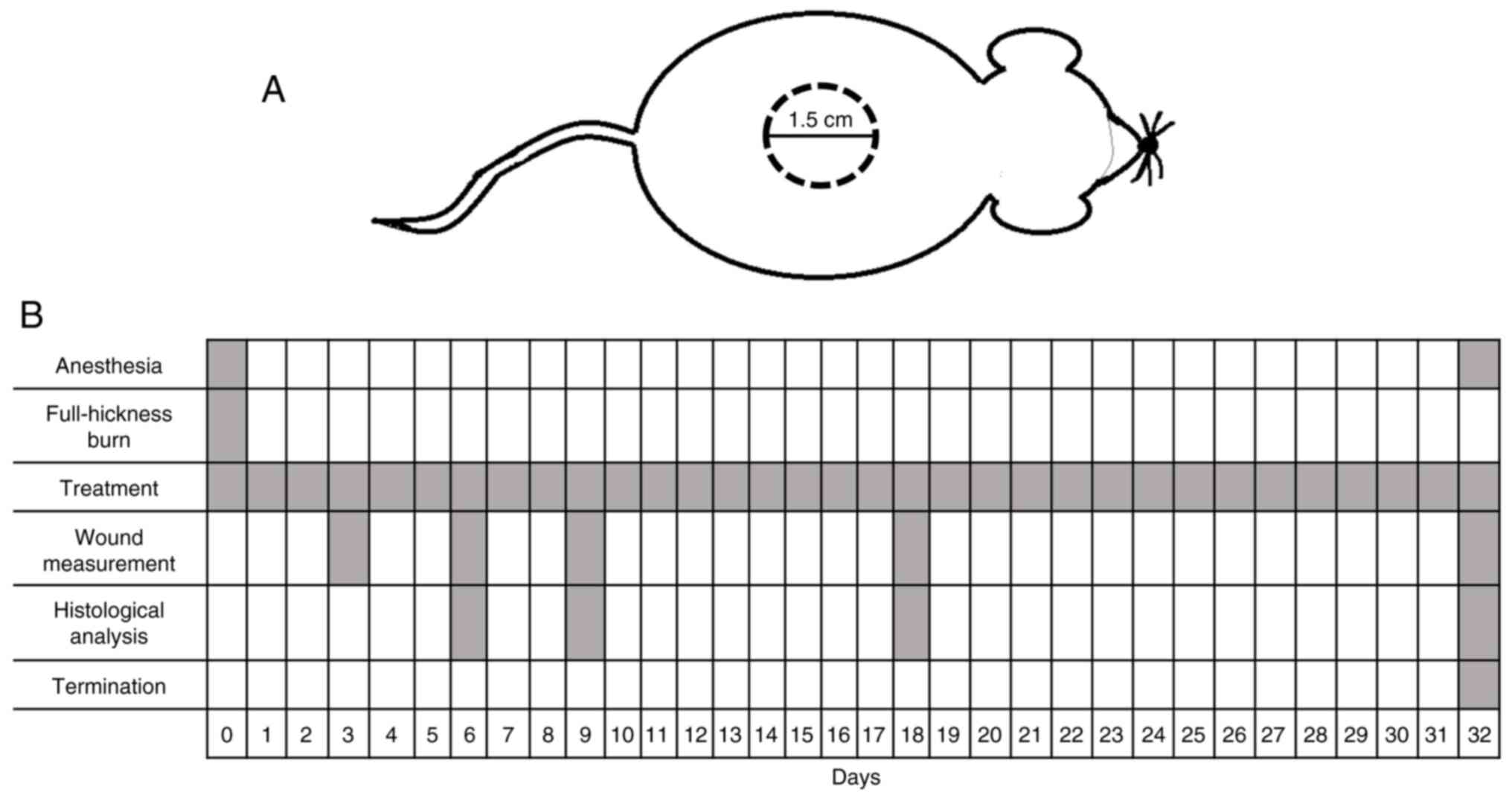
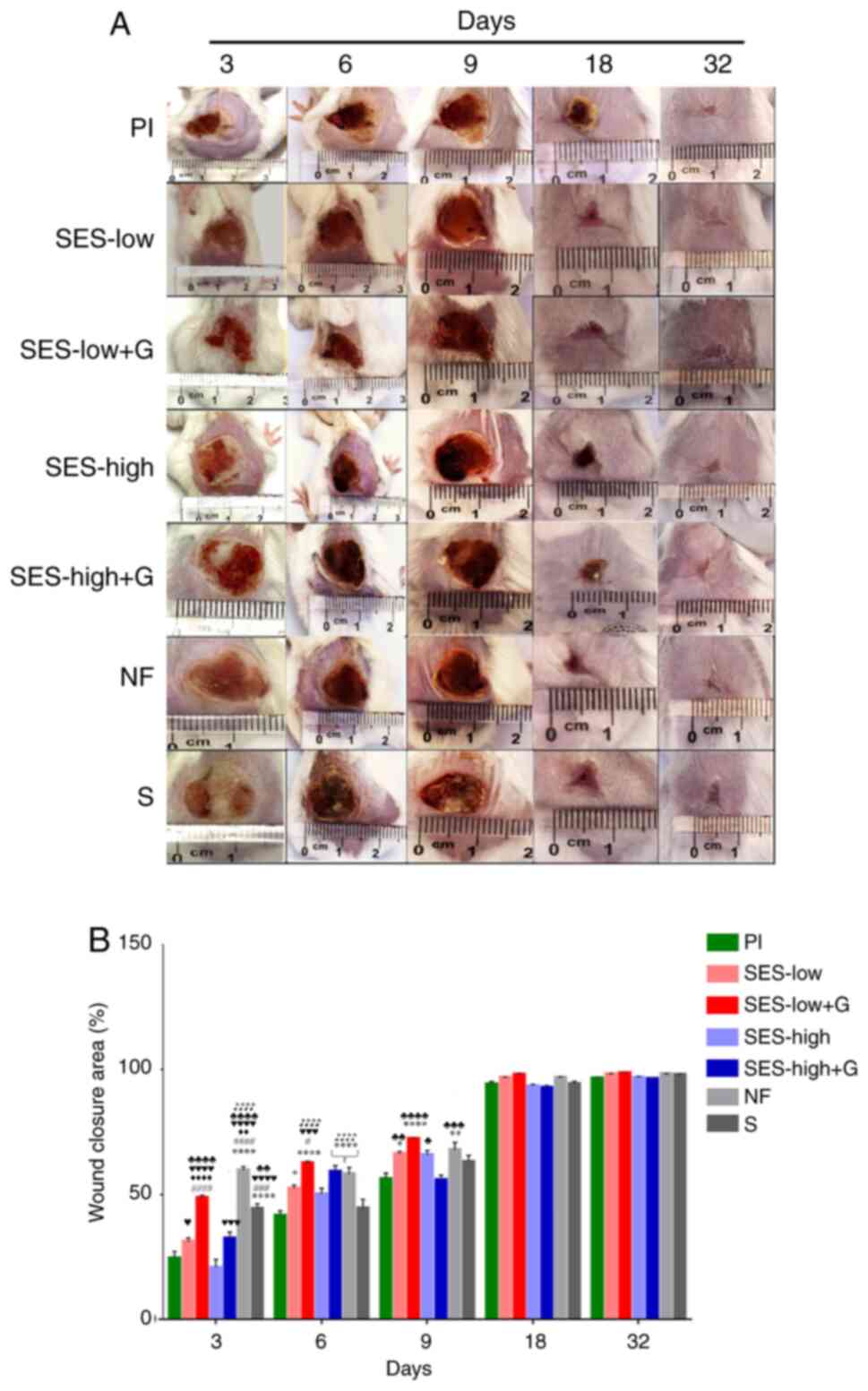
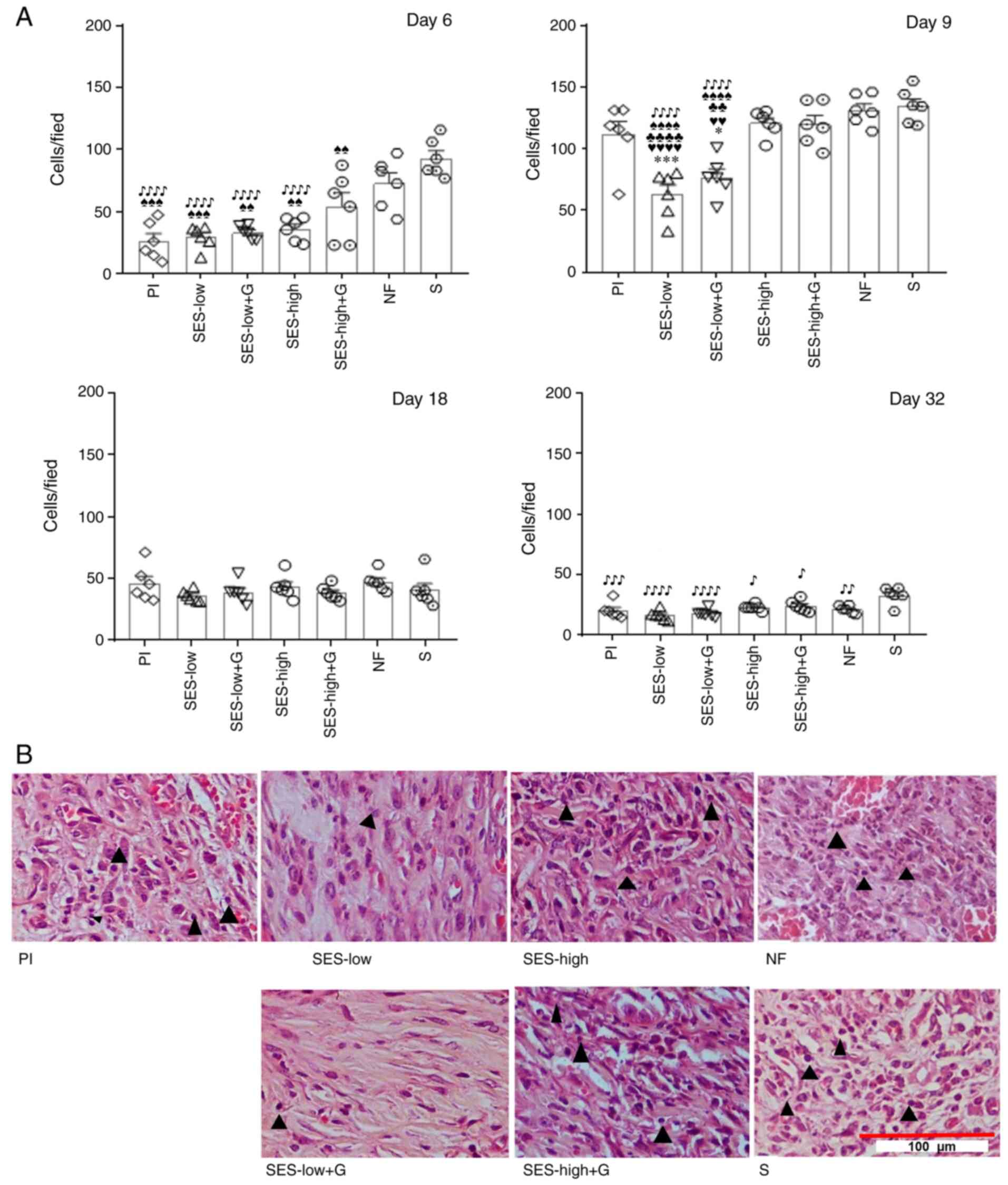
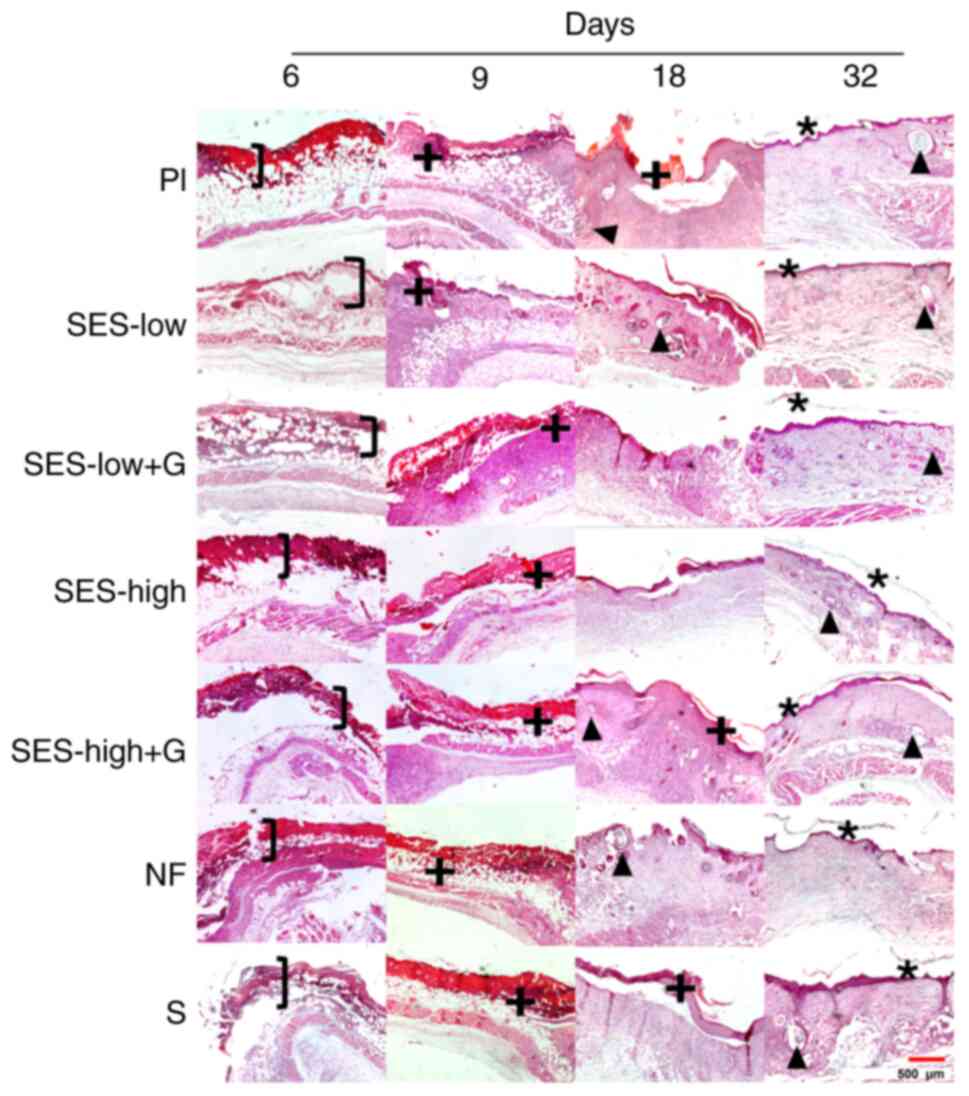
|
1
|
Summer GJ, Puntillo KA, Miaskowski C,
Green PG and Levine JD: Burn injury pain: The continuing challenge.
J Pain. 8:533–548. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Warby R and Maani CV: Burn classification.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing,
2024.
|
|
3
|
Stiles K: Emergency management of burns:
Part 2. Emerg Nurse. 26:36–41. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Eyvaz K, Kement M, Balin S, Acar H, Kündeş
F, Karaoz A, Civil O, Eser M, Kaptanoglu L, Vural S and Bildik N:
Clinical evaluation of negative-pressure wound therapy in the
management of electrical burns. Turk J Trauma Emerg Surg.
24:456–461. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu YT, Chen KH, Ban SL, Tung KY and Chen
LR: Evaluation of leap motion control for hand rehabilitation in
burn patients: An experience in the dust explosion disaster in
Formosa Fun Coast. Burns. 45:157–164. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Markiewicz-Gospodarek A, Kozioł M, Tobiasz
M, Baj J, Radzikowska-Büchner E and Przekora A: Burn wound healing:
Clinical complications, medical care, treatment, and dressing
types: The current state of knowledge for clinical practice. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 19(1338)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
James SL, Lucchesi LR, Bisignano C, Castle
CD, Dingels ZV, Fox JT, Hamilton EB, Henry NJ, McCracken D, Roberts
NLS, et al: Epidemiology of injuries from fire, heat and hot
substances: Global, regional and national morbidity and mortality
estimates from the global burden of disease 2017 study. Inj Prev.
26 (Supp 1):i36–i45. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Abarca L, Guilabert P, Martin N, Usúa G,
Barret JP and Colomina MJ: Epidemiology and mortality in patients
hospitalized for burns in Catalonia, Spain. Sci Rep.
13(14364)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yakupu A, Zhang J, Dong W, Song F, Dong J
and Lu S: The epidemiological characteristic and trends of burns
globally. BMC Public Health. 22(1596)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Giummarra MJ, Casey SL, Devlin A, Ioannou
LJ, Gibson SJ, Georgiou-Karistianis N, Jennings PA, Cameron PA and
Ponsford J: Co-occurrence of posttraumatic stress symptoms, pain,
and disability 12 months after traumatic injury. Pain Rep.
2(e622)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tiwari VK: Burn wound: How it differs from
other wounds? Indian J Plast Surg. 45:364–373. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hoang DM, Pham PT, Bach TQ, Ngo ATL,
Nguyen QT, Phan TTK, Nguyen GH, Le PTT, Hoang VT, Forsyth NR, et
al: Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 7(272)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shu DY, Hutcheon AEK, Zieske JD and Guo X:
Epidermal growth factor stimulates transforming growth factor-beta
receptor type II expression in corneal epithelial cells. Sci Rep.
9(8079)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rothe MJ and Falanga V: Growth factors and
wound healing. Clin Dermatol. 9:553–559. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Negut I, Grumezescu V and Grumezescu A:
Treatment strategies for infected wounds. Molecules.
23(2392)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Norman G, Christie J, Liu Z, Westby MJ,
Jefferies JM, Hudson T, Edwards J, Mohapatra DP, Hassan IA and
Dumville JC: Antiseptics for burns. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
7(CD011821)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lagziel T, Asif M, Born L, Quiroga LH,
Duraes E, Slavin B, Shetty P, Caffrey J and Hultman CS: Evaluating
the efficacy, safety, and tolerance of silver sulfadiazine
dressings once daily versus twice daily in the treatment of burn
wounds. J Burn Care Res. 42:1136–1139. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kazemzadeh J, Yousefiazar A and Zahedi A:
Amniotic membrane dressing versus nitrofurazone-impregnated
dressing in the treatment of second-degree burn wounds: A
randomized clinical trial. Wounds. 34:11–16. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Webber CE, Glanges E and Crenshaw CA:
Treatment of second degree burns: Nitrofurazone, povidone-iodine,
and silver sulfadiazine. JACEP. 6:486–490. 1977.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yamakawa S and Hayashida K: Advances in
surgical applications of growth factors for wound healing. Burns
Trauma. 7(10)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Toral-Freyre SDC, Castillejos-López M,
Hernández A, Becerril-Vargas E, Mújica-Sánchez MA, Mendoza-Romero
VM, Casino-Ríos A, González-Mancera G, Cabrera-Licona A and
Mervitch-Sigal N: Uso de una solución electrolizada de
superoxidación para desinfectar mascarillas de ventilación mecánica
no invasiva. Neumol Cir Torax. 81:224–231. 2022.(In Spanish).
|
|
22
|
Cárdenas AM, Campos-Bijit V, Di Francesco
F, Schwarz F, Cafferata EA and Vernal R: Electrolyzed water for the
microbiologic control in the pandemic dental setting: A systematic
review. BMC Oral Health. 22(579)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yan P, Daliri EBM and Oh DH: New clinical
applications of electrolyzed water: A review. Microorganisms.
9(136)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Delgado-Enciso I, Paz-Garcia J,
Barajas-Saucedo C, Mokay-Ramírez KA, Meza-Robles C, Lopez-Flores R,
Delgado-Machuca M, Murillo-Zamora E, Toscano-Velazquez JA,
Delgado-Enciso J, et al: Safety and efficacy of a COVID-19
treatment with nebulized and/or intravenous neutral electrolyzed
saline combined with usual medical care vs usual medical care
alone: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial. Exp Ther Med.
22(915)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Aurelien-Cabezas NS, Paz-Michel BA,
Jacinto-Cortes I, Delgado-Enciso OG, Montes-Galindo DA,
Cabrera-Licona A, Zaizar-Fregoso SA, Paz-Garcia J, Ceja-Espiritu G,
Melnikov V, et al: Protective effect of neutral electrolyzed saline
on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: Evaluation of histopathologic
parameters in a murine model. Medicina (Kaunas).
59(397)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
González-Cantú CC, Torres-Muñoz Á,
Urrutia-Baca VH, Sánchez-García GA and De La Garza-Ramos MA:
Antibacterial efficacy of a pH-neutral electrolyzed super-oxidized
solution for nonsurgical periodontal treatment. Heliyon.
8(e12291)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gutiérrez-García R, De La Cerda-Ángeles
JC, Cabrera-Licona A, Delgado-Enciso I, Mervitch-Sigal N and
Paz-Michel BA: Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal rinses with neutral
electrolyzed water prevents COVID-19 in front-line health
professionals: A randomized, open-label, controlled trial in a
general hospital in Mexico City. Biomed Rep. 16(11)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Medina-Tamayo J, Sánchez-Miranda E,
Balleza-Tapia H, Ambriz X, Cid ME, González-Espinosa D, Gutiérrez
AA and González-Espinosa C: Super-oxidized solution inhibits
IgE-antigen-induced degranulation and cytokine release in mast
cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:1013–1024. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Fadriquela A, Sajo MEJ, Bajgai J, Kim DH,
Kim CS, Kim SK and Lee KJ: Effects of strong acidic electrolyzed
water in wound healing via inflammatory and oxidative stress
response. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020(2459826)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zaizar-Fregoso SA, Paz-Michel BA,
Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Paz-Garcia J, Aurelien-Cabezas NS,
Tiburcio-Jimenez D, Melnikov V, Murillo-Zamora E, Delgado-Enciso
OG, Cabrera-Licona A, et al: Systemic administration of neutral
electrolyzed saline as a novel treatment for rheumatoid arthritis
reduces mechanical and inflammatory damage to the joints:
Preclinical evaluation in mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2022(1717614)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Opneja A, Kapoor S and Stavrou EX:
Contribution of platelets, the coagulation and fibrinolytic systems
to cutaneous wound healing. Thromb Res. 179:56–63. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mishra B, Sharma DJ and Arora C:
Comparative study of the efficacy of ionic silver solution and
super oxidized solution in the management of chronic wounds. Med J
Armed Forces India. 79:40–45. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
García JP, Maldonado RA, Díaz RI, Muñiz J
and Rodríguez HA: Sustitución del uso de solución salina
fisiológica como irrigante en el manejo de pacientes sépticos y
quirúrgicos por solución electrolizada. Rev Mex Cir Bucal
Maxilofac. 7:46–52. 2011.(In Spanish).
|
|
34
|
Yahagi N, Kono M, Kitahara M, Ohmura A,
Sumita O, Hashimoto T, Hori K, Ning-Juan C, Woodson P, Kubota S, et
al: Effect of electrolyzed water on wound healing. Artif Organs.
24:984–987. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
United Mexican States-Ministry of Health:
Regulation of the General Health Law on Health Research. Official
Journal of the Federation: 1-31, 1987 (In Spanish). https://www.diputados.gob.mx/LeyesBiblio/regley/Reg_LGS_MIS.pdf.
|
|
36
|
Ministry of Agriculture GDRP and A:
Mexican norm NOM-0062-ZOO-1999 entitled Technical specifications
for the production, care and use of laboratory animals. Government
of Mexico, Mexico, 1999 (In Spanish). https://www.fmvz.unam.mx/fmvz/principal/archivos/062ZOO.PDF.
|
|
37
|
de Aluja AS: Laboratory animals and
official Mexican norms (NOM-062-ZOO-1999). Gac Med Mex.
138:295–298. 2002.PubMed/NCBI(In Spanish).
|
|
38
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th
edition. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US), 2011.
|
|
39
|
Mels C, Niebuhr K, Futschik A, Rault JL
and Waiblinger S: Development and evaluation of an animal health
and welfare monitoring system for veterinary supervision of pullet
farms. Prev Vet Med. 217(105929)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Mattsson JL, Spencer PJ and Albee RR: A
performance standard for clinical and functional observational
battery examinations of rats. J Am Coll Toxicol. 15:239–254.
1996.
|
|
41
|
Redfern WS, Dymond A, Strang I, Storey S,
Grant C, Marks L, Barnard C, Heys C, Moyser K, Greenwood K, et al:
The functional observational battery and modified Irwin test as
global neurobehavioral assessments in the rat: Pharmacological
validation data and a comparison of methods. J Pharmacol Toxicol
Methods. 98(106591)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Talbot SR, Biernot S, Bleich A, van Dijk
RM, Ernst L, Häger C, Helgers SOA, Koegel B, Koska I, Kuhla A, et
al: Defining body-weight reduction as a humane endpoint: A critical
appraisal. Lab Anim. 54:99–110. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
McIntyre MK, Clifford JL, Maani CV and
Burmeister DM: Progress of clinical practice on the management of
burn-associated pain: Lessons from animal models. Burns.
42:1161–1172. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Girtler R and Gustorff B: Schmerztherapie
bei verbrennungen. Anaesthesist. 60:243–250. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
45
|
Animal Experimentation Center Ethics
Committee (CEUMA): Surgical Analgesia Refinement in Surgical
Protocols in Experimental Animals. Málaga, 2019 (In Spanish).
https://www.fmvz.unam.mx/fmvz/principal/archivos/cicuae/Protocolos_analgesia_roedores.pdf.
|
|
46
|
American Veterinary Medical Association:
AVMA Guidelines for the euthanasia of animals: 2013 Edition. 5-95,
2013. https://www.in.gov/boah/files/AVMA_Euthanasia_Guidelines.pdf.
|
|
47
|
Abdullahi A, Amini-Nik S and Jeschke MG:
Animal models in burn research. Cell Mol Life Sci. 71:3241–3255.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cortes-Alvarez SI, Delgado-Enciso I,
Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Hernandez-Fuentes GA, Aurelien-Cabezas NS,
Moy-Lopez NA, Cortes-Alvarez NY, Guzman-Muñiz J, Guzman-Esquivel J,
Rodriguez-Sanchez IP, et al: Efficacy of hot tea infusion vs
ethanolic extract of moringa oleifera for the simultaneous
treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver, hyperlipidemia, and
hyperglycemia in a murine model fed with a high-fat diet. J Nutr
Metab. 2024(2209581)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang L, Hu Q, Jin H, Yang Y, Yang Y, Yang
R, Shen Z and Chen P: Effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on second-degree
burn wound healing and FGF-2/PDGF-BB/PDGFR-β pathway modulation.
Chin Med. 16(45)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Gupta A and Kumar P: Assessment of the
histological state of the healing wound. Plast Aesthet Res.
2:239–242. 2015.
|
|
52
|
Santos TS, Santos IDDD, Pereira-Filho RN,
Gomes SVF, Lima-Verde IB, Marques MN, Cardoso JC, Severino P, Souto
EB and Albuquerque-Júnior RLC: Histological evidence of wound
healing improvement in rats treated with oral administration of
hydroalcoholic extract of vitis labrusca. Curr Issues Mol Biol.
43:335–352. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Holzer-Geissler JCJ, Schwingenschuh S,
Zacharias M, Einsiedler J, Kainz S, Reisenegger P, Holecek C,
Hofmann E, Wolff-Winiski B, Fahrngruber H, et al: The impact of
prolonged inflammation on wound healing. Biomedicines.
10(856)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sultana J, Molla MR, Kamal M, Shahidullah
M, Begum F and Bashar MA: Histological differences in wound healing
in Maxillofacial region in patients with or without risk factors.
Bangladesh J Pathol. 24:3–8. 1970.
|
|
55
|
Masson-Meyers DS, Andrade TAM, Caetano GF,
Guimaraes FR, Leite MN, Leite SN and Frade MAC: Experimental models
and methods for cutaneous wound healing assessment. Int J Exp
Pathol. 101:21–37. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Onesti MG, Fioramonti P, Carella S and
Maruccia M: The importance of periwound skin in the treatment of
‘difficult wound’. G Chir. 32:83–88. 2011.PubMed/NCBI(In Italian).
|
|
57
|
Maurizi E, Adamo D, Magrelli FM, Galaverni
G, Attico E, Merra A, Maffezzoni MBR, Losi L, Genna VG, Sceberras V
and Pellegrini G: Regenerative medicine of epithelia: Lessons from
the past and future goals. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
9(652214)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Liew YM, McLaughlin RA, Gong P, Wood FM
and Sampson DD: In vivo assessment of human burn scars through
automated quantification of vascularity using optical coherence
tomography. J Biomed Opt. 18(061213)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Cardoso JC, Veraitch O, Gianotti R,
Ferrara G, Tomasini CF, Singh M, Zalaudek I and Stefanato CM:
‘Hints’ in the horn: Diagnostic clues in the stratum corneum. J
Cutan Pathol. 44:256–278. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Lateef Z, Stuart G, Jones N, Mercer A,
Fleming S and Wise L: The cutaneous inflammatory response to
thermal burn injury in a murine model. Int J Mol Sci.
20(538)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Andritoiu CV, Andriescu CE, Danu M, Lungu
C, Ivanescu B, Havarneanu C and Popa M: Evaluation of the wound
healing potential of some natural polymers on three experimental
models. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 14(465)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Tang X, Wang X, Sun Y, Zhao L, Li D, Zhang
J, Sun H and Yang B: Magnesium oxide-assisted dual-cross-linking
bio-multifunctional hydrogels for wound repair during
full-thickness skin injuries. Adv Funct Mater. 31(2105718)2021.
|
|
63
|
Itoi E, Minagawa H, Yamamoto N, Seki N and
Abe H: Are pain location and physical examinations useful in
locating a tear site of the rotator cuff? Am J Sports Med.
34:256–264. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Ito M, Yang Z, Andl T, Cui C, Kim N,
Millar SE and Cotsarelis G: Wnt-dependent de novo hair follicle
regeneration in adult mouse skin after wounding. Nature.
447:316–320. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Oshimori N and Fuchs E: Paracrine TGF-β
signaling counterbalances BMP-mediated repression in hair follicle
stem cell activation. Cell Stem Cell. 10:63–75. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Schultz GS, Chin GA, Moldawer L and
Diegelmann RF: Principles of wound healing. Fitridge R and Thompson
M (eds). In: Mechanisms of Vascular Disease: A Reference Book for
Vascular Specialists [Internet]. Adelaide (AU): University of
Adelaide Press, 2011.
|
|
67
|
Englbrecht M, Tarner IH, van der Heijde
DM, Manger B, Bombardier C and Müller-Ladner U: Measuring pain and
efficacy of pain treatment in inflammatory arthritis: A systematic
literature review. J Rheumatol Suppl. 90:3–10. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Rose LF and Chan RK: The burn wound
microenvironment. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 5:106–118.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Evers LH, Bhavsar D and Mailänder P: The
biology of burn injury. Exp Dermatol. 19:777–783. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Montesinos-Peña NE, Hernández-Valencia M,
Delgado-Enciso I, Herrera-Leal A and Paz-Michel BA: Evaluación de
un gel antiséptico de aplicación intravaginal para pacientes con
infecciones cervicovaginales multitratadas. Ginecol Obstet Méx.
87:454–466. 2019.
|
|
71
|
You HS, Fadriquela A, Sajo MEJ, Bajgai J,
Ara J, Kim CS, Kim SK, Oh JR, Shim KY, Lim HK and Lee KJ: Wound
healing effect of slightly acidic electrolyzed water on cutaneous
wounds in hairless mice via immune-redox modulation. Biol Pharm
Bull. 40:1423–1431. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Papaccio F, D'Arino A, Caputo S and Bellei
B: Focus on the contribution of oxidative stress in skin aging.
Antioxidants (Basel). 11(1121)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Siwik DA, Pagano PJ and Colucci WS:
Oxidative stress regulates collagen synthesis and matrix
metalloproteinase activity in cardiac fibroblasts. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 280:C53–C60. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Kawaguchi Y, Tanaka H, Okada T, Konishi H,
Takahashi M, Ito M and Asai J: Effect of reactive oxygen species on
the elastin mRNA expression in cultured human dermal fibroblasts.
Free Radic Biol Med. 23:162–165. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Carrim N, Walsh TG, Consonni A, Torti M,
Berndt MC and Metharom P: Role of focal adhesion tyrosine kinases
in GPVI-dependent platelet activation and reactive oxygen species
formation. PLoS One. 9(e113679)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Jang JY, Min JH, Chae YH, Baek JY, Wang
SB, Park SJ, Oh GT, Lee SH, Ho YS and Chang TS: Reactive oxygen
species play a critical role in collagen-induced platelet
activation via SHP-2 oxidation. Antioxid Redox Signal.
20:2528–2540. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Pérez-Sánchez A, Barrajón-Catalán E,
Ruiz-Torres V, Agulló-Chazarra L, Herranz-López M, Valdés A,
Cifuentes A and Micol V: Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) extract
causes ROS-induced necrotic cell death and inhibits tumor growth in
vivo. Sci Rep. 9(808)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Caley MP, Martins VLC and O'Toole EA:
Metalloproteinases and wound healing. Adv Wound Care (New
Rochelle). 4:225–234. 2015.
|
|
79
|
Belkhiri A, Richards C, Whaley M, McQueen
SA and Orr FW: Increased expression of activated matrix
metalloproteinase-2 by human endothelial cells after sublethal H2O2
exposure. Lab Invest. 77:533–539. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Delgado-Enciso I, Paz-Garcia J,
Valtierra-Alvarez J, Preciado-Ramirez J, Olmedo-Buenrostro BA,
Delgado-Enciso J, Guzman-Esquivel J, Barajas-Saucedo CE,
Ceja-Espiritu G, Rodriguez-Sanchez IP, et al: A novel cell-free
formulation for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis generates
better patient-reported health outcomes in more severe cases. J
Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 28(2309499020938121)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Delgado-Enciso I, Paz-Garcia J,
Rodriguez-Hernandez A, Madrigal-Perez VM, Cabrera-Licona A,
Garcia-Rivera A, Soriano-Hernandez AD, Cortes-Bazan JL,
Galvan-Salazar HR, Valtierra-Alvarez J, et al: A promising novel
formulation for articular cartilage regeneration: Preclinical
evaluation of a treatment that produces SOX9 overexpression in
human synovial fluid cells. Mol Med Rep. 17:3503–3510.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhang XR, Ryu U, Najmiddinov B, Trinh TTT,
Choi KM, Nam SY and Heo CY: Effect of silicone patch containing
metal-organic framework on hypertrophic scar suppression. In Vivo.
38:235–245. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Cheng W, Rong Y, Ning F and Zhang GA: The
content and ratio of type I and III collagen in skin differ with
age and injury. Afr J Biotechnol. 10:2524–2529. 2011.
|
|
84
|
Dyson M, Young SR, Hart J, Lynch JA and
Lang S: Comparison of the effects of moist and dry conditions on
the process of angiogenesis during dermal repair. J Invest
Dermatol. 99:729–733. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Vogt PM, Andree C, Breuing K, Liu PY,
Slama J, Helo G and Eriksson E: Dry, moist, and wet skin wound
repair. Ann Plast Surg. 34:493–500. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Barnett A, Berkowitz RL, Mills R and
Vistnes LM: Comparison of synthetic adhesive moisture vapor
permeable and fine mesh gauze dressings for split-thickness skin
graft donor sites. Am J Surg. 145:379–381. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Carter K: Hydropolymer dressings in the
management of wound exudate. Br J Community Nurs. 8 (9
Suppl):S10–S16. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Dai T, Huang YY, Sharma SK, Hashmi JT,
Kurup DB and Hamblin MR: Topical antimicrobials for burn wound
infections. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 5:124–151.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Levin NJ, Erben Y, Li Y, Brigham TJ and
Bruce AJ: A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing burn
healing outcomes between silver sulfadiazine and Aloe vera. Cureus.
14(e30815)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Muller MJ, Hollyoak MA, Moaveni Z, Brown
TLH, Herndon DN and Heggers JP: Retardation of wound healing by
silver sulfadiazine is reversed by Aloe vera and nystatin. Burns.
29:834–836. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Hosseinimehr SJ, Khorasani G, Azadbakht M,
Zamani P, Ghasemi M and Ahmadi A: Effect of aloe cream versus
silver sulfadiazine for healing burn wounds in rats. Acta
Dermatovenerol Croat. 18:2–7. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Cascione M, Rizzello L, Manno D, Serra A
and De Matteis V: Green silver nanoparticles promote inflammation
shutdown in human leukemic monocytes. Materials (Basel).
15(775)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Bartucci R, van der Meer AZ, Boersma YL,
Olinga P and Salvati A: Nanoparticle-induced inflammation and
fibrosis in ex vivo murine precision-cut liver slices and effects
of nanoparticle exposure conditions. Arch Toxicol. 95:1267–1285.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Zomer HD and Trentin AG: Skin wound
healing in humans and mice: Challenges in translational research. J
Dermatol Sci. 90:3–12. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
PLM Latin America: Estericide antiseptic
solution-PLM. PLM: 1, 2023 (In Spanish). https://www.medicamentosplm.com/Home/productos/estericide.solucion.antiseptica.solucion.topica/1365/101/33563/186.
|
|
96
|
Vademecum V: Estericide antiseptic
solution. Vademecum: 1, 2023 (In Spanish). https://www.vademecum.es/mexico/medicamento/1277798/estericide-solucion-antiseptica.
|