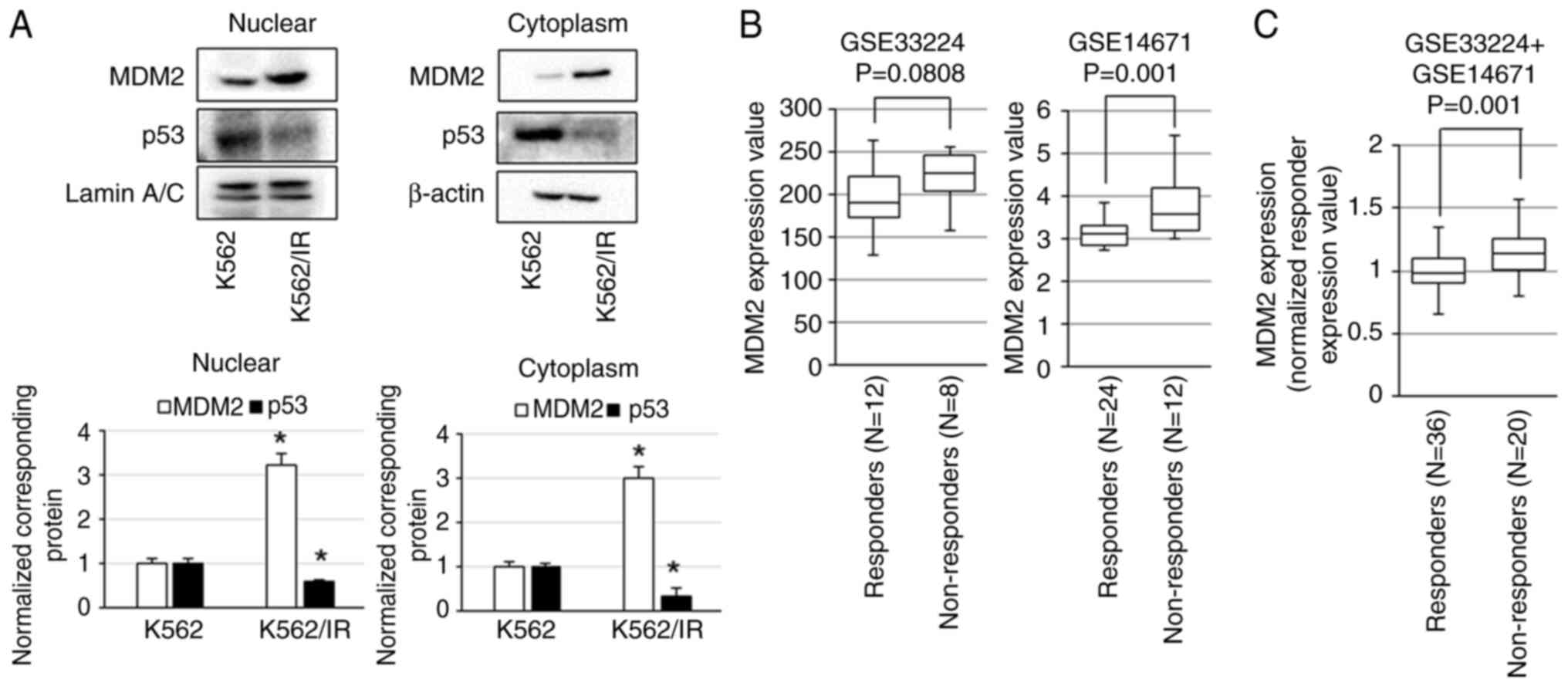
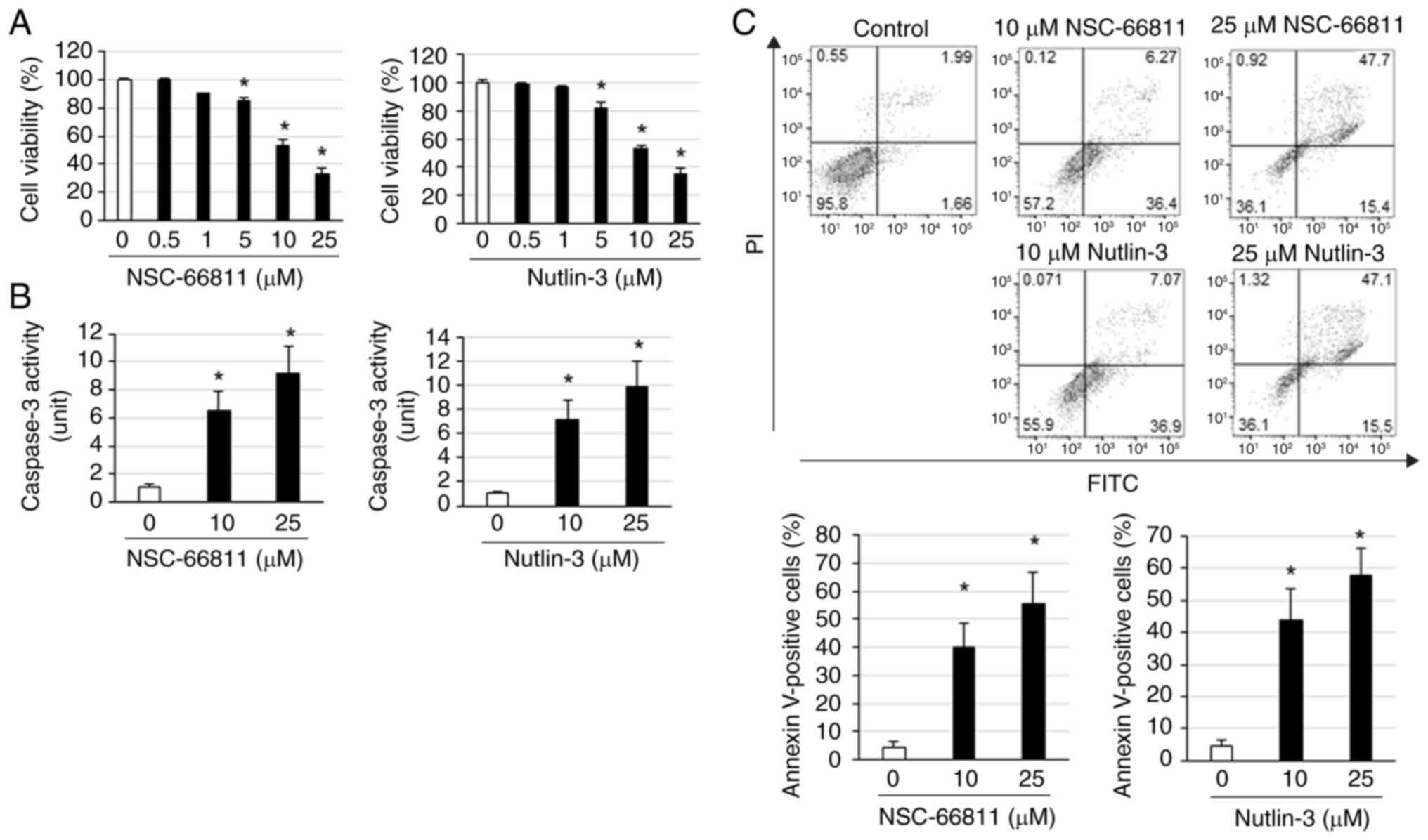
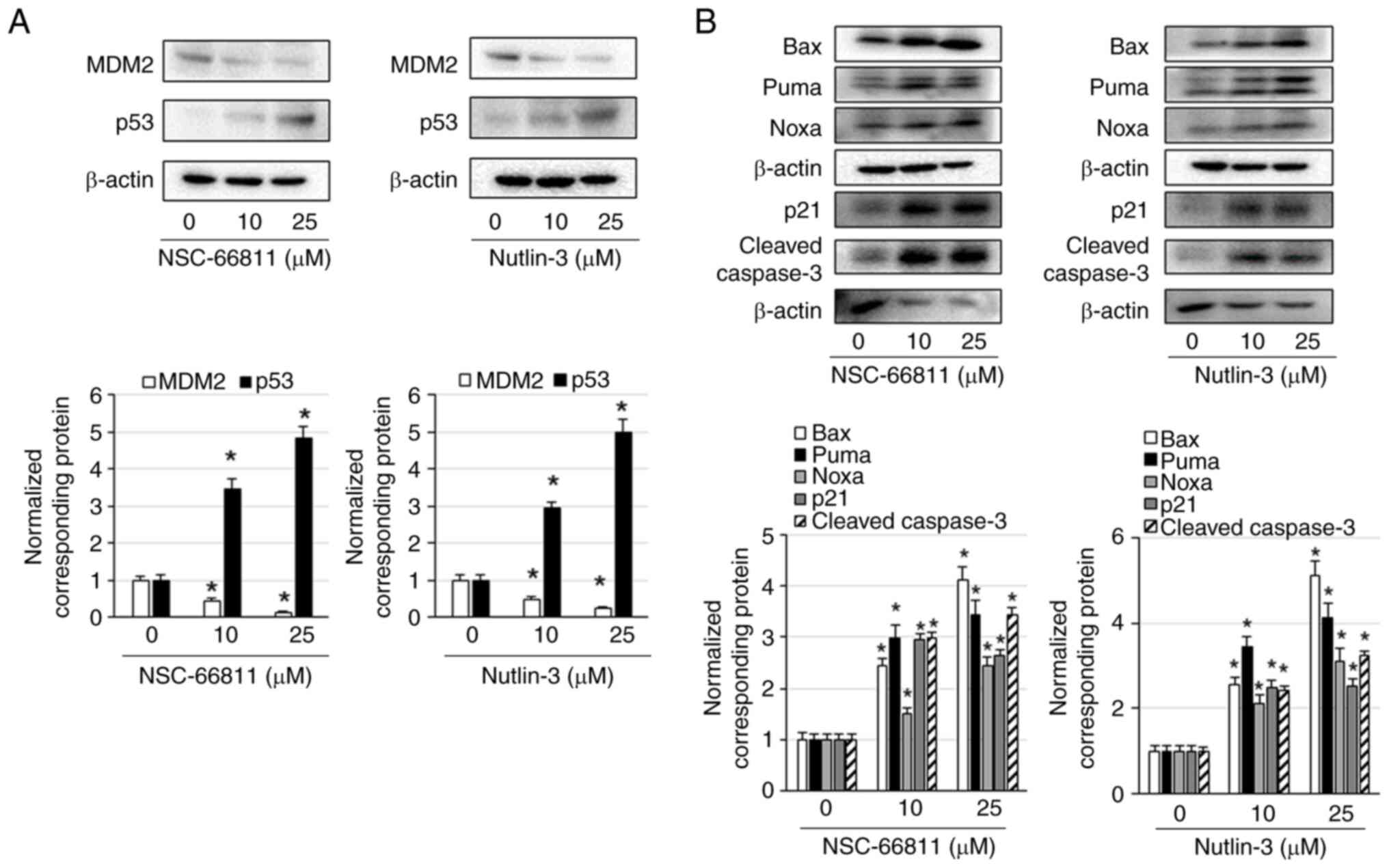
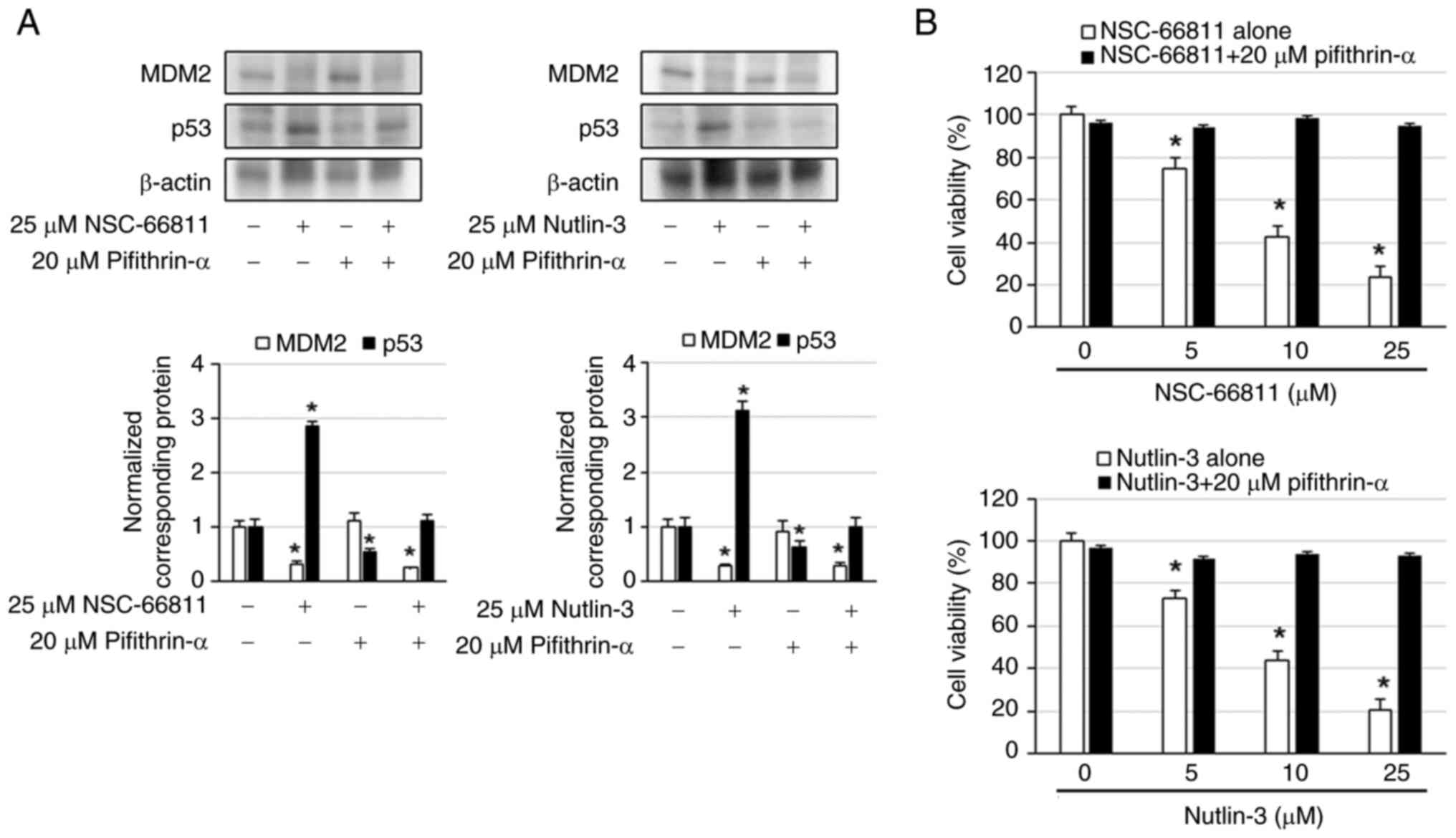
|
1
|
Romero-Morelos P, González-Yebra AL,
Muñoz-López D, Lara-Lona E and González-Yebra B: Frequencies of
BCR::ABL1 transcripts in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: A
meta-analysis. Genes (Basel). 15(232)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sun J, Hu R, Han M, Tan Y, Xie M, Gao S
and Hu JF: Mechanisms underlying therapeutic resistance of tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Biol Sci.
20:175–181. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Held N and Atallah EL: Real-world
management of CML: Outcomes and treatment patterns. Curr Hematol
Malig Rep. 18:167–175. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Marzocchi G, Castagnetti F, Luatti S,
Baldazzi C, Stacchini M, Gugliotta G, Amabile M, Specchia G,
Sessarego M, Giussani U, et al: Variant Philadelphia
translocations: Molecular-cytogenetic characterization and
prognostic influence on frontline imatinib therapy, a GIMEMA
working party on CML analysis. Blood. 117:6793–6800.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
El-Tanani M, Nsairat H, Matalka II, Lee
YF, Rizzo M, Aljabali AA, Mishra V, Mishra Y, Hromić-Jahjefendić A
and Tambuwala MM: The impact of the BCR-ABL oncogene in the
pathology and treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Pathol Res
Pract. 254(155161)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kantarjian HM, Jain N, Garcia-Manero G,
Welch MA, Ravandi F, Wierda WG and Jabbour EJ: The cure of leukemia
through the optimist's prism. Cancer. 128:240–259. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Silver RT,
Schiffer C, Apperley JF, Cervantes F, Clark RE, Cortes JE,
Deininger MW, Guilhot F, et al: European LeukemiaNet 2020
recommendations for treating chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia.
34:966–984. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Poudel G, Tolland MG, Hughes TP and Pagani
IS: Mechanisms of resistance and implications for treatment
strategies in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Cancers (Basel).
14(3300)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Koumoto Y, Usami T,
Matsuda T, Seki S, Sakai K, Nishio K and Nishida S: Activation of
ERK1/2 by MOS and TPL2 leads to dasatinib resistance in chronic
myeloid leukaemia cells. Cell Prolif. 56(e13420)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Kino T, Sakai K, Itoh
T, Imano M, Nakayama T, Nishio K, Satou T and Nishida S:
Contributions of MET activation to BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase
inhibitor resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncotarget.
8:38717–38730. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tuval A, Strandgren C, Heldin A,
Palomar-Siles M and Wiman KG: Pharmacological reactivation of p53
in the era of precision anticancer medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
21:106–120. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Scott MT, Liu W, Mitchell R, Clarke CJ,
Kinstrie R, Warren F, Almasoudi H, Stevens T, Dunn K, Pritchard J,
et al: Activating p53 abolishes self-renewal of quiescent leukaemic
stem cells in residual CML disease. Nat Commun.
15(651)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Trotta R, Vignudelli T, Candini O, Intine
RV, Pecorari L, Guerzoni C, Santilli G, Byrom MW, Goldoni S, Ford
LP, et al: BCR/ABL activates mdm2 mRNA translation via the La
antigen. Cancer Cell. 3:145–160. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Carter BZ, Mak PY, Mak DH, Ruvolo VR,
Schober W, McQueen T, Cortes J, Kantarjian HM, Champlin RE,
Konopleva M and Andreeff M: Synergistic effects of p53 activation
via MDM2 inhibition in combination with inhibition of Bcl-2 or
Bcr-Abl in CD34+ proliferating and quiescent chronic myeloid
leukemia blast crisis cells. Oncotarget. 6:30487–30499.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
You L, Liu H, Huang J, Xie W, Wei J, Ye X
and Qian W: The novel anticancer agent JNJ-26854165 is active in
chronic myeloid leukemic cells with unmutated BCR/ABL and T315I
mutant BCR/ABL through promoting proteosomal degradation of BCR/ABL
proteins. Oncotarget. 8:7777–7790. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Noguchi M, Jinushi M,
Seki S, Morii Y, Shimomura K, Imano M, Satou T and Nishida S:
Overactivation of Akt contributes to MEK inhibitor primary and
acquired resistance in colorectal cancer cells. Cancers (Basel).
11(1866)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Tomonari Y, Koumoto
YI, Imano M, Satou T and Nishida S: Overexpression of HIF-1α
contributes to melphalan resistance in multiple myeloma cells by
activation of ERK1/2, Akt, and NF-κB. Lab Invest. 99:72–84.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Morii Y, Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Otubo R,
Seki S, Yamatomo Y, Imano M, Satou T, Shimomura K and Nishida S:
Perifosine enhances the potential antitumor effect of
5-fluorourasil and oxaliplatin in colon cancer cells harboring the
PIK3CA mutation. Eur J Pharmacol. 898(173957)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
McWeeney SK, Pemberton LC, Loriaux MM,
Vartanian K, Willis SG, Yochum G, Wilmot B, Turpaz Y, Pillai R,
Druker BJ, et al: A gene expression signature of CD34+ cells to
predict major cytogenetic response in chronic-phase chronic myeloid
leukemia patients treated with imatinib. Blood. 115:315–325.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Silveira RA, Fachel AA, Moreira YB, De
Souza CA, Costa FF, Verjovski-Almeida S and Pagnano KBB:
Protein-coding genes and long noncoding RNAs are differentially
expressed in dasatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia patients
with resistance to imatinib. Hematology. 19:31–41. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hao Q, Chen J, Lu H and Zhou X: The ARTS
of p53-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis. J Mol Cell Biol.
14(mjac074)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Aravindhan S, Younus LA, Hadi Lafta M,
Markov A, Ivanovna Enina Y, Yushchenkо NA, Thangavelu L, Mostafavi
SM, Pokrovskii MV and Ahmadi M: P53 long noncoding RNA regulatory
network in cancer development. Cell Biol Int. 45:1583–1598.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu YC, Hsiao HH, Yang WC, Liu TC, Chang
CS, Yang MY, Lin PM, Hsu JF, Lee CP and Lin SF: MDM2 promoter
polymorphism and p53 codon 72 polymorphism in chronic myeloid
leukemia: The association between MDM2 promoter genotype and
disease susceptibility, age of onset, and blast-free survival in
chronic phase patients receiving imatinib. Mol Carcinog.
53:951–959. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wendel HG, de Stanchina E, Cepero E, Ray
S, Emig M, Fridman JS, Veach DR, Bornmann WG, Clarkson B, McCombie
WR, et al: Loss of p53 impedes the antileukemic response to BCR-ABL
inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:7444–7449. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cheng Y, Hao Y, Zhang A, Hu C, Jiang X, Wu
Q and Xu X: Persistent STAT5-mediated ROS production and
involvement of aberrant p53 apoptotic signaling in the resistance
of chronic myeloid leukemia to imatinib. Int J Mol Med. 41:455–463.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ding J, Romani J, Zaborski M, MacLeod RA,
Nagel S, Drexler HG and Quentmeier H: Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR
overcomes nilotinib resistance in BCR-ABL1 positive leukemia cells
through translational down-regulation of MDM2. PLoS One.
8(e83510)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Peterson LF, Mitrikeska E, Giannola D, Lui
Y, Sun H, Bixby D, Malek SN, Donato NJ, Wang S and Talpaz M: p53
stabilization induces apoptosis in chronic myeloid leukemia blast
crisis cells. Leukemia. 25:761–769. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Adnan Awad S, Dufva O, Klievink J,
Karjalainen E, Ianevski A, Pietarinen P, Kim D, Potdar S, Wolf M,
Lotfi K, et al: Integrated drug profiling and CRISPR screening
identify BCR::ABL1-independent vulnerabilities in chronic myeloid
leukemia. Cell Rep Med. 5(101521)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Al-Kuraishy HM, Al-Gareeb AI and
Al-Buhadilly AK: p53 gene (NY-CO-13) levels in patients with
chronic myeloid leukemia: The role of imatinib and nilotinib.
Diseases. 6(13)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhao D and Liu T: The relationship between
MDM2 T309G polymorphism and leukemia in the Chinese population:
Evidence from a meta-analysis. Clin Lab. 63:1639–1645.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Burgess A, Chia KM, Haupt S, Thomas D,
Haupt Y and Lim E: Clinical overview of MDM2/X-targeted therapies.
Front Oncol. 6(7)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Law JC, Ritke MK, Yalowich JC, Leder GH
and Ferrell RE: Mutational inactivation of the p53 gene in the
human erythroid leukemic K562 cell line. Leuk Res. 17:1045–1050.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Usuda J, Inomata M, Fukumoto H, Iwamoto Y,
Suzuki T, Kuh HJ, Fukuoka K, Kato H, Saijo N and Nishio K:
Restoration of p53 gene function in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbor
13-acetate-resistant human leukemia K562/TPA cells. Int J Oncol.
22:81–86. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ray-Coquard I, Blay JY, Italiano A, Le
Cesne A, Penel N, Zhi J, Heil F, Rueger R, Graves B, Ding M, et al:
Effect of the MDM2 antagonist RG7112 on the P53 pathway in patients
with MDM2-amplified, well-differentiated or dedifferentiated
liposarcoma: An exploratory proof-of-mechanism study. Lancet Oncol.
13:1133–1140. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Brennan RC, Federico S, Bradley C, Zhang
J, Flores-Otero J, Wilson M, Stewart C, Zhu F, Guy K and Dyer MA:
Targeting the p53 pathway in retinoblastoma with subconjunctival
Nutlin-3a. Cancer Res. 71:4205–4213. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Matsuda T, Kimura A,
Tanaka R, Nagayoshi S, Hoshida T, Tanabe K and Nishida S:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α inhibitor induces cell death via
suppression of BCR-ABL1 and Met expression in BCR-ABL1 tyrosine
kinase inhibitor sensitive and resistant chronic myeloid leukemia
cells. BMB Rep. 56:78–83. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|