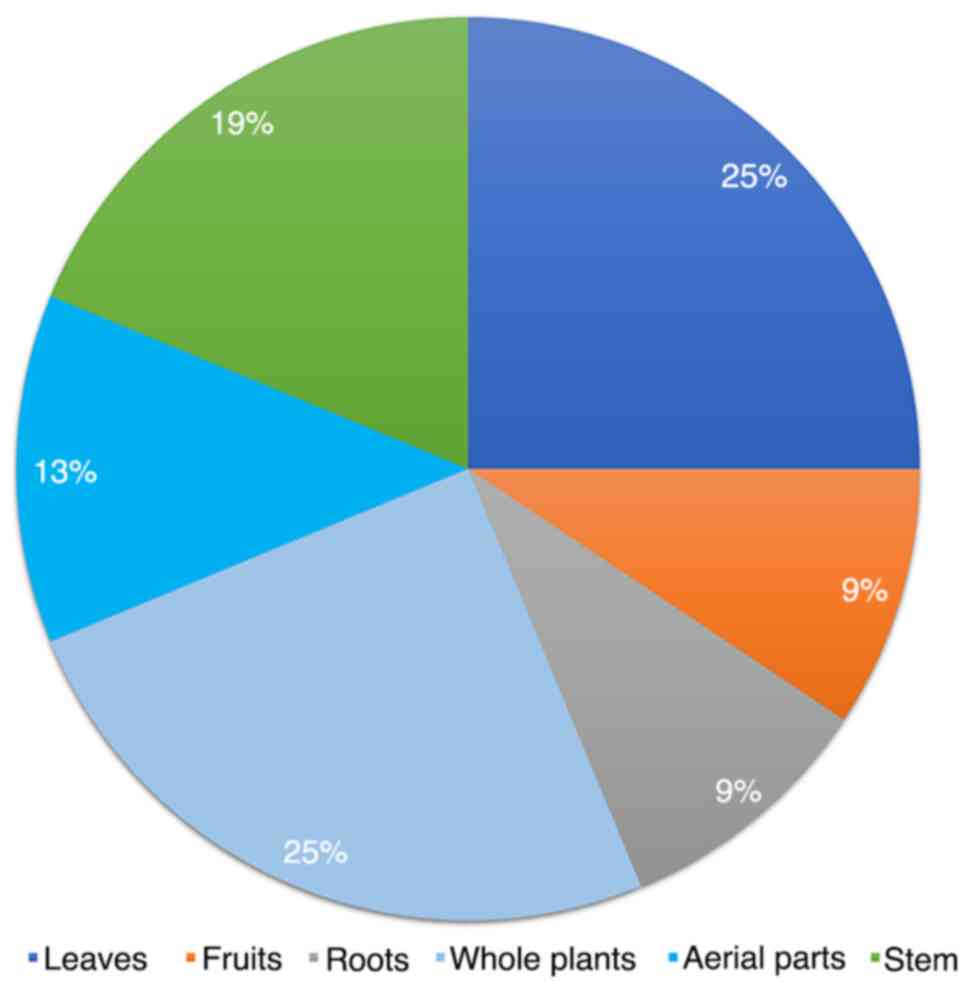
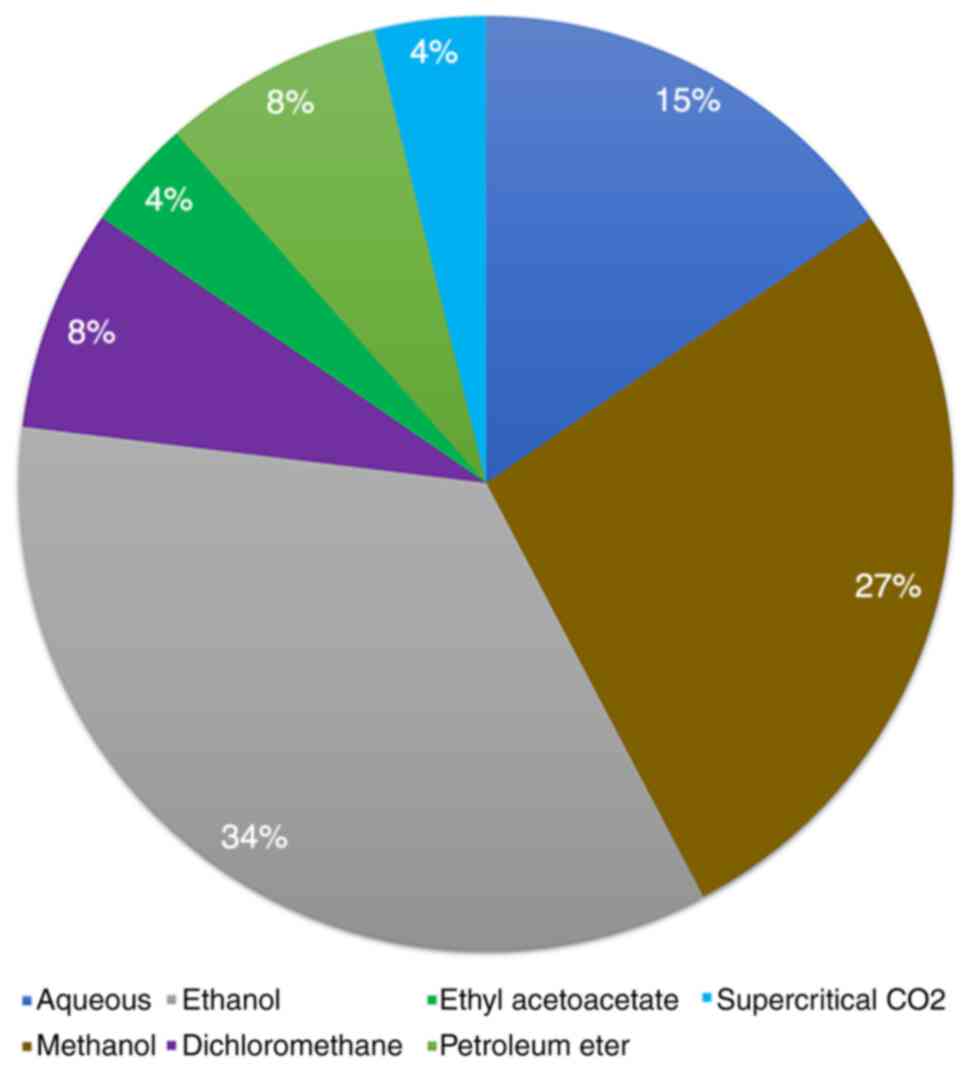
|
1
|
Kasali FM, Tusiimire J, Kadima JN, Tolo
CU, Weisheit A and Agaba AG: Ethnotherapeutic uses and
phytochemical composition of Physalis peruviana L.: An
overview. ScientificWorldJournal. 2021(5212348)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mahklouf MH: The first record of
Physalis angulata L. (Solanaceae) for the flora of
Libya. Biodiv Res Conserv. 53:67–71. 2019.
|
|
3
|
Ramakrishna Pillai J, Wali AF, Menezes GA,
Rehman MU, Wani TA, Arafah A, Zargar S and Mir TM: Chemical
composition analysis, cytotoxic, antimicrobial and antioxidant
activities of Physalis angulata L.: A comparative study of
leaves and fruit. Molecules. 27(1480)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gao CY, Ma T, Luo J and Kong LY: Three new
cytotoxic withanolides from the Chinese folk medicine Physalis
angulata. Nat Prod Commun. 10:2059–2062. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hadiyanti N, Supriyadi S and Pardono P:
Keragaman beberapa tumbuhan ciplukan (Physalis spp.) di lereng
gunung kelud, jawa timur. Berita Biologi. 17:135–146. 2018.
|
|
6
|
Fadhli H, Ruska Sl, Furi M, Suhery WN,
Susanti E and Nasution MR: Ciplukan (Physalis angulata L.):
Review tanaman liar yang berpotensi sebagai tanaman obat. J Farm
Indones. 15:134–141. 2023.
|
|
7
|
Rivera DE, Ocampo YC, Castro JP, Caro D
and Franco LA: Antibacterial activity of Physalis angulata
L., Merremia umbellataL., and Cryptostegia grandiflora Roxb. Ex
R.Br. -medicinal plants of the Colombian Northern Coast. Orient
Pharm Exp Med. 15:95–102. 2015.
|
|
8
|
Hananto H, Rahman A and Fahmi M:
Antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of morel berry
(Physalis angulata L.) towards Staphylococcus aureus.
Malays J Med Health Sci. 17:132–135. 2021.
|
|
9
|
Gagare SB, Chavan SL and Sagade AB:
Antibacterial potential and phytochemical screening of Physalis
angulata and solanum virgianum. Int J Res Biosci Agric Technol.
1:36–40. 2021.
|
|
10
|
Dias FGB, Ferreira MJG, da Silva LMR, de
Sousa Menezes RC and de Figueiredo EAT: Bioaccessibility of the
bioactive compounds and antimicrobial activity of aqueous extracts
of Physalis angulata L. Rev Cienc Agron.
51(e20196619)2020.
|
|
11
|
Cuong LCV, Dat TTH, Nhiem NX, Cuc NT, Yen
DTH and Anh HLT: The anti-microbial activities of secosteroids
isolated from Physalis angulata. Vietnam J Chem. 58:321–326.
2020.
|
|
12
|
Anand U, Jacobo-Herrera N, Altemimi A and
Lakhssassi N: A comprehensive review on medicinal plants as
antimicrobial therapeutics: Potential avenues of biocompatible drug
discovery. Metabolites. 9(258)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chairissy MD, Wulandari LR and Sujuti H:
Pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative effects of Physalis
angulata leaf extract on retinoblastoma cells. Int J
Ophthalmol. 12:1402–1407. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang Y, Yi L, Wang Q, Xie B, Sha C and
Dong Y: Physalin B suppresses inflammatory response to
lipopolysaccharide in RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting NF-κB signaling.
J Chem. 4(7943140)2018.
|
|
15
|
Guimarães ET, Lima MS, Santos LA, Ribeiro
IM, Tomassini TBC, Ribeiro dos Santos R, dos Santos WLC and Soares
MBP: Activity of physalins purified from Physalis angulata
in in vitro and in vivo models of cutaneous leishmaniasis. J
Antimicrob Chemother. 64:84–87. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang A, Wang S, Zhou F, Li P, Wang Y, Gan
L and Lin L: Physalin B induces cell cycle arrest and triggers
apoptosis in breast cancer cells through modulating p53-dependent
apoptotic pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:334–341.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fang C, Chen C, Yang Y, Li K, Gao R, Xu D,
Huang Y, Chen Z, Liu Z, Chen S, et al: Physalin B inhibits cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis in undifferentiated human
gastric cancer HGC-27 cells. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 18:224–231.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Magalhães HI, Veras ML, Torres MR, Alves
AP, Pessoa OD, Silveira ER, Costa-Lotufo LV, de Moraes MO and
Pessoa C: In-vitro and in-vivo antitumour activity of physalins B
and D from Physalis angulata. J Pharm Pharmacol. 58:235–241.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Abdulridha MK, Al-Marzoqi AH, Al-Awsi GRL,
Mubarak SMH, Heidarifard M and Ghasemian A: Anticancer Effects of
herbal medicine compounds and novel formulations: A literature
review. J Gastrointest Cancer. 51:765–773. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Meira CS, Guimarães ET, Bastos TM, Moreira
DR, Tomassini TC, Ribeiro IM, Dos Santos RR and Soares MB:
Physalins B and F, seco-steroids isolated from Physalis
angulata L., strongly inhibit proliferation, ultrastructure and
infectivity of Trypanosoma cruzi. Parasitology.
140:1811–1821. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nogueira RC, Rocha VPC, Nonato FR,
Tomassini TC, Ribeiro IM, dos Santos RR and Soares MB: Genotoxicity
and antileishmanial activity evaluation of Physalis angulata
concentrated ethanolic extract. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol.
36:1304–1311. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sangshetti JN, Khan FAK, Kulkarni AA,
Arote R and Patil RH: Antileishmanial drug discovery: Comprehensive
review of the last 10 years. RSC Adv. 5:32376–32415. 2015.
|
|
23
|
da Silva RR, da Silva BJ, Rodrigues AP,
Farias LH, da Silva MN, Alves DT, Bastos GN, do Nascimento JL and
Silva EO: In vitro biological action of aqueous extract from roots
of Physalis angulata against Leishmania
(Leishmania) amazonensis. BMC Complement Altern Med.
15(249)2015.
|
|
24
|
Hassan AA, Khalid HE, Abdalla AH, Mukhtar
MM, Osman WJ and Efferth T: Antileishmanial activities of medicinal
herbs and phytochemicals in vitro and in vivo: An update for the
years 2015 to 2021. Molecules. 27(7579)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ghasemian M, Owlia S and Owlia MB: Review
of anti-inflammatory herbal medicines. Adv Pharmacol Sci.
2016(9130979)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang YJ, Yi L, Wang Q, Xie BB, Dong Y and
Sha CW: Anti-inflammatory effects of physalin E from Physalis
angulata on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells
through inhibition of NF-κB pathway. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
39:74–79. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yen PH, Cuong LCV, Dat TTH, Thuy DTQ, Hoa
DTN, Cuc NT, Yen DTH, Thao DT and Anh HLT: Withanolides from the
whole plant of Physalis angulata and their anti-inflammatory
activities. Vietnam J Chem. 57:334–338. 2019.
|
|
28
|
Tuan Anh HL, Le Ba V, Do TT, Phan VK, Pham
Thi HY, Bach LG, Tran MH, Tran Thi PA and Kim YH: Bioactive
compounds from Physalis angulata and their anti-inflammatory
and cytotoxic activities. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 23:809–817.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Lu S, Wang L, Xin M, Xu Y, Wang G,
Chen D, Chen L, Liu S and Zhao F: Anti-inflammatory effects of
three withanolides isolated from Physalis angulata L. in
LPS-activated RAW 264.7 cells through blocking NF-κB signaling
pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 276(114186)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ukwubile CA and Oise IE: Analgesic and
anti-inflammatory activity of Physalis angulata Linn
(Solanaceae) Leaf methanolic extract in swiss albino mice.
Int Biol Biomed J Autumn. 2:167–70. 2016.
|
|
31
|
Abdul-Nasir-Deen AY, Boakye YD, Osafo N,
Agyare C, Boamah D, Boamah VE and Agyei EK: Anti-inflammatory and
wound healing properties of methanol leaf extract of Physalis
angulata L. S Afr J Bot. 133:124–131. 2020.
|
|
32
|
do Espírito Santo RF, Lima MDS, Juiz PJL,
Opretzka LCF, Nogueira RC, Ribeiro IM, Tomassini TCB, Soares MBP
and Villarreal CF: Physalis angulata concentrated ethanolic
extract suppresses nociception and inflammation by modulating
cytokines and prostanoid pathways. Nat Prod Res. 35:4675–4679.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Almeida Junior LD, Quaglio AEV, de Almeida
Costa CAR and Di Stasi LC: Intestinal anti-inflammatory activity of
Ground Cherry (Physalis angulata L.) standardized
CO2 phytopharmaceutical preparation. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:4369–4380. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Arruda JCC, Rocha NC, Santos EG, Ferreira
LGB, Bello ML, Penido C, Costa TEMM, Santos JAA, Ribeiro IM,
Tomassini TCB and Faria RX: Physalin pool from Physalis
angulata L. leaves and physalin D inhibit P2X7 receptor
function in vitro and acute lung injury in vivo. Biomed
Pharmacother. 142(112006)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang B, Wu L, Chen J, Dong L, Chen C, Wen
Z, Hu J, Fleming I and Wang DW: Metabolism pathways of arachidonic
acids: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Signal
Transduct Target Ther. 6(94)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Rohmawaty E, Rosdianto AM, Usman HA,
Saragih WAM, Zuhrotun A, Hendriani R, Wardhana YW, Ekawardhani S,
Wiraswati HL, Agustanti N, et al: Antifibrotic effect of the ethyl
acetate fraction of ciplukan (Physalis angulate Linn.) in
rat liver fibrosis induced by CCI4. J Appl Pharm Sci.
11:175–182. 2021.
|
|
37
|
Zhu X, Ye S, Yu D, Zhang Y, Li J, Zhang M,
Leng Y, Yang T, Luo J, Chen X, et al: Physalin B attenuates liver
fibrosis via suppressing LAP2α-HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of the
transcription factor GLI1 and hepatic stellate cell activation. Br
J Pharmacol. 178:3428–3437. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dewi S, Isbagio H, Purwaningsih EH, Kertia
N, Setiabudy R and Setiati S: A double-blind, randomized controlled
trial of ciplukan (Physalis angulata Linn) extract on skin
fibrosis, inflammatory, immunology, and fibrosis biomarkers in
scleroderma patients. Acta Med Indones. 51:303–310. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao M, Wang L, Wang M, Zhou S, Lu Y, Cui
H, Racanelli AC, Zhang L, Ye T, Ding B, et al: Targeting fibrosis,
mechanisms and cilinical trials. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
7(206)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Raju P and Estari M: Anti-diabetic
activity of compound isolated from Physalis angulata fruit
extracts in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Am J Sci Med Res.
1:40–43. 2015.
|
|
41
|
Reddy PA, Vijay KR, Reddy GV, Reddy MK and
Reddy YN: Anti-diabetic and hypolipidemic effect of aqueous and
methanolic root extracts of Physalis angulata in
streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic rats. Int J Pharm Res
Scholars. 3:402–409. 2014.
|
|
42
|
Kibiti CM and Afolayan AJ: Herbal therapy:
A review of emerging pharmacological tools in the management of
diabetes mellitus in Africa. Pharmacogn Mag. 11 (Suppl
2):S258–S274. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Daltro SRT, Santos IP, Barros PL, Moreira
DRM, Tomassini TCB, Ribeiro IM, Ribeiro Dos Santos R, Meira CS and
Soares MBP: In vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory activity of
Physalis angulata concentrated ethanolic extract. Planta
Med. 87:160–168. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Azwanida NN: A review on the extraction
methods use in medicinal plants, principle, strength, and
limitation. Med Aromat Plants. 4:1–6. 2015.
|
|
45
|
Sulaiman SF, Sajak AAB, Ooi KL, Supriatno
and Seow EM: Effect of solvents in extracting polyphenols
and antioxidants of selected raw vegetables. J Food Compos Anal.
24:506–515. 2011.
|
|
46
|
Abubakar AR and Haque M: Preparation of
medicinal plants: Basic extraction and fractionation procedures for
experimental purposes. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 12:1–10.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Pandey A and Tripathi S: Concept of
standardization, extraction and pre-phytochemical screening
strategies for herbal drug. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2:115–119.
2014.
|
|
48
|
Sasidharan S, Chen Y, Saravanan D, Sundram
KM and Yoga Latha L: Extraction, isolation and characterization of
bioactive compounds from plants' extracts. Afr J Tradit Complement
Altern Med. 8:1–10. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Altemimi A, Lakhssassi N, Baharlouei A,
Watson DG and Lightfoot DA: Phytochemicals: Extraction, isolation,
and identification of bioactive compounds from plant extracts.
Plants (Basel). 6(42)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Das K, Tiwari RKS and Shrivastava DK:
Techniques for evaluation of medicinal plant products as
antimicrobial agent: Current methods and future trends. J Med
Plants Res. 4:104–111. 2010.
|
|
51
|
Sukandar EY and Sheba SH: Acute and
Sub-chronic toxicity studies of combination of Physalis
angulata L. (Cecendet) extract and methylprednisolone on
animals. Int J Integr Health Sci. 7:48–55. 2019.
|
|
52
|
Rathore C, Dutt KR, Sahu S and Deb L:
Antiasthmatic activity of the methanolic extract of Physalis
angulate Linn. J Med Plants Res. 5:5351–5355. 2011.
|
|
53
|
Pereda MDCV, Dieamant G, Nogueira C,
Eberlin S, Facchini G, Mussi L, Polezel MA, Martins-Oliveira D,
Rosa PTV and Di Stasi LC: Sterol-standardized phytopharmaceutical
from ground cherry: Corticoid-like properties on human
keratinocytes and fibroblasts and its effects in a randomized
double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Cosmet Dermatol.
18:1516–1528. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Vieceli PS, Juiz PJL, Lauria PSS, Couto
RD, Tomassini TCB, Ribeiro IM, Soares MBP and Villarreal CF:
Physalis angulata reduces the progression of chronic
experimental periodontitis by immunomodulatory mechanisms. J
Ethnopharmacol. 273(113986)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Meira CS, Guimarães ET, Dos Santos JA,
Moreira DR, Nogueira RC, Tomassini TC, Ribeiro IM, de Souza CV,
Ribeiro Dos Santos R and Soares MB: In vitro and in vivo
antiparasitic activity of Physalis angulata L. concentrated
ethanolic extract against Trypanosoma cruzi. Phytomedicine.
22:969–974. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
da Silva BJM, Rodrigues APD, Farias LHS,
Hage AAP, Do Nascimento JL and Silva EO: Physalis angulata
induces in vitro differentiation of murine bone marrow cells into
macrophages. BMC Cell Biol. 15(37)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Pinto NB, Morais TC, Carvalho KMB, Silva
CR, Andrade GM, Brito GAC, Veras ML, Pessoa ODL, Rao VS and Santos
FA: Topical anti-inflammatory potential of Physalin E from
Physalis angulata on experimental dermatitis in mice.
Phytomedicine. 17:740–743. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|