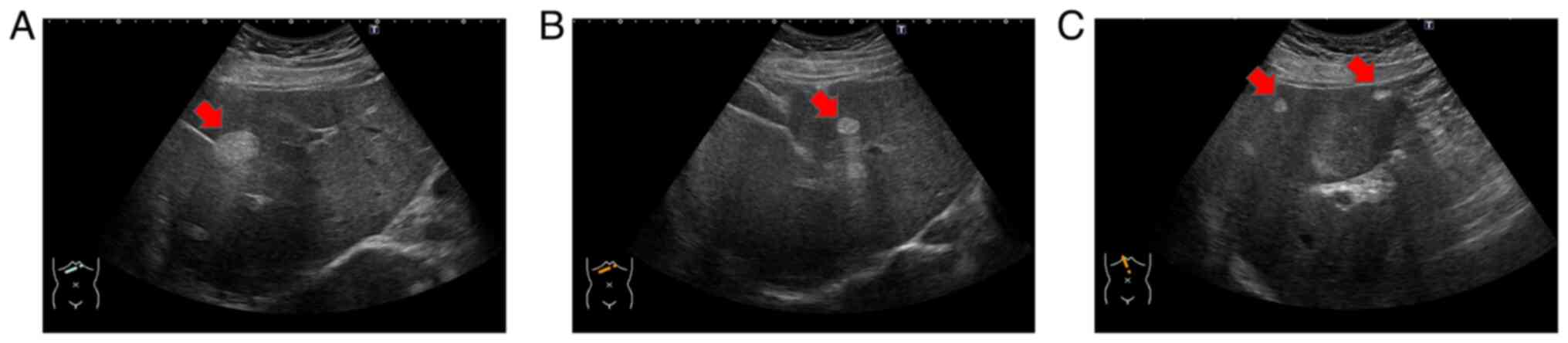
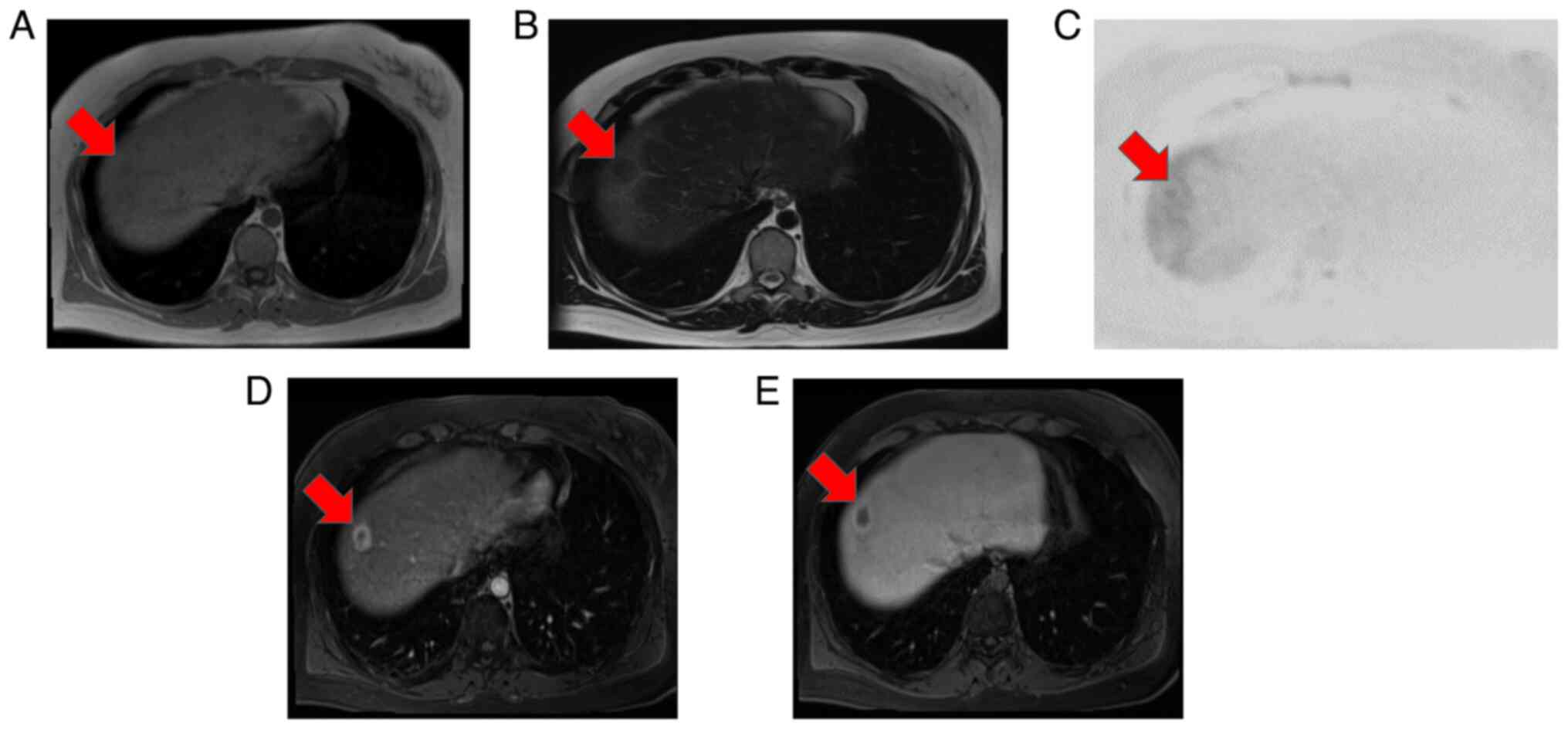
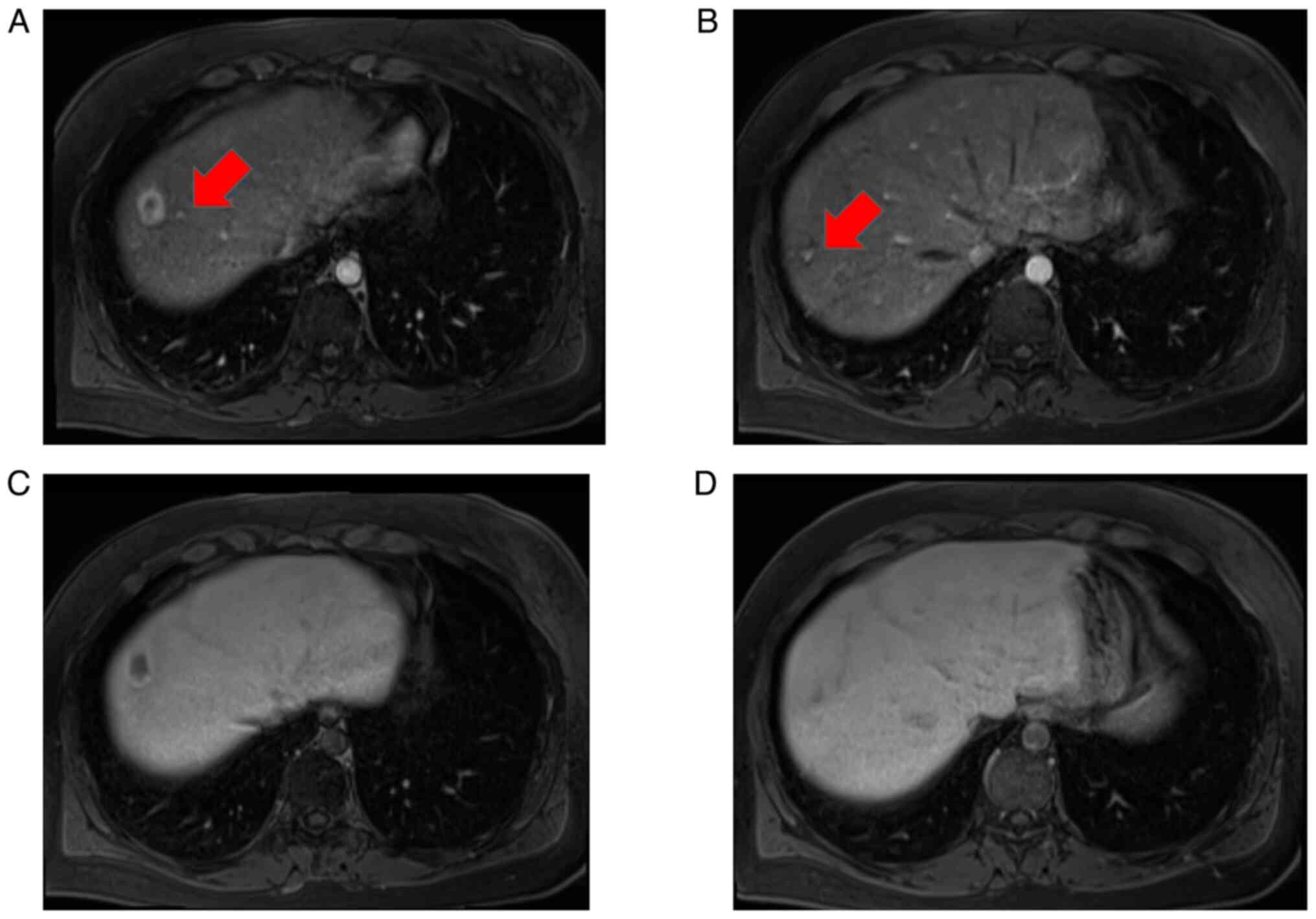
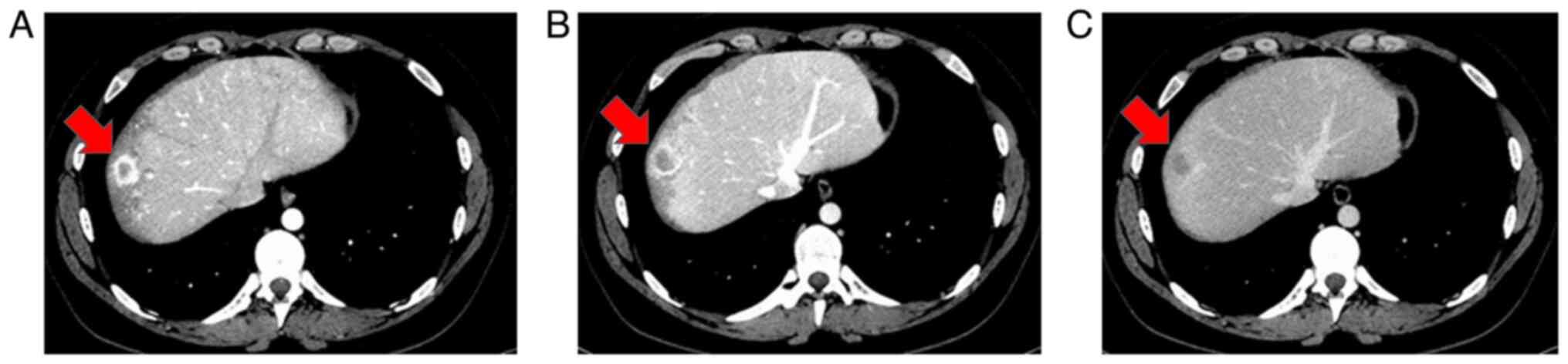
|
1
|
Li FP, Fraumeni JF Jr, Mulvihill JJ,
Blattner WA, Dreyfus MG, Tucker MA and Miller RW: A cancer family
syndrome in twenty-four kindreds. Cancer Res. 48:5358–5362.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yoshida GJ, Fuchimoto Y, Osumi T, Shimada
H, Hosaka S, Morioka H, Mukai M, Masugi Y, Sakamoto M and Kuroda T:
Li-Fraumeni syndrome with simultaneous osteosarcoma and liver
cancer: Increased expression of a CD44 variant isoform after
chemotherapy. BMC Cancer. 12(444)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Amadou A, Achatz MIW and Hainaut P:
Revisiting tumor patterns and penetrance in germline TP53 mutation
carriers: Temporal phases of Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Curr Opin Oncol.
30:23–29. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Peng G, Bojadzieva J, Ballinger ML, Li J,
Blackford AL, Mai PL, Savage SA, Thomas DM, Strong LC and Wang W:
Estimating TP53 mutation carrier probability in families with
Li-Fraumeni syndrome using LFSPRO. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 26:837–844. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gonzalez KD, Noltner KA, Buzin CH, Gu D,
Wen-Fong CY, Nguyen VQ, Han JH, Lowstuter K, Longmate J, Sommer SS
and Weitzel JN: Beyond Li Fraumeni syndrome: Clinical
characteristics of families with p53 germline mutations. J Clin
Oncol. 27:1250–1256. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bonetti F, Pea M, Martignoni G and Zamboni
G: PEC and sugar. Am J Surg Pathol. 16:307–308. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Folpe AL and Kwiatkowski DJ: Perivascular
epithelioid cell neoplasms: Pathology and pathogenesis. Hum Pathol.
41:1–15. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Galera López MDM, Márquez Rodas I, Agra
Pujol C, García Pérez Á, Velasco Sánchez E and Álvarez Álvarez R:
Simultaneous diagnosis of liver PEComa in a family with known
Li-Fraumeni syndrome: A case report. Clin Sarcoma Res.
10(24)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Neofytou K, Famularo S and Khan AZ: PEComa
in a young patient with known Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Case Rep Med.
2015(906981)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Butz H, Lövey J, Szentkereszty M, Bozsik
A, Tóth E and Patócs A: Case report: A novel pathomechanism in
PEComa by the loss of heterozygosity of TP53. Front Oncol.
12(849004)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang Y, Lee J, Woo CG, Lee OJ and Son SM:
Epithelioid angiomyolipoma of the liver in a patient with
Li-Fraumeni syndrome: A case report. Diagn Pathol.
19(16)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Funato M, Tsunematsu Y, Yamazaki F, Tamura
C, Kumamoto T, Takagi M, Kato S, Sugimura H and Tamura K:
Characteristics of Li-Fraumeni syndrome in Japan; a review study by
the special committee of JSHT. Cancer Sci. 112:2821–2834.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sato M, Kojima M, Nagatsuma AK, Nakamura
Y, Saito N and Ochiai A: Optimal fixation for total preanalytic
phase evaluation in pathology laboratories: A comprehensive study
including immunohistochemistry, DNA, and mRNA assays. Pathol Int.
64:209–216. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kumamoto T, Yamazaki F, Nakano Y, Tamura
C, Tashiro S, Hattori H, Nakagawara A and Tsunematsu Y: Medical
guidelines for Li-Fraumeni syndrome. 2019, version 1.1. Int J Clin
Oncol. 26:2161–2178. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bougeard G, Renaux-Petel M, Flaman JM,
Charbonnier C, Fermey P, Belotti M, Gauthier-Villars M,
Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Consolino E, Brugières L, et al: Revisiting
Li-Fraumeni syndrome from TP53 mutation carriers. J Clin Oncol.
33:2345–2352. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jeon IS and Lee SM: Multimodal treatment
using surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy in a patient with a
perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the uterus. J Pediatr
Hematol Oncol. 27:681–684. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liu CH, Chao WT, Lin SC, Lau HY, Wu HH and
Wang PH: Malignant perivascular epithelioid cell tumor in the
female genital tract: Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses. Medicine (Baltimore).
98(e14072)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Khaja F, Carilli A, Baidas S, Sriharan A
and Norford S: PEComa: A perivascular epithelioid cell tumor in the
liver-a case report and review of the literature. Case Rep Med.
2013(904126)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fang SH, Zhou LN, Jin M and Hu JB:
Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor of the liver: A report of two
cases and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol.
13:5537–5539. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Armah HB and Parwani AV: Perivascular
epithelioid cell tumor. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 133:648–654.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kirste S, Kayser G, Zipfel A, Grosu AL and
Brunner T: Unresectable hepatic PEComa: A rare malignancy treated
with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) followed by
complete resection. Radiat Oncol. 13(28)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lin KH, Chang NJ, Liou LR, Su MS, Tsao MJ
and Huang ML: Successful management of perivascular epithelioid
cell tumor of the rectum with recurrent liver metastases: A case
report. Medicine (Baltimore). 97(e11679)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Folpe AL, Mentzel T, Lehr HA, Fisher C,
Balzer BL and Weiss SW: Perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms of
soft tissue and gynecologic origin: A clinicopathologic study of 26
cases and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1558–1575.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tan Y, Zhang H and Xiao EH: Perivascular
epithelioid cell tumour: Dynamic CT, MRI and clinicopathological
characteristics-analysis of 32 cases and review of the literature.
Clin Radiol. 68:555–561. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zheng RQ, Kudo M, Ishikawa E, Chung H,
Minami Y, Ogawa C, Sakaguchi Y, Kitano M, Kawasaki T and Maekawa K:
Hepatic angiomyolipoma: Identification of an efferent vessel as a
hepatic vein by contrast-enhanced harmonic sonography. J Med
Ultrason (2001). 32:191–196. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Akitake R, Kimura H, Sekoguchi S, Nakamura
H, Seno H, Chiba T and Fujimoto S: Perivascular epithelioid cell
tumor (PEComa) of the liver diagnosed by contrast-enhanced
ultrasonography. Intern Med. 48:2083–2086. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sun L, Sun X, Li Y and Xing L: The role of
(18)F-FDG PET/CT imaging in patient with malignant PEComa treated
with mTOR inhibitor. Onco Targets Ther. 8:1967–1970.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Takahashi M, Nojima H, Kuboki S, Horikoshi
T, Yokota T, Yoshitomi H, Furukawa K, Takayashiki T, Takano S and
Ohtsuka M: Comparing prognostic factors of Glut-1 expression and
maximum standardized uptake value by FDG-PET in patients with
resectable pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 20:1205–1212.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Agaram NP, Sung YS, Zhang L, Chen CL, Chen
HW, Singer S, Dickson MA, Berger MF and Antonescu CR: Dichotomy of
genetic abnormalities in PEComas with therapeutic implications. Am
J Surg Pathol. 39:813–825. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bing Z, Yao Y, Pasha T, Tomaszewski JE and
Zhang PJ: p53 in pure epithelioid PEComa: An immunohistochemistry
study and gene mutation analysis. Int J Surg Pathol. 20:115–122.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rakheja R, Abikhzer G, Alabed YZ, Nahal A
and Lisbona R: The appearance of osseous PEComa on F-18 FDG PET/CT.
Clin Nucl Med. 37:190–192. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wagner AJ, Ravi V, Riedel RF, Ganjoo K,
Van Tine BA, Chugh R, Cranmer L, Gordon EM, Hornick JL, Du H, et
al: nab-Sirolimus for patients with malignant perivascular
epithelioid cell tumors. J Clin Oncol. 39:3660–3670.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|