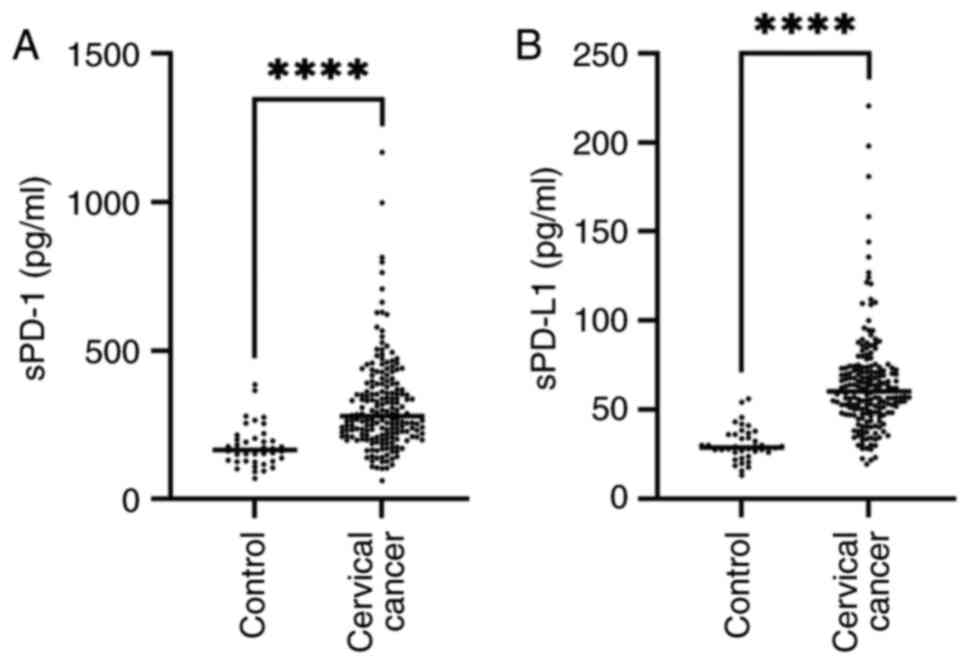
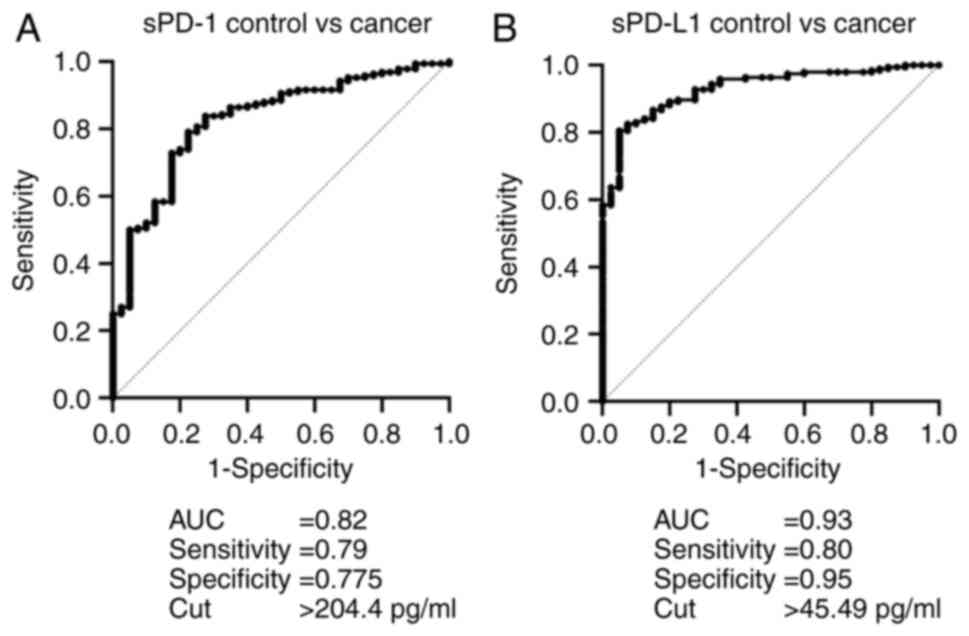
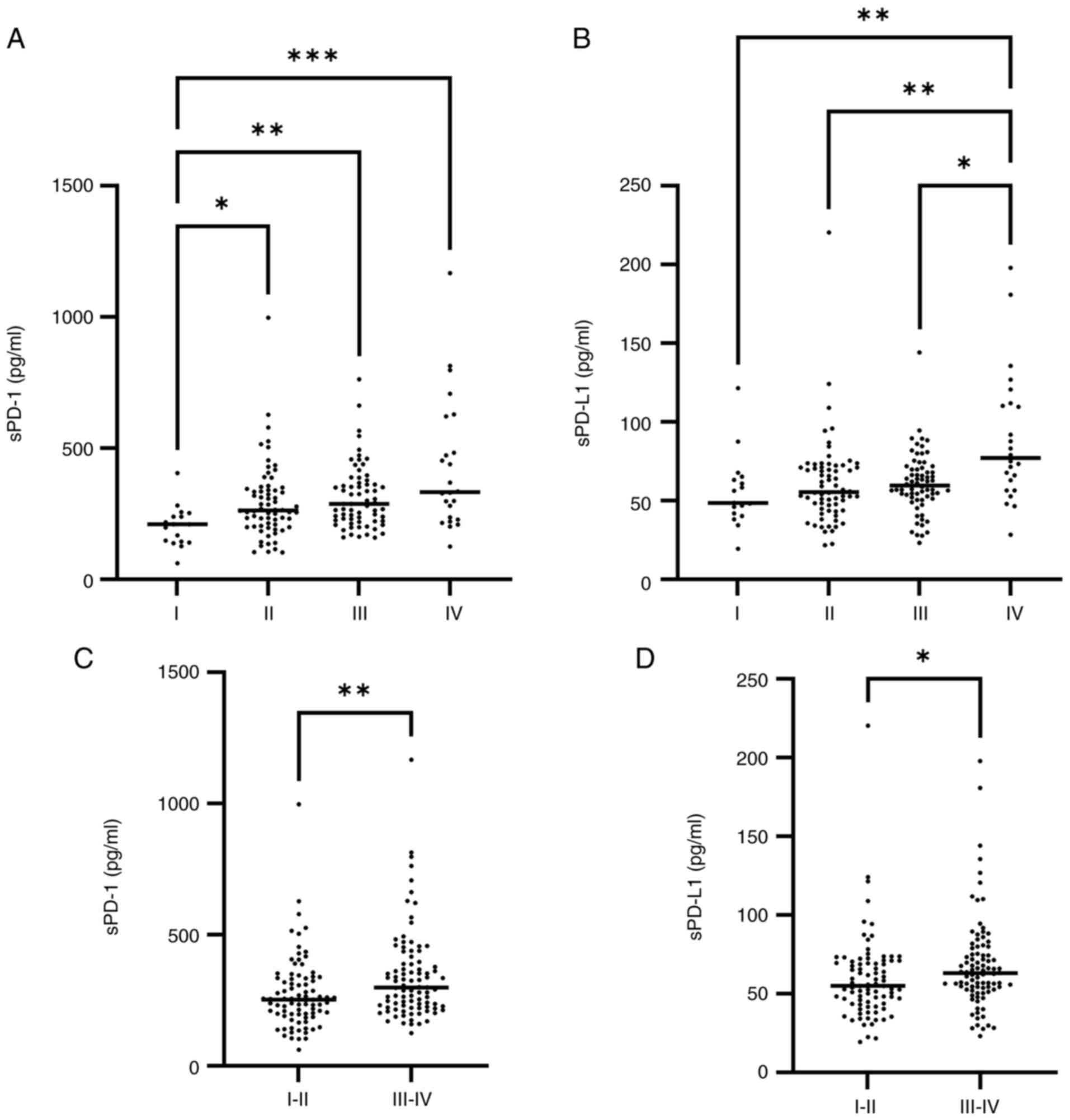
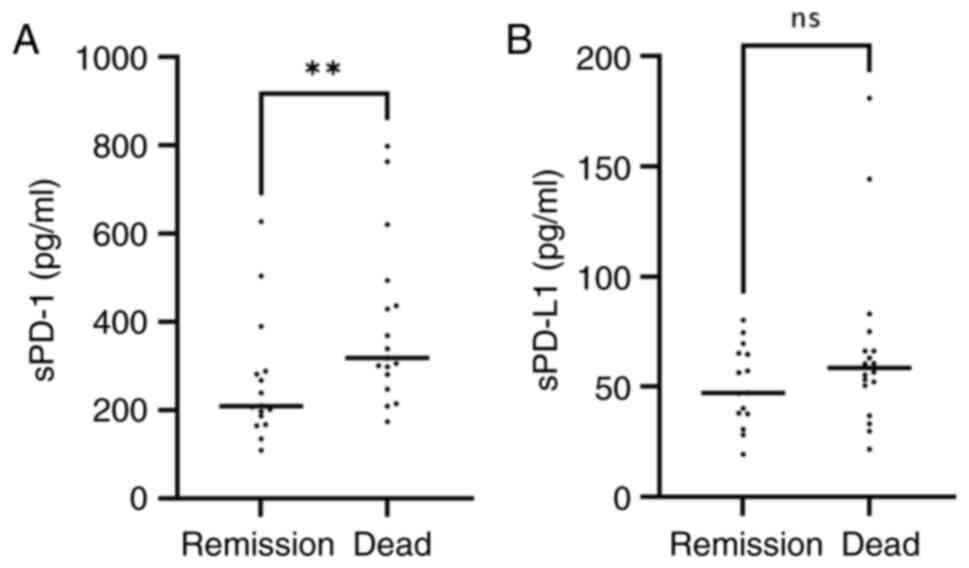
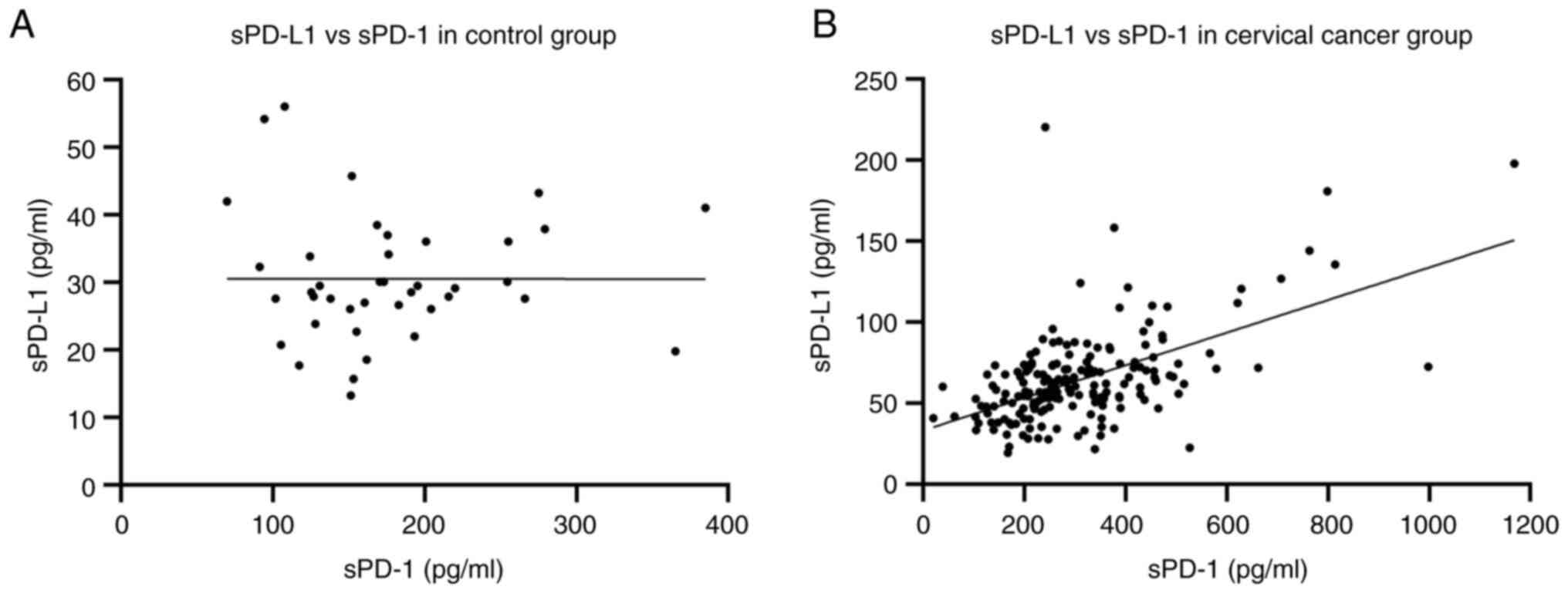
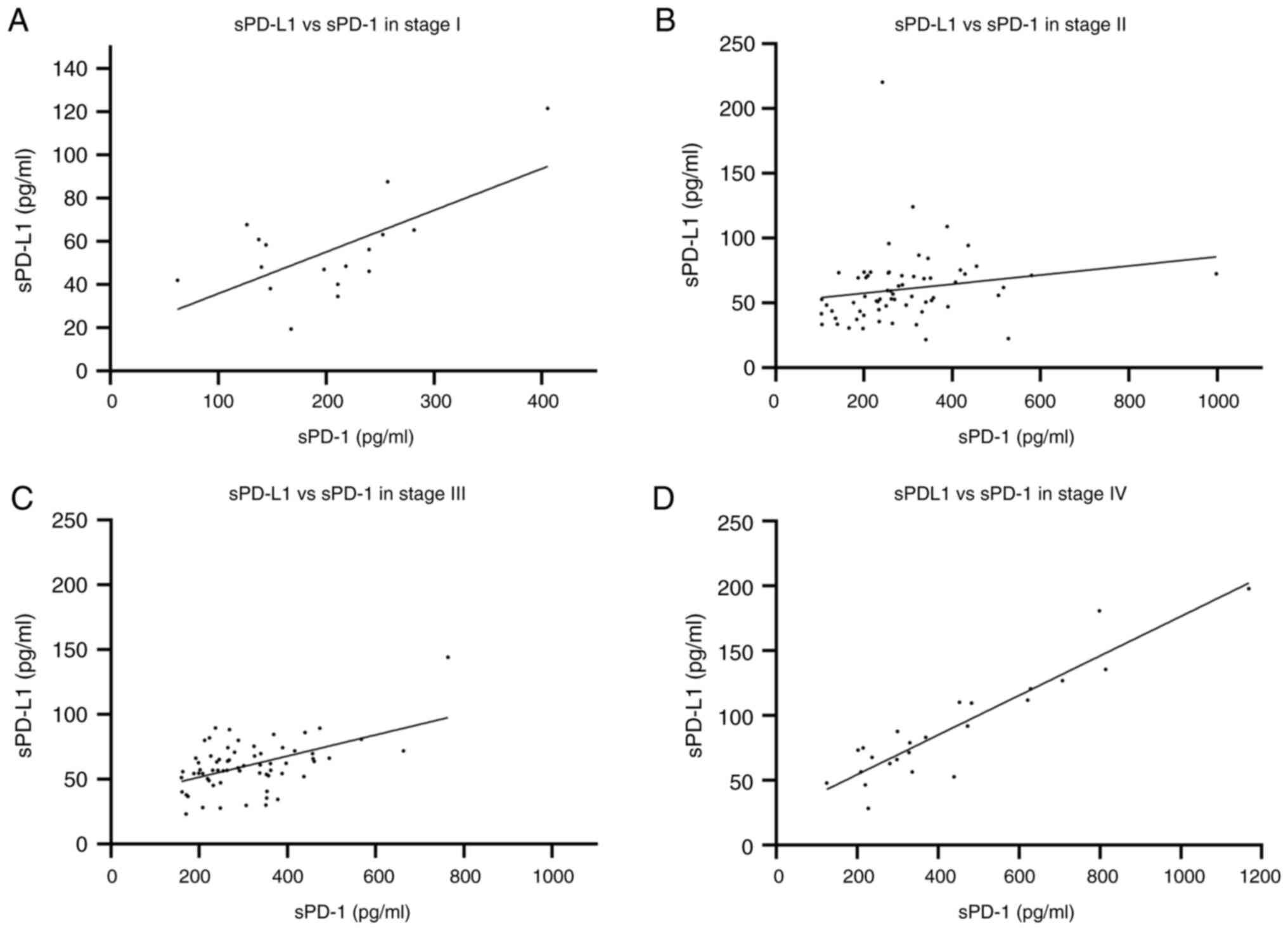
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mohamud A, Høgdall C and Schnack T:
Prognostic value of the 2018 FIGO staging system for cervical
cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 165:506–513. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hsu HC, Li X, Curtin JP, Goldberg JD and
Schiff PB: Surveillance epidemiology and end results analysis
demonstrates improvement in overall survival for cervical cancer
patients treated in the era of concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Front
Oncol. 5(81)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rocha Martins P, Luciano Pereira Morais K,
de Lima Galdino NA, Jacauna A, Paula SOC, Magalhães WCS, Zuccherato
LW, Campos LS, Salles PGO and Gollob KJ: Linking tumor immune
infiltrate and systemic immune mediators to treatment response and
prognosis in advanced cervical cancer. Sci Rep.
13(22634)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li C, Cang W, Gu Y, Chen L and Xiang Y:
The anti-PD-1 era of cervical cancer: Achievement, opportunity, and
challenge. Front Immunol. 14(1195476)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lou H, Cai H, Huang X, Li G, Wang L, Liu
F, Qin W, Liu T, Liu W, Wang ZM, et al: Cadonilimab combined with
chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab as first-line treatment in
recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer (COMPASSION-13): A phase 2
study. Clin Cancer Res. 30:1501–1508. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sharpe AH, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R and Freeman
GJ: The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in
regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat Immunol. 8:239–245.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ai L, Xu A and Xu J: Roles of PD-1/PD-L1
pathway: Signaling, cancer, and beyond. Adv Exp Med Biol.
1248:33–59. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Alsaab HO, Sau S, Alzhrani R, Tatiparti K,
Bhise K, Kashaw SK and Iyer AK: PD-1 and PD-L1 checkpoint signaling
inhibition for cancer immunotherapy: Mechanism, combinations, and
clinical outcome. Front Pharmacol. 8(561)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chen B, Hu J, Hu X, Chen H, Bao R, Zhou Y,
Ye Y, Zhan M, Cai W, Li H and Li HB: DENR controls JAK2 translation
to induce PD-L1 expression for tumor immune evasion. Nat Commun.
13(2059)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Twa DD, Chan FC, Ben-Neriah S, Woolcock
BW, Mottok A, Tan KL, Slack GW, Gunawardana J, Lim RS, McPherson
AW, et al: Genomic rearrangements involving programmed death
ligands are recurrent in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma.
Blood. 123:2062–2065. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gupta S, Cheville JC, Jungbluth AA, Zhang
Y, Zhang L, Chen YB, Tickoo SK, Fine SW, Gopalan A, Al-Ahmadie HA,
et al: JAK2/PD-L1/PD-L2 (9p24.1) amplifications in renal cell
carcinomas with sarcomatoid transformation: Implications for
clinical management. Mod Pathol. 32:1344–1358. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gupta S, Vanderbilt CM, Cotzia P,
Arias-Stella JA III, Chang JC, Zehir A, Benayed R, Nafa K, Razavi
P, Hyman DM, et al: Next-generation sequencing-based assessment of
JAK2, PD-L1, and PD-L2 copy number alterations at 9p24.1 in breast
cancer: Potential implications for clinical management. J Mol
Diagn. 21:307–317. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ikeda S, Okamoto T, Okano S, Umemoto Y,
Tagawa T, Morodomi Y, Kohno M, Shimamatsu S, Kitahara H, Suzuki Y,
et al: PD-L1 is upregulated by simultaneous amplification of the
PD-L1 and JAK2 genes in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
11:62–71. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dezutter-Dambuyant C, Durand I, Alberti L,
Bendriss-Vermare N, Valladeau-Guilemond J, Duc A, Magron A, Morel
AP, Sisirak V, Rodriguez C, et al: A novel regulation of PD-1
ligands on mesenchymal stromal cells through MMP-mediated
proteolytic cleavage. Oncoimmunology. 5(e1091146)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hayashi H, Chamoto K, Hatae R, Kurosaki T,
Togashi Y, Fukuoka K, Goto M, Chiba Y, Tomida S and Ota T: Soluble
immune checkpoint factors reflect exhaustion of antitumor immunity
and response to PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest.
134(e168318)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nielsen C, Ohm-Laursen L, Barington T,
Husby S and Lillevang ST: Alternative splice variants of the human
PD-1 gene. Cell Immunol. 235:109–116. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sharpe AH and Pauken KE: The diverse
functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:153–167. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang W and Zhang T: Expression and
analysis of PD-L1 in peripheral blood circulating tumor cells of
lung cancer. Future Oncol. 17:1625–1635. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bailly C, Thuru X and Quesnel B: Soluble
programmed death ligand-1 (sPD-L1): A pool of circulating proteins
implicated in health and diseases. Cancers (Basel).
13(3034)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kawasaki K, Noma K, Kato T, Ohara T,
Tanabe S, Takeda Y, Matsumoto H, Nishimura S, Kunitomo T, Akai M,
et al: PD-L1-expressing cancer-associated fibroblasts induce tumor
immunosuppression and contribute to poor clinical outcome in
esophageal cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 72:3787–3802.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hira-Miyazawa M, Nakamura H, Hirai M,
Kobayashi Y, Kitahara H, Bou-Gharios G and Kawashiri S: Regulation
of programmed-death ligand in the human head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma microenvironment is mediated through matrix
metalloproteinase-mediated proteolytic cleavage. Int J Oncol.
52:379–388. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Guo X, Wang J, Jin J, Chen H, Zhen Z,
Jiang W, Lin T, Huang H, Xia Z and Sun X: High serum level of
soluble programmed death ligand 1 is associated with a poor
prognosis in Hodgkin lymphoma. Transl Oncol. 11:779–785.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Krafft U, Olah C, Reis H, Kesch C, Darr C,
Grünwald V, Tschirdewahn S, Hadaschik B, Horvath O, Kenessey I, et
al: High serum PD-L1 levels are associated with poor survival in
urothelial cancer patients treated with chemotherapy and immune
checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Cancers (Basel).
13(2548)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bian B, Fanale D, Dusetti N, Roque J,
Pastor S, Chretien AS, Incorvaia L, Russo A, Olive D and Iovanna J:
Prognostic significance of circulating PD-1, PD-L1, pan-BTN3As,
BTN3A1 and BTLA in patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Oncoimmunology. 8(e1561120)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fanale D, Incorvaia L, Badalamenti G, De
Luca I, Algeri L, Bonasera A, Corsini LR, Brando C, Russo A,
Iovanna JL, et al: Prognostic role of plasma PD-1, PD-L1,
pan-BTN3As and BTN3A1 in patients affected by metastatic
gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Can immune checkpoints act as a
sentinel for short-term survival? Cancers (Basel).
13(2118)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chang B, Huang T, Wei H, Shen L, Zhu D, He
W, Chen Q, Zhang H, Li Y, Huang R, et al: The correlation and
prognostic value of serum levels of soluble programmed death
protein 1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
68:353–363. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu C, Li X, Li A, Zou W, Huang R, Hu X,
Yu J, Zhang X and Yue J: Concurrent chemoradiotherapy increases the
levels of soluble immune checkpoint proteins in patients with
locally advanced cervical cancer. J Immunol Res.
2022(9621466)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
DeLong ER, DeLong DM and Clarke-Pearson
DL: Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver
operating characteristic curves: A nonparametric approach.
Biometrics. 44:837–845. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheng HY, Kang PJ, Chuang YH, Wang YH, Jan
MC, Wu CF, Lin CL, Liu CJ, Liaw YF, Lin SM, et al: Circulating
programmed death-1 as a marker for sustained high hepatitis B viral
load and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
9(e95870)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li N, Zhou Z, Li F, Sang J, Han Q, Lv Y,
Zhao W, Li C and Liu Z: Circulating soluble programmed death-1
levels may differentiate immune-tolerant phase from other phases
and hepatocellular carcinoma from other clinical diseases in
chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Oncotarget. 8:46020–46033.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zvirble M, Survila Z, Bosas P,
Dobrovolskiene N, Mlynska A, Zaleskis G, Jursenaite J, Characiejus
D and Pasukoniene V: Prognostic significance of soluble PD-L1 in
prostate cancer. Front Immunol. 15(1401097)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ancın B, Özercan MM, Yılmaz YM, Uysal S,
Kumbasar U, Sarıbaş Z, Dikmen E, Doğan R and Demircin M: The
correlation of serum sPD-1 and sPD-L1 levels with clinical,
pathological characteristics and lymph node metastasis in nonsmall
cell lung cancer patients. Turk J Med Sci. 52:1050–1057.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li JW, Wei P, Guo Y, Shi D, Yu BH, Su YF,
Li XQ and Zhou XY: Clinical significance of circulating exosomal
PD-L1 and soluble PD-L1 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma,
nasal-type. Am J Cancer Res. 10:4498–4512. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chivu-Economescu M, Herlea V, Dima S,
Sorop A, Pechianu C, Procop A, Kitahara S, Necula L, Matei L, Dragu
D, et al: Soluble PD-L1 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in
resectable gastric cancer patients. Gastric Cancer. 26:934–946.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Incorvaia L, Fanale D, Badalamenti G,
Porta C, Olive D, De Luca I, Brando C, Rizzo M, Messina C, Rediti
M, et al: Baseline plasma levels of soluble PD-1, PD-L1, and BTN3A1
predict response to nivolumab treatment in patients with metastatic
renal cell carcinoma: A step toward a biomarker for therapeutic
decisions. Oncoimmunology. 9(1832348)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Qin YE, Tang WF, Xu Y, Wan FR and Chen AH:
Ultrasound-mediated co-delivery of miR-34a and sPD-1 complexed with
microbubbles for synergistic cancer therapy. Cancer Manag Res.
12:2459–2469. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hassen G, Kasar A, Jain N, Berry S, Dave
J, Zouetr M, Priyanka Ganapathiraju VLN, Kurapati T, Oshai S, Saad
M, et al: Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) positivity and factors
associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer: An
umbrella meta-analysis. Cureus. 14(e23845)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|