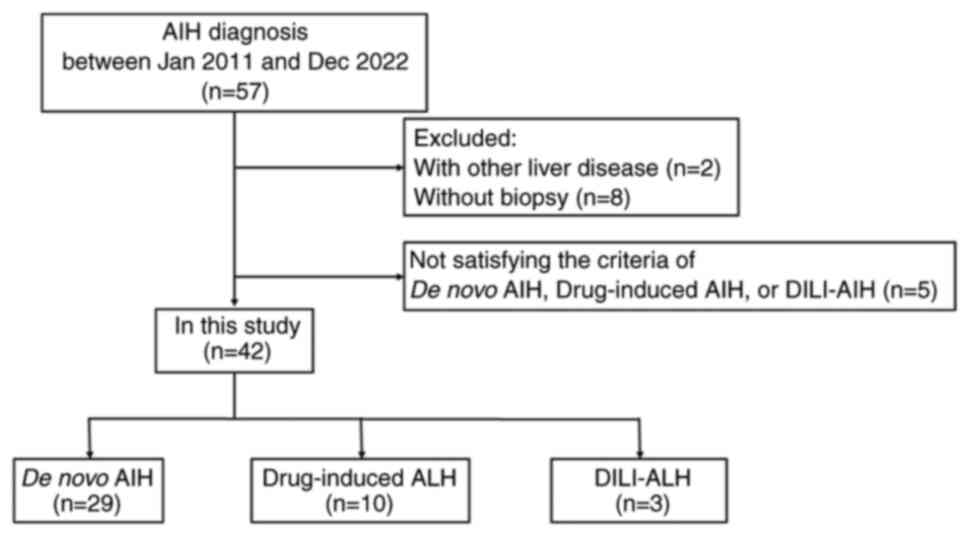
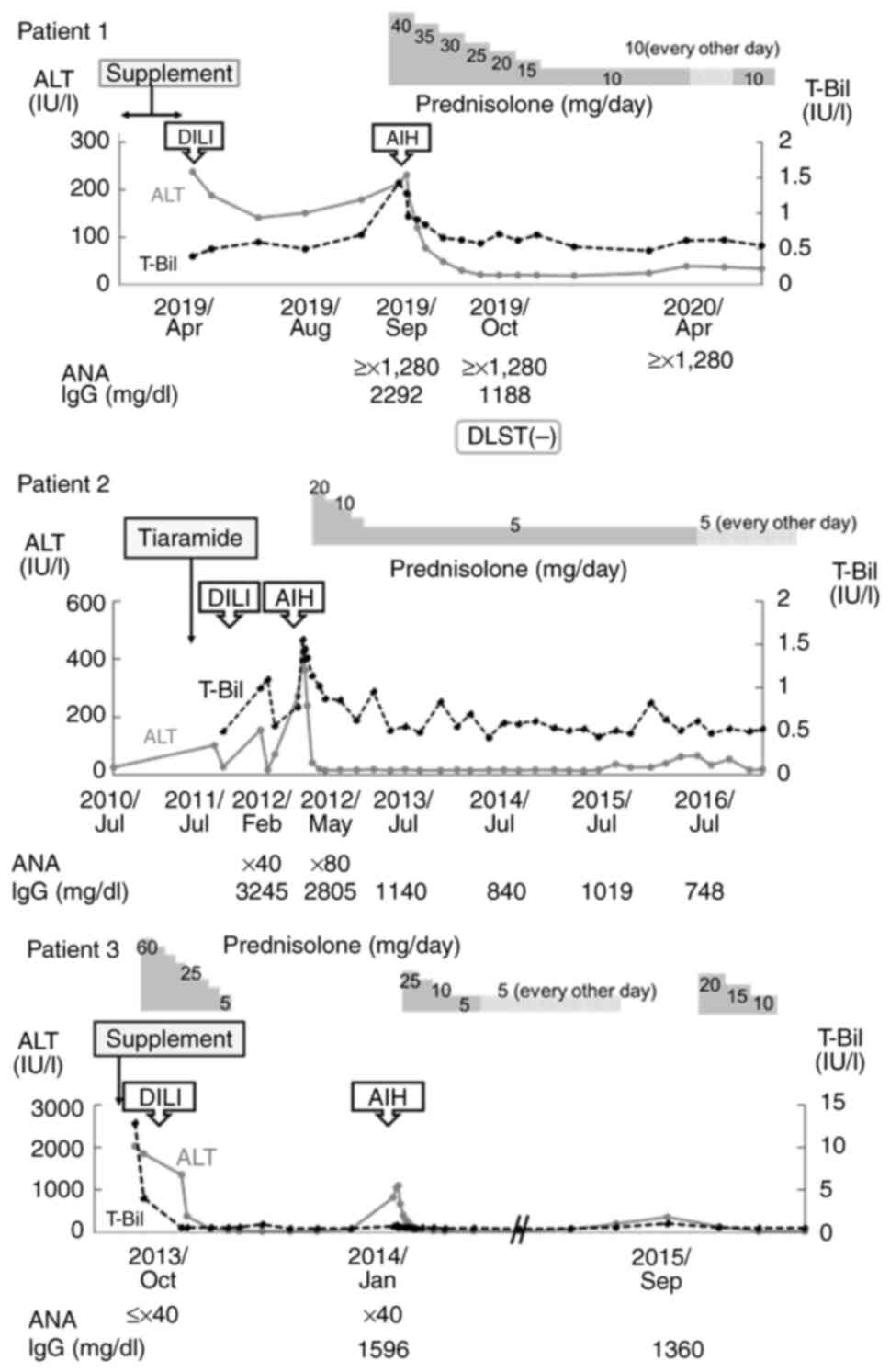
|
1
|
Björnsson E, Talwalkar J, Treeprasertsuk
S, Kamath PS, Takahashi N, Sanderson S, Neuhauser M and Lindor K:
Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: Clinical characteristics and
prognosis. Hepatology. 51:2040–2048. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liberal R, Longhi MS, Mieli-Vergani G and
Vergani D: Pathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis. Best Pract Res
Clin Gastroenterol. 25:653–664. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Manns MP, Lohse AW and Vergani D:
Autoimmune hepatitis-update 2015. J Hepatol. 62 (Suppl
1):S100–S111. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sebode M, Schulz L and Lohse AW:
‘Autoimmune(-like)’ drug and herb induced liver injury: New
insights into molecular pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
18(1954)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lammert C, Chalasani SN, Atkinson EJ,
McCauley BM and Lazaridis KN: Environmental risk factors are
associated with autoimmune hepatitis. Liver Int. 41:2396–2403.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chalasani NP, Maddur H, Russo MW, Wong RJ
and Reddy KR: Practice Parameters Committee of the American College
of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: Diagnosis and
management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Am J
Gastroenterol. 116:878–898. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Autoimmune hepatitis. J
Hepatol. 63:971–1004. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European
Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice
guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury. J Hepatol. 70:1222–1261.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mack CL, Adams D, Assis DN, Kerkar N,
Manns MP, Mayo MJ, Vierling JM, Alsawas M, Murad MH and Czaja AJ:
Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis in adults and
children: 2019 Practice guidance and guidelines from the American
association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology.
72:671–722. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Weiler-Normann C and Schramm C: Drug
induced liver injury and its relationship to autoimmune hepatitis.
J Hepatol. 55:747–749. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Castiella A, Zapata E, Lucena MI and
Andrade RJ: Drug-induced autoimmune liver disease: A diagnostic
dilemma of an increasingly reported disease. World J Hepatol.
6:160–168. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
de Boer YS, Kosinski AS, Urban TJ, Zhao Z,
Long N, Chalasani N, Kleiner DE and Hoofnagle JH: Drug-Induced
Liver Injury Network. Features of autoimmune hepatitis in patients
with drug-induced liver injury. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
15:103–112.e2. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lammert C, Zhu C, Lian Y, Raman I, Eckert
G, Li QZ and Chalasani N: Exploratory study of autoantibody
profiling in drug-induced liver injury with an autoimmune
phenotype. Hepatol Commun. 4:1651–1663. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tan CK, Ho D, Wang LM and Kumar R:
Drug-induced autoimmune hepatitis: A minireview. World J
Gastroenterol. 28:2654–2666. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Björnsson ES, Medina-Caliz I, Andrade RJ
and Lucena MI: Setting up criteria for drug-induced autoimmune-like
hepatitis through a systematic analysis of published reports.
Hepatol Commun. 6:1895–1909. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Andrade RJ, Aithal GP, de Boer YS, Liberal
R, Gerbes A, Regev A, Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B, Schramm C,
Kleiner DE, De Martin E, et al: Nomenclature, diagnosis and
management of drug-induced autoimmune-like hepatitis (DI-ALH): An
expert opinion meeting report. J Hepatol. 79:853–866.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Andrade RJ, Chalasani N, Björnsson ES,
Suzuki A, Kullak-Ublick GA, Watkins PB, Devarbhavi H, Merz M,
Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N and Aithal GP: Drug-induced liver injury.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5(58)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N, Hallal H,
Castiella A, García-Bengoechea M, Otazua P, Berenguer M, Fernandez
MC, Planas R and Andrade RJ: Recurrent drug-induced liver injury
(DILI) with different drugs in the Spanish Registry: The dilemma of
the relationship to autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 55:820–827.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yeong TT, Lim KH, Goubet S, Parnell N and
Verma S: Natural history and outcomes in drug induced autoimmune
hepatitis. Hepatol Res. 46:E79–E88. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Björnsson ES, Stephens C, Atallah E,
Robles-Diaz M, Alvarez-Alvarez I, Gerbes A, Weber S, Stirnimann G,
Kullak-Ublick G, Cortez-Pinto H, et al: A new framework for
advancing in drug-induced liver injury research. The prospective
European DILI registry. Liver Int. 43:115–126. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ueno M, Takabatake H, Kayahara T, Morimoto
Y, Notohara K and Mizuno M: Long-term outcomes of drug-induced
autoimmune-like hepatitis after pulse steroid therapy. Hepatol Res.
53:1073–1083. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sugimoto K, Ito T, Yamamoto N and Shiraki
K: Seven cases of autoimmune hepatitis that developed after
drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 54:1892–1893.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Alvarez F, Berg PA, Bianchi FB, Bianchi L,
Burroughs AK, Cancado EL, Chapman RW, Cooksley WG, Czaja AJ, Desmet
VJ, et al: International autoimmune hepatitis group report: Review
of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol.
31:929–938. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Benichou C, Danan G and Flahault A:
Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs-II. An original
model for validation of drug causality assessment methods: Case
reports with positive rechallenge. J Clin Epidemiol. 46:1331–1336.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ichida F, Tsuji T, Omata M, Ichida T,
Inoue K, Kamimura T, Yamada G, Hino K, Yokosuka O and Suzuki H: New
Inuyama classification; new criteria for histological assessment of
chronic hepatitis. Int Hepatol Commun. 6:112–119. 1996.
|
|
26
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Huppertz HI, Triechel U, Gassel AM,
Jeschke R and Büschenfelde KHMZ: Autoimmune hepatitis following
hepatitis A virus infection. J Hepatology. 23:204–208.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Singh G, Palaniappan S, Rotimi O and
Hamlin PJ: Autoimmune hepatitis triggered by hepatitis A. Gut.
56(304)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Rigopoulou EI, Zachou K, Gatselis N,
Koukoulis GK and Dalekos GN: Autoimmune hepatitis in patients with
chronic HBV and HCV infections: Patterns of clinical
characteristics, disease progression and outcome. Ann Hepatol.
13:127–135. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pischke S, Gisa A, Suneetha PV, Wiegand
SB, Taubert R, Schlue J, Wursthorn K, Bantel H, Raupach R, Bremer
B, et al: Increased HEV seroprevalence in patients with autoimmune
hepatitis. PLoS One. 9(e85330)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zellos A, Spoulou V, Roma-Giannikou E,
Karentzou O, Dalekos GN and Theodoridou M: Autoimmune hepatitis
type-2 and Epstein-Barr virus infection in a toddler: Art of facts
or an artifact? Ann Hepatol. 12:147–151. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Martínez-Casas OY, Díaz-Ramírez GS,
Marín-Zuluaga JI, Muñoz-Maya O, Santos O, Donado-Gómez JH and
Restrepo-Gutiérrez JC: Differential characteristics in drug-induced
autoimmune hepatitis. JGH Open. 2:97–104. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Stephens C, Robles-Diaz M, Medina-Caliz I,
Garcia-Cortes M, Ortega-Alonso A, Sanabria-Cabrera J,
Gonzalez-Jimenez A, Alvarez-Alvarez I, Slim M, Jimenez-Perez M, et
al: Comprehensive analysis and insights gained from long-term
experience of the Spanish DILI registry. J Hepatol. 75:86–97.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Takahashi A, Arinaga-Hino T, Ohira H,
Torimura T, Zeniya M, Abe M, Yoshizawa K, Takaki A, Suzuki Y, Kang
JH, et al: Autoimmune hepatitis in Japan: Trends in a nationwide
survey. J Gastroenterol. 52:631–640. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang H, Fu J, Liu G, Wang L, Yan A and
Wang G: Drug induced autoimmune hepatitis (DIAIH): Pathological and
clinical study. Biomed Res. 28:6028–6034. 2017.
|