Over the past two decades, the rapid aging of the
population has led to a 30% increase in the prevalence of OSA
(1). Epidemiological research
estimates that ~936 million adults aged 30-69 globally are affected
by OSA, with a prevalence of ~22% in males and 17% in females
(2). The COVID-19 pandemic has
further exacerbated the incidence of OSA (3), solidifying its status as a common
sleep-related breathing disorder in clinical settings (4). OSA is characterized by recurrent
obstruction of the upper airway during sleep, leading to periodic
hypoxemia, disturbances in sleep continuity and increased
respiratory effort. OSA is characterized by intermittent hypoxia
during sleep, which activates HIF-1. This activation leads to
oxidative stress, damaging cellular components such as DNA,
proteins and lipids. The repeated cycles of hypoxia and subsequent
oxidative stress create an environment conducive to genetic
alterations that may drive the malignant transformation of lung
cells (5). OSA triggers a systemic
inflammatory response. The intermittent hypoxia and sleep
fragmentation associated with OSA activate the sympathetic nervous
system, releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α
and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP). Chronic
inflammation disrupts normal cellular functions and tissue
homeostasis, fostering an immunosuppressive microenvironment in the
lungs that allows cancer cells to evade immune surveillance and
elimination. In addition, inflammatory mediators can directly
stimulate cell proliferation and angiogenesis, both crucial for
tumor growth and metastasis (6).
OSA is linked to significant metabolic changes, disrupting normal
lipid metabolism and leading to abnormal lipid profiles, while also
affecting glucose metabolism, resulting in insulin resistance and
elevated blood glucose levels. These metabolic alterations create a
favorable environment for cancer cells to thrive, as hyperglycemia
provides an abundant energy source and can stimulate growth factor
production (7,8). Notably, OSA has been emerged as a new
risk factor for lung cancer (9) and
is known to disrupt normal lipid metabolism (10,11).
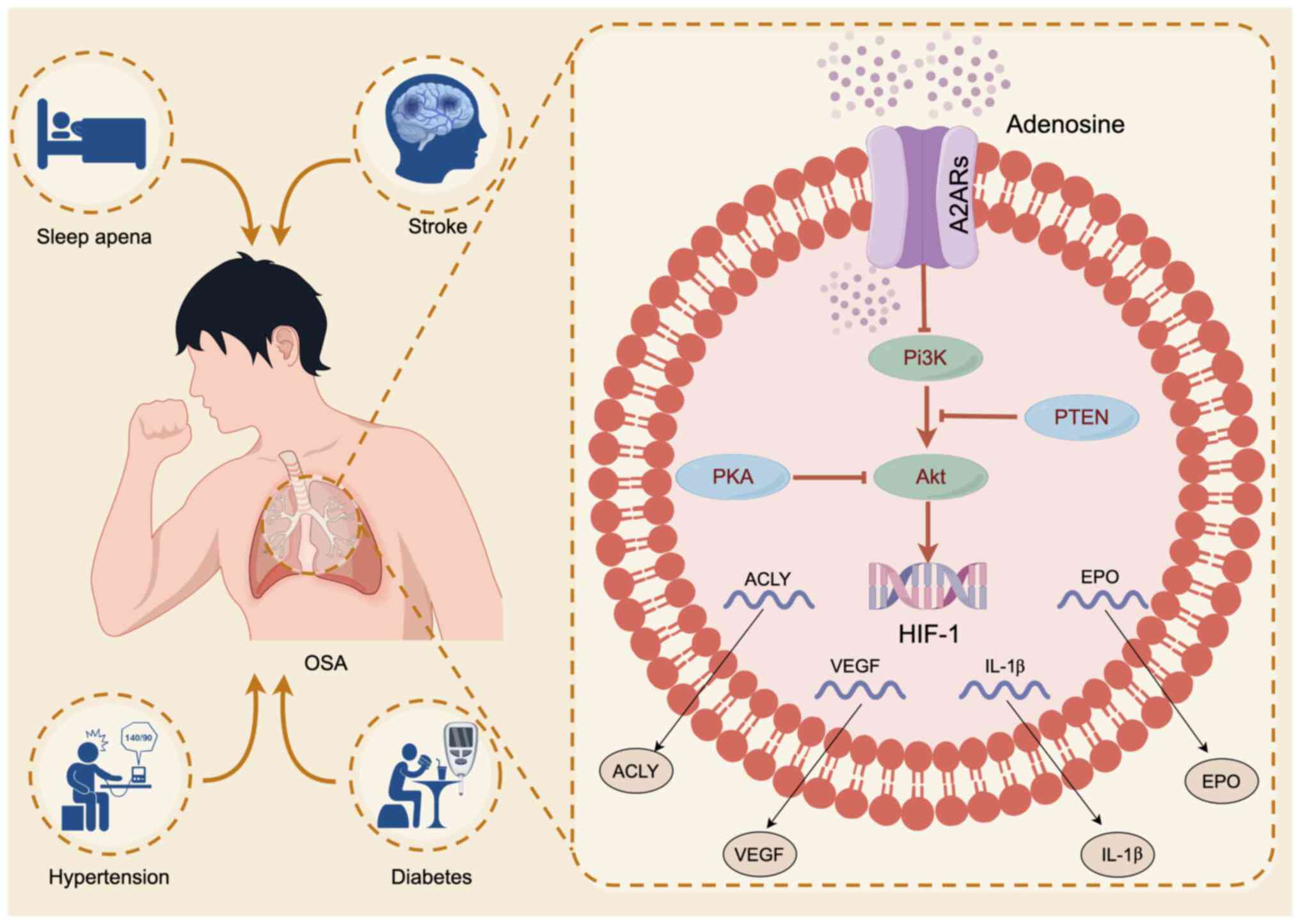
A hallmark molecular feature of hypoxia in OSA is
the upregulation and stabilization of HIF-1 (12-14),
a critical genomic mediator of cellular adaptation to low oxygen
levels. HIF-1 plays an essential role in regulating inflammatory
pathways by modulating inflammatory responses, particularly
preventing excessive reactions. In addition, it is associated with
the regulation of genes such as MCAD and LCAD, both of which are
involved in lipid metabolism. Recent research has highlighted the
potential of A2A receptor (A2AR) blockade to disrupt the
hypoxia/HIF-1-adenosine immunosuppressive axis, enhancing the
effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy (15). Additionally, A2AR is indispensable
for tissue protection under hypoxic conditions and for the
regulation of lipid metabolism (16).
OSA is mainly mediated by intermittent hypoxia,
which leads to low-grade inflammation (17). Adenosine receptors (ARs) have been
shown to mitigate hypoxia-induced inflammation, particularly in the
context of acute lung injury. During ischemic and hypoxic events,
extracellular concentrations of adenosine, a crucial
neurotransmitter involved in the immune response, can increase
markedly, reaching levels ≤100 times higher than normal. The
upregulation of adenosine and the induction of HIF-1 in response to
hypoxia are directly linked, suggesting that HIF-1 activation
through A2AR may contribute to anti-inflammatory responses and
tissue protection. Although persistently elevated adenosine levels
appear to trigger the release of inflammatory cytokines, A2AR is
predominantly expressed in mature dendritic cells, leading to a
reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines (18). Previous studies have demonstrated
that hypoxia activates adenosine signaling via A2AR (19-21).
Additionally, the HIF-1/adenosine axis provides protective effects
for the lungs during conditions such as acute respiratory distress
syndrome, although it may contribute to inflammation and injury in
chronic lung diseases (22).
Based on these findings, along with research showing
that targeting the hypoxic-A2AR pathway can release anti-tumor T
cells with immunosuppressive properties (23), A2AR has emerged as a critical
receptor for mediating hypoxia-related tissue protection and
regulating HIF-1 due to its anti-inflammatory effects (16). The molecular process by which A2AR
regulates HIF-1 involves cytokine interactions and the activation
of intracellular pathways such as Protein Kinase C (PKC),
ATP-sensitive Potassium Channel (KATP), p38 MAPK and PI3K/Akt
(24,25). These intricate networks present a
promising therapeutic target for A2AR, particularly through the
PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway in the treatment of OSA (Fig. 1). The present study aimed to clarify
the current prevalence of OSA and its associated hazards, including
intermittent hypoxia, sleep disorders and its role as a risk factor
for diseases such as lung cancer. It provided an in-depth
exploration of the pharmacological mechanisms of A2AR in OSA,
focusing on its effects on inflammation and lipid metabolism
related to OSA through the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway.
The oxidative stress caused by OSA has complex and
multifaceted effects on lipid metabolism and cardiovascular health
(26). In terms of lipid
metabolism, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced by oxidative
stress will attack the polyunsaturated fatty acids in the lipids,
causing lipid peroxidation, such as the oxidation of low-density
lipoprotein (LDL), which is more likely to be absorbed by the
macrophages in the artery wall to form foam cells and start the
formation of atherosclerotic plaque (27-29).
Meanwhile, oxidative stress can alter the activity of enzymes
involved in lipid metabolism, such as lipoprotein lipase (LpL),
disrupting the balance between lipid synthesis and breakdown
(30). It can also interfere with
cholesterol transport and metabolism, affecting LDL receptors and
related functions such as hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase,
leading to lipid metabolism disorders (31). In terms of cardiovascular health,
due to oxidative stress generated by OSA, LDL oxidation is the key
to the development of atherosclerosis. Its accumulation in the
arterial wall triggers inflammatory reaction, forms fat stripes and
develops into plaques; and plaque rupture can cause thrombosis and
cardiovascular events (32,33). In addition, oxidative stress damages
endothelial cells, reducing their release of NO, leading to
vasoconstriction, increased platelet aggregation and causing
problems such as hypertension (34,35).
In addition, oxidative stress activates inflammatory pathways and
immune system, promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines,
intensifies the process of atherosclerosis and affects the function
of immune cells (36-38).
It also directly damages mitochondria in myocardial cells, affects
energy production, leads to the decline of myocardial contractility
and interferes with calcium ion regulation to damage myocardial
function (39-41).
It can be seen that oxidative stress caused by OSA has a
significant effect on lipid metabolism and cardiovascular
health.
The sleep disorder and intermittent hypoxia
characteristic of OSA can trigger sympathetic excitation and
inflammation, leading to vascular endothelial damage, altered
coagulation function, abnormal lipid metabolism and disruptions in
glucose homeostasis (42,43). The physiological consequences of OSA
activate the sympathetic nervous system, induce oxidative stress
and trigger systemic inflammatory responses (44). The systemic inflammatory cascade is
thought to play a crucial role in both the onset and progression of
OSA (45). Studies have shown that
systemic inflammation associated with OSA is caused by the overflow
of inflammatory cytokines from the upper airway mucosa to the
bloodstream (46). Clinical studies
have measured plasma concentrations of inflammatory markers in
patients with OSA compared with control groups, revealing elevated
levels of hsCRP, IL-6, TNF-α and pentraxin-3 among individuals with
OSA (47). In addition, in a mouse
experiment, the changes of atherosclerosis induced by intermittent
hypoxia occurs with the increased expression of proinflammatory
cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules, the increased
migration of inflammatory cells and the expansion of the population
of macrophages in the arterial wall (48,49).
Other studies have also confirmed that the hypoxic state of OSA
preferentially activated the pro-inflammatory factor NF-κB-mediated
pathway, possibly caused by an inflammatory response to hypoxic
exposure via adipocytes (50-52).
This inflammatory shift is further associated with increased
polarization of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages, elevated
expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and worsening insulin
resistance (53). This inflammatory
response mechanism plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of
OSA-related cardiometabolic processes, ultimately leading to the
development of cardiovascular disease and establishing a vicious
cycle (54).
A growing body of evidence indicating that A2AR
mediates potent anti-inflammatory responses in various cell types
across multiple inflammation models (70,71)
has spurred the development of A2AR agonists aimed at attenuating
inflammation in disorders such as chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease (COPD) and asthma (72).
Research has shown that A2AR agonists can modulate immune responses
by reducing the infiltration of pro-inflammatory T cells into the
central nervous system, an essential mechanism for controlling
flare-ups in multiple sclerosis (73). In a mouse model of
carrageenan-induced pleurisy, the administration of the A2AR
agonist CGS 21680 markedly reduced neutrophil infiltration, nitric
oxide levels, cytokine production, NF-κB expression and PARP
activation (74). By contrast, A2AR
knockout mice exhibited increased inflammation characterized
primarily by enhanced activity of macrophages and neutrophils,
along with elevated mucin production in the bronchial airways and
increased levels of the chemoattractant proteins chemokine (C-X-C
motif) ligand and MCP-1 (75,76).
These findings suggest that A2AR plays a protective role in
pulmonary inflammation. Furthermore, the positive allosteric
modulator AEA061 enhances inosine-mediated A2AR activation, leading
to inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokine
production by splenic monocytes (77). Studies have also demonstrated that
activating A2AR can restore cAMP levels in myocardial tissue while
inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, markedly improving cardiac
dysfunction associated with cirrhosis and exerting both
anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects (78). In the context of psoriasis, A2AR
activation inhibits M1 macrophage activation through the
NF-κB-KRT16 pathway, which is crucial for initiating both innate
and adaptive immunity (75).
Additionally, inhalation of A2AR agonists has shown therapeutic
potential for patients suffering from COVID-19-related inflammatory
lung disease (79). These findings
collectively highlight the therapeutic promise of A2AR modulation
in various inflammatory conditions.
A2A receptors play a crucial role in regulating
various physiological and pathological processes in adipocytes
(80). Activation of A2AR can
induce anti-inflammatory effects that are essential for the
survival of beta cells, enhance insulin secretion, reduce food
intake and promote thermogenesis and fat breakdown (81). For instance, studies have
demonstrated that A2AR agonists, such as CGS21680 and PSB-0777,
activate lipolysis in both humans and mice (82-84),
improve glucose tolerance and protect C57Bl/6 mice from
diet-induced obesity, highlighting the promising thermogenic
effects of adenosine. Further investigations showed that the A2AR
agonist CGS21680, when injected into Swiss strain mice fed a
high-fat diet, produced similar effects on glucose homeostasis
without significant changes in weight or obesity rates, while also
decreasing certain inflammatory markers (85). Additionally, A2AR signaling has been
linked to the regulation of CD8+ T cell responses through the
coordination of glutathione metabolism (86). Notably, stimulation of A2AR
expression on macrophages has been shown to release cholesterol,
which inhibits the formation of foam cells (84). The structural dynamics of A2AR are
influenced by its phospholipid environment and cholesterol,
resulting in a propensity to bind lipid isoform modulators
(87). In therapeutic applications,
liposome treatments combined with adenosine or specific A2AR
agonists have markedly improved joint scores in post-traumatic
osteoarthritis rats and mice with high-fat diet-induced
osteoarthritis (88). In addition,
research indicates that the loss of A2AR in macrophages and liver
cells leads to increased inflammation, elevated expression and
transcriptional activity of SREBP1c and enhanced adipogenic events,
exacerbating the severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
(89). Studies have also shown that
deficiencies in C3a and C5a receptors can promote adipocyte
browning and reduce diet-induced obesity by activating the
inosine/A2AR pathway (90,91). Lastly, ongoing research and
development efforts are focusing on dual-active adenosine A2A/A3
receptor ligands, such as LJ-4378, which have demonstrated
anti-obesity effects and offer new treatment strategies for obesity
and related metabolic diseases (92).
A2AR plays a significant role in exerting
anti-inflammatory and tissue-protective effects, particularly in
hypoxic environments, by modulating the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 signaling
pathway. OSA is associated with chronic inflammation and tissue
remodeling, leading to progressive declines in pulmonary function
(26). In OSA mouse models, a
notable accumulation of proinflammatory M1-like macrophages,
characterized by heightened CD36 expression, has been observed in
the aorta, alongside elevated levels of inflammation-related
transcription factors (93). During
intermittent hypoxia, OSA triggers the release of proinflammatory
factors, including TNF, CRP, IL-6 and IL-8, while increased NF-κB
and TNF-α levels have been linked to OSA-related daytime sleepiness
(94-96).
In this context, A2AR mitigates inflammation through
the PI3K/Akt pathway. Notably, while serotonin receptor inhibition
can limit the efficacy of intermittent hypercapnic-hypoxia
therapies, blocking the A2AR pathway has demonstrated enhanced
respiratory recovery (97).
Additionally, A2AR influences the regulation of apnea, particularly
in conditions such as apnea of prematurity, where its effects are
mediated by caffeine inhibitors (98). The flavonoid compound Baicalin has
also been shown to alleviate chronic hypoxia-induced pulmonary
hypertension by activating the A2AR-induced Stromal Cell-Derived
Factor 1(SDF-1)/C-X-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4 (CXCR4)/PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway (95). In cases
of liver ischemia/reperfusion injury, inhalation of high hydrogen
concentrations has demonstrated ameliorative effects via the
A2AR-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway (94).
Research has confirmed that A2AR inhibits the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which is essential for limiting
inflammation and promoting anti-inflammatory responses in
TLR-induced macrophages (99,100).
This pathway negatively regulates TLR and NF-κB signaling in
macrophages (101,102). The Bu-Shen-Fang-Chuan formula,
commonly prescribed for COPD in China, has been shown to reduce
TNF-α and IL-6 levels in bronchoalveolar fluid and serum, curbing
cigarette smoke-induced inflammation, partially mediated through
the PI3K/Akt pathway (103). A2AR
also modulates HIF-1 expression; studies indicate that both Akt and
HIF-1 protein levels increase in human mesenchymal stem cells in
response to hypoxia, with Akt expression peaking earlier than HIF-1
(104,105). The use of PI3K inhibitors such as
LY294002 and dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitors such asNVP-BEZ235 suppresses
Akt activation, as well as HIF-1 and VEGF expression induced by
hypoxia. Wortmannin, an Akt inhibitor, also inhibits HIF-1
expression at the protein level without affecting mRNA levels
(104).
Activation of specific HIF-1 target genes can induce
proinflammatory genes, notably IL-1β (106-108).
However, in hypoxic macrophages, the activation of the PI3K/Akt
pathway upregulates TLR4 expression through HIF-1 activation
(109). The HIF-1 dimer then binds
to the hypoxia response element in the promoter region, initiating
the expression of over 100 genes involved in hypoxic adaptation,
including those that promote VEGF and EPO, which promote
angiogenesis and erythropoiesis (110,111). HIF-1 also regulates NF-κB, leading
to increased levels of cytokines such as IL-8 (112,113), while IL-17 levels correlate with
OSA severity (114). Therefore,
A2AR inhibits the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt, indirectly
downregulating HIF-1(115). This
mechanism drives the reduction of immune and inflammatory
responses, thereby protecting tissues in hypoxic conditions
(116).
A2AR plays a significant role in regulating lipid
metabolism through the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway (115). Activation of A2AR inhibits the
phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt, crucial steps in lipid metabolism
regulation. Notably, HIF-1, activated downstream of this pathway,
promotes lipid droplet accumulation and fatty acid reprogramming
under hypoxic conditions.
Endogenous cannabinoids are naturally occurring
lipids that bind to cannabinoid receptors and play a crucial role
in regulating metabolism, particularly in energy balance, fat
storage and glucose homeostasis (117). In the context of OSA, these
cannabinoids can contribute to metabolic disorders and exacerbate
conditions such as obesity, insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Elevated levels of endogenous cannabinoids, particularly anandamide
and ethanolamine, have been observed in patients with OSA, along
with increased levels of saturated fatty acids and n-3 fatty acids,
which can enhance appetite and promote fat accumulation, both of
which are linked to sleep quality (118,119). Additionally, patients with OSA
often exhibit elevated levels of adenosine, adrenaline,
norepinephrine and aldosterone, further complicating their
metabolic profiles (120). In
another animal study, intermittent hypoxia was demonstrated to
mediate the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1αin pancreatic
β-cells. This leads to increased reactive oxygen species and
ultimately resulted in insulin resistance (12).
A2AR activation not only stimulates lipolysis and
thermogenesis but also enhances the browning of adipose tissue.
Specifically, A2AR activation enhances reverse cholesterol
transport from peripheral tissues back to the liver, aided by
macrophages, which helps prevent their transformation into foam
cells (121). Furthermore,
supplementation with adenosine has been shown to increase A2AR
protein levels and enhance the expression of key lipolytic genes,
such as ATGL and HSL, in adipose tissue, thereby providing a
protective effect against diet-induced obesity. Additionally,
elevated levels of inflammatory factors in the upper and lower
airways of hypoxic mice, combined with the detrimental cycle
between OSA and airway inflammation, contribute markedly to insulin
resistance (122).
Metabolic changes in patients with OSA include
increased lactic acid and specific fatty acids, such as arabinose
and glyceraldehyde (123).
Additionally, genes involved in cholesterol metabolism, such as
malic enzyme and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, are impaired due to
hypoxia associated with OSA (124,125). The role of HIF-1 in lipid uptake
is crucial, as it induces the expression of fatty acid binding
proteins (FABP3 and FABP7) and adipocyte differentiation-related
protein (ADRP), necessary for lipid droplet formation. HIF-1 also
promotes fatty acid synthase expression, enhancing fatty acid
synthesis while inhibiting the oxygen-dependent stearoyl-CoA
desaturase enzyme, which can affect cellular membrane integrity
(126).
Furthermore, HIF-1 targets ATP citrate lyase (ACLY),
which is upregulated in hypoxic tumor cells, influencing fatty acid
biosynthesis and acetyl-CoA production. For example, in goose liver
cells, insulin regulates lipid deposition through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway, while HIF-2α upregulation under hypoxia activates lipid
synthesis, promoting the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease and hepatocellular carcinoma (127).
The synthesis of fatty acids leads to increased
production of neutral triacylglycerols (TAGs), stored as lipid
droplets for energy. HIF-1 induces key enzymes such asAGPAT2 and
lipin-1, which facilitate LD accumulation and viability, also
contributing to chemoresistance in hypoxic environments. The
products of AGPAT2 can further be utilized for new membrane
formation. Under hypoxia, unsaturated fatty acid oleate is
preferentially released from TAGs into the phospholipid pool to
balance saturated lipid accumulation (128). In addition, lipid signaling
molecules such as sphingosine kinase 1 can stimulate HIF-1
activity. In summary, A2AR regulates dyslipidemia in OSA through
the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway, highlighting its potential as a
therapeutic target in managing lipid metabolism disorders.
Adenosine, deriving from ATP degradation, mediates
its physiological effects through four distinct subtypes of
G-protein-coupled receptors named A1R, A2AR, A2BR and A3R. Previous
research has shown that hypoxia and inflammation can lead to the
accumulation of extracellular ATP/ADP due to the cell membrane
damage (129). Consequently, it is
important to investigate the pharmacological effects of adenosine
receptors in the context of OSA (129-135)
(Table I). During sleep apnea,
adenosine is released as a response to hypoxia, which can promote
sleep and reduce apnea episodes through the activation of A1R/A3R
(131) and the inhibition of A2AR
(136). High doses of caffeine, a
well-known adenosine receptor antagonist, may provide an improved
means of apnea management (137).
In addition, adenosine plays a role in sensitizing the carotid body
during intermittent hypoxia (134). Caffeine has been shown to decrease
both baseline and hypoxia-induced (5% O2) chemosensory
activity in the carotid sinus nerve of rats with intermittent
hypoxia (134). Therefore,
blocking adenosine receptors and modulating adenosine metabolism in
the carotid body could aid in the management of sleep apnea
(135). Other research indicates
that increased expression of A2AR during hypoxia may help protect
cells from the damaging effects of low oxygen levels (138). Conversely, A2AR deficiency has
been linked to airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness
(139). Mirtazapine, a
prescription drug that acts as an A2AR antagonist, appears to be
ineffective in markedly improving sleep apnea and may even
contribute to weight gain, potentially worsening OSA (140). There is speculation that
appropriate use of A2AR agonists could inhibit the PI3K/Akt
pathway, indirectly reducing the expression of HIF-1 and
pro-inflammatory cytokines while enhancing lipid metabolism.
Notably, the inhibitory effect of A2AR activation on respiratory
drive appears to vary with age. Thus, further research is needed to
clarify the pharmacological effects of A2AR in the treatment of OSA
and clinical trials should be conducted to explore its potential
therapeutic applications.
Intermittent hypoxia in OSA can contribute to
inflammation-related cardiac metabolic diseases, with vascular
inflammation and remodeling linked to increased
leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions and T cell activation.
While HIF-1 is expressed in unstimulated cells, NECA (an A2AR
agonist) does not enhance HIF-1 mRNA expression in the absence of
LPS stimulation. This indicates that LPS-induced A2AR expression
crucial for the LPS/NECA-mediated upregulation of HIF-1. The NF-κB
pathway is influenced by HIF-1, acting as a potent inflammatory
activator that drives the release of TNF, IL-6, IL-8 and C-C motif
chemokine ligand 2/monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1).
Although OSA is hypothesized to elevate ROS levels, more evidence
is necessary to fully support this (141). HIF-1 regulates the expression of
various factors, including EPO, VEGF, inducible nitric oxide
synthase and heme oxygenase, along with molecules involved in
glucose metabolism, mitochondrial function and cellular adaptation
to intermittent hypoxia during oxidative stress. Inhibition of
HIF-1 reduces the expression of VEGF and Bcl2 interacting protein
3, thereby protecting against delayed cell death. Notably, the
protective effects mediated by the PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 pathways may
be reversed in the hypoxic microenvironment of cancer, highlighting
the regulatory role of A2AR on HIF-1 as a potential therapeutic
target for OSA. Intermittent hypoxia can downregulate endothelial
nitric oxide synthase and enhance endothelin-1 production through
the Erk1/2 pathway, while also increasing phosphorylation via the
PI3K/Akt pathway, leading to endothelial dysfunction (142). Beyond the influences of
inflammation and lipid metabolism, further investigation into the
pharmacological effects of the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway on glucose
metabolism, mitochondrial function and cell apoptosis in relation
to OSA is warranted.
In addition, repeated exposure to hypoxic conditions
can lead to significant alterations in gene transcription and
post-translational protein modifications, resulting in changes in
plasma concentrations of lipids, proteins and other biological
compounds (143). The advent of
large metabolomic datasets has enabled the use of metabolites as
biomarkers for disease progression (46). Research indicates that the
pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease and metabolic complications
associated with OSA may be markedly linked to specific metabolic
changes. Mendelian randomization studies have identified
associations between OSA and >10 metabolites, including the
plasma metabolite 3-Dehydrocarnitine. The biosynthetic pathway of
valine, leucine and isoleucine is implicated in OSA pathogenesis
(144). However, there is a lack
of exploration into how inflammation alters metabolic pathways in
the development of OSA and its complications. Therefore,
understanding the involvement of metabolites in inflammation is
critical for unraveling OSA pathogenesis and identifying potential
therapeutic targets (145).
In the clinical management of OSA, a variety of
treatment approaches are currently available, each with its own
distinct characteristics and implications. These treatment
modalities primarily encompass continuous positive airway pressure
(CPAP), oral appliance therapy, surgical interventions, lifestyle
changes, drug treatment and hypoglossal nerve stimulation. CPAP is
effective for moderate to severe OSA, improving symptoms and
quality of life, but requires maintenance and can be uncomfortable
(146,147). Oral appliances are portable and
work well for mild OSA, though less effective for severe cases and
may cause discomfort (148).
Surgical options, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty, offer
long-term benefits for patients with clear anatomical issues but
carry risks and long recovery times (149,150). Lifestyle changes complement
treatments with no major side effects, though their impact is
gradual (151). Drug treatments
may help mild OSA but are generally limited (152-154).
Hypoglossal nerve stimulation is a less invasive alternative to
CPAP or surgery, with good tolerance but concerns over cost and
long-term efficacy (155).
Consequently, given the diverse nature of these treatment options
for OSA, it becomes of utmost importance to conduct a comprehensive
comparison of different treatments for OSA (Table II) Such a comparison can provide
valuable insights for healthcare providers and patients alike,
enabling them to make more informed decisions regarding the most
appropriate treatment approach based on individual circumstances
(149).
The relationship between OSA and lipid profiles
remains a complex area of study. While some clinical evidence
indicates that CPAP devices can improve certain aspects of
dyslipidemia by alleviating apnea-hypopnea, much of this data are
derived from observational studies. CPAP may lead to reductions in
inflammatory cytokines and inhibit lipid peroxidation, as evidenced
by decreased levels of malondialdehyde and endothelial lectin-like
oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) (156). However, its effect on oxidized
low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) levels in patients with OSA with
comorbidities appears negligible after one year of treatment
(157). By contrast, randomized
controlled trials assessing the effects of CPAP on lipid metabolism
have produced inconclusive results, with two meta-analyses yielding
conflicting evidence (57). Large
population-based studies generally highlight a relationship between
OSA and dyslipidemia; however, they often fail to adequately
control for confounding factors such as diet, exercise and the use
of lipid-lowering medications, introducing potential biases. Thus,
there is a pressing need for new clinical studies with larger
sample sizes that account for these variables. Such research should
also facilitate the screening of comorbid conditions for more
timely interventions, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
The use of A2AR agonists presents several
limitations and challenges that must be carefully addressed. These
agonists may exhibit non-specific effects on other adenosine
receptors, potentially leading to side effects, so enhancing their
specificity and selectivity is crucial. Additionally, the
pharmacological efficacy and pharmacokinetics of A2AR agonists can
impact their clinical application, making it essential to optimize
drug structure to improve bioavailability, stability and half-life
(158). This optimization could
enhance efficacy and reduce dosing frequency, contributing to more
convenient and effective treatment. Safety and tolerability are
paramount, as long-term use of A2AR agonists may result in adverse
reactions, particularly in the cardiovascular, digestive and
nervous systems. Comprehensive evaluations of safety and
tolerability are necessary to establish appropriate dosing and
treatment plans (159).
Furthermore, given the complex and multifactorial nature of
inflammatory diseases, relying solely on A2AR agonists may yield
limited effectiveness (160).
Exploring combination therapies with other drugs represents a
promising avenue for future research, aiming to enhance overall
treatment efficacy while minimizing side effects. In addition,
individual patient responses to A2AR agonists can vary markedly,
making it vital to understand each patient's genetic background,
disease subtype and immune status for developing personalized
treatment plans, which could substantially improve treatment
effectiveness and reduce adverse reactions (161).
The present study made significant contributions to
our understanding of OSA and its associated aspects, proving
valuable to the scientific community. It explored various elements
related to OSA, examining traditional mechanisms such as
intermittent hypoxia and sleep disruptions while focusing on
adenosine receptors, particularly A2AR. By integrating the effects
of A2AR on inflammation, lipid and glucose metabolism,
mitochondrial function and cell apoptosis through the
PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway, the current review presented a
comprehensive view of the complex interactions within OSA. This
holistic understanding aids researchers in developing more targeted
hypotheses and experimental designs, revealing previously
overlooked connections among physiological processes. In contrast
to earlier reviews that primarily addressed basic OSA
pathophysiology and the effects of intermittent hypoxia on vascular
endothelial damage and systemic inflammation (162), the present review offered a deeper
analysis of the molecular mechanisms of A2AR and broader
implications. It built on this foundation by exploring the
regulatory role of A2AR in the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway and its
consequences for inflammation and lipid metabolism, providing a
more nuanced perspective on OSA. In addition, the present review
emphasized the intricate interplay between inflammation and
metabolic changes in OSA. It highlighted how specific metabolites
contribute to OSA pathogenesis and how inflammation affects
metabolic pathways, addressing an area less explored in prior
research. This focused approach encourages further investigation
into these interactions, potentially leading to the identification
of novel biomarkers for early diagnosis and new therapeutic targets
for more effective treatments. By contrast, another previous review
centered on the relationship of OSA with cardiovascular diseases,
examining how OSA-induced changes in blood pressure, lipid profiles
and endothelial function contribute to cardiovascular morbidity
(57). While this is an important
area, it did not comprehensively address the role of metabolites or
the interaction between inflammation and metabolism as our review
does. By specifically focusing on these aspects, the present study
underscored the significance of understanding metabolite
involvement in inflammation, which could reveal new insights into
the pathogenesis of OSA and therapeutic opportunities.
Additionally, the present review discussed the potential clinical
applications of A2AR agonists in treating inflammatory diseases
beyond COPD and asthma, highlighting their limitations and
challenges. By broadening the scope of the clinical utility of
A2AR, it provided critical insights for researchers and clinicians,
guiding future research and optimizing the use of A2AR agonists in
various disease contexts. By contrast, a previous review primarily
focused on traditional OSA treatment options, such as CPAP, oral
appliances and surgery, without exploring the emerging potential of
A2AR agonists (163). In
conclusion, the present review stands out for its comprehensive
integration of multiple mechanisms, its focus on the interplay
between inflammation and metabolism and its exploration of clinical
applications and limitations. Compared to earlier reviews, it
offers a more detailed and multi-faceted perspective, advancing
knowledge in the field of OSA and providing valuable resources for
future research and clinical applications.
Although the significance of inflammation and
metabolic changes in OSA is recognized, there are still several
areas that require further research. First, the mechanism of A2AR
in OSA needs deeper exploration. This includes understanding its
effect on different cell types and signaling pathways.
Additionally, the effects of A2AR on different age groups and its
influence on respiratory drive demand further investigation.
Exploring the potential value of A2AR agonists in treating OSA and
determining the optimal dosage and treatment duration is crucial.
Large-scale randomized controlled trials should be conducted to
evaluate the effectiveness of CPAP and other treatment methods on
various aspects of patients with OSA. Currently, the effect of CPAP
on lipid metabolism is controversial and most existing studies are
observational, lacking large-scale randomized controlled trials to
determine its exact efficacy. Finally, by employing modern
technologies such as metabolomics and genomics, further research
can be carried out on the detailed interaction mechanisms between
inflammation and metabolism in OSA. Studying OSA-related
metabolites and biomarkers can improve the accuracy of early
diagnosis, enable timely intervention, reduce the occurrence of
complications and help discover new therapeutic targets. However,
the role of specific metabolites in the pathogenesis of OSA still
needs further clarification. In summary, further research is needed
in multiple aspects of OSA, including the mechanism of A2AR, the
effectiveness of treatment methods such asCPAP and the role of
metabolites in pathogenesis. These efforts will enhance our
understanding of OSA and lead to improved diagnosis and treatment
strategies.
OSA is intricately linked to inflammation and
dyslipidemia, conditions often exacerbated by OSA-related
comorbidities. The present study delved into the molecular
mechanisms underlying OSA, emphasizing the role of A2AR in
modulating these processes. It found that A2AR exerts an inhibitory
effect on the PI3K/Akt/HIF-1 pathway, markedly influencing
inflammation and lipid metabolism associated with OSA. This
supports the hypothesis that adenosine receptors are the main
molecular process drivers of OSA onset. Furthermore, A2AR
activation appears to stimulate key factors such as Akt and HIF-1,
which are known to play roles in the regulation of intermittent
hypoxia. However, the complexity of interactions among these
factors suggests that further investigation is warranted. The
potential of A2AR as an anti-inflammatory agent and a regulator of
lipid metabolism, particularly through its influence on the
PI3K-Akt-HIF-1 pathway under hypoxic conditions, is promising.
Additionally, non-selective adenosine receptor antagonists, such as
caffeine, have been shown to improve sleep apnea symptoms,
indicating that A2AR may serve as a viable target for
pharmacological interventions aimed at alleviating inflammation and
dyslipidemia associated with OSA. Future research should explore
the implications of OSA-related comorbidities, particularly the
pathways involved in OSA-associated dyslipidemia. These insights
could illuminate the cellular processes driving OSA and aid in
identifying potential therapeutic targets for prevention and
treatment.
Not applicable.
Funding: The present study was supported by National Natural
Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 82074576 and 81704190),
Sichuan Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine
(grant no. 2021MS444) and Key Laboratory of Sports Medicine of
Sichuan Province (grant no. 2023-A037).
Not applicable.
NM wrote the first draft of the manuscript. PL
prepared the review tables and figures. NL, YH, NM and LK were
responsible for critical revisions of the article. YH contributed
to the acquisition of funds. Data authentication is not applicable.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
|
1
|
Gottlieb DJ and Punjabi NM: Diagnosis and
Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A review. JAMA.
323:1389–1400. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Benjafield AV, Ayas NT, Eastwood PR,
Heinzer R, Ip MSM, Morrell MJ, Nunez CM, Patel SR, Penzel T, Pépin
JL, et al: Estimation of the global prevalence and burden of
obstructive sleep apnoea: A literature-based analysis. Lancet
Respir Med. 7:687–698. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mohamadian M, Chiti H, Shoghli A, Biglari
S, Parsamanesh N and Esmaeilzadeh A: COVID-19: Virology, biology
and novel laboratory diagnosis. J Gene Med.
23(e3303)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Franklin KA and Lindberg E: Obstructive
sleep apnea is a common disorder in the population-a review on the
epidemiology of sleep apnea. J Thorac Dis. 7:1311–1322.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gu X, Zhang J, Shi Y, Shen H, Li Y, Chen Y
and Liang L: ESM1/HIF-1α pathway modulates chronic intermittent
hypoxia-induced non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation, stemness
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep. 45:1226–1234.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hirsch Allen AJ, Kendzerska T, Bhatti P,
Jen R, Myers R, Hajipour M, van Eeden SF and Ayas N: Obstructive
sleep apnea severity, circulating biomarkers, and cancer risk. J
Clin Sleep Med. 20:1415–1422. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ni W, Niu Y, Cao S, Fan C, Fan J, Zhu L
and Wang X: Intermittent hypoxia exacerbates anxiety in high-fat
diet-induced diabetic mice by inhibiting TREM2-regulated IFNAR1
signaling. J Neuroinflammation. 21(166)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yang M, Cai W, Lin Z, Tuohuti A and Chen
X: Intermittent Hypoxia Promotes TAM-Induced Glycolysis in
Laryngeal Cancer Cells via Regulation of HK1 Expression through
Activation of ZBTB10. Int J Mol Sci. 24(14808)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cheong AJY, Tan BKJ, Teo YH, Tan NKW, Yap
DWT, Sia CH, Ong TH, Leow LC, See A and Toh ST: Obstructive Sleep
Apnea and Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann
Am Thorac Soc. 19:469–475. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tang SS, Liang CH, Liu YL, Wei W, Deng XR,
Shi XY, Wang LM, Zhang LJ and Yuan HJ: Intermittent hypoxia is
involved in gut microbial dysbiosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus and
obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. World J Gastroenterol.
28:2320–2333. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Almendros I, Martinez-Garcia MA, Farré R
and Gozal D: Obesity, sleep apnea, and cancer. Int J Obes (Lond).
44:1653–1667. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Prabhakar NR, Peng YJ and Nanduri J:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and obstructive sleep apnea. J Clin
Invest. 130:5042–5051. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Moriondo G, Soccio P, Minoves M, Scioscia
G, Tondo P, Foschino Barbaro MP, Pépin JL, Briançon-Marjollet A and
Lacedonia D: Intermittent Hypoxia Mediates Cancer Development and
Progression Through HIF-1 and miRNA Regulation. Arch Bronconeumol.
59:629–637. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Spanish).
|
|
14
|
Wang N, Su X, Sams D, Prabhakar NR and
Nanduri J: P300/CBP Regulates HIF-1-Dependent Sympathetic
Activation and Hypertension by Intermittent Hypoxia. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 70:110–118. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Halpin-Veszeleiova K and Hatfield SM:
Oxygenation and A2AR blockade to eliminate
hypoxia/HIF-1α-adenosinergic immunosuppressive axis and improve
cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 53:84–90.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu Z, Yan S, Wang J, Xu Y, Wang Y, Zhang
S, Xu X, Yang Q, Zeng X, Zhou Y, et al: Endothelial adenosine A2a
receptor-mediated glycolysis is essential for pathological retinal
angiogenesis. Nat Commun. 8(584)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Belaidi E, Morand J, Gras E, Pépin JL and
Godin-Ribuot D: Targeting the ROS-HIF-1-endothelin axis as a
therapeutic approach for the treatment of obstructive sleep
apnea-related cardiovascular complications. Pharmacol Ther.
168:1–11. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Guan S, Suman S, Amann JM, Wu R, Carbone
DP, Wang J and Dikov MM: Metabolic reprogramming by adenosine
antagonism and implications in non-small cell lung cancer therapy.
Neoplasia. 32(100824)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bruzzese L, Fromonot J, By Y, Durand-Gorde
JM, Condo J, Kipson N, Guieu R, Fenouillet E and Ruf J: NF-κB
enhances hypoxia-driven T-cell immunosuppression via upregulation
of adenosine A(2A) receptors. Cell Signal. 26:1060–1067.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sitkovsky MV, Kjaergaard VJ, Lukashev D
and Ohta A: Hypoxia-adenosinergic immunosuppression: Tumor
protection by T regulatory cells and cancerous tissue hypoxia. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:5947–5952. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ke RH, Xiong J, Liu Y and Ye ZR: Adenosine
A2a receptor induced gliosis via Akt/NF-kappaB pathway in vitro.
Neurosci Res. 65:280–285. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Eckle T, Kewley EM, Brodsky KS, Tak E,
Bonney S, Gobel M, Anderson D, Glover LE, Riegel AK, Colgan SP and
Eltzschig HK: Identification of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-1A as
transcriptional regulator of the A2B adenosine receptor during
acute lung injury. J Immunol. 192:1249–1256. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Steingold JM and Hatfield SM: Targeting
Hypoxia-A2A Adenosinergic Immunosuppression of Antitumor T Cells
During Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol.
11(570041)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Castillo CA, León D, Ruiz MA, Albasanz JL
and Martín M: Modulation of adenosine A1 and A2A receptors in C6
glioma cells during hypoxia: Involvement of endogenous adenosine. J
Neurochem. 105:2315–2329. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pang L, Ng KT, Liu J, Yeung WO, Zhu J,
Chiu TS, Liu H, Chen Z, Lo CM and Man K: Plasmacytoid dendritic
cells recruited by HIF-1α/eADO/ADORA1 signaling induce
immunosuppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
522:80–92. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Orrù G, Storari M, Scano A, Piras V, Taibi
R and Viscuso D: Obstructive Sleep Apnea, oxidative stress,
inflammation and endothelial dysfunction-An overview of predictive
laboratory biomarkers. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:6939–6948.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Fang S, Sun S, Cai H, Zou X, Wang S, Hao
X, Wan X, Tian J, Li Z, He Z, et al: IRGM/Irgm1 facilitates
macrophage apoptosis through ROS generation and MAPK signal
transduction: Irgm1(+/-) mice display increases atherosclerotic
plaque stability. Theranostics. 11:9358–9375. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lin YF, Li MH, Huang RH, Zhang SZ, Xu XF,
Zhou HM, Liu MH, Liao XX, Liao LZ, Guo Y and Zhuang XD: GP73
enhances the ox-LDL-induced inflammatory response in THP-1 derived
macrophages via affecting NLRP3 inflammasome signaling. Int J
Cardiol. 387(131109)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Balzan S and Lubrano V: LOX-1 receptor: A
potential link in atherosclerosis and cancer. Life Sci. 198:79–86.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sylvers-Davie KL and Davies BSJ:
Regulation of lipoprotein metabolism by ANGPTL3, ANGPTL4, and
ANGPTL8. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 321:E493–E508.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li W and Wang W: Causal modulation of
lipid metabolism may shape the inflammatory microenvironment and
potentially augment immunotherapy: A comprehensive genetic
landscape revealed by Mendelian randomization analysis. Int
Immunol. 36:291–302. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yuan T, Yang T, Chen H, Fu D, Hu Y, Wang
J, Yuan Q, Yu H, Xu W and Xie X: New insights into oxidative stress
and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated
atherosclerosis. Redox Biol. 20:247–260. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lara-Guzmán OJ, Gil-Izquierdo A, Medina S,
Osorio E, Álvarez-Quintero R, Zuluaga N, Oger C, Galano JM, Durand
T and Muñoz-Durango K: Oxidized LDL triggers changes in oxidative
stress and inflammatory biomarkers in human macrophages. Redox
Biol. 15:1–11. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Incalza MA, D'Oria R, Natalicchio A,
Perrini S, Laviola L and Giorgino F: Oxidative stress and reactive
oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with
cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul Pharmacol. 100:1–19.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xu D, Hu YH, Gou X, Li FY, Yang XY, Li YM
and Chen F: Oxidative Stress and Antioxidative Therapy in Pulmonary
Arterial Hypertension. Molecules. 27(3724)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li M, Xin S, Gu R, Zheng L, Hu J, Zhang R
and Dong H: Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers Related to Oxidative Stress
and Macrophage Ferroptosis in Atherosclerosis. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2022(8917947)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kattoor AJ, Pothineni NVK, Palagiri D and
Mehta JL: Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler
Rep. 19(42)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Batty M, Bennett MR and Yu E: The Role of
Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis. Cells. 11(3843)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ranjbarvaziri S, Kooiker KB, Ellenberger
M, Fajardo G, Zhao M, Vander Roest AS, Woldeyes RA, Koyano TT, Fong
R, Ma N, et al: Altered Cardiac Energetics and Mitochondrial
Dysfunction in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation.
144:1714–1731. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Tian L, Cao W, Yue R, Yuan Y, Guo X, Qin
D, Xing J and Wang X: Pretreatment with Tilianin improves
mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxidative stress in rats with
myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1 alpha
signaling pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 139:352–360. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dikalova AE, Pandey A, Xiao L, Arslanbaeva
L, Sidorova T, Lopez MG, Billings FT 4th, Verdin E, Auwerx J,
Harrison DG and Dikalov SI: Mitochondrial Deacetylase Sirt3 Reduces
Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension While Sirt3 Depletion in
Essential Hypertension Is Linked to Vascular Inflammation and
Oxidative Stress. Circ Res. 126:439–452. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kent BD, Grote L, Ryan S, Pépin JL,
Bonsignore MR, Tkacova R, Saaresranta T, Verbraecken J, Lévy P,
Hedner J and McNicholas WT: Diabetes mellitus prevalence and
control in sleep-disordered breathing: The European Sleep Apnea
Cohort (ESADA) study. Chest. 146:982–990. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Giampá SQC, Lorenzi-Filho G and Drager LF:
Obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic syndrome. Obesity (Silver
Spring). 31:900–911. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lévy P, Kohler M, McNicholas WT, Barbé F,
McEvoy RD, Somers VK, Lavie L and Pépin JL: Obstructive sleep
apnoea syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1(15015)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Unnikrishnan D, Jun J and Polotsky V:
Inflammation in sleep apnea: An update. Rev Endocr Metab Disord.
16:25–34. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Alterki A, Abu-Farha M, Al Shawaf E,
Al-Mulla F and Abubaker J: Investigating the Relationship between
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea, Inflammation and Cardio-Metabolic
Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 24(6807)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chen Z, Zeng J, Pei X, Zhao J, Zhao F,
Zhang G, Liang K, Li J and Zhao X: Causal Relationships Between
Circulating Inflammatory Proteins and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A
Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Nat Sci Sleep.
16:787–800. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Malicki M, Karuga FF, Szmyd B, Sochal M
and Gabryelska A: Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Circadian Clock
Disruption, and Metabolic Consequences. Metabolites.
13(60)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gras E, Belaidi E, Briançon-Marjollet A,
Pépin JL, Arnaud C and Godin-Ribuot D: Endothelin-1 mediates
intermittent hypoxia-induced inflammatory vascular remodeling
through HIF-1 activation. J Appl Physiol (1985). 120:437–443.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Taylor CT, Kent BD, Crinion SJ, McNicholas
WT and Ryan S: Human adipocytes are highly sensitive to
intermittent hypoxia induced NF-kappaB activity and subsequent
inflammatory gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
447:660–665. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Imamura T, Poulsen O and Haddad GG:
Intermittent hypoxia induces murine macrophage foam cell formation
by IKK-β-dependent NF-κB pathway activation. J Appl Physiol (1985).
121:670–677. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lv R, Zhao Y, Wang X, He Y, Dong N, Min X,
Liu X, Yu Q, Yuan K, Yue H and Yin Q: GLP-1 analogue liraglutide
attenuates CIH-induced cognitive deficits by inhibiting oxidative
stress, neuroinflammation, and apoptosis via the Nrf2/HO-1 and
MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol.
142(113222)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Murphy AM, Thomas A, Crinion SJ, Kent BD,
Tambuwala MM, Fabre A, Pepin JL, Roche HM, Arnaud C and Ryan S:
Intermittent hypoxia in obstructive sleep apnoea mediates insulin
resistance through adipose tissue inflammation. Eur Respir J.
49(1601731)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Arnaud C, Poulain L, Lévy P and Dematteis
M: Inflammation contributes to the atherogenic role of intermittent
hypoxia in apolipoprotein-E knock out mice. Atherosclerosis.
219:425–431. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Huang T, Sands SA, Stampfer MJ, Tworoger
SS, Hu FB and Redline S: Insulin Resistance, Hyperglycemia, and
Risk of Developing Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Men and Women in the
United States. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 19:1740–1749. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Meng X, Wen H and Lian L: Association
between triglyceride glucose-body mass index and obstructive sleep
apnea: A study from NHANES 2015-2018. Front Nutr.
11(1424881)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Barros D and García-Río F: Obstructive
sleep apnea and dyslipidemia: From animal models to clinical
evidence. Sleep. 42(zsy236)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Tang H, Zhou Q, Zheng F, Wu T, Tang YD and
Jiang J: The Causal Effects of Lipid Profiles on Sleep Apnea. Front
Nutr. 9(910690)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Sun J, Hu J, Tu C, Zhong A and Xu H:
Obstructive Sleep Apnea Susceptibility Genes in Chinese Population:
A Field Synopsis and Meta-Analysis of Genetic Association Studies.
PLoS One. 10(e0135942)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Uyrum E, Balbay O, Annakkaya AN, Gulec
Balbay E, Silan F and Arbak P: The relationship between obstructive
sleep apnea syndrome and apolipoprotein E genetic variants.
Respiration. 89:195–200. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Meszaros M and Bikov A: Obstructive Sleep
Apnoea and Lipid Metabolism: The Summary of Evidence and Future
Perspectives in the Pathophysiology of OSA-Associated
Dyslipidaemia. Biomedicines. 10(2754)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Burke SL, Hu T, Spadola CE, Li T, Naseh M,
Burgess A and Cadet T: Mild cognitive impairment: associations with
sleep disturbance, apolipoprotein e4, and sleep medications. Sleep
Med. 52:168–176. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Huguenard CJC, Cseresznye A, Darcey T,
Nkiliza A, Evans JE, Hazen SL, Mullan M, Crawford F and Abdullah L:
Age and APOE affect L-carnitine system metabolites in the brain in
the APOE-TR model. Front Aging Neurosci. 14(1059017)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Turner AD, Locklear CE, Oruru D, Briggs
AQ, Bubu OM and Seixas A: Exploring the combined effects of sleep
apnea and APOE-e4 on biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging
Neurosci. 14(1017521)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Kim JK, Fillmore JJ, Chen Y, Yu C, Moore
IK, Pypaert M, Lutz EP, Kako Y, Velez-Carrasco W, Goldberg IJ, et
al: Tissue-specific overexpression of lipoprotein lipase causes
tissue-specific insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:7522–7527. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Wang N, Shi XF, Khan SA, Wang B, Semenza
GL, Prabhakar NR and Nanduri J: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates
pancreatic β-cell dysfunction by intermittent hypoxia. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 319:C922–C932. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Fang Y, Zhang Q, Tan J, Li L, An X and Lei
P: Intermittent hypoxia-induced rat pancreatic β-cell apoptosis and
protective effects of antioxidant intervention. Nutr Diabetes.
4(e131)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Dempsey JA, Veasey SC, Morgan BJ and
O'Donnell CP: Pathophysiology of sleep apnea. Physiol Rev.
90:47–112. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Zeng S, Wang Y, Ai L, Huang L, Liu Z, He
C, Bai Q and Li Y: Chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced oxidative
stress activates TRB3 and phosphorylated JNK to mediate insulin
resistance and cell apoptosis in the pancreas. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 51(e13843)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Nascimento DC, Viacava PR, Ferreira RG,
Damaceno MA, Piñeros AR, Melo PH, Donate PB, Toller-Kawahisa JE,
Zoppi D, Veras FP, et al: Sepsis expands a CD39(+) plasmablast
population that promotes immunosuppression via adenosine-mediated
inhibition of macrophage antimicrobial activity. Immunity.
54:2024–2041.e8. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Pasquini S, Contri C, Borea PA, Vincenzi F
and Varani K: Adenosine and Inflammation: Here, There and
Everywhere. Int J Mol Sci. 22(7685)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Haskó G, Linden J, Cronstein B and Pacher
P: Adenosine receptors: therapeutic aspects for inflammatory and
immune diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:759–770. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Junqueira SC, Dos Santos Coelho I,
Lieberknecht V, Cunha MP, Calixto JB, Rodrigues ALS, Santos ARS and
Dutra RC: Inosine, an Endogenous Purine Nucleoside, Suppresses
Immune Responses and Protects Mice from Experimental Autoimmune
Encephalomyelitis: A Role for A2A Adenosine Receptor. Mol
Neurobiol. 54:3271–3285. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Impellizzeri D, Di Paola R, Esposito E,
Mazzon E, Paterniti I, Melani A, Bramanti P, Pedata F and Cuzzocrea
S: CGS 21680, an agonist of the adenosine (A2A) receptor, decreases
acute lung inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 668:305–316.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Lu Y, Zhu W, Zhang GX, Chen JC, Wang QL,
Mao MY, Deng SC, Jin LP, Liu H and Kuang YH: Adenosine A2A receptor
activation regulates the M1 macrophages activation to initiate
innate and adaptive immunity in psoriasis. Clin Immunol.
266(110309)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Mohsenin A, Mi T, Xia Y, Kellems RE, Chen
JF and Blackburn MR: Genetic removal of the A2A adenosine receptor
enhances pulmonary inflammation, mucin production, and angiogenesis
in adenosine deaminase-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 293:L753–L761. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Welihinda AA, Kaur M, Raveendran KS and
Amento EP: Enhancement of inosine-mediated A(2A)R signaling through
positive allosteric modulation. Cell Signal. 42:227–235.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Zhao N, Shao Z, Xia G, Liu H, Zhang L,
Zhao X, Dang S, Qian L, Xu W, Yu Z and Wang R: Protective role of
the CD73-A2AR axis in cirrhotic cardiomyopathy through negative
feedback regulation of the NF-κB pathway. Front Immunol.
15(1428551)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Correale P, Caracciolo M, Bilotta F, Conte
M, Cuzzola M, Falcone C, Mangano C, Falzea AC, Iuliano E, Morabito
A, et al: Therapeutic effects of adenosine in high flow 21% oxygen
aereosol in patients with Covid19-pneumonia. PLoS One.
15(e0239692)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Tozzi M and Novak I: Purinergic Receptors
in Adipose Tissue As Potential Targets in Metabolic Disorders.
Front Pharmacol. 8(878)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Kotańska M, Dziubina A, Szafarz M, Mika K,
Bednarski M, Nicosia N, Temirak A, Müller CE and Kieć-Kononowicz K:
Preliminary Evidence of the Potent and Selective Adenosine A2B
Receptor Antagonist PSB-603 in Reducing Obesity and Some of Its
Associated Metabolic Disorders in Mice. Int J Mol Sci.
23(13439)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhao W, Ma L, Cai C and Gong X: Caffeine
Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Suppressing MAPK/NF-κB
and A2aR Signaling in LPS-Induced THP-1 Macrophages. Int J Biol
Sci. 15:1571–1581. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Zohair B, Chraa D, Rezouki I, Benthami H,
Razzouki I, Elkarroumi M, Olive D, Karkouri M and Badou A: The
immune checkpoint adenosine 2A receptor is associated with
aggressive clinical outcomes and reflects an immunosuppressive
tumor microenvironment in human breast cancer. Front Immunol.
14(1201632)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Leiva A, Guzmán-Gutiérrez E,
Contreras-Duarte S, Fuenzalida B, Cantin C, Carvajal L, Salsoso R,
Gutiérrez J, Pardo F and Sobrevia L: Adenosine receptors:
Modulators of lipid availability that are controlled by lipid
levels. Mol Aspects Med. 55:26–44. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
DeOliveira CC, Paiva Caria CR, Ferreira
Gotardo EM, Ribeiro ML and Gambero A: Role of A(1) and A(2A)
adenosine receptor agonists in adipose tissue inflammation induced
by obesity in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 799:154–159. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Chen S, Fan J, Xie P, Ahn J, Fernandez M,
Billingham LK, Miska J, Wu JD, Wainwright DA, Fang D, et al: CD8+ T
cells sustain antitumor response by mediating crosstalk between
adenosine A2A receptor and glutathione/GPX4. J Clin Invest.
134(e170071)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Bruzzese A, Dalton JAR and Giraldo J:
Insights into adenosine A2A receptor activation through cooperative
modulation of agonist and allosteric lipid interactions. PLoS
Comput Biol. 16(e1007818)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Friedman B, Corciulo C, Castro CM and
Cronstein BN: Adenosine A2A receptor signaling promotes FoxO
associated autophagy in chondrocytes. Sci Rep.
11(968)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Cai Y, Li H, Liu M, Pei Y, Zheng J, Zhou
J, Luo X, Huang W, Ma L, Yang Q, et al: Disruption of adenosine 2A
receptor exacerbates NAFLD through increasing inflammatory
responses and SREBP1c activity. Hepatology. 68:48–61.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Kong LR, Chen XH, Sun Q, Zhang KY, Xu L,
Ding L, Zhou YP, Zhang ZB, Lin JR and Gao PJ: Loss of C3a and C5a
receptors promotes adipocyte browning and attenuates diet-induced
obesity via activating inosine/A2aR pathway. Cell Rep.
42(112078)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Lim J, Iyer A, Suen JY, Seow V, Reid RC,
Brown L and Fairlie DP: C5aR and C3aR antagonists each inhibit
diet-induced obesity, metabolic dysfunction, and adipocyte and
macrophage signaling. FASEB J. 27:822–831. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Kim K, Im H, Son Y, Kim M, Tripathi SK,
Jeong LS and Lee YH: Anti-obesity effects of the dual-active
adenosine A(2A)/A(3) receptor-ligand LJ-4378. Int J Obes (Lond).
46:2128–2136. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Shamsuzzaman A, Amin RS, Calvin AD,
Davison D and Somers VK: Severity of obstructive sleep apnea is
associated with elevated plasma fibrinogen in otherwise healthy
patients. Sleep Breath. 18:761–766. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Li H, Chen O, Ye Z, Zhang R, Hu H, Zhang
N, Huang J, Liu W and Sun X: Inhalation of high concentrations of
hydrogen ameliorates liver ischemia/reperfusion injury through
A(2A) receptor mediated PI3K-Akt pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
130:83–92. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Huang X, Wu P, Huang F, Xu M, Chen M,
Huang K, Li GP, Xu M, Yao D and Wang L: Baicalin attenuates chronic
hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension via adenosine A(2A)
receptor-induced SDF-1/CXCR4/PI3K/AKT signaling. J Biomed Sci.
24(52)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Dal-Cim T, Poluceno GG, Lanznaster D, de
Oliveira KA, Nedel CB and Tasca CI: Guanosine prevents oxidative
damage and glutamate uptake impairment induced by oxygen/glucose
deprivation in cortical astrocyte cultures: involvement of A(1) and
A(2A) adenosine receptors and PI3K, MEK, and PKC pathways.
Purinergic Signal. 15:465–476. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Wen MH, Wu MJ, Vinit S and Lee KZ:
Modulation of Serotonin and Adenosine 2A Receptors on Intermittent
Hypoxia-Induced Respiratory Recovery following Mid-Cervical
Contusion in the Rat. J Neurotrauma. 36:2991–3004. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Mathew OP: Apnea of prematurity:
Pathogenesis and management strategies. J Perinatol. 31:302–310.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Lv B, Yang L, Gao Y and Li G:
Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids Attenuate LPS-Induced NIH/3T3 Cell
Fibrosis through the A(2A)R and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways. Bull
Exp Biol Med. 177:185–189. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Mori Y, Higuchi M, Masuyama N and Gotoh Y:
Adenosine A2A receptor facilitates calcium-dependent protein
secretion through the activation of protein kinase A and
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in PC12 cells. Cell Struct Funct.
29:101–110. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Vergadi E, Ieronymaki E, Lyroni K,
Vaporidi K and Tsatsanis C: Akt Signaling Pathway in Macrophage
Activation and M1/M2 Polarization. J Immunol. 198:1006–1014.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Troutman TD, Bazan JF and Pasare C:
Toll-like receptors, signaling adapters and regulation of the
pro-inflammatory response by PI3K. Cell Cycle. 11:3559–3567.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Li Q, Wang G, Xiong SH, Cao Y, Liu B, Sun
J, Li L, Mohammadtursun N, Yu H, Dong J and Wu J:
Bu-Shen-Fang-Chuan formula attenuates cigarette smoke-induced
inflammation by modulating the PI3K/Akt-Nrf2 and NF-κB signalling
pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 261(113095)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Li L, Qu Y, Mao M, Xiong Y and Mu D: The
involvement of phosphoinositid 3-kinase/Akt pathway in the
activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the developing rat
brain after hypoxia-ischemia. Brain Res. 1197:152–158.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Li L, Yin X, Ma N, Lin F, Kong X, Chi J
and Feng Z: Desferrioxamine regulates HIF-1 alpha expression in
neonatal rat brain after hypoxia-ischemia. Am J Transl Res.
6:377–383. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Hutami IR, Izawa T, Khurel-Ochir T,
Sakamaki T, Iwasa A and Tanaka E: Macrophage Motility in Wound
Healing Is Regulated by HIF-1α via S1P Signaling. Int J Mol Sci.
22(8992)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Förster
I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, Haase VH, Jaenisch R, Corr M, Nizet V,
et al: HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated
inflammation. Cell. 112:645–657. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Peyssonnaux C, Datta V, Cramer T, Doedens
A, Theodorakis EA, Gallo RL, Hurtado-Ziola N, Nizet V and Johnson
RS: HIF-1alpha expression regulates the bactericidal capacity of
phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 115:1806–1815. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Kim SY, Jeong E, Joung SM and Lee JY:
PI3K/Akt contributes to increased expression of Toll-like receptor
4 in macrophages exposed to hypoxic stress. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 419:466–471. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Kunze R, Zhou W, Veltkamp R, Wielockx B,
Breier G and Marti HH: Neuron-specific prolyl-4-hydroxylase domain
2 knockout reduces brain injury after transient cerebral ischemia.
Stroke. 43:2748–2756. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ and Simon MC:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol
Cell. 40:294–309. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Vgontzas AN, Papanicolaou DA, Bixler EO,
Kales A, Tyson K and Chrousos GP: Elevation of plasma cytokines in
disorders of excessive daytime sleepiness: Role of sleep
disturbance and obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 82:1313–1316.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Ryan S: Adipose tissue inflammation by
intermittent hypoxia: Mechanistic link between obstructive sleep
apnoea and metabolic dysfunction. J Physiol. 595:2423–2430.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Toujani S, Kaabachi W, Mjid M, Hamzaoui K,
Cherif J and Beji M: Vitamin D deficiency and interleukin-17
relationship in severe obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome.
Ann Thorac Med. 12:107–113. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Gao C, Koko MYF, Ding M, Hong W, Li J,
Dong N and Hui M: Intestinal alkaline phosphatase (IAP, IAP
Enhancer) attenuates intestinal inflammation and alleviates insulin
resistance. Front Immunol. 13(927272)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Xie Y, Shi X, Sheng K, Han G, Li W, Zhao
Q, Jiang B, Feng J, Li J and Gu Y: PI3K/Akt signaling transduction
pathway, erythropoiesis and glycolysis in hypoxia (Review). Mol Med
Rep. 19:783–791. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Rahman SMK, Uyama T, Hussain Z and Ueda N:
Roles of Endocannabinoids and Endocannabinoid-Like Molecules in
Energy Homeostasis and Metabolic Regulation: A Nutritional
Perspective. Annu Rev Nutr. 41:177–202. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Murillo-Rodríguez E: The Endocannabinoid
System as Prognostic Biomarker of the Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Morbidity in COVID-19-Recovered Individuals. Sleep Vigil.
5:205–211. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Wu YQ, Wang B, Song L, Wang Q, Chen XY and
Liu ZL: A study on the endogenous cannabinoid system synthetic and
catabolic enzyme levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.
Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 34:359–361. 2011.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
120
|
Gonzaga CC, Gaddam KK, Ahmed MI, Pimenta
E, Thomas SJ, Harding SM, Oparil S, Cofield SS and Calhoun DA:
Severity of obstructive sleep apnea is related to aldosterone
status in subjects with resistant hypertension. J Clin Sleep Med.
6:363–368. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Reiss AB, Carsons SE, Anwar K, Rao S,
Edelman SD, Zhang H, Fernandez P, Cronstein BN and Chan ES:
Atheroprotective effects of methotrexate on reverse cholesterol
transport proteins and foam cell transformation in human THP-1
monocyte/macrophages. Arthritis Rheum. 58:3675–3683.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Lee EJ, Heo W, Kim JY, Kim H, Kang MJ, Kim
BR, Kim JH, Park DY, Kim CH, Yoon JH and Cho HJ: Alteration of
inflammatory mediators in the upper and lower airways under chronic
intermittent hypoxia: Preliminary Animal Study. Mediators Inflamm.
2017(4327237)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Papandreou C: Independent associations
between fatty acids and sleep quality among obese patients with
obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. J Sleep Res. 22:569–572.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Lebkuchen A, Carvalho VM, Venturini G,
Salgueiro JS, Freitas LS, Dellavance A, Martins FC, Lorenzi-Filho
G, Cardozo KHM and Drager LF: Metabolomic and lipidomic profile in
men with obstructive sleep apnoea: Implications for diagnosis and
biomarkers of cardiovascular risk. Sci Rep. 8(11270)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Xu H, Zheng X, Qian Y, Guan J, Yi H, Zou
J, Wang Y, Meng L, Zhao A, Yin S and Jia W: Metabolomics Profiling
for Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Simple Snorers. Sci Rep.
6(30958)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Kamphorst JJ, Cross JR, Fan J, de
Stanchina E, Mathew R, White EP, Thompson CB and Rabinowitz JD:
Hypoxic and Ras-transformed cells support growth by scavenging
unsaturated fatty acids from lysophospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 110:8882–8887. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Chen J, Chen J, Huang J, Li Z, Gong Y, Zou
B, Liu X, Ding L, Li P, Zhu Z, et al: HIF-2α upregulation mediated
by hypoxia promotes NAFLD-HCC progression by activating lipid
synthesis via the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. Aging (Albany NY).
11:10839–10860. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Ackerman D, Tumanov S, Qiu B,
Michalopoulou E, Spata M, Azzam A, Xie H, Simon MC and Kamphorst
JJ: Triglycerides Promote Lipid Homeostasis during Hypoxic Stress
by Balancing Fatty Acid Saturation. Cell Rep. 24:2596–2605.e5.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Le TT, Berg NK, Harting MT, Li X,
Eltzschig HK and Yuan X: Purinergic Signaling in Pulmonary
Inflammation. Front Immunol. 10(1633)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Hanidziar D and Robson SC: Synapomorphic
features of hepatic and pulmonary vasculatures include comparable
purinergic signaling responses in host defense and modulation of
inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
321:G200–G212. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Guieu R, Deharo JC, Maille B, Crotti L,
Torresani E, Brignole M and Parati G: Adenosine and the
Cardiovascular System: The Good and the Bad. J Clin Med.
9(1366)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Vecchio EA, White PJ and May LT: The
adenosine A(2B) G protein-coupled receptor: Recent advances and
therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther. 198:20–33.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Bahreyni A, Avan A, Shabani M, Ryzhikov M,
Fiuji H, Soleimanpour S, Khazaei M and Hassanian SM: Therapeutic
potential of A2 adenosine receptor pharmacological regulators in
the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, recent progress, and
prospective. J Cell Physiol. 234:1295–1299. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Sacramento JF, Gonzalez C, Gonzalez-Martin
MC and Conde SV: Adenosine Receptor Blockade by Caffeine Inhibits
Carotid Sinus Nerve Chemosensory Activity in Chronic Intermittent
Hypoxic Animals. Adv Exp Med Biol. 860:133–137. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Conde SV, Monteiro EC and Sacramento JF:
Purines and Carotid Body: New Roles in Pathological Conditions.
Front Pharmacol. 8(913)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Li XC, Hong FF, Tu YJ, Li YA, Ma CY, Yu
CY, Fang L, Chen JY, Li ZL, Bao SJ, et al: Blockade of adenosine
A(2A) receptor alleviates cognitive dysfunction after chronic
exposure to intermittent hypoxia in mice. Exp Neurol.
350(113929)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Aranda JV and Beharry KD:
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and metabolism of caffeine in
newborns. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 25(101183)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Kobayashi S and Millhorn DE: Stimulation
of expression for the adenosine A2A receptor gene by hypoxia in
PC12 cells. A potential role in cell protection. J Biol Chem.
274:20358–20365. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Nadeem A, Fan M, Ansari HR, Ledent C and
Jamal Mustafa S: Enhanced airway reactivity and inflammation in A2A
adenosine receptor-deficient allergic mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell
Mol Physiol. 292:L1335–L1344. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Marshall NS, Yee BJ, Desai AV, Buchanan
PR, Wong KK, Crompton R, Melehan KL, Zack N, Rao SG, Gendreau RM,
et al: Two randomized placebo-controlled trials to evaluate the
efficacy and tolerability of mirtazapine for the treatment of
obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep. 31:824–831. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Kent BD, Ryan S and McNicholas WT:
Obstructive sleep apnea and inflammation: relationship to
cardiovascular co-morbidity. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 178:475–481.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Peng L, Li Y, Li X, Du Y, Li L, Hu C,
Zhang J, Qin Y, Wei Y and Zhang H: Extracellular vesicles derived
from intermittent hypoxia-treated red blood cells impair
endothelial function through regulating eNOS phosphorylation and
ET-1 expression. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 35:901–913. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Lv R, Liu X, Zhang Y, Dong N, Wang X, He
Y, Yue H and Yin Q: Pathophysiological mechanisms and therapeutic
approaches in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 8(218)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Popadic V, Brajkovic M, Klasnja S, Milic
N, Rajovic N, Lisulov DP, Divac A, Ivankovic T, Manojlovic A,
Nikolic N, et al: Correlation of dyslipidemia and inflammation with
obstructive sleep apnea severity. Front Pharmacol.
13(897279)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Sun X, Wang C, He Y, Chen K and Miao Y:
Effect of inflammatory cytokines and plasma metabolome on OSA: A
bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study and
mediation analysis. Front Immunol. 15(1416870)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Andrade RGS, Viana FM, Nascimento JA,
Drager LF, Moffa A, Brunoni AR, Genta PR and Lorenzi-Filho G: Nasal
vs Oronasal CPAP for OSA Treatment: A Meta-Analysis. Chest.
153:665–674. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Shen C, Ou Y, Ouyang R and Zong D:
Prevalence and characteristics of pain in moderate-to-severe
obstructive sleep apnea patients and effect of CPAP treatment. Sci
Rep. 13(15758)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Lorenzi-Filho G, Almeida FR and Strollo
PJ: Treating OSA: Current and emerging therapies beyond CPAP.
Respirology. 22:1500–1507. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
149
|
Chang JL, Goldberg AN, Alt JA, Mohammed A,
Ashbrook L, Auckley D, Ayappa I, Bakhtiar H, Barrera JE, Bartley
BL, et al: International Consensus Statement on Obstructive Sleep
Apnea. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 13:1061–1482. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
MacKay S, Carney AS, Catcheside PG,
Chai-Coetzer CL, Chia M, Cistulli PA, Hodge JC, Jones A, Kaambwa B,
Lewis R, et al: Effect of multilevel upper airway surgery vs
medical management on the apnea-hypopnea index and patient-reported
daytime sleepiness among patients with moderate or severe
obstructive sleep apnea: The SAMS Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA.
324:1168–1179. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Sánchez AI, Martínez P, Miró E, Bardwell
WA and Buela-Casal G: CPAP and behavioral therapies in patients
with obstructive sleep apnea: Effects on daytime sleepiness, mood,
and cognitive function. Sleep Med Rev. 13:223–233. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Schmickl CN, Landry SA, Orr JE, Chin K,
Murase K, Verbraecken J, Javaheri S, Edwards BA, Owens RL and
Malhotra A: Acetazolamide for OSA and Central Sleep Apnea: A
Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Chest.
158:2632–2645. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Ulrich S, Nussbaumer-Ochsner Y, Vasic I,
Hasler E, Latshang TD, Kohler M, Muehlemann T, Wolf M and Bloch KE:
Cerebral oxygenation in patients with OSA: effects of hypoxia at
altitude and impact of acetazolamide. Chest. 146:299–308.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
Chapman JL, Vakulin A, Hedner J, Yee BJ
and Marshall NS: Modafinil/armodafinil in obstructive sleep apnoea:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Respir J. 47:1420–1428.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Mashaqi S, Patel SI, Combs D, Estep L,
Helmick S, Machamer J and Parthasarathy S: The hypoglossal nerve
stimulation as a novel therapy for treating obstructive sleep
apnea-a literature review. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
18(1642)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Akinnusi ME, Laporta R and El-Solh AA:
Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 modulates
endothelial apoptosis in obstructive sleep apnea. Chest.
140:1503–1510. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Feres MC, Fonseca FA, Cintra FD,
Mello-Fujita L, de Souza AL, De Martino MC, Tufik S and Poyares D:
An assessment of oxidized LDL in the lipid profiles of patients
with obstructive sleep apnea and its association with both
hypertension and dyslipidemia, and the impact of treatment with
CPAP. Atherosclerosis. 241:342–349. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Trevethick MA, Mantell SJ, Stuart EF,
Barnard A, Wright KN and Yeadon M: Treating lung inflammation with
agonists of the adenosine A2A receptor: Promises, problems and
potential solutions. Br J Pharmacol. 155:463–474. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Guo D, Mulder-Krieger T, IJzerman AP and
Heitman LH: Functional efficacy of adenosine A2A
receptor agonists is positively correlated to their receptor
residence time. Br J Pharmacol. 166:1846–1859. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
de Lera Ruiz M, Lim YH and Zheng J:
Adenosine A2A receptor as a drug discovery target. J Med Chem.
57:3623–3650. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Al-Attraqchi OHA, Attimarad M, Venugopala
KN, Nair A and Al-Attraqchi NHA: Adenosine A2A receptor as a
potential drug target-current status and future perspectives. Curr
Pharm Des. 25:2716–2740. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Kohler M and Stradling JR: Mechanisms of
vascular damage in obstructive sleep apnea. Nat Rev Cardiol.
7:677–685. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Gambino F, Zammuto MM, Virzì A, Conti G
and Bonsignore MR: Treatment options in obstructive sleep apnea.
Intern Emerg Med. 17:971–978. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|