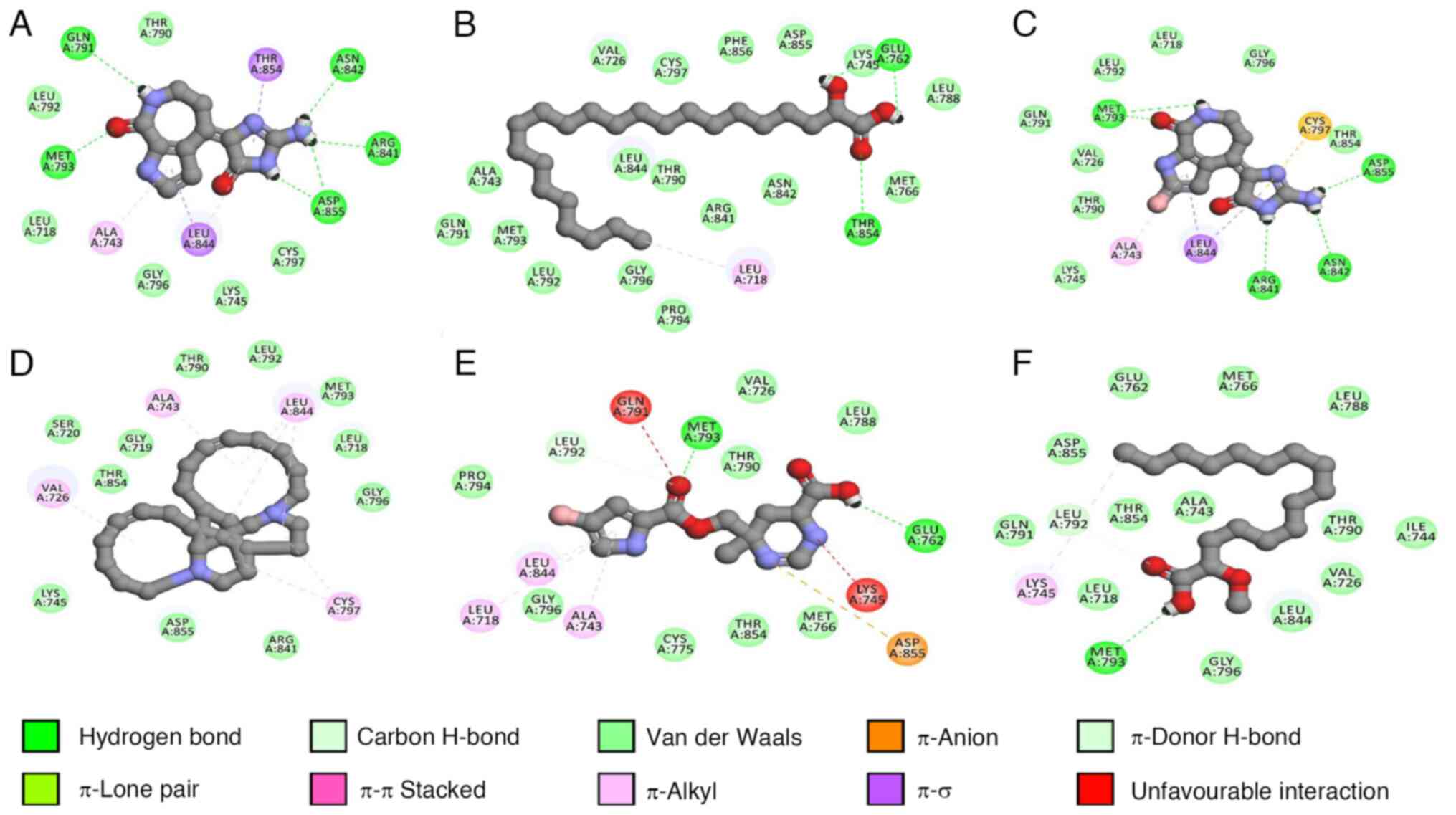
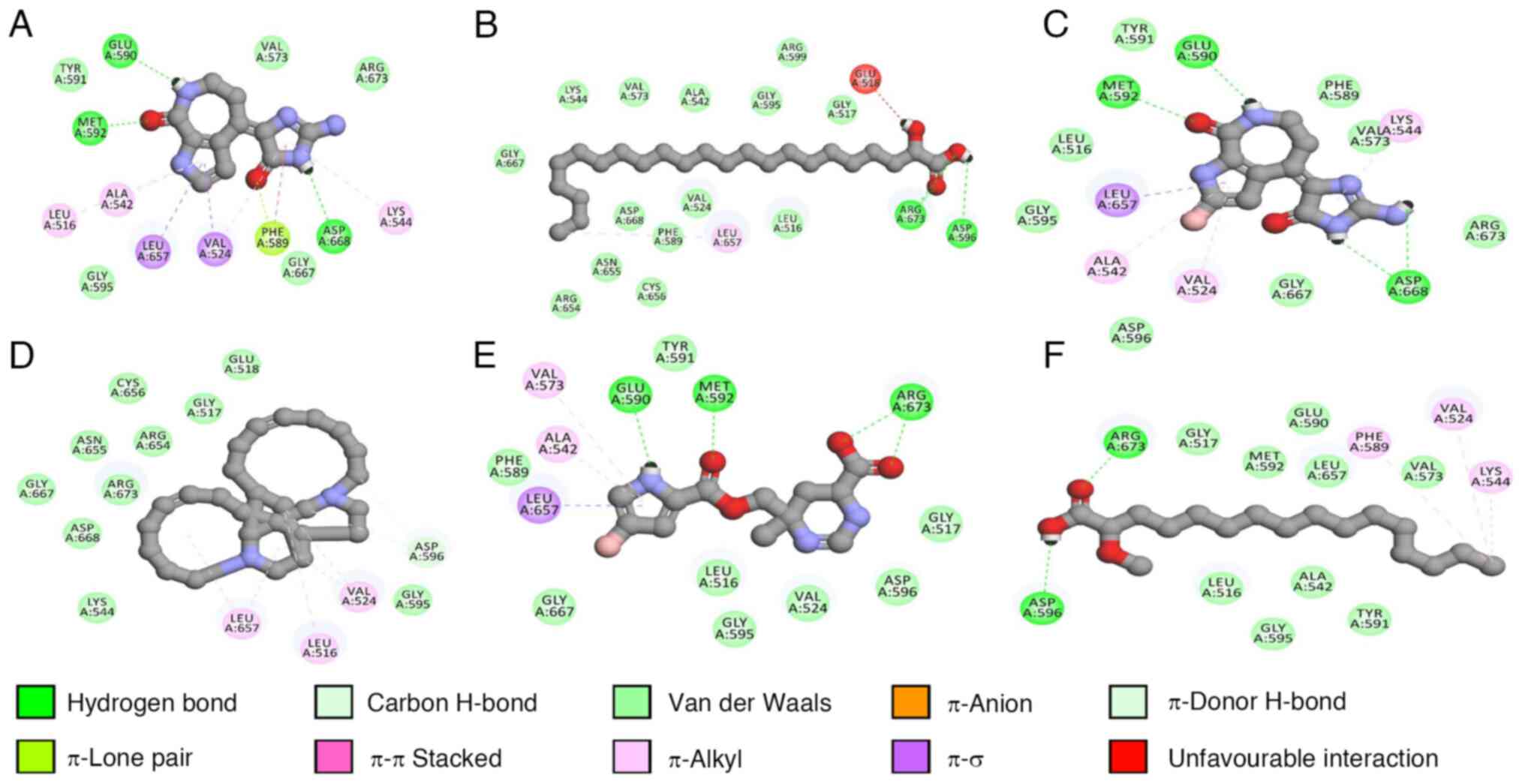
|
1
|
Gerstberger S, Jiang Q and Ganesh KJC:
Metastasis. Cell. 186:1564–1579. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, CA Cancer J. Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bazeed AY, Day CM and Garg SJC: Pancreatic
cancer: Challenges and opportunities in locoregional therapies.
Cancers (Basel). 14(4257)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vasan N, Baselga J and Hyman DM: A view on
drug resistance in cancer. Nature. 575:299–309. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hossain CM, Gera M and Ali KA: Current
status and challenges of herbal drug development and regulatory
aspect: A global perspective. Asian J Pharmaceutical Clin Res.
15:31–41. 2022.
|
|
6
|
Abdussalam-Mohammed W: Review of
therapeutic applications of nanotechnology in medicine field and
its side effects. J Chem Rev. 1:243–251. 2019.
|
|
7
|
Nirmala MJ, Kizhuveetil U, Johnson A,
Balaji G, Nagarajan R and Muthuvijayan V: Cancer nanomedicine: A
review of nano-therapeutics and challenges ahead. RSC Adv.
13:8606–8629. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bhattacharjee S: Craft of co-encapsulation
in nanomedicine: A struggle to achieve synergy through reciprocity.
ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 5:278–298. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fan H, Sun Q, Dukenbayev K, Benassi E,
Manarbek L, Nurkesh AA, Khamijan M, Mu C, Li C, Razbekova M, et al:
Carbon nanoparticles induce DNA repair and PARP inhibitor
resistance associated with nanozyme activity in cancer cells. Res
Square. 13(39)2022.
|
|
10
|
Elmehrath S, Nguyen HL, Karam SM, Amin A
and Greish YE: BioMOF-based anti-cancer drug delivery systems.
Nanomaterials. 13(953)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
El-kharrag R, Abdel Halim SS, Amin A,
Greish YE and Biomaterials P: Synthesis and characterization of
chitosan-coated magnetite nanoparticles using a modified wet method
for drug delivery applications. Int J Polymeric Materials Polymeric
Biomaterials. 68:73–82. 2019.
|
|
12
|
Ibrahim S, Baig B, Hisaindee S, Darwish H,
Abdel-Ghany A, El-Maghraby H, Amin A and Greish Y: Development and
evaluation of crocetin-functionalized pegylated magnetite
nanoparticles for hepatocellular carcinoma. Molecules.
28(2882)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shaimoldina A, Sergazina A, Myrzagali S,
Nazarbek G, Omarova Z, Mirza O, Fan H, Amin A, Zhou W and Xie Y:
Carbon nanoparticles neutralize carbon dioxide (CO2) in
cytotoxicity: Potent carbon emission induced resistance to
anticancer nanomedicine and antibiotics. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
273(116024)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
El-Kharrag R, Amin A and Greish YEJCI: Low
temperature synthesis of monolithic mesoporous magnetite
nanoparticles. Ceramics Int. 38:627–634. 2012.
|
|
15
|
Benassi E, Fan H, Sun Q, Dukenbayev K,
Wang Q, Shaimoldina A, Tassanbiyeva A, Nurtay L, Nurkesh A,
Kutzhanova A and Mu C: Generation of particle assemblies mimicking
enzymatic activity by processing of herbal food: The case of
rhizoma polygonati and other natural ingredients in traditional
Chinese medicine. Nanoscale Adv. 3:2222–2235. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nazarbek G, Kutzhanova A, Nurtay L, Mu C,
Kazybay B, Li X, Ma C, Amin A and Xie Y: Nano-evolution and
protein-based enzymatic evolution predicts novel types of natural
product nanozymes of traditional Chinese medicine: Cases of
herbzymes of Taishan-Huangjing (Rhizoma polygonati) and Goji
(Lycium chinense). Nanoscale Adv. 3:6728–6738.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xie Y, Shaimoldina A, Fan H, Myrzagali S,
Nazarbek G, Myrzagalieva A, Orassay A, Amin A and Benassi E:
Characterisation of a phosphatase-like nanozyme developed by baking
cysteine and its application in reviving mung bean sprouts damaged
by ash. Environ Sci.: Nano. 11:266–277. 2024.
|
|
18
|
Paiva L, Fidalgo T, Da Costa L, Maia LC,
Balan L, Anselme K, Ploux L and Thiré RMSM: Antibacterial
properties and compressive strength of new one-step preparation
silver nanoparticles in glass ionomer cements (NanoAg-GIC). J Dent.
69:102–109. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huy TQ, Thanh NTH, Thuy NT, Chung PV, Hung
PN, Le AT and Hong Hanh NT: Cytotoxicity and antiviral activity of
electrochemical-synthesized silver nanoparticles against
poliovirus. J Virol Methods. 241:52–57. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pawar A, Korde SK, Rakshe DS, William P,
Jawale M and Deshpande N: Analysis of Silver Nanoparticles as
Carriers of Drug Delivery System. J Nano-Electron Phys.
15(04015)2023.
|
|
21
|
Naseer F, Ahmed M, Majid A, Kamal W and
Phull AR: Green nanoparticles as multifunctional nanomedicines:
Insights into anti-inflammatory effects, growth signaling and
apoptosis mechanism in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 86:310–324.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sharma P, Hasan MR, Khanuja M, Rawal R,
Shivani Pilloton R and Narang J: Aptamer-based silver nanoparticle
decorated paper platform for electrochemical detection ovarian
cancer biomarker PDGF. Materials Chemistry Physics.
306(128114)2023.
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Han X, Liu Y, Wang S, Han X and
Cheng C: Research progress on nano-sensitizers for enhancing the
effects of radiotherapy. Materials Adv. 3:3709–3725. 2022.
|
|
24
|
Kitic D, Miladinovic B, Randjelovic M,
Szopa A, Seidel V, Prasher P, Sharma M, Fatima R, Arslan Ateşşahin
D, Calina D and Sharifi-Rad J: Anticancer and chemopreventive
potential of Morinda citrifolia L. bioactive compounds: A
comprehensive update. Phytother Res. 38:1932–1950. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Minhas LA, Kaleem M, Farooqi HMU, Kausar
F, Waqar R, Bhatti T, Aziz S, Jung DW and Mumtaz AS: Algae-derived
bioactive compounds as potential nutraceuticals for cancer therapy:
A comprehensive review. Algal Res. 78(103396)2024.
|
|
26
|
Al-Hrout A, Baig B, Hilal-Alnaqbi A and
Amin A: Cancer and biotechnology: A matchup that should never
slowdown. In: Biotechnology and Production of Anti-Cancer
Compounds, Springer International, (pp.73-97), 2017.
|
|
27
|
Sahoo A, Mandal AK, Kumar M, Dwivedi K and
Singh D: Prospective challenges for patenting and clinical trials
of anticancer compounds from natural products: Coherent review.
Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 18:470–494. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Amin A and Buratovich M: The anti-cancer
charm of flavonoids: A cup-of-tea will do! Recent Pat Anticancer
Drug Discov. 2:109–117. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xie Y, Mu C, Kazybay B, Sun Q, Kutzhanova
A, Nazarbek G, Xu N, Nurtay L, Wang Q, Amin A and Li X: Network
pharmacology and experimental investigation of Rhizoma
polygonati extract targeted kinase with herbzyme activity for
potent drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 28:2187–2197. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Badran MM, Alouny NN, Aldosari BN,
Alhusaini AM and Abou El Ela AES: Transdermal glipizide delivery
system based on chitosan-coated deformable liposomes: development,
ex vivo, and in vivo studies. Pharmaceutics. 14(826)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Murali C, Mudgil P, Gan CY, Tarazi H,
El-Awady R, Abdalla Y, Amin A and Maqsood S: Camel whey protein
hydrolysates induced G2/M cellcycle arrest in human colorectal
carcinoma. Sci Rep. 11(7062)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mathew BT, Torky Y, Amin A, Mourad AI,
Ayyash MM, El-Keblawy A, Hilal-Alnaqbi A, AbuQamar SF and
El-Tarabily KA: Halotolerant marine rhizosphere-competent
actinobacteria promote Salicornia bigelovii growth and seed
production using seawater irrigation. Front Microbiol.
11(552)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ortigosa-Palomo A, Quiñonero F, Ortiz R,
Sarabia F, Prados J and Melguizo C: Natural products derived from
marine sponges with antitumor potential against lung cancer: A
systematic review. Mar Drugs. 22(101)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shady NH, Fouad MA, Salah Kamel M,
Schirmeister T and Abdelmohsen UR: Natural product repertoire of
the genus Amphimedon. Mar Drugs. 17(19)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hardani IN, Damara FA, Nugrahani AD and
Bashari MH: Ethanol extract of Stylissa carteri induces cell
death in parental and paclitaxel-resistant cervical cancer cells.
IJIHS. 6:91–96. 2018.
|
|
36
|
Al-Soub A, Khleifat K, Al-Tarawneh A,
Al-Limoun M, Alfarrayeh I, Sarayreh AA, Qaisi YA, Qaralleh H,
Alqaraleh M and Albashaireh A: Silver nanoparticles biosynthesis
using an airborne fungal isolate, Aspergillus flavus:
Optimization, characterization and antibacterial activity. Iran J
Microbiol. 14:518–528. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jaidev L and Narasimha G: Fungal mediated
biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles, characterization and
antimicrobial activity. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 81:430–433.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hooper JN and Van Soest RW: Systema
Porifera. A guide to the classification of sponges. In: Systema
Porifera: A guide to the classification of sponges. Springer,
pp1-7, 2002.
|
|
39
|
Helmy T and Van Soest R: Amphimedon
species (Porifera: Niphatidae) from the Gulf of Aqaba, Northern Red
Sea: Filling the gaps in the distribution of a common pantropical
genus. Zootaxa. 859(1)2005.
|
|
40
|
O'Rourke A, Kremb S, Duggan BM, Sioud S,
Kharbatia N, Raji M, Emwas AH, Gerwick WH and Voolstra CR:
Identification of a 3-alkylpyridinium compound from the red sea
sponge Amphimedon chloros with in vitro inhibitory activity
against the West Nile Virus NS3 protease. Molecules.
23(1472)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bashari MH, Huda F, Tartila TS, Shabrina
S, Putri T, Qomarilla N, Atmaja H, Subhan B, Sudji IR and Meiyanto
E: Bioactive compounds in the ethanol extract of marine sponge
Stylissa carteri demonstrates potential anti-cancer activity
in breast cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 20:1199–1206.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kandler NM, Wooster MK, Leray M, Knowlton
N, de Voogd NJ, Paulay G and Berumen ML: Hyperdiverse macrofauna
communities associated with a common sponge, Stylissa
carteri, shift across ecological gradients in the Central Red
Sea. Diversity. 11(18)2019.
|
|
43
|
Ebada SS, Edrada RA, Lin W and Proksch P:
Methods for isolation, purification and structural elucidation of
bioactive secondary metabolites from marine invertebrates. Nat
Protoc. 3:1820–1831. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Bayona LM, Videnova M and Choi YH:
Increasing metabolic diversity in marine sponges extracts by
controlling extraction parameters. Mar Drugs.
16(393)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Al-Tawarah NM, Qaralleh H, Khlaifat AM,
Nebih Nofal M, Khleifat KM, Al-Limoun MO, Alqaraleh M and Ahmed Al
Shhab M: Anticancer and antibacterial properties of verthemia
iphionides essential oil/silver nanoparticles. Biomed Pharmacol J.
13:1175–1185. 2020.
|
|
46
|
Alqaraleh M, Khleifat KM, Abu Hajleh MN,
Farah HS and Ahmed KAA: Fungal-mediated silver nanoparticle and
biochar synergy against colorectal cancer cells and pathogenic
bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel). 12(597)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Nikalje APG and Gadikar R: A simple liquid
chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of
aceclofenac, methyl salicylate, and benzyl alcohol in
pharmaceuticals. J Pharmacy Res. 12(283)2018.
|
|
48
|
Murray BW, Rogers E, Zhai D, Deng W, Chen
X, Sprengeler PA, Zhang X, Graber A, Reich SH, Stopatschinskaja S,
et al: Molecular characteristics of repotrectinib that enable
potent inhibition of TRK fusion proteins and resistant mutations.
Mol Cancer Ther. 20:2446–2456. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gajiwala KS, Feng J, Ferre R, Ryan K,
Brodsky O, Weinrich S, Kath JC and Stewart A: Insights into the
aberrant activity of mutant EGFR kinase domain and drug
recognition. Structure. 21:209–219. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF,
Belew RK, Goodsell DS and Olson AJ: AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4:
Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput
Chem. 30:2785–2791. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bouabdallah S, Brinza I, Boiangiu RS,
Ibrahim MH, Honceriu I, Al-Maktoum A, Cioanca O, Hancianu M, Amin
A, Ben-Attia M and Hritcu L: The effect of a Tribulus-based
formulation in alleviating cholinergic system impairment and
scopolamine-induced memory loss in zebrafish (Danio rerio):
Insights from molecular docking and in vitro/in vivo approaches.
Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 17(200)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Saqallah FG, Hamed WM, Talib WH, Dianita R
and Wahab HA: Antimicrobial activity and molecular docking
screening of bioactive components of Antirrhinum majus
(snapdragon) aerial parts. Heliyon. 8(e10391)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Shtaiwi M, Alemleh M, Abu-Safieh KA,
Salameha BA, Shtaiwi A, Alwahsh M, Hamadneh L and Khanfar MA:
Design, synthesis, crystal structure, biological activity and
molecular modeling of novel schiff bases derived from chalcones and
5-Hydrazino-1,3-Dimethyl-4-Nitropyrazole as anticancer agents.
Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. 44:4178–4196. 2023.
|
|
54
|
Biovia: Discovery Studio Modeling
Environment. Dassault-Systèmes, San Diego, CA, 2016.
|
|
55
|
Al Qaisi YT, Khleifat KM, Oran SA, Al
Tarawneh AA, Qaralleh H, Al-Qaisi TS and Farah HS: Ruta graveolens,
Peganum harmala, and Citrullus colocynthis methanolic extracts have
in vitro protoscolocidal effects and act against bacteria isolated
from echinococcal hydatid cyst fluid. Arch Microbiol.
204(228)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Institute (CLSI): Performance standards for antimicrobial
susceptibility testing. CLSI, Wayne, PA, 2011.
|
|
57
|
Qaralleh H, Khleifat K, Al-Limoun M,
Al-Tarawneh A, Khleifat W, Almajali L, Buqain R, Shadid KA and
Aslowayeh N: Antibacterial activity of airborne fungal mediated
nanoparticles in combination with Foeniculum vulgare essential oil.
J Herbmed Pharmacol. 11:419–427. 2022.
|
|
58
|
Amirjani A, Firouzi F and Haghshenas DF:
Predicting the size of silver nanoparticles from their optical
properties. J Plasmonics. 15:1077–1082. 2020.
|
|
59
|
Abbas R, Luo J, Qi X, Naz A, Khan IA, Liu
H, Yu S and Wei J: Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, structure,
properties and applications. Nanomaterials (Basel).
14(1425)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Al-Samydai A, Abu Hajleh MN, Al-Sahlawi F,
Nsairat H, Khatib AA, Alqaraleh M and Ibrahim AK: Advancements of
metallic nanoparticles: A promising frontier in cancer treatment.
Sci Prog. 107(368504241274967)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Leary M, Heerboth S, Lapinska K and Sarkar
S: Sensitization of drug resistant cancer cells: A matter of
combination therapy. Cancers. 10(483)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Chenthamara D, Subramaniam S, Ramakrishnan
SG, Krishnaswamy S, Essa MM, Lin FH and Qoronfleh MW: Therapeutic
efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater
Res. 23(20)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Brunetto de Farias C, Rosemberg DB, Heinen
TE, Koehler-Santos P, Abujamra AL, Kapczinski F, Brunetto AL,
Ashton-Prolla P, Meurer L, Reis Bogo M, et al: BDNF/TrkB content
and interaction with gastrin-releasing peptide receptor blockade in
colorectal cancer. Oncology. 79:430–439. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Seo JH, Jung KH, Son MK, Yan HH, Ryu YL,
Kim J, Lee JK, Hong S and Hong SS: Anti-cancer effect of HS-345, a
new tropomyosin-related kinase A inhibitor, on human pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Lett. 338:271–281. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Chen B, Liang Y, He Z, An Y, Zhao W and Wu
J: Autocrine activity of BDNF induced by the STAT3 signaling
pathway causes prolonged TrkB activation and promotes human
non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation. Sci Rep.
6(30404)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Kyker-Snowman K, Hughes RM, Yankaskas CL,
Cravero K, Karthikeyan S, Button B, Waters I, Rosen DM, Dennison L,
Hunter N, et al: TrkA overexpression in non-tumorigenic human
breast cell lines confers oncogenic and metastatic properties.
Breast Cancer Res. 179:631–642. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Griffin N, Marsland M, Roselli S,
Oldmeadow C, Attia J, Walker MM, Hondermarck H and Faulkner S: The
receptor tyrosine kinase TrkA is increased and targetable in
HER2-positive breast cancer. Biomolecules. 10(1329)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Nwaefulu ON, Sagineedu S, Islam MK and
Stanslas J: Pancreatic cancer treatment with targeted therapies:
Are we there yet? Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 26:367–381.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
de Chiffre JMD, Ormstrup TE, Kusk MW and
Hess S: Patients from general practice with non-specific cancer
symptoms: A retrospective study of symptoms and imaging. BJGP Open.
8(BJGPO.2023.0058)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Park JW and Han JW: Targeting epigenetics
for cancer therapy. Arch Pharm Res. 42:159–170. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Grześ M, Jaiswar A, Grochowski M, Wojtyś
W, Kaźmierczak W, Olesiński T, Lenarcik M, Nowak-Niezgoda M, Kołos
M, Canarutto G, et al: A common druggable signature of oncogenic
c-Myc, mutant KRAS and mutant p53 reveals functional redundancy and
competition among oncogenes in cancer. Cell Death.
15(638)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Perurena N, Situ L and Cichowski K:
Combinatorial strategies to target RAS-driven cancers. Nat Rev
Cancer. 24:316–337. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Liu B, Zhou H, Tan L, Siu KTH and Guan XY:
Exploring treatment options in cancer: Tumor treatment strategies.
Signal Transduction Targeted Ther. 9(175)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Mattiuzzi C and Lippi G: Current cancer
epidemiology. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 9:217–222. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
De Angelis R, Demuru E, Baili P, Troussard
X, Katalinic A, Chirlaque Lopez MD, Innos K, Santaquilani M, Blum
M, Ventura L, et al: Complete cancer prevalence in Europe in 2020
by disease duration and country (EUROCARE-6): A population-based
study. Lancet Oncol. 25:293–307. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Naqvi SZH, Kiran U, Ali MI, Jamal A,
Hameed A, Ahmed S and Ali N: Combined efficacy of biologically
synthesized silver nanoparticles and different antibiotics against
multidrug-resistant bacteria. Int J Nanomedicine. 8:3187–3195.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Govindaraju K, Tamilselvan S, Kiruthiga V
and Singaravelu G: Biogenic silver nanoparticles by Solanum torvum
and their promising antimicrobial activity. J Biopesticides.
3:394–399. 2010.
|
|
79
|
Bhainsa KC and D'souza SF: Extracellular
biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus Aspergillus
fumigatus. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 47:160–164.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Ahmad A, Mukherjee P, Senapati S, Mandal
D, Khan MI, Kumar R and Sastry M: Extracellular biosynthesis of
silver nanoparticles using the fungus Fusarium oxysporum.
Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 28:313–318. 2003.
|
|
81
|
Jain N, Bhargava A, Majumdar S, Tarafdar J
and Panwar J: Extracellular biosynthesis and characterization of
silver nanoparticles using Aspergillus flavus NJP08: A mechanism
perspective. Nanoscale. 3:635–641. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhang X, Yan S, Tyagi R and Surampalli
RJC: Synthesis of nanoparticles by microorganisms and their
application in enhancing microbiological reaction rates.
Chemosphere. 82:489–494. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Al-Limoun M, Qaralleh HN, Khleifat KM,
Al-Anber M, Al-Tarawneh A, Al-sharafa K, Kailani MH, Zaitoun MA,
Matar SA and Al-soub T: Culture media composition and reduction
potential optimization of mycelia-free filtrate for the
biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using the fungus
Tritirachium oryzae W5H. Curr Nanosci. 16:757–769. 2020.
|
|
84
|
Khleifat K, Alqaraleh M, Al-Limoun M,
Alfarrayeh I, Khatib R, Qaralleh H, Alsarayreh A, Al Qaisi Y and
Abu Hajleh M: The ability of Rhizopus stolonifer MR11 to
biosynthesize silver nanoparticles in response to various culture
media components and optimization of process parameters required at
each stage of biosynthesis. J Ecol Eng. 23:89–100. 2022.
|
|
85
|
Khleifat K, Qaralleh H and Al-Limoun M:
Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized by
Aspergillus flavus and its synergistic effect with
antibiotics. J Pure Appl Microbiol. 16:1722–1735. 2022.
|
|
86
|
Abu Hajleh MN, Al-Limoun M, Al-Tarawneh A,
Hijazin TJ, Alqaraleh M, Khleifat K, Al-Madanat OY, Qaisi YA,
AlSarayreh A, Al-Samydai A, et al: Synergistic effects of AgNPs and
biochar: A potential combination for combating lung cancer and
pathogenic bacteria. Molecules. 28(4757)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Curman D, Cinel B, Williams DE, Rundle N,
Block WD, Goodarzi AA, Hutchins JR, Clarke PR, Zhou BB, Lees-Miller
SP, et al: Inhibition of the G2 DNA damage checkpoint and of
protein kinases Chk1 and Chk2 by the marine sponge alkaloid
debromohymenialdisine. J Biol Chem. 276:17914–17919.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Leirós M, Alonso E, Rateb ME, Houssen WE,
Ebel R, Jaspars M, Alfonso A and Botana LM: Bromoalkaloids protect
primary cortical neurons from induced oxidative stress. ACS Chem
Neurosci. 6:331–338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Jakubec P, Farley AJ and Dixon DJ: Towards
the total synthesis of keramaphidin B. Beilstein J Org Chem.
12:1096–1100. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Lee SM, Kim NH, Lee S, Kim YN, Heo JD, Rho
JR and Jeong EJ: (10 Z)-Debromohymenialdisine from marine sponge
stylissa sp. regulates intestinal inflammatory responses in
Co-culture model of epithelial Caco-2 cells and THP-1 macrophage
cells. Molecules. 24(3394)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Abdullah N, Al Balushi N, Hasan SI, Al
Bahlani S, Dobretsov S, Tamimi Y and Burney IA: Hymenialdisine is
cytotoxic against cisplatin-sensitive but not against
cisplatin-resistant cell lines. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J.
21:632–634. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Ueda G, Matsuo Y, Murase H, Aoyama Y, Kato
T, Omi K, Hayashi Y, Imafuji H, Saito K, Tsuboi K, et al:
10Z-Hymenialdisine inhibits angiogenesis by suppressing NF-κB
activation in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep.
47(48)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Esposito R, Federico S, Glaviano F, Somma
E, Zupo V and Costantini M: Bioactive compounds from marine sponges
and algae: Effects on cancer cell metabolome and chemical
structures. Int J Mol Sci. 23(10680)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
El-Naggar HA, Bashar MA, Rady I, El-Wetidy
MS, Suleiman WB, Al-Otibi FO, Al-Rashed SA, Abd El-Maoula LM, Salem
EL-S, Attia EMH, et al: Two red sea sponge extracts (Negombata
magnifica and Callyspongia siphonella) induced
anticancer and antimicrobial activity. Applied Sci.
12(1400)2022.
|
|
95
|
Murugesan A, Mani SK, Koochakkhani S,
Subramanian K, Kandhavelu J, Thiyagarajan R, Gurbanov AV, Mahmudov
KT and Kandhavelu M: Design, synthesis and anticancer evaluation of
novel arylhydrazones of active methylene compounds. Int J Biol
Macromol. 254(127909)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Ramezani-Aliakbari M, Soltanabadi A,
Sadeghi-aliabadi H, Varshosaz J, Yadollahi B, Hassanzadeh F and
Rostami M: Eudesmic acid-polyoxomolybdate Organo-conjugate as novel
anticancer agent. J Mol Structure. 1240(130612)2021.
|
|
97
|
Cuenya BR and Behafarid F: Nanocatalysis:
Size-and shape-dependent chemisorption and catalytic reactivity.
Surface Sci Rep. 70:135–187. 2015.
|
|
98
|
Lakkim V, Reddy MC, Pallavali RR, Reddy
KR, Reddy CV, Inamuddin Bilgrami AL and Lomada D: Green synthesis
of silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their antibacterial
activity against multidrug-resistant bacteria and wound healing
efficacy using a murine model. Antibiotics (Basel).
9(902)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Rahman NIA, Ramzi MM, Rawi NN, Siong JYF,
Bakar K, Bhubalan K, Ariffin F, Saidin J, Azemi AK and Ismail N:
Characterization of antibiofilm compound from marine sponge
Stylissa carteri. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int.
31:37552–37563. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Hawas UW, Shaher F, Ghandourah M, Abou
El-Kassem LT, Satheesh S and Al-Sofyani AMA: Lipids and free fatty
acids of Red Sea Avrainvillea amadelpha, Holothuria atra, and
Sarcocornia fruticosa inhibit marine bacterial biofilms.
Lett Organic Chemistry. 17:466–471. 2020.
|
|
101
|
Hamed AN, Schmitz R, Bergermann A, Totzke
F, Kubbutat M, Müller WEG, Youssef DTA, Bishr MM, Kamel MS,
Edrada-Ebel R, et al: Bioactive pyrrole alkaloids isolated from the
Red Sea: Marine sponge Stylissa carteri. Z Naturforsch C J
Biosci. 73:199–210. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Althagbi HI, Alarif WM, Al-Footy KO and
Abdel-Lateff A: Marine-derived macrocyclic alkaloids (MDMAs):
Chemical and biological diversity. Mar Drugs.
18(368)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Júnior ACV, de Castro Nogueira Diniz
Pontes M, Barbosa JP, Höfling JF, Araújo RM, Boniek D, de Resende
Stoianoff MA and Andrade VS: Antibiofilm and Anti-candidal
activities of the extract of the marine sponge agelas dispar.
Mycopathologia. 186:819–832. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Al-Shamayleh W, Qaralleh H, Al-Madadheh
OA, Al Qaisi Y and AlSarayreh A: Inhibitory effect of the marine
sponge amphimidon chloros extracts against multidrug-resistant
bacteria. Tropical J Natural Product Res. (8)2024.
|
|
105
|
Barbosa F, Pinto E, Kijjoa A, Pinto M and
Sousa E: Targeting antimicrobial drug resistance with marine
natural products. Int J Antimicrob Agents.
56(106005)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Chen S, Liu D, Zhang Q, Guo P, Ding S,
Shen J, Zhu K and Lin W: A marine antibiotic kills
multidrug-resistant bacteria without detectable high-level
resistance. ACS Infect Dis. 7:884–893. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Schneider YK: Bacterial natural product
drug discovery for new antibiotics: strategies for tackling the
problem of antibiotic resistance by efficient bioprospecting.
Antibiotics (Basel). 10(842)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Jacob MR, Hossain CF, Mohammed KA, Smillie
TJ, Clark AM, Walker LA and Nagle DG: Reversal of fluconazole
resistance in multidrug efflux-resistant fungi by the dysidea a
renaria sponge sterol 9α, 11α-epoxycholest-7-ene-3β, 5α, 6α,
19-tetrol 6-acetate. J Nat Prod. 66:1618–1622. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Saravanakumar K, Abinaya M, Mehnath S,
Shanmuga Priya V, Jeyaraj M, Al-Rashed S and Muthuraj V: Nano Ag@
bioactive microspheres from marine sponge clathria frondifera:
Fabrication, fortification, characterization, anticancer and
antibacterial potential evaluation. Environ Res.
206(112282)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Bayona LM, de Voogd NJ and Choi YH:
Metabolomics on the study of marine organisms. Metabolomics.
18(17)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|