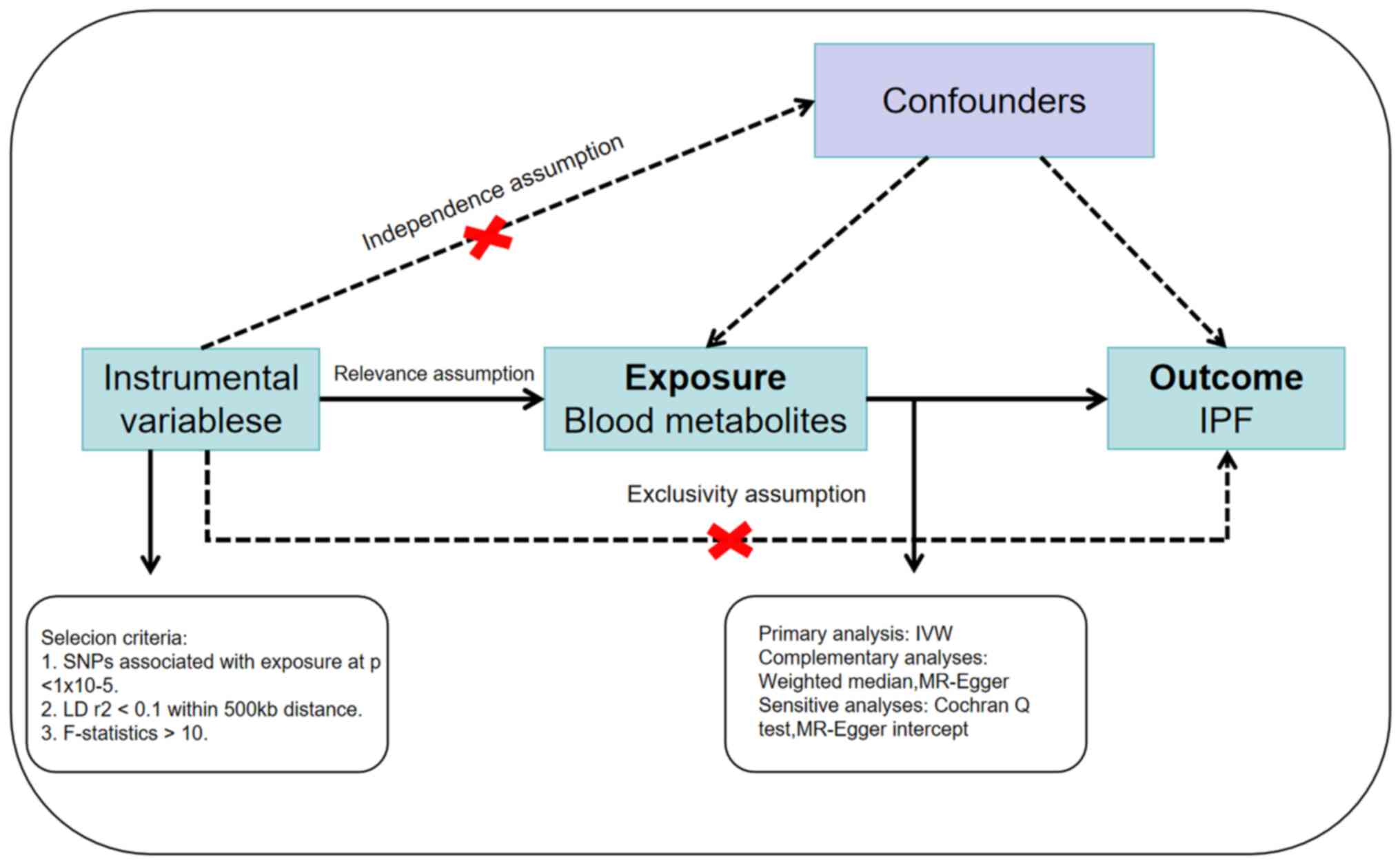
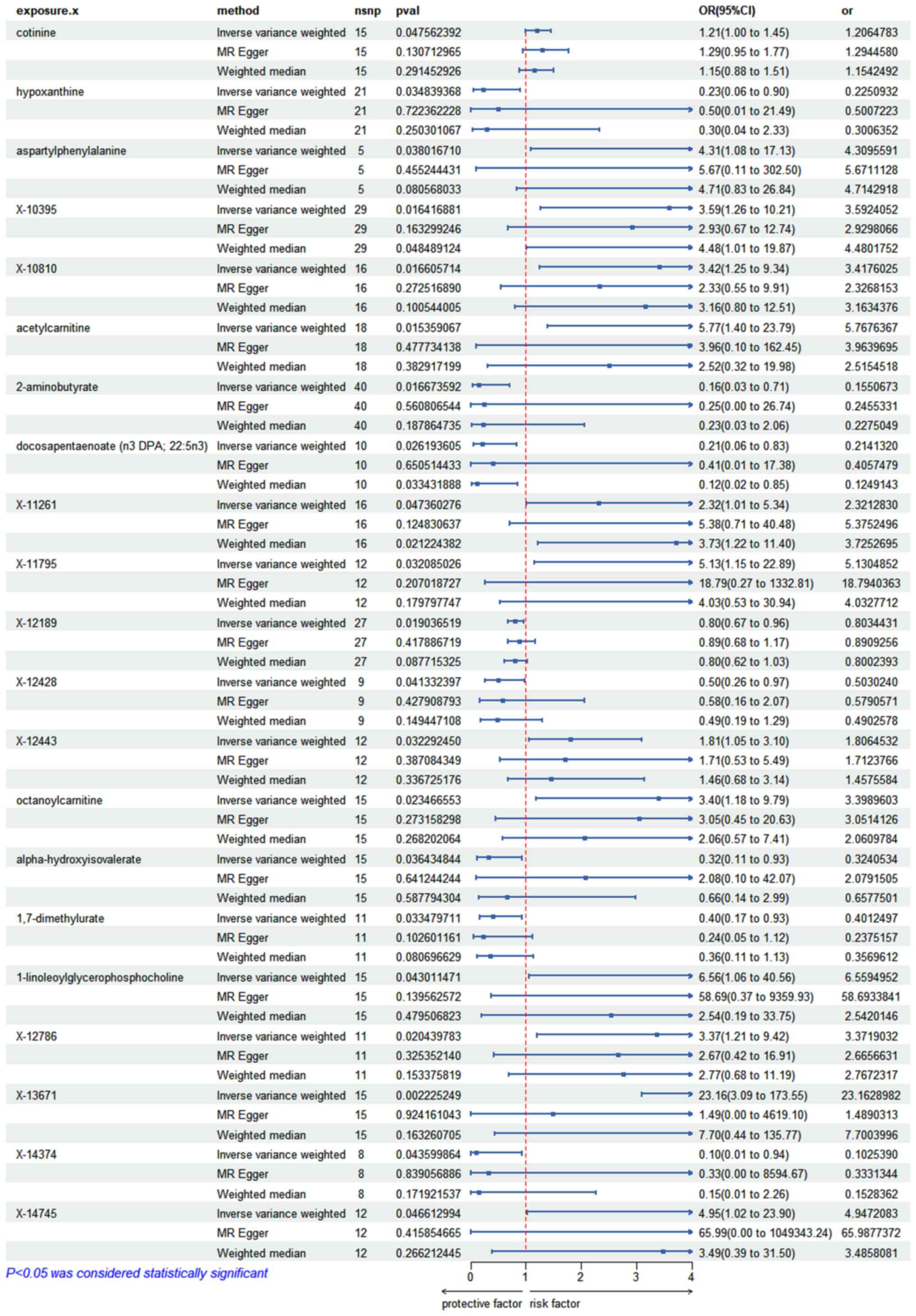
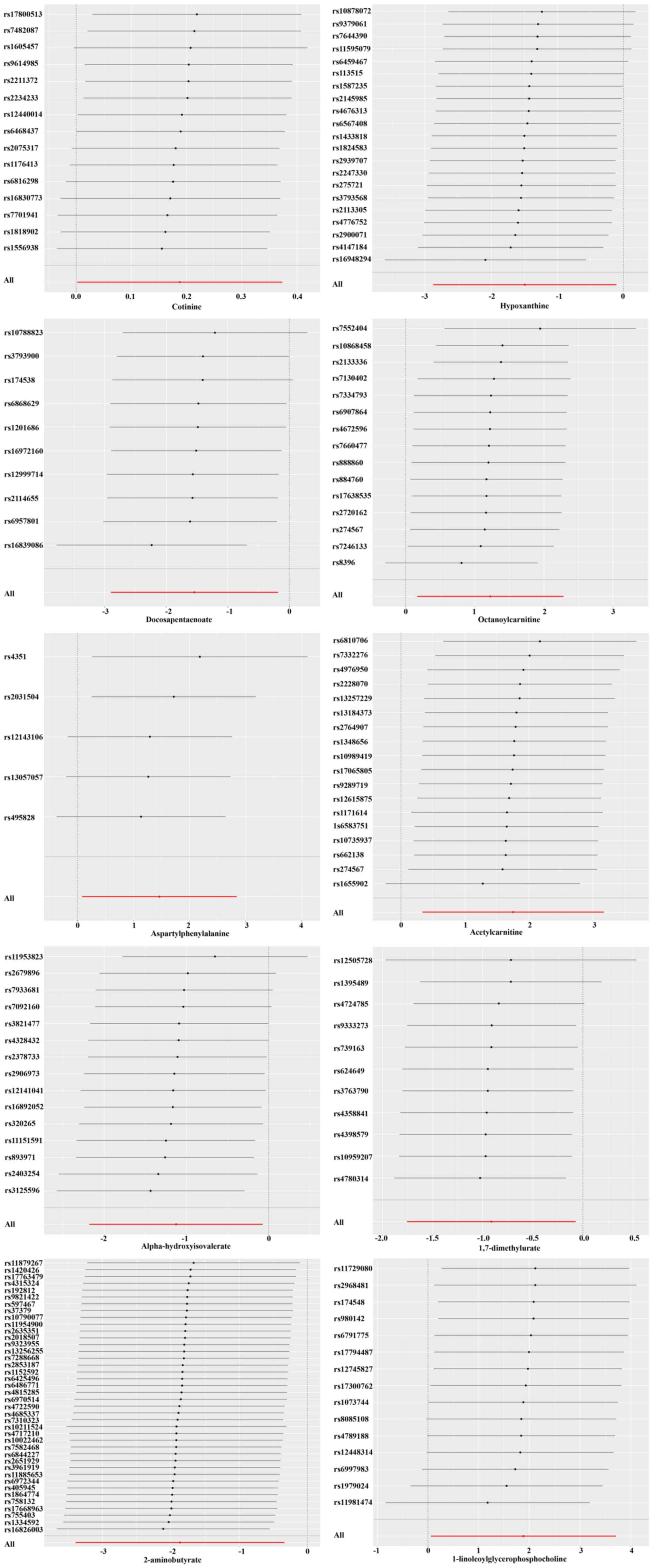
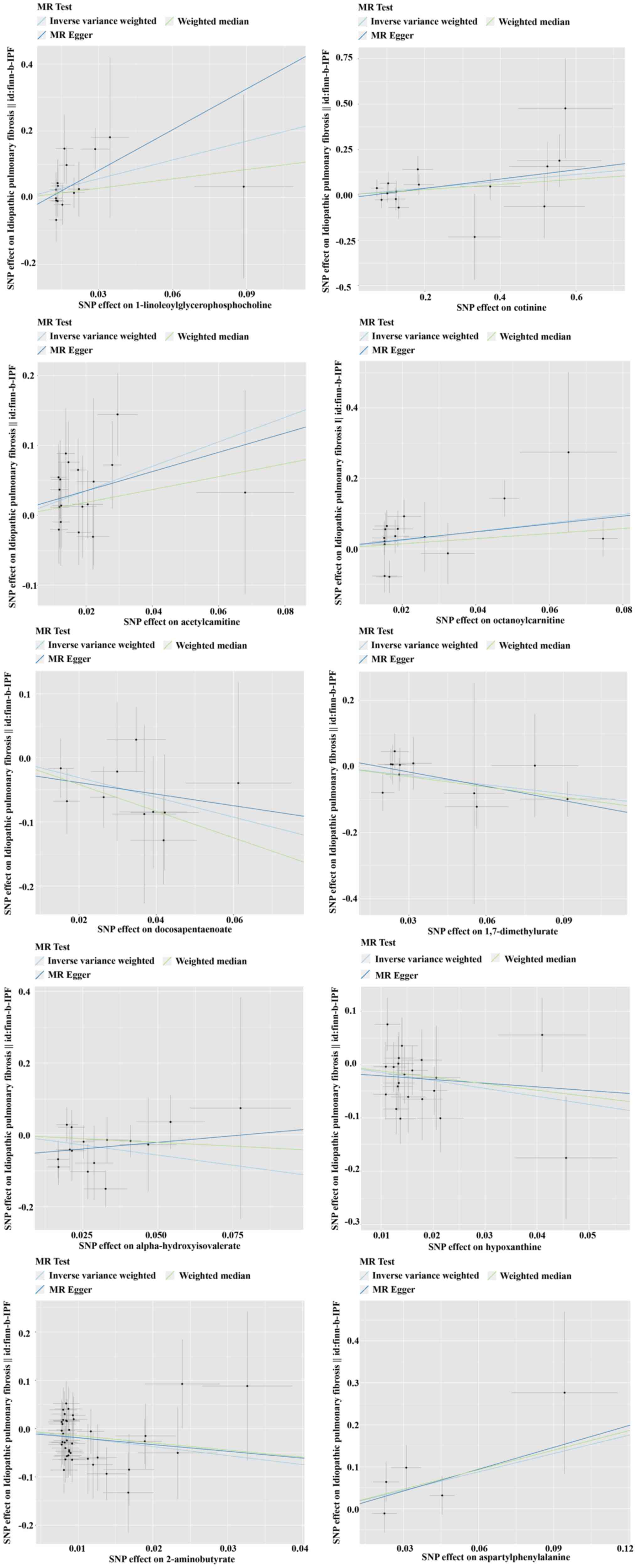
|
1
|
Podolanczuk AJ, Thomson CC, Remy-Jardin M,
Richeldi L, Martinez FJ, Kolb M and Raghu G: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: State of the art for 2023. Eur Respir J.
61(2200957)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Moss BJ, Ryter SW and Rosas IO: Pathogenic
mechanisms underlying idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Annu Rev
Pathol. 17:515–546. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Thiam F, Phogat S, Abokor FA and Osei ET:
In vitro co-culture studies and the crucial role of
fibroblast-immune cell crosstalk in IPF pathogenesis. Respir Res.
24(298)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Platenburg MGJP, van Moorsel CHM, Wiertz
IA, van der Vis JJ, Vorselaars ADM, Veltkamp M and Grutters JC:
Improved survival of IPF patients treated with antifibrotic drugs
compared with untreated patients. Lung. 201:335–343.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tomassetti S, Ravaglia C, Piciucchi S, Ryu
J, Wells A, Donati L, Dubini A, Klersy C, Luzzi V, Gori L, et al:
Historical eye on IPF: A cohort study redefining the mortality
scenario. Front Med (Lausanne). 10(1151922)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ogura T, Inoue Y, Azuma A, Homma S, Kondoh
Y, Tanaka K, Ochiai K, Sugiyama Y and Nukiwa T: Real-world safety
and tolerability of nintedanib in patients with idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis: Interim report of a post-marketing surveillance
in Japan. Adv Ther. 40:1474–1493. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Spagnolo P and Lee JS: Recent advances in
the genetics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med.
29:399–405. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Alonso-Gonzalez A, Tosco-Herrera E,
Molina-Molina M and Flores C: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and the
role of genetics in the era of precision medicine. Front Med
(Lausanne). 10(1152211)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rajesh R, Atallah R and Bärnthaler T:
Dysregulation of metabolic pathways in pulmonary fibrosis.
Pharmacol Ther. 246(108436)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Roque W and Romero F: Cellular
metabolomics of pulmonary fibrosis, from amino acids to lipids. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 320:C689–C695. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Johnson CH, Ivanisevic J and Siuzdak G:
Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 17:451–459. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Selvarajah B, Azuelos I, Anastasiou D and
Chambers RC: Fibrometabolism-An emerging therapeutic frontier in
pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Signal. 14(eaay1027)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhao YD, Yin L, Archer S, Lu C, Zhao G,
Yao Y, Wu L, Hsin M, Waddell TK, Keshavjee S, et al: Metabolic
heterogeneity of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A metabolomic
study. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 4(e000183)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gaugg MT, Engler A, Bregy L,
Nussbaumer-Ochsner Y, Eiffert L, Bruderer T, Zenobi R, Sinues P and
Kohler M: Molecular breath analysis supports altered amino acid
metabolism in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respirology.
24:437–444. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mamazhakypov A, Schermuly RT, Schaefer L
and Wygrecka M: Lipids - two sides of the same coin in lung
fibrosis. Cell Signal. 60:65–80. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tedesco S, Scattolini V, Albiero M,
Bortolozzi M, Avogaro A, Cignarella A and Fadini GP: Mitochondrial
calcium uptake is instrumental to alternative macrophage
polarization and phagocytic activity. Int J Mol Sci.
20(4966)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kim HS, Moon SJ, Lee SE, Hwang GW, Yoo HJ
and Song JW: The arachidonic acid metabolite
11,12-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid alleviates pulmonary fibrosis. Exp
Mol Med. 53:864–874. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Xie Z, Wan N, Yang L, Jin Z, Jin
F, Huang Z, Chen M, Wang H and Feng J: Potential biomarkers for
diagnosis and disease evaluation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Chin Med J (Engl). 136:1278–1290. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40(Database
issue):D109–D114. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dhindsa RS, Mattsson J, Nag A, Wang Q,
Wain LV, Allen R, Wigmore EM, Ibanez K, Vitsios D, Deevi SVV, et
al: Identification of a missense variant in SPDL1 associated with
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Commun Biol. 4(392)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BAR,
Yarmolinsky J, Davies NM, Swanson SA, VanderWeele TJ, Higgins JPT,
Timpson NJ, Dimou N, et al: Strengthening the reporting of
observational studies in epidemiology using mendelian
randomization: The STROBE-MR statement. JAMA. 326:1614–1621.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Slob EAW and Burgess S: A comparison of
robust Mendelian randomization methods using summary data. Genet
Epidemiol. 44:313–329. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yang X, Zhu Q, Zhang L, Pei Y, Xu X, Liu
X, Lu G, Pan J and Wang Y: Causal relationship between gut
microbiota and serum vitamin D: Evidence from genetic correlation
and Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 76:1017–1023.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Roze D: Causes and consequences of linkage
disequilibrium among transposable elements within eukaryotic
genomes. Genetics. 224(iyad058)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kamat MA, Blackshaw JA, Young R, Surendran
P, Burgess S, Danesh J, Butterworth AS and Staley JR: PhenoScanner
V2: An expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype
associations. Bioinformatics. 35:4851–4853. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sekula P, Del Greco MF, Pattaro C and
Köttgen A: Mendelian randomization as an approach to assess
causality using observational data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:3253–3265.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhao L, Wu R, Wu Z, Liu X, Li J, Zhang L
and Zhang S: Genetically predicted 486 blood metabolites concerning
risk of systemic lupus erythematosus: A Mendelian randomization
study. Sci Rep. 13(22543)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Burgess S and Thompson SG: Interpreting
findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method.
Eur J Epidemiol. 32:377–389. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pierce BL, Ahsan H and VanderWeele TJ:
Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian
randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int J
Epidemiol. 40:740–752. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hemani G, Bowden J and Davey Smith G:
Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in mendelian
randomization studies. Hum Mol Genet. 27:R195–R208. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Burgess S, Bowden J, Fall T, Ingelsson E
and Thompson SG: Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference
from Mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic
variants. Epidemiology. 28:30–42. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rappaport SM, Barupal DK, Wishart D,
Vineis P and Scalbert A: The blood exposome and its role in
discovering causes of disease. Environ Health Perspect.
122:769–774. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li Y, He Y, Chen S, Wang Q, Yang Y, Shen
D, Ma J, Wen Z, Ning S and Chen H: S100A12 as biomarker of disease
severity and prognosis in patients with idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis. Front Immunol. 13(810338)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fang L, Chen H, Kong R and Que J:
Endogenous tryptophan metabolite 5-Methoxytryptophan inhibits
pulmonary fibrosis by downregulating the TGF-β/SMAD3 and PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Life Sci. 260(118399)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bai L, Bernard K, Tang X, Hu M, Horowitz
JC, Thannickal VJ and Sanders YY: Glutaminolysis epigenetically
regulates antiapoptotic gene expression in idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 60:49–57.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Senoo S, Higo H, Taniguchi A, Kiura K,
Maeda Y and Miyahara N: Pulmonary fibrosis and type-17 immunity.
Respir Investig. 61:553–562. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lei T, Li M, Zhu Z, Yang J, Hu Y and Hua
L: Comprehensive evaluation of serum cotinine on human health:
Novel evidence for the systemic toxicity of tobacco smoke in the US
general population. Sci Total Environ. 892(164443)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Álvarez-Hernández J, Matía-Martín P,
Cáncer-Minchot E and Cuerda C: NUTRICOVID study group of SENDIMAD.
Long-term outcomes in critically ill patients who survived
COVID-19: The NUTRICOVID observational cohort study. Clin Nutr.
42:2029–2035. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen Z, Li H, Song C, Sun J and Liu W:
Association between serum cotinine and muscle mass: Results from
NHANES 2011-2018. BMC Public Health. 24(2093)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
She D, Jiang S and Yuan S: Association
between serum cotinine and hepatic steatosis and liver fibrosis in
adolescent: A population-based study in the United States. Sci Rep.
14(11424)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Qiu G, Lin Y, Ouyang Y, You M, Zhao X,
Wang H, Niu R, Li W, Xu X, Yan Q, et al: Nontargeted metabolomics
revealed novel association between serum metabolites and incident
acute coronary syndrome: A mendelian randomization study. J Am
Heart Assoc. 12(e028540)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Stegink LD, Lindgren SD, Brummel MC,
Stumbo PJ and Wolraich ML: Erythrocyte L-aspartyl-L-phenylalanine
hydrolase activity and plasma phenylalanine and aspartate
concentrations in children consuming diets high in aspartame. Am J
Clin Nutr. 62:1206–1211. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Meng J, Liu W, Wu Y, Xiao Y, Tang H and
Gao S: Is it necessary to wear compression stockings and how long
should they be worn for preventing post thrombotic syndrome? A
meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Thromb Res.
225:79–86. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Dambrova M, Makrecka-Kuka M, Kuka J,
Vilskersts R, Nordberg D, Attwood MM, Smesny S, Sen ZD, Guo AC,
Oler E, et al: Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, biomarkers,
therapeutic potential, drug targets, and clinical trials. Pharmacol
Rev. 74:506–551. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Vangipurapu J, Fernandes Silva L,
Kuulasmaa T, Smith U and Laakso M: Microbiota-related metabolites
and the risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 43:1319–1325.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zou X, Wang L, Wang S, Zhang Y, Ma J, Chen
L, Li Y, Yao TX, Zhou H, Wu L, et al: Promising therapeutic targets
for ischemic stroke identified from plasma and cerebrospinal fluid
proteomes: A multicenter Mendelian randomization study. Int J Surg.
110:766–776. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Meng J, Tang H, Xiao Y, Liu W, Wu Y, Xiong
Y and Gao S: Appropriate thromboprophylaxis strategy for COVID-19
patients on dosage, antiplatelet therapy, outpatient, and
postdischarge prophylaxis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled
trials. Int J Surg. 110:3910–3922. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lu Y, Li D, Wang L, Zhang H, Jiang F,
Zhang R, Xu L, Yang N, Dai S, Xu X, et al: Comprehensive
investigation on associations between dietary intake and blood
levels of fatty acids and colorectal cancer risk. Nutrients.
15(730)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kaplan RC, Williams-Nguyen JS, Huang Y,
Mossavar-Rahmani Y, Yu B, Boerwinkle E, Gellman MD, Daviglus M,
Chilcoat A, Van Horn L, et al: Identification of dietary
supplements associated with blood metabolites in the hispanic
community health study/study of latinos cohort study. J Nutr.
153:1483–1492. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Purpura M, Jäger R and Falk M: An
assessment of mutagenicity, genotoxicity, acute-, subacute and
subchronic oral toxicity of paraxanthine (1,7-dimethylxanthine).
Food Chem Toxicol. 158(112579)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|