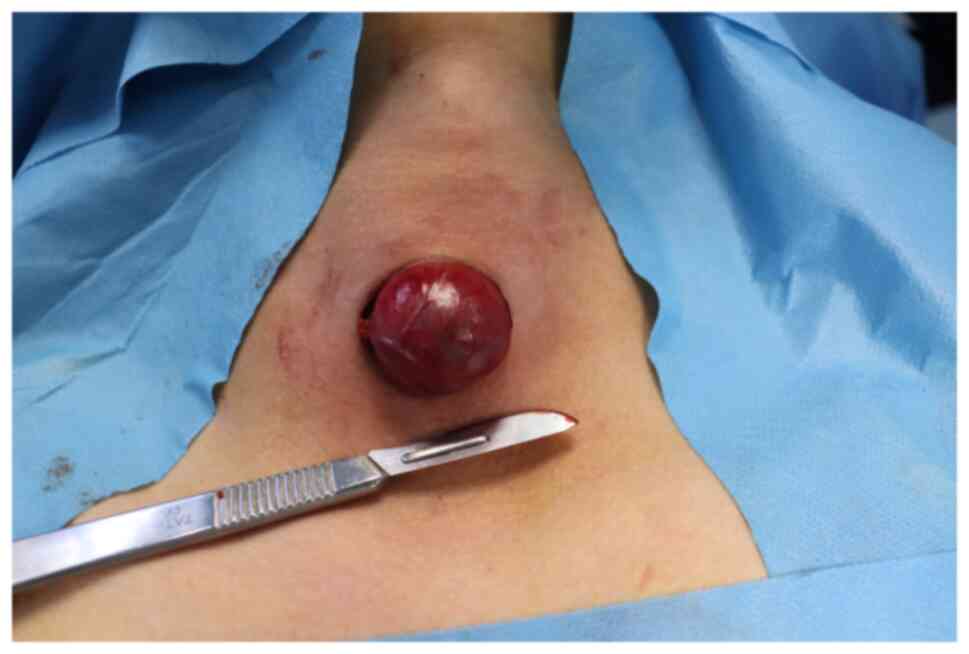
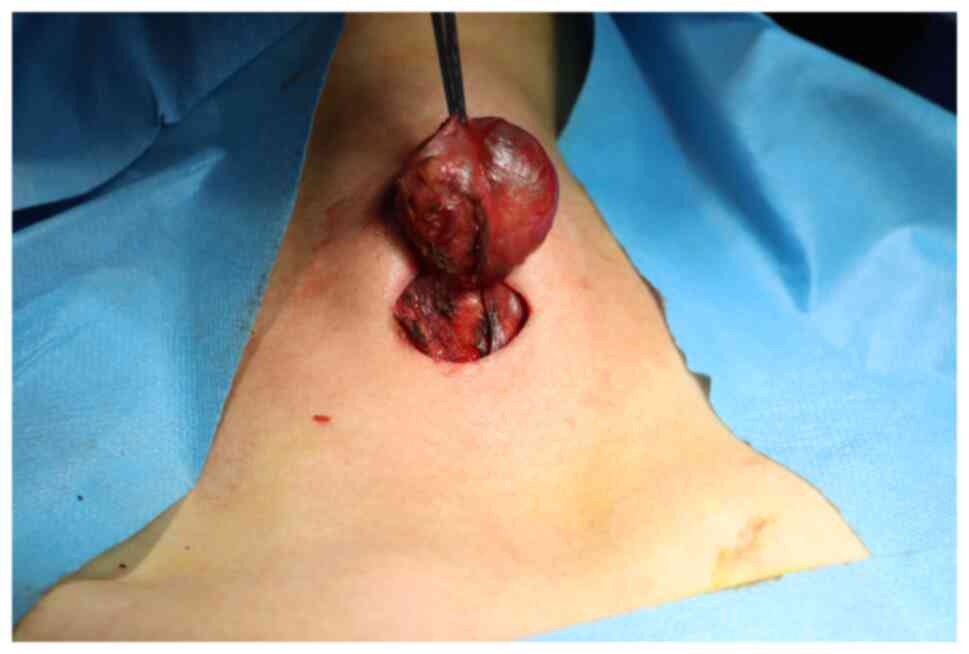
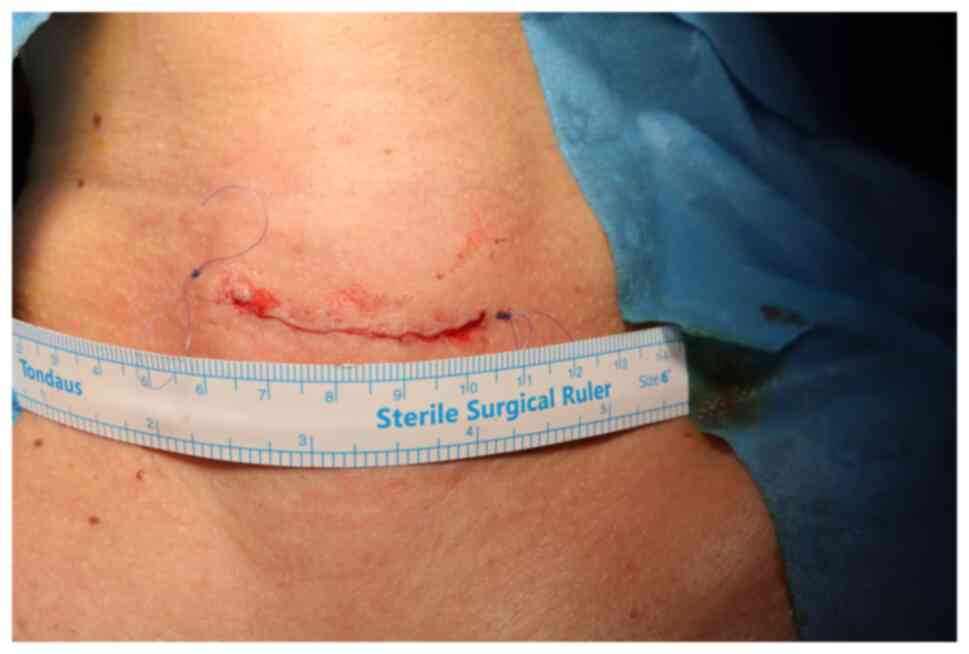
|
1
|
Guth S, Theune U, Aberle J, Galach A and
Bamberger CM: Very high prevalence of thyroid nodules detected by
high frequency (13 MHz) ultrasound examination. Eur J Clin Invest.
39:699–706. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Grussendorf M, Ruschenburg I and Brabant
G: Malignancy rates in thyroid nodules: A long-term cohort study of
17,592 patients. Eur Thyroid J. 11(e220027)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Durante C, Hegedüs L, Czarniecka A,
Paschke R, Russ G, Schmitt F, Soares P, Solymosi T and Papini E:
2023 European Thyroid Association clinical practice guidelines for
thyroid nodule management. European Thyroid J.
12(e230067)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Patel KN, Yip L, Lubitz CC, Grubbs EG,
Miller BS, Shen W, Angelos P, Chen H, Doherty GM, Fahey TJ III, et
al: The American Association of Endocrine Surgeons guidelines for
the definitive surgical management of thyroid disease in adults.
Ann Surg. 271:e21–e93. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sarkis LM, Norlen O, Sywak M and Delbridge
L: Minimally invasive thyroid nodulectomy reduces post-operative
hypothyroidism when compared with thyroid lobectomy. ANZ J Surg.
87:360–363. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ali SZ, Baloch ZW, Cochand-Priollet B,
Schmitt FC, Vielh P and VanderLaan PA: The 2023 bethesda system for
reporting thyroid cytopathology. Thyroid. 33:1039–1044.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
WHO/UNICEF/ICCIDD Chapter 2: Selecting
target groups and Chapter 5: Selecting appropriate indicators:
Biochemical indicators. In: Indicators for Assessing Iodine
Deficiency Disorder and their Control Through Salt Iodination. WHO,
Geneva, 1994.
|
|
8
|
Tessler FN, Middleton WD, Grant EG, Hoang
JK, Berland LL, Teefey SA, Cronan JJ, Beland MD, Desser TS, Frates
MC, et al: ACR thyroid imaging, reporting and data system
(TI-RADS): White paper of the ACR TI-RADS committee. J Am Coll
Radiol. 14:587–595. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jasim S, Baranski TJ, Teefey SA and
Middleton WD: Investigating the effect of thyroid nodule location
on the risk of thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 30:401–407. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Grani G, Sponziello M, Pecce V, Ramundo V
and Durante C: Contemporary thyroid nodule evaluation and
management. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 105:2869–2883. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kumbhar SS, O'Malley RB, Robinson TJ,
Maximin S, Lalwani N, Byrd DR and Wang CL: Why thyroid surgeons are
frustrated with radiologists: Lessons learned from pre-and
postoperative US. Radiographics. 36:2141–2153. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Brito JP, Gionfriddo MR, Al Nofal A,
Boehmer KR, Leppin AL, Reading C, Callstrom M, Elraiyah TA, Prokop
LJ, Stan MN, et al: The accuracy of thyroid nodule ultrasound to
predict thyroid cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 99:1253–1263. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Na DG, Baek JH, Jung SL, Kim JH, Sung JY,
Kim KS, Lee JH, Shin JH, Choi YJ, Ha EJ, et al: Core needle biopsy
of the thyroid: 2016 consensus statement and recommendations from
Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Korean J Radiol. 18:217–237.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hwang SH, Sung JM, Kim EK, Moon HJ and
Kwak JY: Imaging-cytology correlation of thyroid nodules with
initially benign cytology. Int J Endocrinol.
2014(491508)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sclabas GM, Staerkel GA, Shapiro SE,
Fornage BD, Sherman SI, Vassillopoulou-Sellin R, Lee JE and Evans
DB: Fine-needle aspiration of the thyroid and correlation with
histopathology in a contemporary series of 240 patients. Am J Surg.
186:702–710. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Trimboli P, Castellana M, Sconfienza LM,
Virili C, Pescatori LC, Cesareo R, Giorgino F, Negro R, Giovanella
L and Mauri G: Efficacy of thermal ablation in benign
non-functioning solid thyroid nodule: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Endocrine. 67:35–43. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang M, Tufano RP, Russell JO, Zhang Y,
Zhang Y, Qiao Z and Luo Y: Ultrasound-guided radiofrequency
ablation versus surgery for low-risk papillary thyroid
microcarcinoma: Results of over 5 years' follow-up. Thyroid.
30:408–417. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
De Carlucci D, Tavares MR, Obara MT,
Martins LA, Hojaij FC and Cernea CR: Thyroid function after
unilateral total lobectomy: Risk factors for postoperative
hypothyroidism. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 134:1076–1079.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Grani G, Lamartina L, Biffoni M,
Giacomelli L, Maranghi M, Falcone R, Ramundo V, Cantisani V,
Filetti S and Durante C: Sonographically estimated risks of
malignancy for thyroid nodules computed with five standard
classification systems: Changes over time and their relation to
malignancy. Thyroid. 28:1190–1197. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Norlén O, Popadich A, Kruijff S, Gill AJ,
Sarkis LM, Delbridge L, Sywak M and Sidhu S: Bethesda III thyroid
nodules: The role of ultrasound in clinical decision making. Ann
Surg Oncol. 21:3528–3533. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ramouz A, Rasihashemi SZ, Daghigh F,
Faraji E and Rouhani S: Predisposing factors for seroma formation
in patients undergoing thyroidectomy: Cross-sectional study. Ann
Med Surg (Lond). 23:8–12. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|