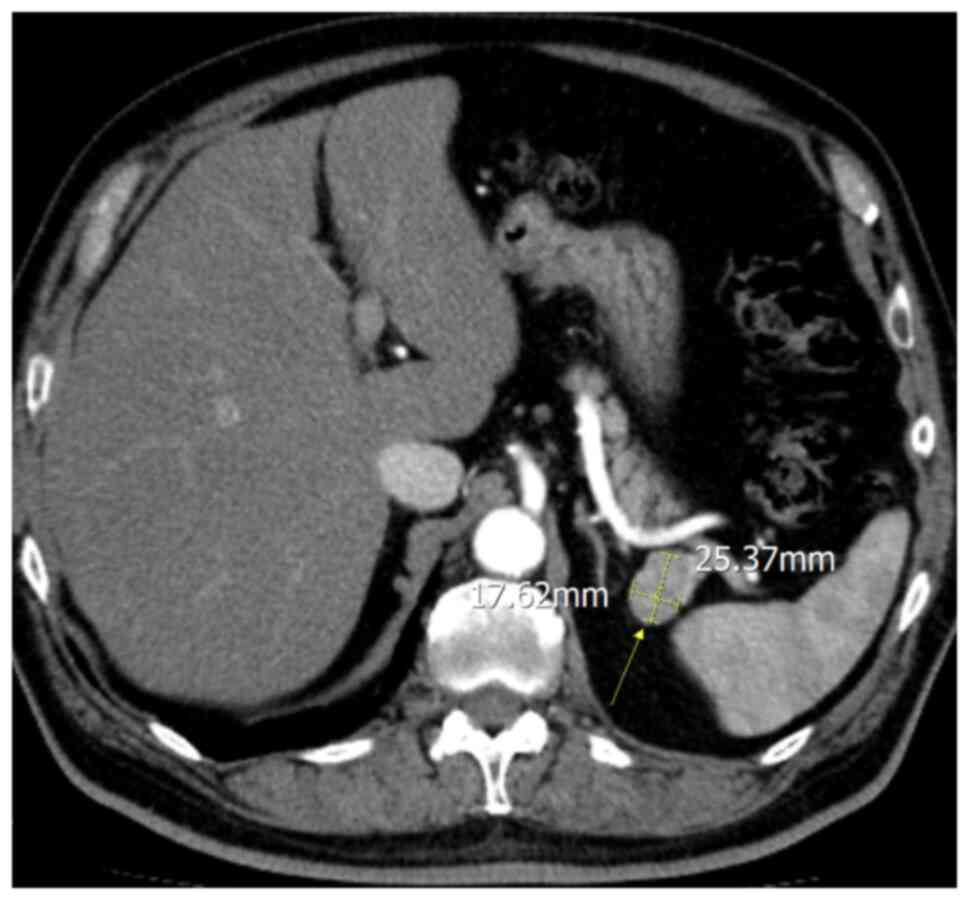
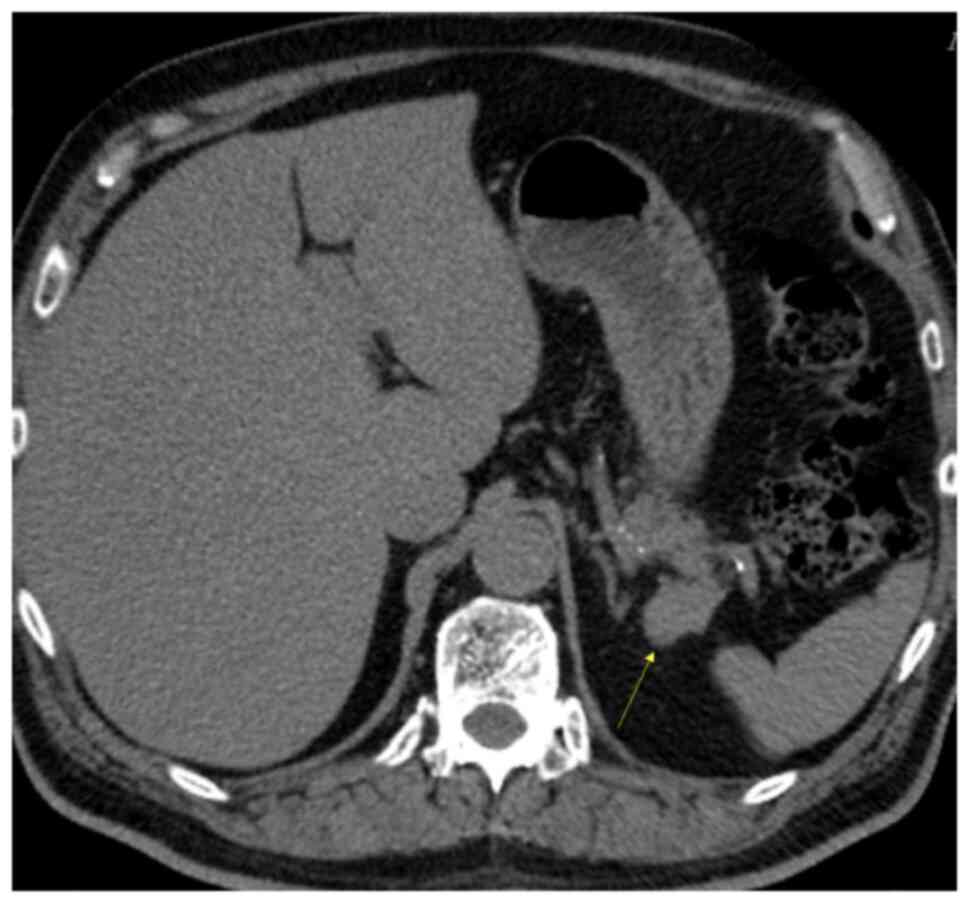
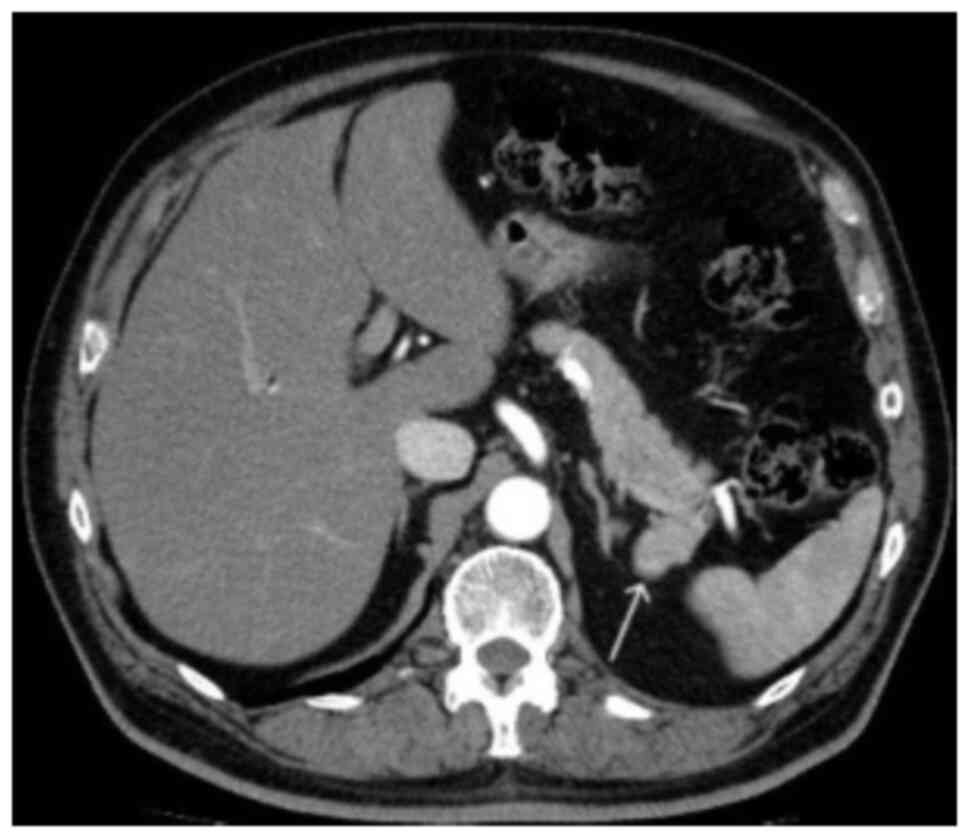
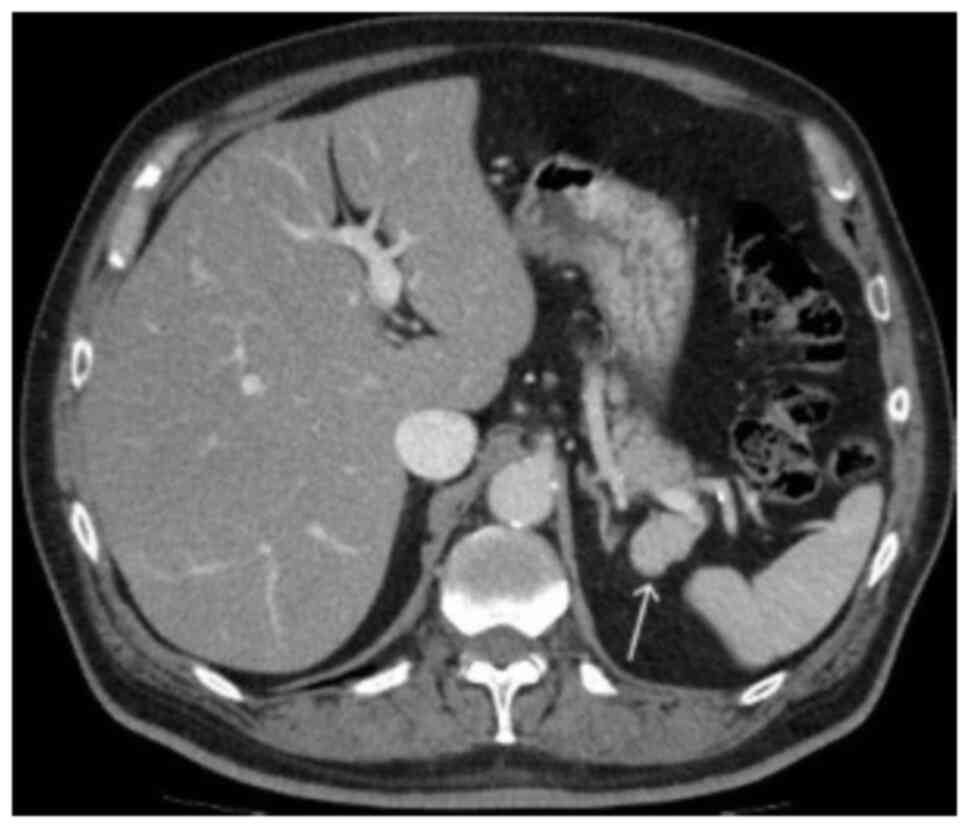
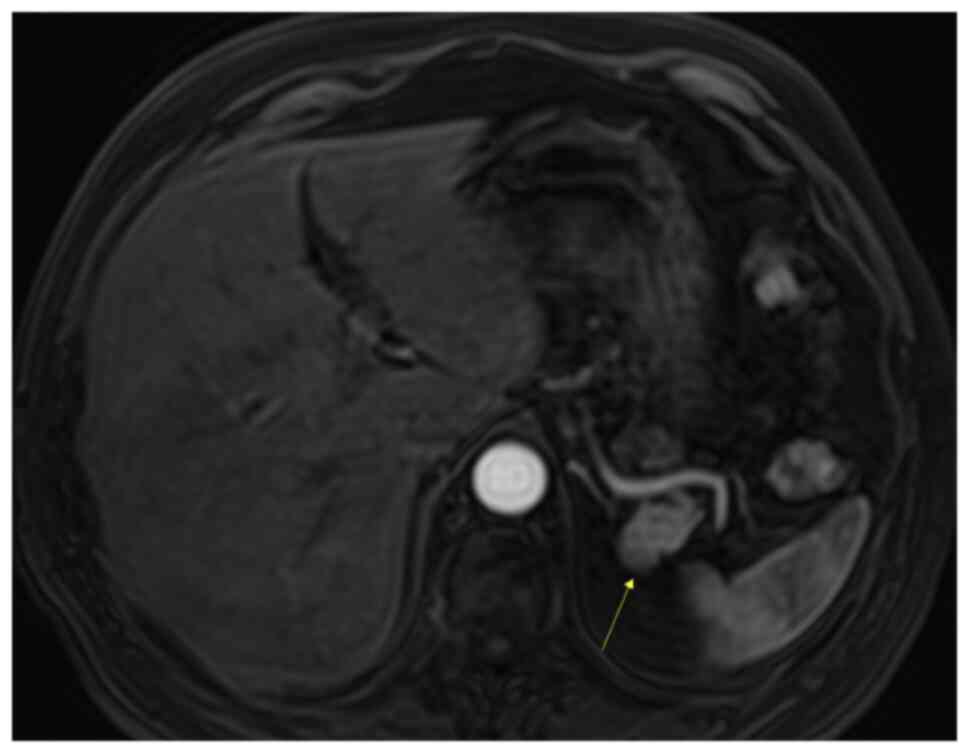
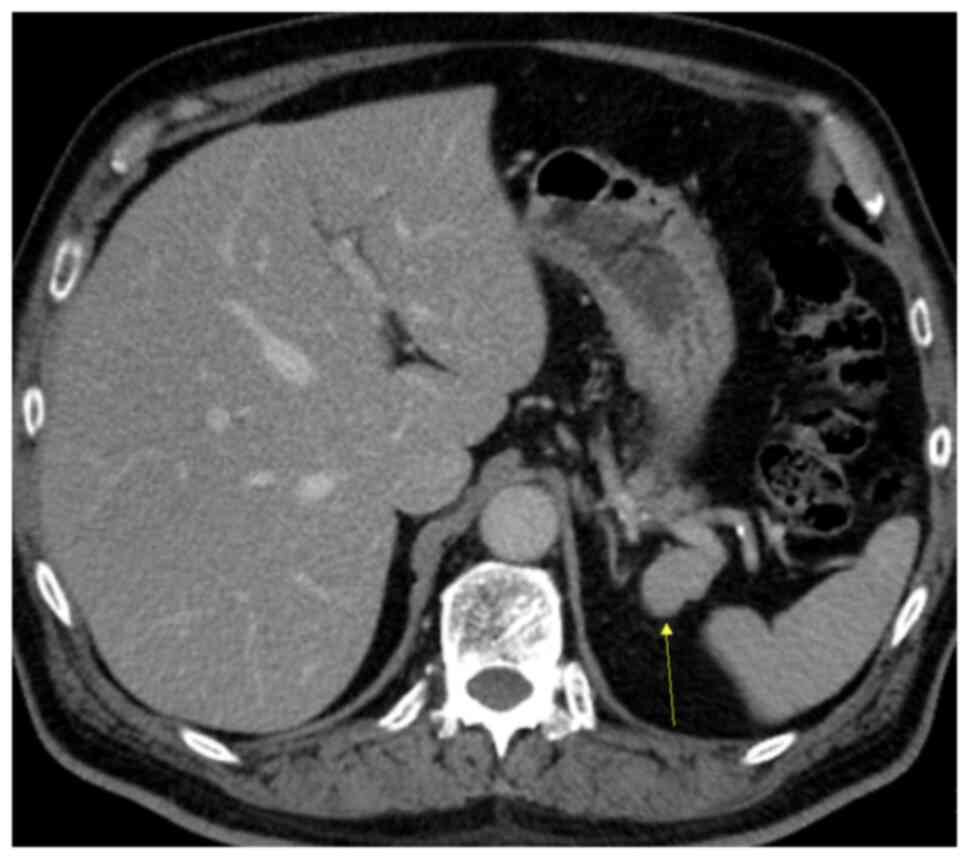
|
1
|
Marques S, Bispo M and Noia L:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: A diagnosis not to forget! Case
Rep. Gastroenterol. 10:749–754. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kim SH, Lee JM, Han JK, Lee JY, Kim KW,
Cho KC, Cho KC and Choi BI: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen:
Findings on MR imaging, CT, US and scintigraphy, and the pathologic
analysis. Korean J Radiol. 9:162–174. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hwang HS, Lee SS, Kim SC, Seo DW and Kim
J: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Clinicopathologic analysis of
12 cases. Pancreas. 40:956–965. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Osher E, Scapa E, Klausner J, Greenman Y,
Tordjman K, Melhem A, Nachmany I, Sofer Y, Geva R, Blachar A, et
al: Pancreatic incidentaloma: Differentiating nonfunctioning
pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours from intrapancreatic accessory
spleen. Endocr Pract. 22:773–779. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Massani M, Maccatrozzo P, Morana G, Fabris
L, Ruffolo C, Bonariol L, Pauletti B and Bassi N: Diagnostic
difficulties and therapeutic choices in intrapancreatic accessory
spleen: Case reports. Open Access Surg. 9:15–20. 2016.
|
|
6
|
Spencer LA, Spizarny DL and Williams TR:
Imaging features of intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Br J Radiol.
83:668–673. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Santo E and Bar-Yishay I: Pancreatic solid
incidentalomas. Endosc Ultrasound. 6 (Suppl 3):S99–S103.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rahbar H, Bhargava P, Vaidya S and Medverd
JR: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Radiol Case Rep.
5(386)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Loureiro AL, Ferreira AO, Palmeiro M and
Penedo JP: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: A misleading
diagnosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2013(bcr2012008471)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Guo W, Han W, Liu J, Jin L, Li JS, Zhang
ZT and Wang Y: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: A case report and
review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. 15:1141–1143.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kykalos S, Machairas N, Molmenti EP and
Sotiropoulos G: Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: Two case reports
of a rare entity. Cureus. 12(e8797)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li BQ, Xu XQ and Guo JC: Intrapancreatic
accessory spleen: A diagnostic dilemma. HPB (Oxford). 20:1004–1011.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Munk-Madsen MZ, Zakarian K, Sandor Oturai
P, Hansen CP, Federspiel B, Fallentin E and Linno Willemoe G:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen mimicking malignant tumour: Three
case reports. Acta Radiol Open. 8(2058460119859347)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Contractor U, Henderson I and Zaitoun MD:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: An important differential to
consider before surgery. Hum Pathol Case Rep. 1:49–51. 2014.
|
|
15
|
Chavan N, Desai GS, Tampi C and Wagle P:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: An enigmatic entity. BMJ Case
Rep. 12(e228510)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hashimoto K, Nishimura S, Ito T, Oka N and
Akagi M: Limitations and usefulness of biopsy techniques for the
diagnosis of metastatic bone and soft tissue tumours. Ann Med Surg
(Lond). 68(102581)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
García AF and Sanjuanbenito Dehesa A:
Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: A rare cause of recurrence of
immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Clin Case Rep. 4:979–981.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Obuchi T, Takagane A, Sato K, Yonezawa H,
Funato O and Kobayashi M: Single-incision laparoscopic excision of
symptomatic accessory spleen in the pelvis: An initial report. J
Minim Access Surg. 13:321–322. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hems TE and Bellringer JF: Torsion of an
accessory spleen in an elderly patient. Postgrad Med J. 66:838–839.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
O'Riordan B, Rodendo O and Stafford A:
Laparoscopic distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy for an
intrapancreatic accessory spleen-a case report and review of the
literature. Mesentery Peritoneum. 6(AB154)2022.
|