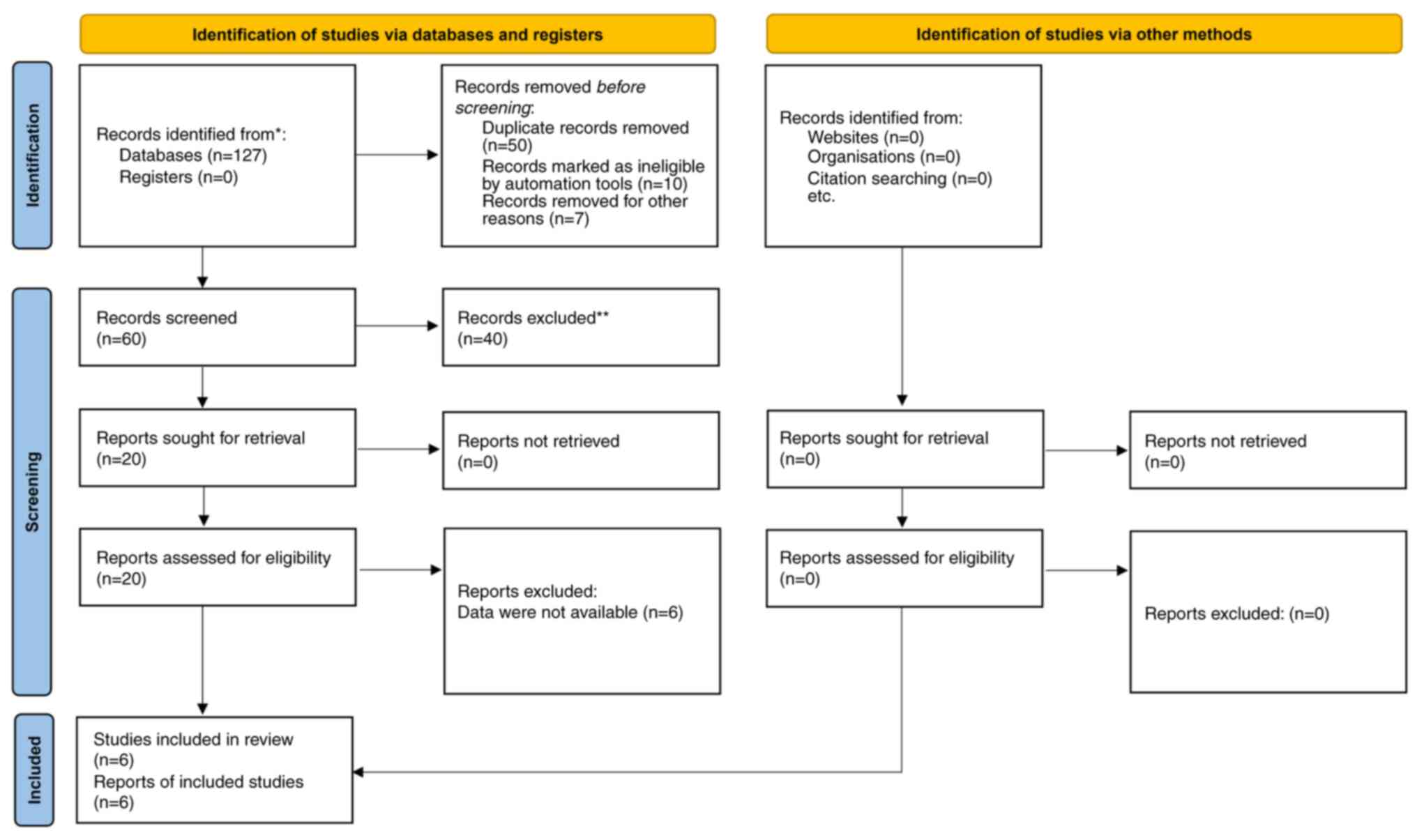
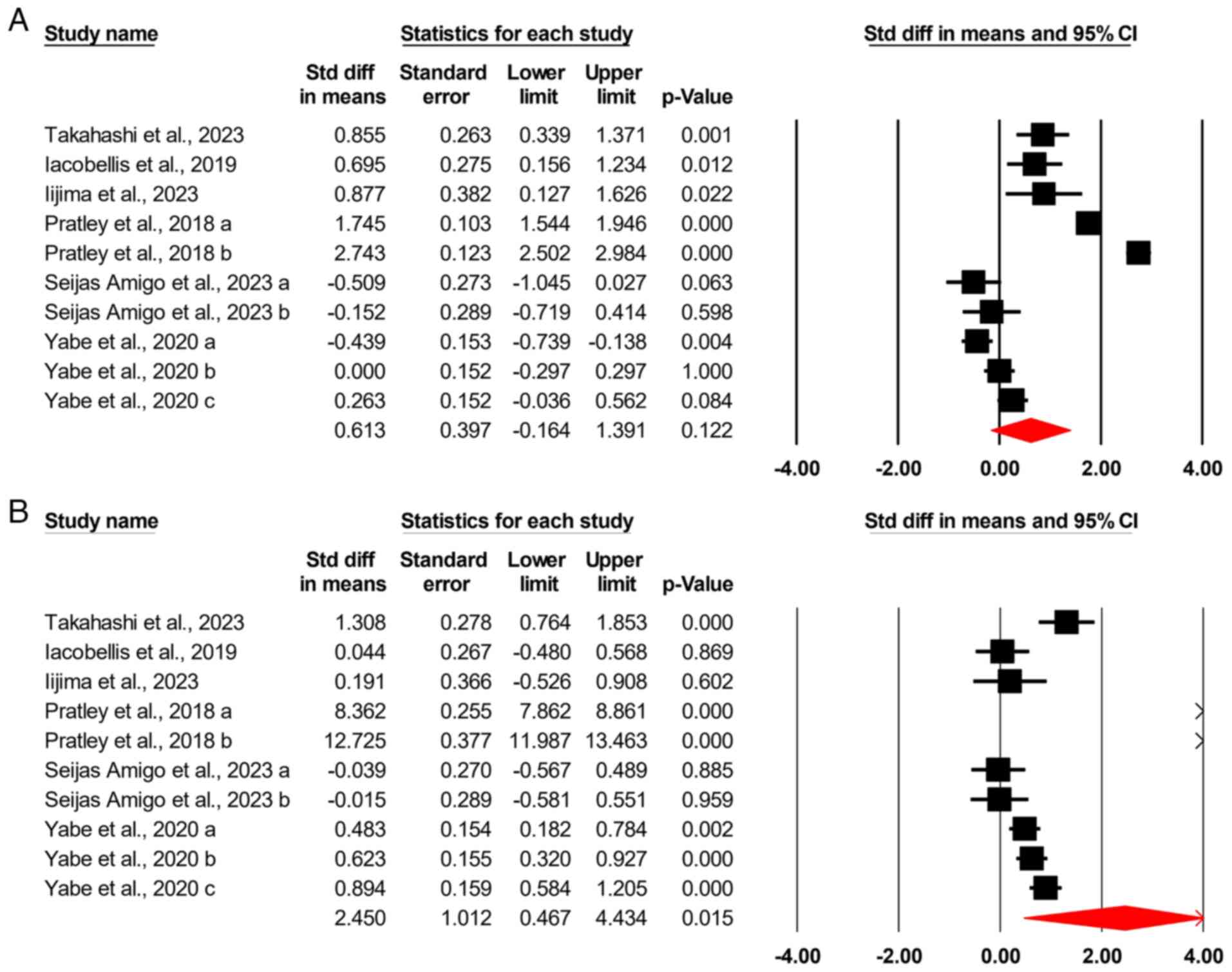
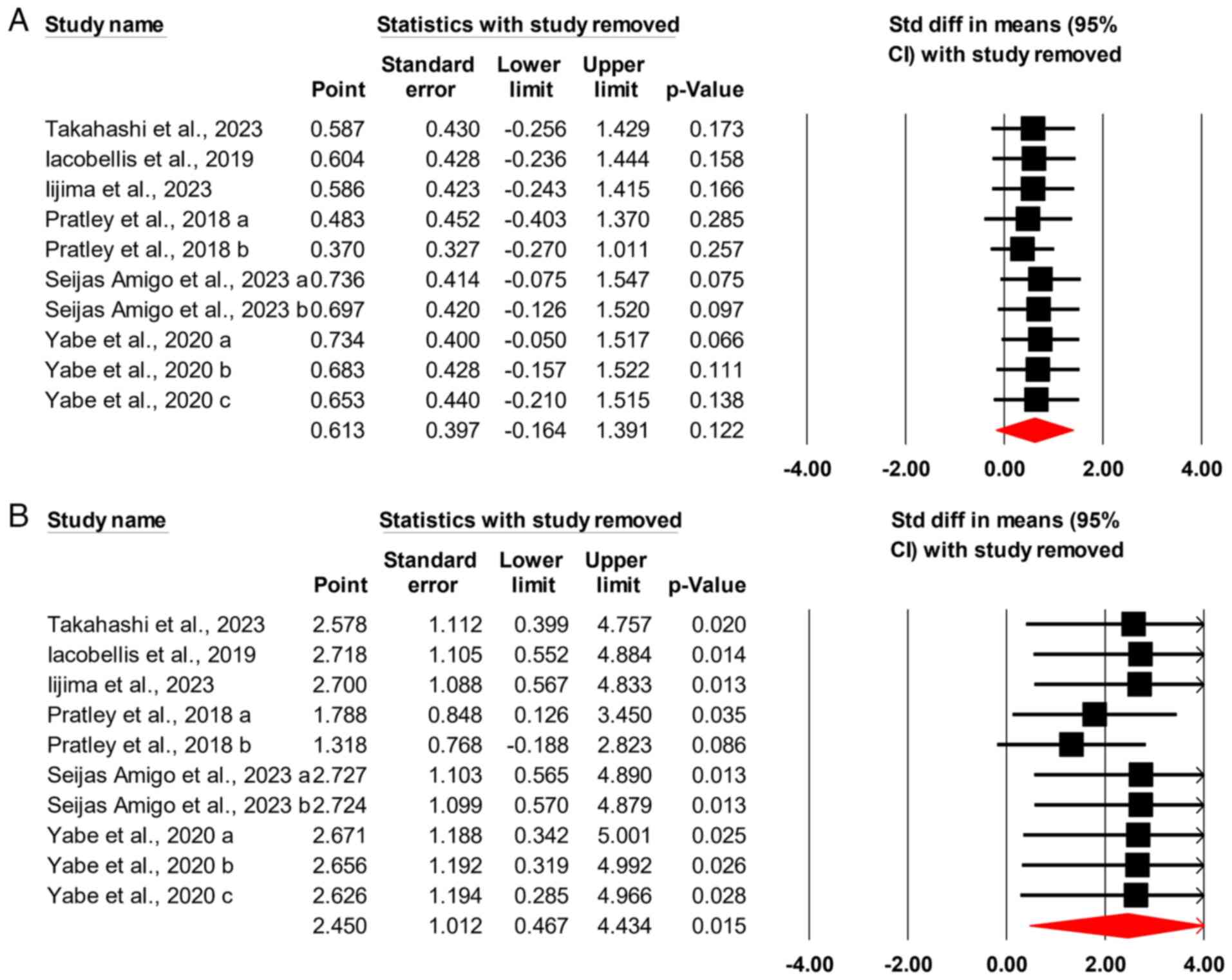
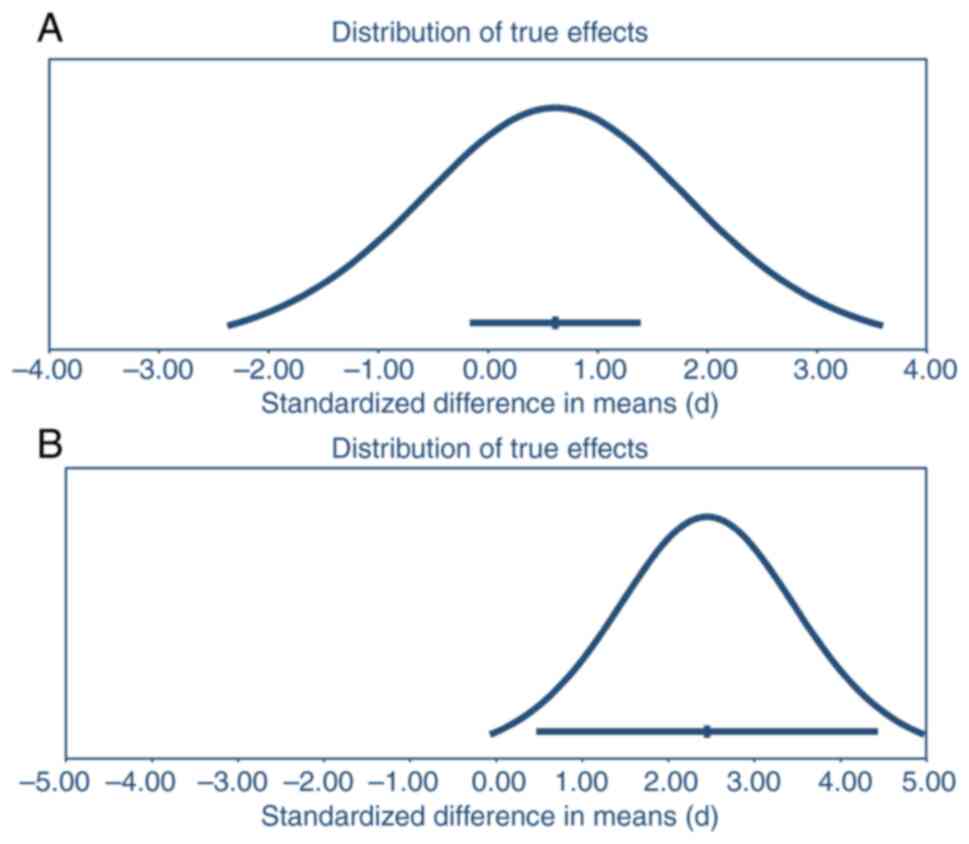
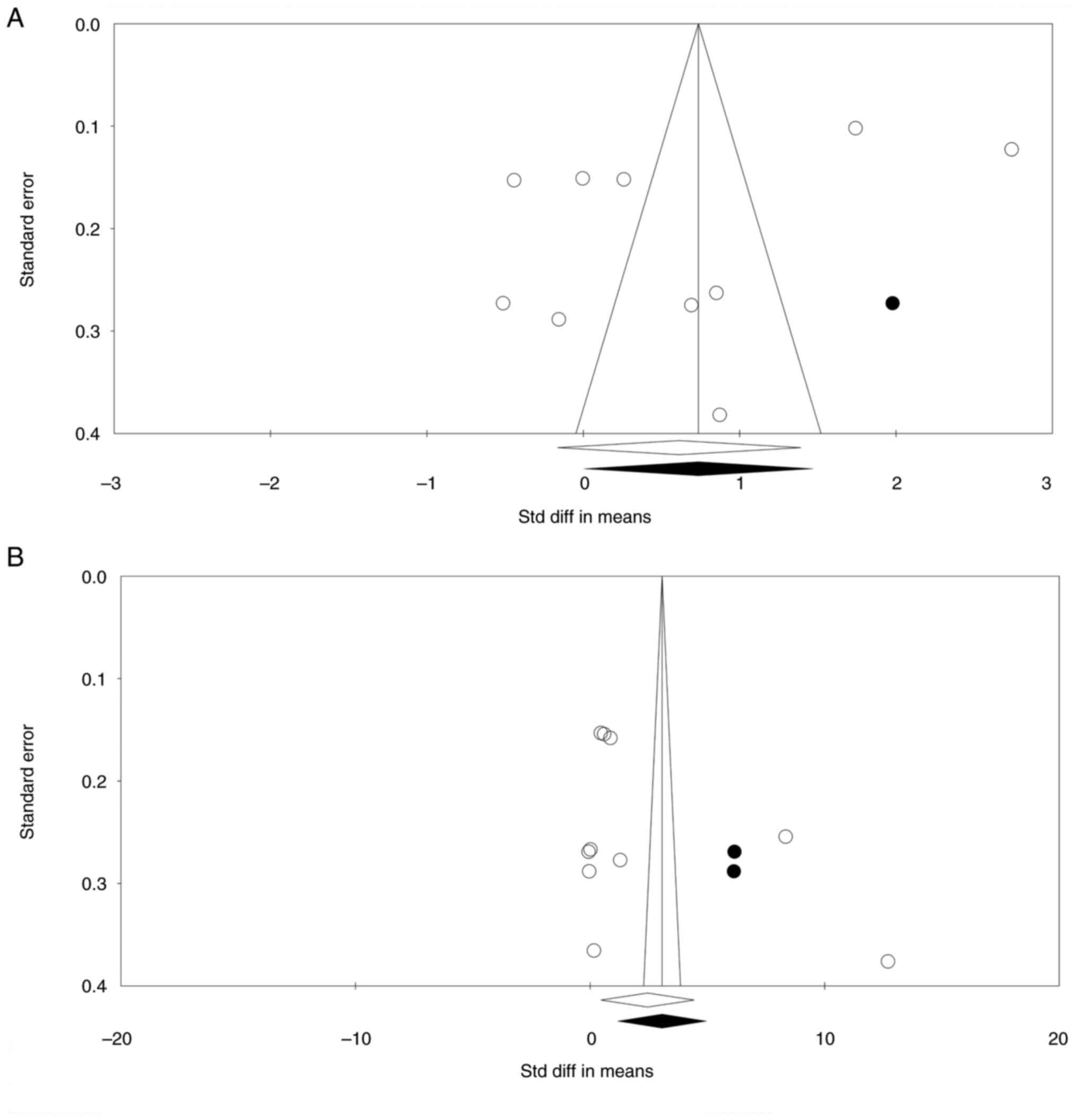
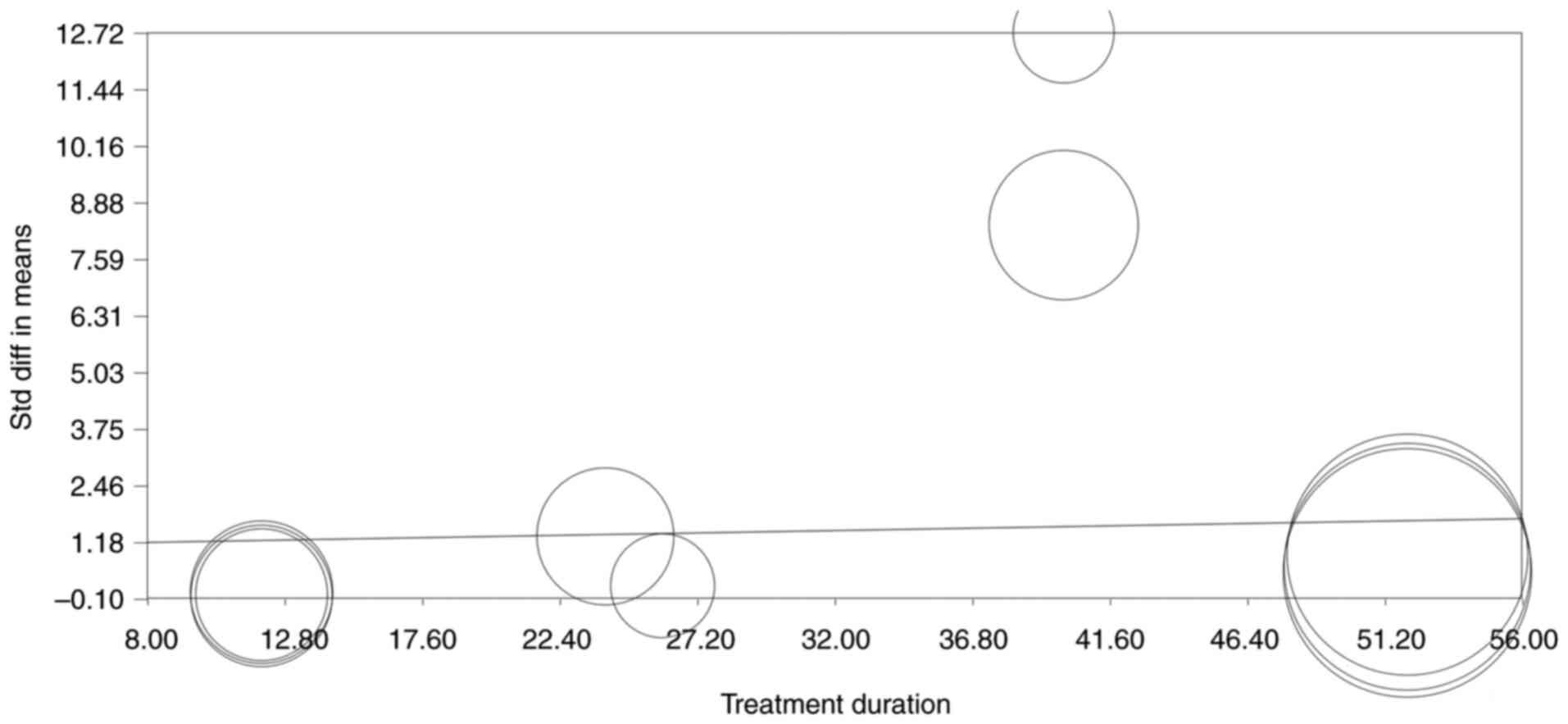
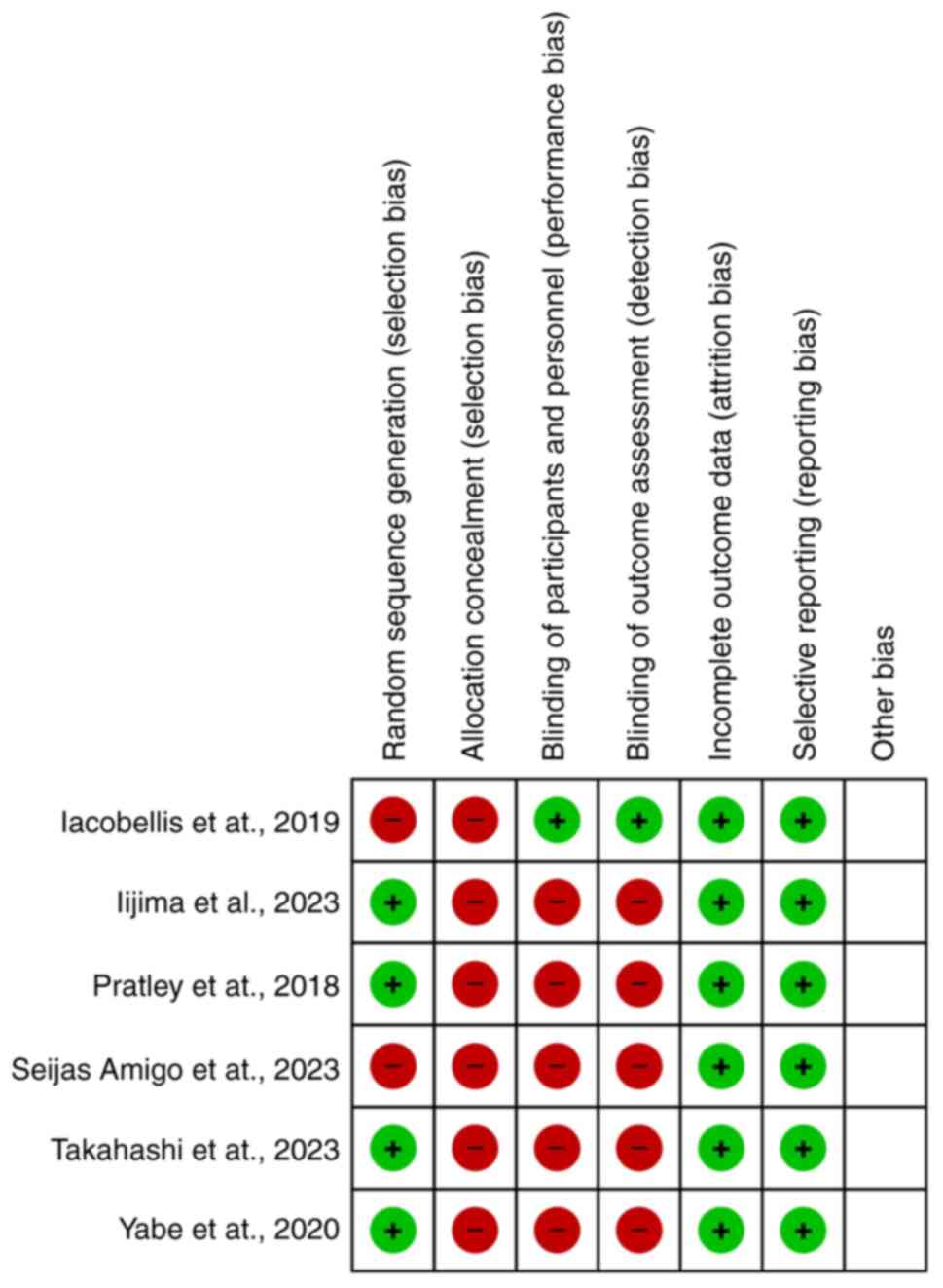
|
1
|
Tönnies T, Rathmann W, Hoyer A, Brinks R
and Kuss O: Quantifying the underestimation of projected global
diabetes prevalence by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF)
Diabetes Atlas. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care.
9(e002122)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
American-diabetes-association. Improving
care and promoting health in populations: Standards of medical
care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 44:S7–S14.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Campbell JE and Drucker DJ: Pharmacology,
physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab.
17:819–837. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nauck MA and Meier JJ: The incretin effect
in healthy individuals and those with type 2 diabetes: Physiology,
pathophysiology, and response to therapeutic interventions. Lancet
Diabetes Endocrinol. 4:525–536. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hinnen D: Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor
agonists for type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 30:202–210.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Seijas-Amigo J, Salgado-Barreira Á,
Castelo-Dominguez R, Pérez-Álvarez MT, Ponce-Piñón B,
Fernández-Silva M, Rodríguez-Barreiro M, Pereira-Pía M,
Iglesias-Moreno JM, Gago-García M, et al: Differences in weight
loss and safety between the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
agonists: A non-randomized multicenter study from the titration
phase. Prim Care Diabetes. 17:366–372. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kononenko IV, Smirnova OM, Mayorov AY and
Shestakova MV: Classification of diabetes. World Health
Organization 2019. What's new? Diabetes Mellitus. 23:329–339.
2020.
|
|
9
|
American-diabetes-association. 2.
Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: Standards of medical care
in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care. 45:S17–S38. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JAC, et
al: The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343(d5928)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Higgins JP and Green S (eds): Cochrane
handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane
Collaboration, 2008.
|
|
12
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Graham PL and Moran JL: Robust
meta-analytic conclusions mandate the provision of prediction
intervals in meta-analysis summaries. J Clin Epidemiol. 65:503–510.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bloch MH: Meta-analysis and moderator
analysis: Can the field develop further? J Am Acad Child Adolesc
Psychiatry. 53:135–137. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pratley RE, Aroda VR, Lingvay I, Lüdemann
J, Andreassen C, Navarria A and Viljoen A: SUSTAIN 7 investigators.
Semaglutide versus dulaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2
diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): A randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 6:275–286. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yabe D, Nakamura J, Kaneto H, Deenadayalan
S, Navarria A, Gislum M and Inagaki N: PIONEER 10 Investigators.
Safety and efficacy of oral semaglutide versus dulaglutide in
Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (PIONEER 10): An open-label,
randomised, active-controlled, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes
Endocrinol. 8:392–406. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Iijima T, Shibuya M, Ito Y and Terauchi Y:
Effects of switching from liraglutide to semaglutide or dulaglutide
in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. J
Diabetes Investig. 14:774–781. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Iacobellis G and Villasante Fricke AC:
Effects of semaglutide versus dulaglutide on epicardial fat
thickness in subjects with type 2 diabetes and obesity. J Endocr
Soc. 4(bvz042)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Takahashi Y, Nomoto H, Yokoyama H, Takano
Y, Nagai S, Tsuzuki A, Cho KY, Miya A, Kameda H, Takeuchi J, et al:
Improvement of glycaemic control and treatment satisfaction by
switching from liraglutide or dulaglutide to subcutaneous
semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre,
prospective, randomized, open-label, parallel-group comparison
study (SWITCH-SEMA 1 study). Diabetes Obes Metab. 25:1503–1511.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Patoulias D, Popovic DS, Stoian AP, Janez
A, Sahebkar A and Rizzo M: Effect of semaglutide versus other
glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardio-metabolic risk
factors in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of head-to-head, phase 3, randomized controlled
trials. J Diabetes Complications. 37(108529)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shi FH, Li H, Cui M, Zhang ZL, Gu ZC and
Liu XY: Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide for the
treatment of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
of randomized controlled trials. Front Pharmacol.
9(576)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mishriky BM, Cummings DM, Powell JR,
Sewell KA and Tanenberg RJ: Comparing once-weekly semaglutide to
incretin-based therapies in patients with type 2 diabetes: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. 45:102–109.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Witkowski M, Wilkinson L, Webb N, Weids A,
Glah D and Vrazic H: A systematic literature review and network
meta-analysis comparing once-weekly semaglutide with other glp-1
receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes previously
receiving 1-2 oral anti-diabetic drugs. Diabetes Ther. 9:1149–1167.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tang Y, Zhang L, Zeng Y, Wang X and Zhang
M: Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide in patients with type 2
diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol.
13(1016639)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Andreadis P, Karagiannis T, Malandris K,
Avgerinos I, Liakos A, Manolopoulos A, Bekiari E, Matthews DR and
Tsapas A: Semaglutide for type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab. 20:2255–2263.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
West SL, Gartlehner G, Mansfield AJ, Poole
C, Tant E, Lenfestey N, Lux LJ, Amoozegar J, Morton SC, Carey TC,
et al: AHRQ methods for effective health care. In: Comparative
effectiveness review methods: Clinical heterogeneity. Agency for
Healthcare Research and Quality (US), Rockville (MD), 2010.
|
|
27
|
Borenstein M: In a meta-analysis, the
I-squared statistic does not tell us how much the effect size
varies. J Clin Epidemiol. 152:281–284. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|