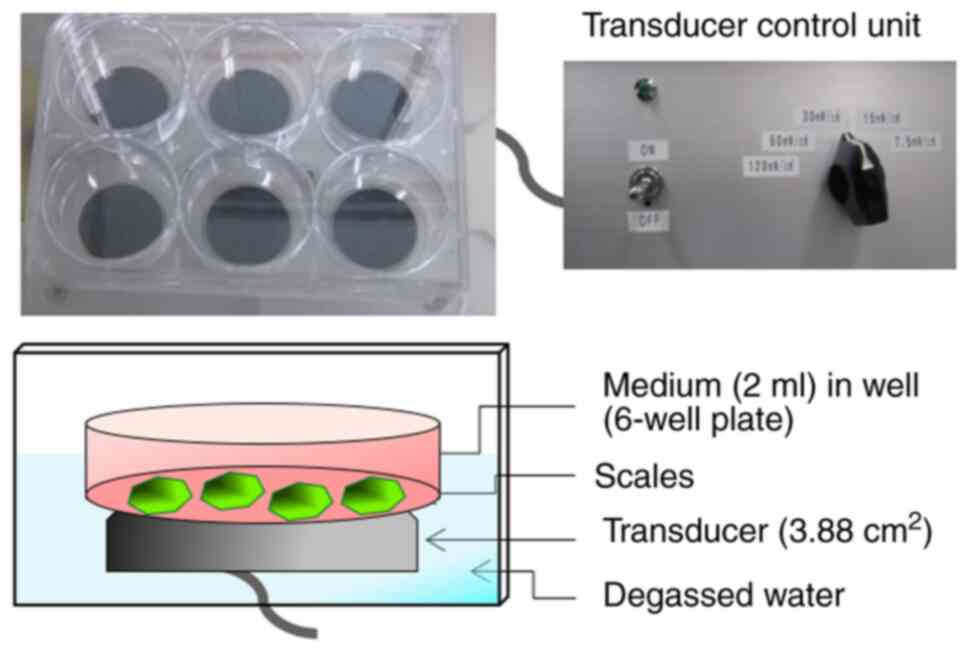
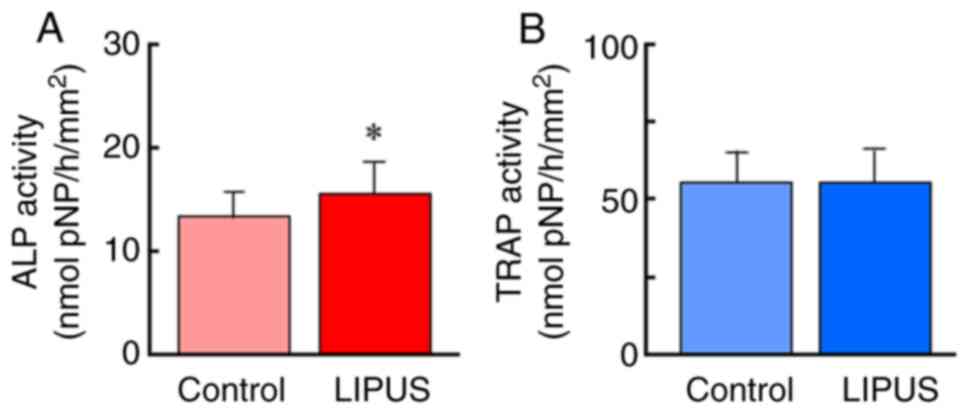
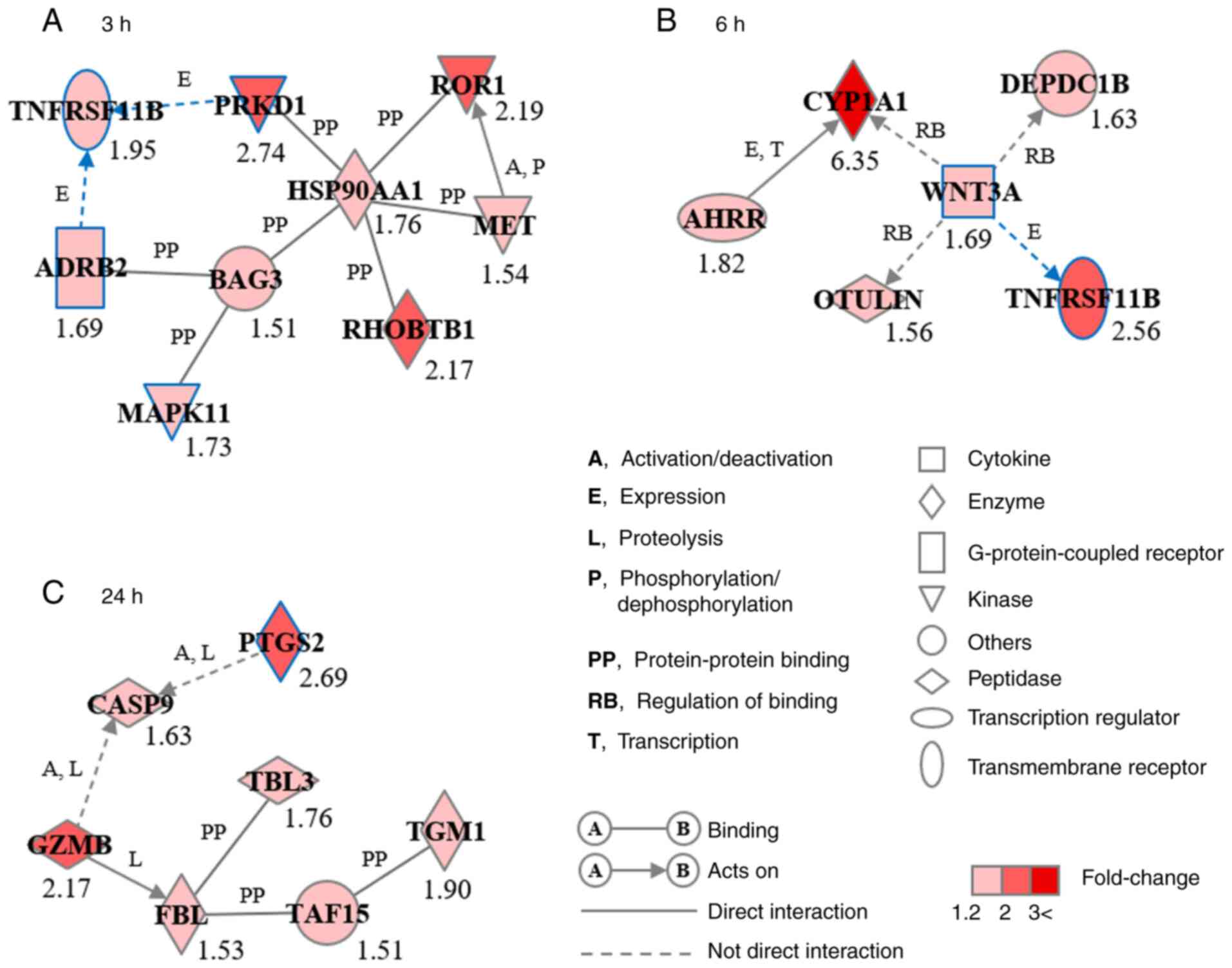
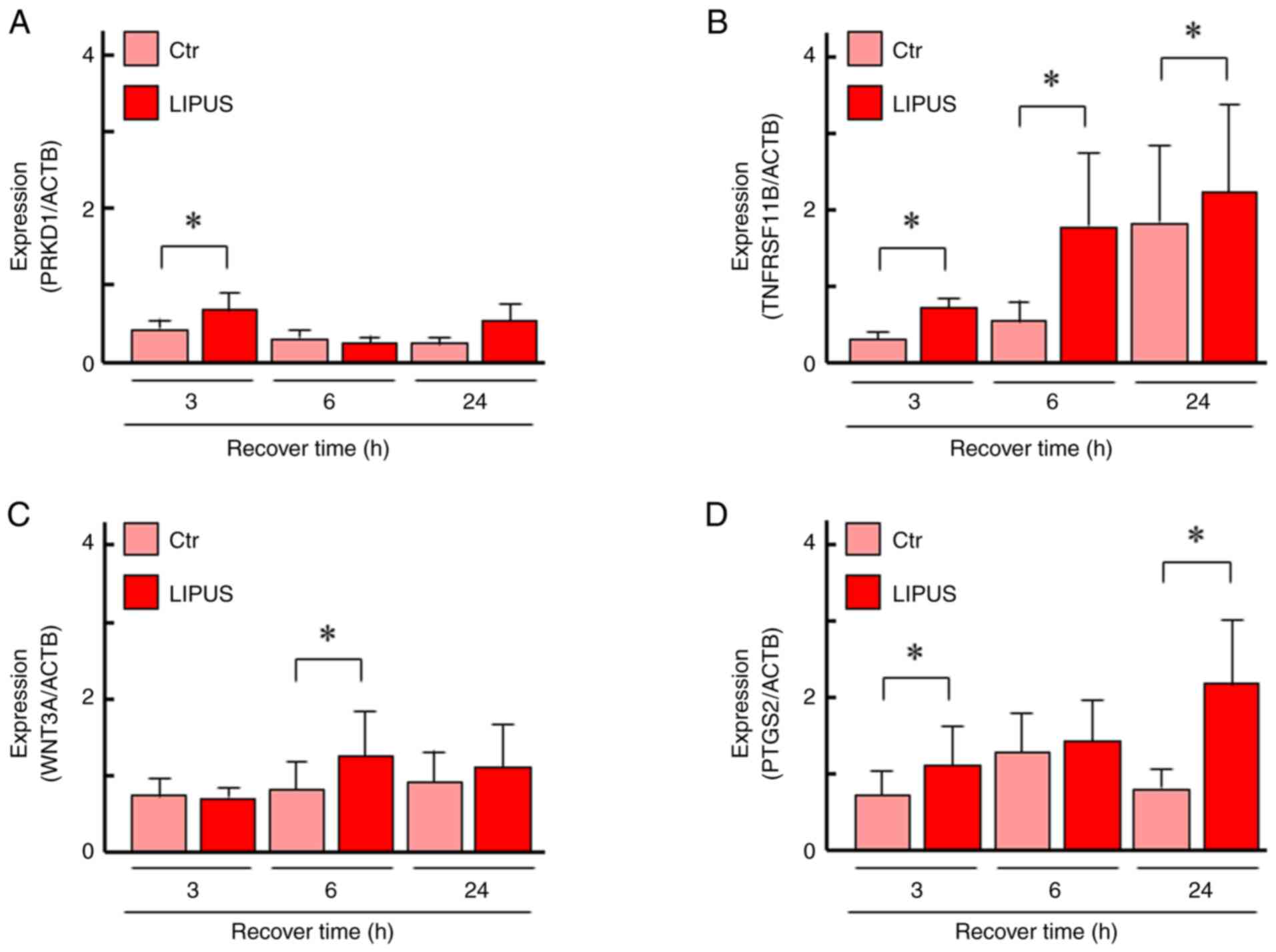
|
1
|
Barnett SB, Ter Haar GR, Ziskin MC, Rott
HD, Duck FA and Maeda K: International recommendations and
guidelines for the safe use of diagnostic ultrasound in medicine.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 26:355–366. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Snehota M, Vachutka J, Ter Haar G, Dolezal
L and Kolarova H: Therapeutic ultrasound experiments in vitro:
Review of factors influencing outcomes and reproducibility.
Ultrasonics. 107(106167)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Padilla F, Puts R, Vico L and Raum K:
Stimulation of bone repair with ultrasound: A review of the
possible mechanic effects. Ultrasonics. 54:1125–1145.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Harrison A, Lin S, Pounder N and
Mikuni-Takagaki Y: Mode & mechanism of low intensity pulsed
ultrasound (LIPUS) in fracture repair. Ultrasonics. 70:45–52.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kennedy JE: High-intensity focused
ultrasound in the treatment of solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:321–327. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Uchida T, Nakano M, Hongo S, Shoji S,
Nagata Y, Satoh T, Baba S, Usui Y and Terachi T: High-intensity
focused ultrasound therapy for prostate cancer. Int J Urol.
19:187–201. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Duarte LR: The stimulation of bone growth
by ultrasound. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (1978). 101:153–159.
1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Azuma Y, Ito M, Harada Y, Takagi H, Ohta T
and Jingushi S: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates rat
femoral fracture healing by acting on the various cellular
reactions in the fracture callus. J Bone Miner Res. 16:671–680.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cheung WH, Chow SK, Sun MH, Qin L and
Leung KS: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerated callus
formation, angiogenesis and callus remodeling in osteoporotic
fracture healing. Ultrasound Med Biol. 37:231–238. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Naruse K, Sekiya H, Harada Y, Iwabuchi S,
Kozai Y, Kawamata R, Kashima I, Uchida K, Urabe K, Seto K, et al:
Prolonged endochondral bone healing in senescence is shortened by
low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in a manner dependent on COX-2.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 36:1098–1108. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Heckman JD, Ryaby JP, McCabe J, Frey JJ
and Kilcoyne RF: Acceleration of tibial fracture-healing by
non-invasive, low-intensity pulsed ultrasound. J Bone Joint Surg
Am. 76:26–34. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kristiansen TK, Ryaby JP, McCabe J, Frey
JJ and Roe LR: Accelerated healing of distal radial fractures with
the use of specific, low-intensity ultrasound. A multicenter,
prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 79:961–973. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tang CH, Yang RS, Huang TH, Lu DY, Chuang
WJ, Huang TF and Fu WM: Ultrasound stimulates cyclooxygenase-2
expression and increases bone formation through integrin, focal
adhesion kinase, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and Akt pathway in
osteoblasts. Mol Pharmacol. 69:2047–2057. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Unsworth J, Kaneez S, Harris S, Ridgway J,
Fenwick S, Chenery D and Harrison A: Pulsed low intensity
ultrasound enhances mineralisation in preosteoblast cells.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 9:1468–1474. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Borsje MA, Ren Y, de Haan-Visser HW and
Kuijer R: Comparison of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and pulsed
electromagnetic field treatments on OPG and RANKL expression in
human osteoblast-like cells. Angle Orthod. 80:498–503.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kitamura K, Suzuki N, Sato Y, Nemoto T,
Ikegame M, Shimizu N, Kondo T, Furusawa Y, Wada S and Hattori A:
Osteoblast activity in the goldfish scale responds sensitively to
mechanical stress. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol.
156:357–363. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Costa V, Carina V, Fontana S, De Luca A,
Monteleone F, Pagani S, Sartori M, Setti S, Faldini C, Alessandro
R, et al: Osteogenic commitment and differentiation of human
mesenchymal stem cells by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound
stimulation. J Cell Physiol. 233:1558–1573. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chiu CY, Tsai TL, Vanderby R Jr, Bradica
G, Lou SL and Li WJ: Osteoblastogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells
in 3-D culture enhanced by low-intensity pulsed ultrasound through
soluble receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 41:1842–1852. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Miyasaka M, Nakata H, Hao J, Kim YK,
Kasugai S and Kuroda S: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation
enhances heat-shock protein 90 and mineralized nodule formation in
mouse calvaria-derived osteoblasts. Tissue Eng Part A.
21:2829–2839. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang Z, Ma Y, Guo S, He Y, Bai G and
Zhang W: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation facilitates in
vitro osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem
cells via up-regulation of heat shock protein (HSP)70, HSP90, and
bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signaling pathway. Biosci Rep.
38(BSR20180087)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Zhu Y, Ai D, Zhou M, Li H, Fu Y
and Song J: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound regulates
osteoblast-osteoclast crosstalk via EphrinB2/EphB4 signaling for
orthodontic alveolar bone remodeling. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
11(1192720)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Florencio-Silva R, Sasso GR, Sasso-Cerri
E, Simões MJ and Cerri PS: Biology of bone tissue: Structure,
function, and factors that influence bone cells. Biomed Res Int.
2015(421746)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mikuni-Takagaki Y: Mechanical responses
and signal transduction pathways in stretched osteocytes. J Bone
Miner Metab. 17:57–60. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Klein-Nulend J, Bakker AD, Bacabac RG,
Vatsa A and Weinbaum S: Mechanosensation and transduction in
osteocytes. Bone. 54:182–190. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ma Q, Miri Z, Haugen HJ, Moghanian A and
Loca D: Significance of mechanical loading in bone fracture
healing, bone regeneration, and vascularization. J Tissue Eng.
14(20417314231172573)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bereiter-Hahn J and Zylberberg L:
Regeneration of teleost fish scale. Comp Biochem Physiol.
105A:625–641. 1993.
|
|
27
|
Suzuki N, Kitamura K, Omori K, Nemoto T,
Satoh Y, Tabata MJ, Ikegame M, Yamamoto T, Ijiri K, Furusawa Y, et
al: Response of osteoblasts and osteoclasts in regenerating scales
to gravity loading. Biol Sci Space. 23:211–217. 2009.
|
|
28
|
Hirayama J, Hattori A, Takahashi A,
Furusawa Y, Tabuchi Y, Shibata M, Nagamatsu A, Yano S, Maruyama Y,
Matsubara H, et al: Physiological consequences of space flight,
including abnormal bone metabolism, space radiation injury, and
circadian clock dysregulation: Implications of melatonin use and
regulation as a countermeasure. J Pineal Res.
74(e12834)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yamamoto T, Ikegame M, Hirayama J,
Kitamura KI, Tabuchi Y, Furusawa Y, Sekiguchi T, Endo M, Mishima H,
Seki A, et al: Expression of sclerostin in the regenerating scales
of goldfish and its increase under microgravity during space
flight. Biomed Res. 41:279–288. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ikegame M, Hattori A, Tabata MJ, Kitamura
KI, Tabuchi Y, Furusawa Y, Maruyama Y, Yamamoto T, Sekiguchi T,
Matsuoka R, et al: Melatonin is a potential drug for the prevention
of bone loss during space flight. J Pineal Res.
67(e12594)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Suzuki N, Hanmoto T, Yano S, Furusawa Y,
Ikegame M, Tabuchi Y, Kondo T, Kitamura K, Endo M, Yamamoto T, et
al: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound induces apoptosis in
osteoclasts: Fish scales are a suitable model for the analysis of
bone metabolism by ultrasound. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr
Physiol. 195:26–31. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hanmoto T, Tabuchi Y, Ikegame M, Kondo T,
Kitamura KI, Endo M, Kobayashi I, Mishima H, Sekiguchi T, Urata M,
et al: Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on osteoclasts:
Analysis with goldfish scales as a model of bone. Biomed Res.
38:71–77. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Haas BJ, Papanicolaou A, Yassour M,
Grabherr M, Blood PD, Bowden J, Couger MB, Eccles D, Li B, Lieber
M, et al: De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq
using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis.
Nat Protoc. 8:1494–1512. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Furusawa Y, Yamamoto T, Hattori A, Suzuki
N, Hirayama J, Sekiguchi T and Tabuchi Y: De novo transcriptome
analysis and gene expression profiling of fish scales isolated from
Carassius auratus during space flight: Impact of melatonin on gene
expression in response to space radiation. Mol Med Rep.
22:2627–2636. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Percie du Sert N, Ahluwalia A, Alam S,
Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl U,
Emerson M, et al: Reporting animal research: Explanation and
elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol.
18(e3000411)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Iwabuchi S, Ito M, Hata J, Chikanishi T,
Azuma Y and Haro H: In vitro evaluation of low-intensity pulsed
ultrasound in herniated disc resorption. Biomaterials.
26:7104–7114. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tabuchi Y, Hasegawa H, Suzuki N, Furusawa
Y, Hirano T, Nagaoka R, Hirayama J, Hoshi N and Mochizuki T:
Genetic response to low-intensity ultrasound on mouse ST2 bone
marrow stromal cells. Mol Med Rep. 23(173)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shen W, Le S, Li Y and Hu F: SeqKit: A
cross-platform and ultrafast toolkit for FASTA/Q file manipulation.
PLoS One. 11(e0163962)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P and Pachter
L: Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat
Biotechnol. 34:525–527. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Robinson MD and Oshlack A: A scaling
normalization method for differential expression analysis of
RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 11(R25)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Tabuchi Y, Takasaki I, Doi T, Ishii Y,
Sakai H and Kondo T: Genetic networks responsive to sodium butyrate
in colonic epithelial cells. FEBS Lett. 580:3035–3041.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Larionov A, Krause A and Miller W: A
standard curve based method for relative real time PCR data
processing. BMC Bioinformatics. 6(62)2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tabuchi Y, Ohta S, Arai Y, Kawahara M,
Ishibashi K, Sugiyama N, Horiuchi T, Furusawa M, Obinata M, Fuse H,
et al: Establishment and characterization of a colonic epithelial
cell line MCE301 from transgenic mice harboring
temperature-sensitive simian virus 40 large T-antigen gene. Cell
Struct Funct. 25:297–307. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hanyu R, Wehbi VL, Hayata T, Moriya S,
Feinstein TN, Ezura Y, Nagao M, Saita Y, Hemmi H, Notomi T, et al:
Anabolic action of parathyroid hormone regulated by the
β2-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:7433–7438.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bollag WB, Choudhary V, Zhong Q, Ding KH,
Xu J, Elsayed R, Yu K, Su Y, Bailey LJ, Shi XM, et al: Deletion of
protein kinase D1 in osteoprogenitor cells results in decreased
osteogenesis in vitro and reduced bone mineral density in vivo. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 461:22–31. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Bucay N, Sarosi I, Dunstan CR, Morony S,
Tarpley J, Capparelli C, Scully S, Tan HL, Xu W, Lacey DL, et al:
Osteoprotegerin-deficient mice develop early onset osteoporosis and
arterial calcification. Genes Dev. 12:1260–1268. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Greenblatt MB, Shim JH, Zou W, Sitara D,
Schweitzer M, Hu D, Lotinun S, Sano Y, Baron R, Park JM, et al: The
p38 MAPK pathway is essential for skeletogenesis and bone
homeostasis in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:2457–2473. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jensen ED, Gopalakrishnan R and Westendorf
JJ: Bone morphogenic protein 2 activates protein kinase D to
regulate histone deacetylase 7 localization and repression of
Runx2. J Biol Chem. 284:2225–2234. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yu H, de Vos P and Ren Y: Overexpression
of osteoprotegerin promotes preosteoblast differentiation to mature
osteoblasts. Angle Orthod. 81:100–106. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Si W, Kang Q, Luu HH, Park JK, Luo Q, Song
WX, Jiang W, Luo X, Li X, Yin H, et al: CCN1/Cyr61 is regulated by
the canonical Wnt signal and plays an important role in
Wnt3A-induced osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 26:2955–2964. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Zhang X, Schwarz EM, Young DA, Puzas JE,
Rosier RN and O'Keefe RJ: Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates mesenchymal
cell differentiation into the osteoblast lineage and is critically
involved in bone repair. J Clin Invest. 109:1405–1415.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ford JJ, Yeh LC, Schmidgal EC, Thompson
JF, Adamo ML and Lee JC: Protein kinase D1 is essential for bone
acquisition during pubertal growth. Endocrinology. 154:4182–4191.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Yang B, Li S, Chen Z, Feng F, He L, Liu B,
He T, Wang X, Chen R, Chen Z, et al: Amyloid β peptide promotes
bone formation by regulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling and the
OPG/RANKL/RANK system. FASEB J. 34:3583–3593. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lacey DL, Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Kostenuik
PJ, Dougall WC, Sullivan JK, San Martin J and Dansey R: Bench to
bedside: elucidation of the OPG-RANK-RANKL pathway and the
development of denosumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:401–419.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hoter A, El-Sabban ME and Naim HY: The
HSP90 family: Structure, regulation, function, and implications in
health and disease. Int J Mol Sci. 19(2560)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Palumbo S and Li WJ: Osteoprotegerin
enhances osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng
Part A. 19:2176–2187. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Sena K, Leven RM, Mazhar K, Sumner DR and
Virdi AS: Early gene response to low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in
rat osteoblastic cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 31:703–708.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Tabuchi Y, Hasegawa H, Suzuki N, Furusawa
Y, Hirano T, Nagaoka R, Takeuchi SI, Shiiba M and Mochizuki T:
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the expression of
immediate-early genes in mouse ST2 bone marrow stromal cells. J Med
Ultrason (2001). 47:193–201. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Veronick JA, Assanah F, Piscopo N, Kutes
Y, Vyas V, Nair LS, Huey BD and Khan Y: Mechanically loading
cell/hydrogel constructs with low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for
bone repair. Tissue Eng Part A. 24:254–263. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Choudhary S, Halbout P, Alander C, Raisz L
and Pilbeam C: Strontium ranelate promotes osteoblastic
differentiation and mineralization of murine bone marrow stromal
cells: Involvement of prostaglandins. J Bone Miner Res.
22:1002–1010. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Allen HL, Wase A and Bear WT: Indomethacin
and aspirin: Effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents on the
rate of fracture repair in the rat. Acta Orthop Scand. 51:595–600.
1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Elmstedt E, Lindholm TS, Nilsson OS and
Törnkvist H: Effect of ibuprofen on heterotopic ossification after
hip replacement. Acta Orthop Scand. 56:25–27. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Omori K, Wada S, Maruyama Y, Hattori A,
Kitamura K, Sato Y, Nara M, Funahashi H, Yachiguchi K, Hayakawa K,
et al: Prostaglandin E2 increases both osteoblastic and
osteoclastic activities in the scales of goldfish and participates
in the calcium metabolism in goldfish. Zoolog Sci. 29:499–504.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Zuehlke AD, Beebe K, Neckers L and Prince
T: Regulation and function of the human HSP90AA1 gene. Gene.
570:8–16. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Akerfelt M, Morimoto RI and Sistonen L:
Heat shock factors: Integrators of cell stress, development and
lifespan. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:545–555. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|