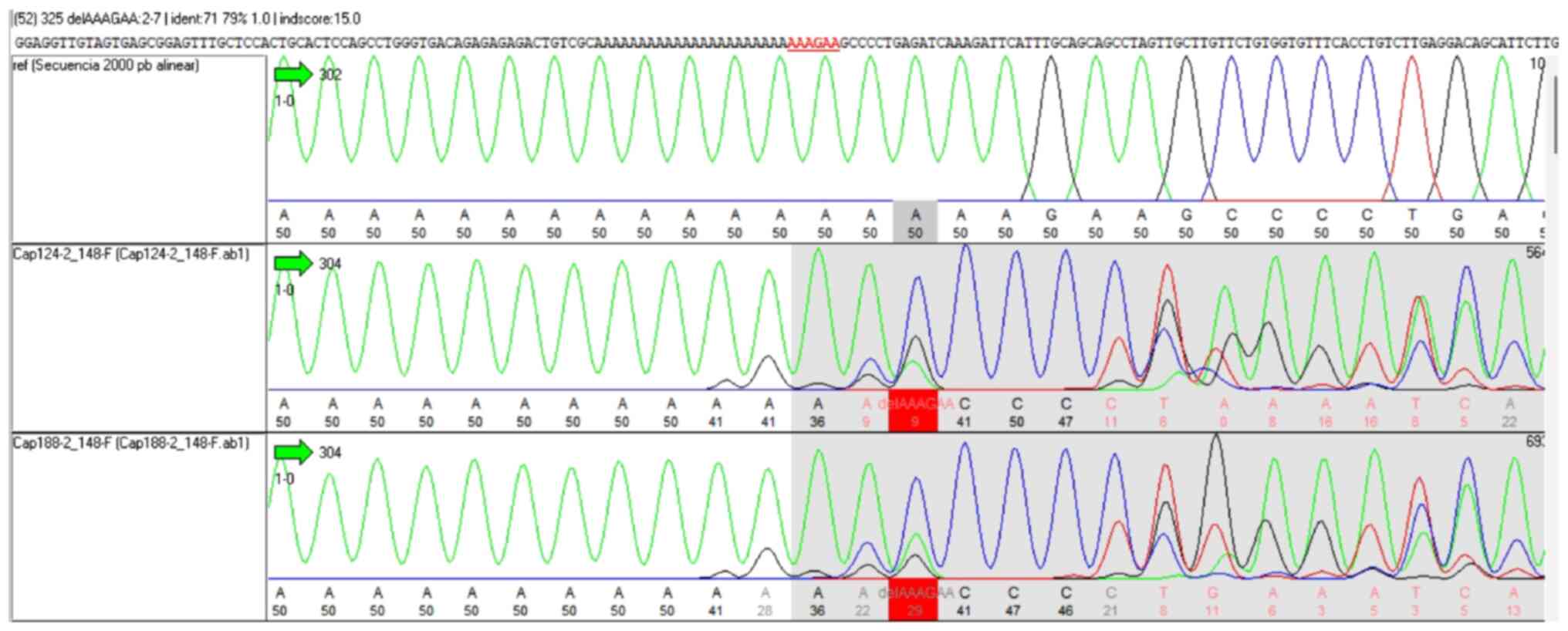
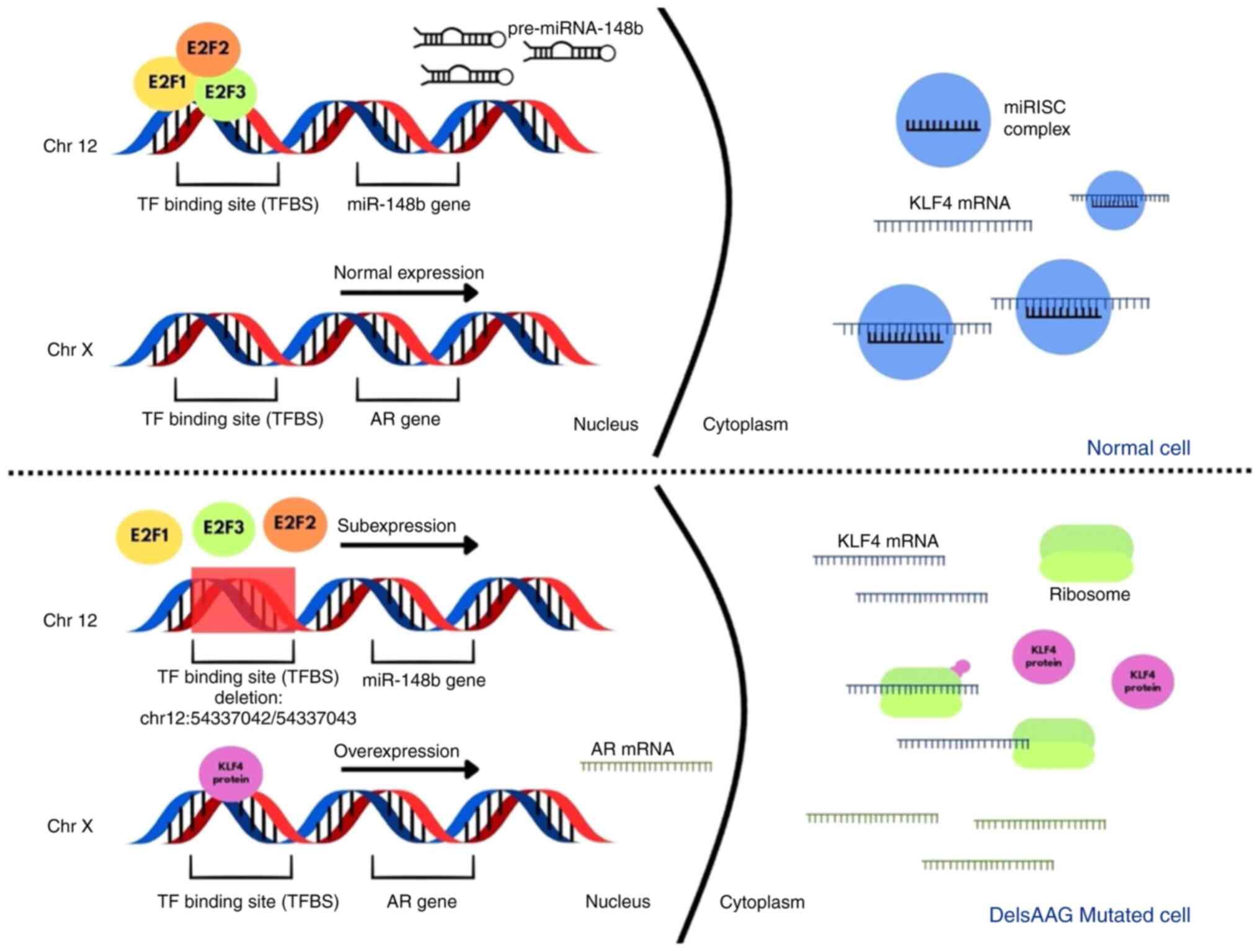
|
1
|
Xiao J, Gong AY, Eischeid AN, Chen D, Deng
C, Young CY and Chen XM: miR-141 modulates androgen receptor
transcriptional activity in human prostate cancer cells through
targeting the small heterodimer partner protein. Prostate.
72:1514–1522. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sun Q, Zhao X, Liu X, Wang Y, Huang J,
Jiang B, Chen Q and Yu J: miR-146a functions as a tumor suppressor
in prostate cancer by targeting Rac1. Prostate. 74:1613–1621.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bergez-Hernández F, Arámbula-Meraz E,
Alvarez-Arrazola M, Irigoyen-Arredondo M, Luque-Ortega F,
Martínez-Camberos A, Cedano-Prieto D, Contreras-Gutiérrez J,
Martínez-Valenzuela C and García-Magallanes N: Expression Analysis
of miRNAs and their potential role as biomarkers for prostate
cancer detection. Am J Mens Health.
16(15579883221120989)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Arámbula-Meraz E, Bergez-Hernández F,
Leal-León E, Romo-Martínez E, Picos-Cárdenas V, Luque-Ortega F,
Romero-Quintana J, Alvarez-Arrazola M and García-Magallanes N:
Expression of miR-148b-3p is correlated with overexpression of
biomarkers in prostate cancer. Genet Mol Biol.
43(e20180330)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu WX, Liu Z, Deng F, Wang DD, Li XW, Tian
T, Zhang J and Tang JH: MiR-145: A potential biomarker of cancer
migration and invasion. Am J Transl Res. 11:6739–6753.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jin W, Fei X, Wang X, Song Y and Chen F:
Detection and prognosis of prostate cancer using blood-based
biomarkers. Mediators Inflamm. 2020(8730608)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chu H, Zhong D, Tang J, Li J, Xue Y, Tong
N, Qin C, Yin C, Zhang Z and Wang M: A functional variant in
miR-143 promoter contributes to prostate cancer risk. Arch Toxicol.
90:403–414. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kotarac N, Dobrijevic Z, Matijasevic S,
Savic-Pavicevic D and Brajuskovic G: Analysis of association of
potentially functional genetic variants within genes encoding
miR-34b/c, miR-378 and miR-143/145 with prostate cancer in Serbian
population. EXCLI J. 18:515–529. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Watahiki A and Wang Y, Morris J, Dennis K,
O'Dwyer HM, Gleave M, Gleave M, Gout PW and Wang Y: MicroRNAs
associated with metastatic prostate cancer. PLoS One.
6(e24950)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen X, Wang G, Lu X, Gao P, Song Y, Sun
J, Li A, Xu Y, Xu H and Wang Z: Polymorphisms and haplotypes of the
miR-148/152 family are associated with the risk and
clinicopathological features of gastric cancer in a Northern
Chinese population. Mutagenesis. 29:401–407. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chomczynski P: A reagent for the
single-step simultaneous isolation of RNA, DNA and proteins from
cell and tissue samples. Biotechniques. 15:532–4, 536-7.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim YG, Kim MJ, Lee JS, Lee JA, Song JY,
Cho SI, Park SS and Seong MW: SnackVar: An open-source software for
sanger sequencing analysis optimized for clinical use. J Mol Diagn.
23:140–148. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rijk PD and Del-Favero J: novoSNP3:
Variant detection and sequence annotation in resequencing projects.
Methods Mol Biol. 396:331–344. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Taylor SC, Nadeau K, Abbasi M, Lachance C,
Nguyen M and Fenrich J: The Ultimate qPCR experiment: Producing
publication quality, reproducible data the first time. Trends
Biotechnol. 37:761–774. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Akalin I, Erol B, Aslan E, Ozkanli SS,
Efiloglu O, Yildirim S, Caskurlu T, Yildirim A and Karaman MI: A
new promising pathway in aggressive prostate cancer:
Treg/mir-let8c/lin28b. Arch Esp Urol. 75:459–466. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liu S, Zhao Y, Zhao Y and Tang X: The
prognostic value of miR-487a in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and
its influence on cell biological behavior. Arch Esp Urol.
75:346–353. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Z, Zhu X, Zhai H, Wang Y and Hao G:
Integrated analysis of mRNA-single nucleotide polymorphism-microRNA
interaction network to identify biomarkers associated with prostate
cancer. Front Genet. 13(922712)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Camargo JA, Lopes RE, Ferreira GFD, Viana
NI, Guimaraes V, Leite KRM, Nahas WC, Srougi M, Antunes AA and Reis
ST: The role of single nucleotide polymorphisms of miRNAs 100 and
146a as prognostic factors for prostate cancer. Int J Biol Markers.
36:50–56. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xu B, Feng NH, Li PC, Tao J, Wu D, Zhang
ZD, Tong N, Wang JF, Song NH, Zhang W, et al: A functional
polymorphism in Pre-miR-146a gene is associated with prostate
cancer risk and mature miR-146a expression in vivo. Prostate.
70:467–472. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang S, Cui H, Lou Z, Wang X, Chen L, Xie
Z, Hehir M, Yao X, Ren Y, Cen D and Weng G: Association of
rs3787016 in Long Non-coding RNAs POLR2E and rs2910164 in
MiRNA-146a with prostate cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Iran J Public Health. 47:623–632. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao CG, Xu HB and Xu B: The rs4705342
gene mutation in the promoter region of the miR-143/145 cluster
associated with the risk of prostate cancer in the Chinese Han
population. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 25:696–702. 2019.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, Baker J,
Phan L, Smigielski EM and Sirotkin K: dbSNP: The NCBI database of
genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:308–311. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chacon-Cortes D, Smith RA, Haupt LM, Lea
RA, Youl PH and Griffiths LR: Genetic association analysis of miRNA
SNPs implicates MIR145 in breast cancer susceptibility. BMC Med
Genet. 16(107)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zaman MS, Chen Y, Deng G, Shahryari V, Suh
SO, Saini S, Majid S, Liu J, Khatri G, Tanaka Y and Dahiya R: The
functional significance of microRNA-145 in prostate cancer. Br J
Cancer. 103:256–264. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bellissimo T, Ganci F, Gallo E, Sacconi A,
Tito C, De Angelis L, Pulito C, Masciarelli S, Diso D, Anile M, et
al: Thymic Epithelial Tumors phenotype relies on miR-145-5p
epigenetic regulation. Mol Cancer. 16(88)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Donzelli S, Mori F, Bellissimo T, Sacconi
A, Casini B, Frixa T, Roscilli G, Aurisicchio L, Facciolo F,
Pompili A, et al: Epigenetic silencing of miR-145-5p contributes to
brain metastasis. Oncotarget. 6:35183–35201. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xue G, Ren Z, Chen Y, Zhu J, Du Y, Pan D,
Li X and Hu B: A feedback regulation between miR-145 and DNA
methyltransferase 3b in prostate cancer cell and their responses to
irradiation. Cancer Lett. 361:121–127. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Suh SO, Chen Y, Zaman MS, Hirata H,
Yamamura S, Shahryari V, Liu J, Tabatabai ZL, Kakar S, Deng G, et
al: MicroRNA-145 is regulated by DNA methylation and p53 gene
mutation in prostate cancer. Carcinogenesis. 32:772–778.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nesta AV, Tafur D and Beck CR: Hotspots of
human mutation. Trends Genet. 37:717–729. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gemayel R, Cho J, Boeynaems S and
Verstrepen KJ: Beyond junk-variable tandem repeats as facilitators
of rapid evolution of regulatory and coding sequences. Genes
(Basel). 3:461–480. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vieira ML, Santini L, Diniz AL and Munhoz
Cde F: Microsatellite markers: What they mean and why they are so
useful. Genet Mol Biol. 39:312–328. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fishilevich S, Nudel R, Rappaport N, Hadar
R, Plaschkes I, Iny Stein T, Rosen N, Kohn A, Twik M, Safran M, et
al: GeneHancer: Genome-wide integration of enhancers and target
genes in GeneCards. Database (Oxford). 2017(bax028)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Peng Y and Zhang Y: Enhancer and
super-enhancer: Positive regulators in gene transcription. Animal
Model Exp Med. 1:169–179. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cunningham F, Allen JE, Allen J,
Alvarez-Jarreta J, Amode MR, Armean IM, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov
AG, Barnes I, Bennett R, et al: Ensembl 2022. Nucleic Acids Res.
50:D988–D995. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sylvestre Y, De Guire V, Querido E,
Mukhopadhyay UK, Bourdeau V, Major F, Ferbeyre G and Chartrand P:
An E2F/miR-20a autoregulatory feedback loop. J Biol Chem.
282:2135–2143. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Woods K, Thomson JM and Hammond SM: Direct
regulation of an oncogenic micro-RNA cluster by E2F transcription
factors. J Biol Chem. 282:2130–2134. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
de Santiago I, Liu W, Yuan K, O'Reilly M,
Chilamakuri CS, Ponder BA, Meyer KB and Markowetz F: BaalChIP:
Bayesian analysis of allele-specific transcription factor binding
in cancer genomes. Genome Biol. 18(39)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Huang Q, Whitington T, Gao P, Lindberg JF,
Yang Y, Sun J, Väisänen MR, Szulkin R, Annala M, Yan J, et al: A
prostate cancer susceptibility allele at 6q22 increases RFX6
expression by modulating HOXB13 chromatin binding. Nat Genet.
46:126–135. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang P, Tillmans LS, Thibodeau SN and
Wang L: Single-Nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing identifies
candidate functional variants at prostate cancer risk loci. Genes
(Basel). 10(547)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Eickhardt E, Als TD, Grove J, Boerglum AD
and Lescai F: Estimating the functional impact of INDELs in
transcription factor binding sites: A Genome-Wide Landscape.
Bioinformatics, 2016 Jun. Available from: http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/057604.
|
|
42
|
Tomeva E, Switzeny OJ, Heitzinger C, Hippe
B and Haslberger AG: Comprehensive approach to distinguish patients
with solid tumors from healthy controls by combining androgen
receptor mutation p. H875Y with Cell-Free DNA methylation and
circulating miRNAs. Cancers (Basel). 14(462)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Feng F, Liu H, Chen A, Xia Q, Zhao Y, Jin
X and Huang J: miR-148-3p and miR-152-3p synergistically regulate
prostate cancer progression via repressing KLF4. J Cell Biochem.
120:17228–17239. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wei LZ, Wang YQ, Chang YL, An N, Wang X,
Zhou PJ, Zhu HH, Fang YX and Gao WQ: Imbalance of a KLF4-miR-7
auto-regulatory feedback loop promotes prostate cancer cell growth
by impairing microRNA processing. Am J Cancer Res. 8:226–244.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Siu MK, Suau F, Chen WY, Tsai YC, Tsai HY,
Yeh HL and Liu YN: KLF4 functions as an activator of the androgen
receptor through reciprocal feedback. Oncogenesis.
5(e282)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Desai K, McManus JM and Sharifi N:
Hormonal therapy for prostate cancer. Endocr Rev. 42:354–373.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Auchus RJ and Sharifi N: Sex Hormones and
Prostate Cancer. Annu Rev Med. 71:33–45. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|