|
1
|
Aranha MM, Matos AR, Teresa Mendes A, Vaz
Pinto V, Rodrigues CM and Arrabaça JD: Dinitro-o-cresol induces
apoptosis-like cell death but not alternative oxidase expression in
soybean cells. J Plant Physiol. 164:675–684. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mariot P, Prevarskaya N, Roudbaraki MM, Le
Bourhis X, Van Coppenolle F, Vanoverberghe K and Skryma R: Evidence
of functional ryanodine receptor involved in apoptosis of prostate
cancer (LNCaP) cells. Prostate. 43:205–214. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yue Z, She RP, Bao HH, Tian J, Yu P, Zhu
J, Chang L, Ding Y and Sun Q: Necrosis and apoptosis of renal
tubular epithelial cells in rats exposed to 3-methyl-4-nitrophenol.
Environ Toxicol. 27:653–661. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hsu JE, Lo SH, Lin YY, Wang HT and Chen
CY: Effects of essential oil mixtures on nitrogen metabolism and
odor emission via in vitro simulated digestion and in vivo growing
pig experiments. J Sci Food Agric. 102:1939–1947. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Saleh-E-In MM, Bhattacharyya P and Van
Staden J: Chemical composition and cytotoxic activity of the
essential oil and oleoresins of in vitro micropropagated Ansellia
africana Lindl: A Vulnerable Medicinal Orchid of Africa. Molecules.
26(4556)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tanaka S, Yano S, Sheikh AM, Nagai A and
Sugimoto T: Effects of uremic toxin p-cresol on proliferation,
apoptosis, differentiation, and glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 cells.
Artif Organs. 38:566–571. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
de Carvalho JT Jr, Dalboni MA, Watanabe R,
Peres AT, Goes MA, Manfredi SR, Canziani ME, Cendoroglo GS,
Guimaraes-Souza N, Batista MC and Cendoroglo M: Effects of
spermidine and p-cresol on polymorphonuclear cell apoptosis and
function. Artif Organs. 35:E27–E32. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Letertre MPM, Myridakis A, Whiley L,
Camuzeaux S, Lewis MR, Chappell KE, Thaikkatil A, Dumas ME,
Nicholson JK, Swann JR and Wilson ID: A targeted ultra performance
liquid chromatography-Tandem mass spectrometric assay for tyrosine
and metabolites in urine and plasma: Application to the effects of
antibiotics on mice. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci.
1164(122511)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
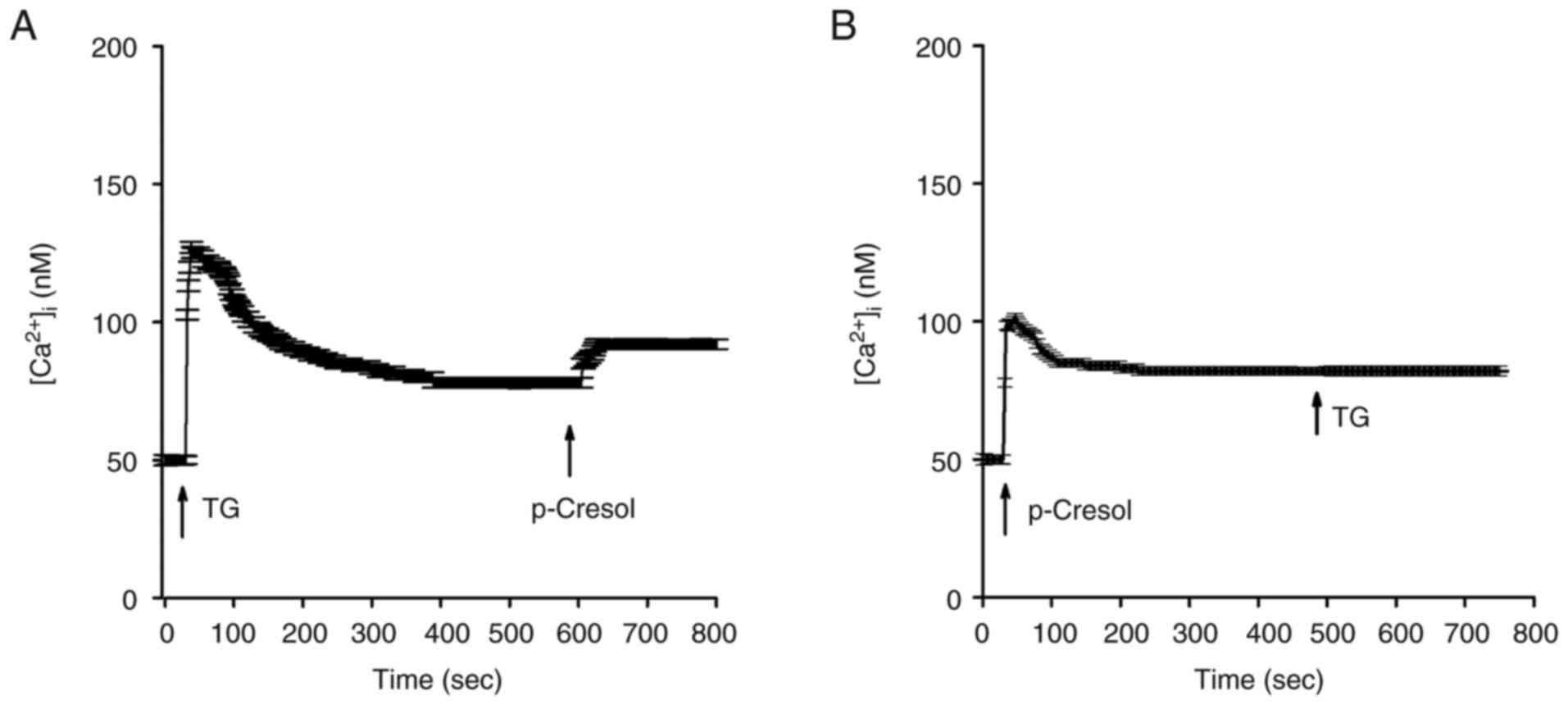
Berridge MJ: Calcium signalling in health
and disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 485(5)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bootman MD and Bultynck G: Fundamentals of
cellular calcium signaling: A Primer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 12(a038802)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Al-Mousa F and Michelangeli F: Commonly
used ryanodine receptor activator, 4-chloro-m-cresol(4CmC), is also
an inhibitor of SERCA Ca2+ pumps. Pharmacol Rep.
61:838–842. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lin AH, Sun H, Paudel O, Lin MJ and Sham
JS: Conformation of ryanodine receptor-2 gates store-operated
calcium entry in rat pulmonary arterial myocytes. Cardiovasc Res.
111:94–104. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hauser CJ, Kannan KB, Deitch EA and
Itagaki K: Non-specific effects of 4-chloro-m-cresol may cause
calcium flux and respiratory burst in human neutrophils. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 336:1087–1095. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Arai S, Ikeda M, Ide T, Matsuo Y, Fujino
T, Hirano K, Sunagawa K and Tsutsui H: Functional loss of DHRS7C
induces intracellular Ca2+ overload and myotube
enlargement in C2C12 cells via calpain activation. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 312:C29–C39. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Suzuki D, Hori T, Saitoh N and Takahashi
T: 4-Chloro-m-cresol, an activator of ryanodine receptors, inhibits
voltage-gated K+ channels at the rat calyx of Held. Eur
J Neurosci. 26:1530–1536. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Baqri W, Rzadki K, Habbous S and Das S:
Treatment, healthcare utilization and outcomes in patients with
glioblastoma in Ontario: A 10-year cohort study. J Neurooncol.
168:473–485. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liang T, Gu L, Kang X, Li J, Song Y, Wang
Y and Ma W: Programmed cell death disrupts inflammatory tumor
microenvironment (TME) and promotes glioblastoma evolution. Cell
Commun Signal. 22(333)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Srivastava R, Dodda M, Zou H, Li X and Hu
B: Tumor Niches: Perspectives for targeted therapies in
glioblastoma. Antioxid Redox Signal. 39:904–922. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Stachulski AV, Knausenberger TB, Shah SN,
Hoyles L and McArthur S: A host-gut microbial amino acid
co-metabolite, p-cresol glucuronide, promotes blood-brain barrier
integrity in vivo. Tissue Barriers. 11(2073175)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chang KF, Liu CY, Huang YC, Hsiao CY and
Tsai NM: Downregulation of VEGFR2 signaling by cedrol abrogates
VEGF-driven angiogenesis and proliferation of glioblastoma cells
through AKT/P70S6K and MAPK/ERK1/2 pathways. Oncol Lett.
26(342)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ertilav K and Nazıroğlu M: Honeybee venom
melittin increases the oxidant activity of cisplatin and kills
human glioblastoma cells by stimulating the TRPM2 channel. Toxicon.
222(106993)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Akyuva Y and Nazıroğlu M: Silver
nanoparticles potentiate antitumor and oxidant actions of cisplatin
via the stimulation of TRPM2 channel in glioblastoma tumor cells.
Chem Biol Interact. 369(110261)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
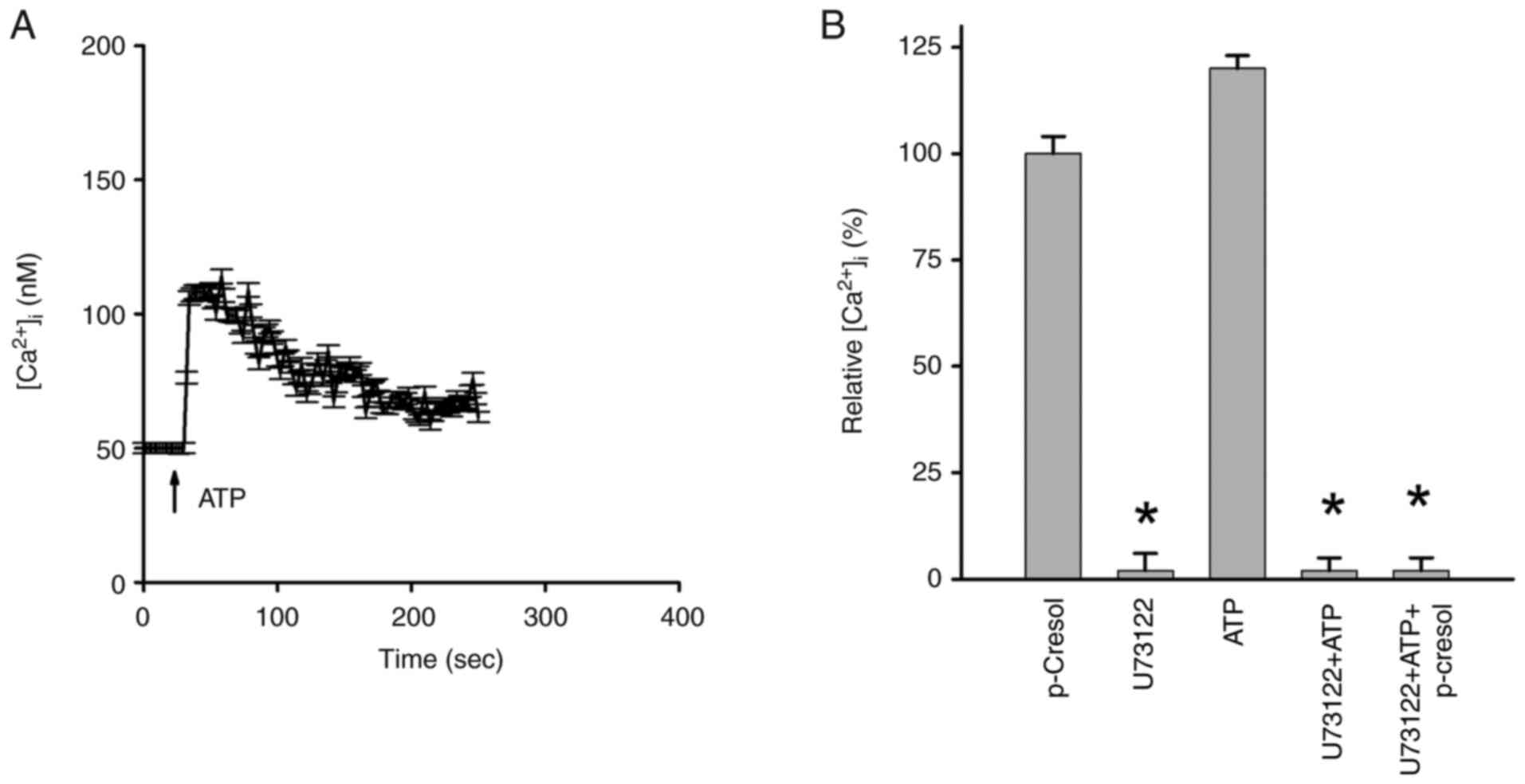
Ashokan A and Aradhyam GK: Measurement of
intracellular Ca2+ mobilization to study GPCR signal
transduction. Methods Cell Biol. 142:59–66. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Absi M, Eid BG, Ashton N, Hart G and
Gurney AM: Simvastatin causes pulmonary artery relaxation by
blocking smooth muscle ROCK and calcium channels: Evidence for an
endothelium-independent mechanism. PLoS One.
14(e0220473)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Segal S and Yaniv Y:
Ca2+-Driven selectivity of the effect of the cardiotonic
steroid marinobufagenin on rabbit sinoatrial node function. Cells.
12(1881)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gruszczynska-Biegala J, Strucinska K,
Maciag F, Majewski L, Sladowska M and Kuznicki J: STIM
Protein-NMDA2 receptor interaction decreases NMDA-Dependent calcium
levels in cortical neurons. Cells. 9(160)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hsu WL, Hsieh YC, Yu HS, Yoshioka T and Wu
CY: 2-Aminoethyl diphenylborinate inhibits bleomycin-induced skin
and pulmonary fibrosis via interrupting intracellular
Ca2+ regulation. J Dermatol Sci. 103:101–108.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chiu KM, Lee MY, Lu CW, Lin TY and Wang
SJ: Plantainoside D reduces depolarization-evoked glutamate release
from rat cerebral cortical synaptosomes. Molecules.
28(1313)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tauskela JS, Brunette E, Aylsworth A and
Zhao X: Neuroprotection against supra-lethal ‘stroke in a dish’
insults by an anti-excitotoxic receptor antagonist cocktail.
Neurochem Int. 158(105381)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Couly S, Yasui Y, Foncham S, Grammatikakis
I, Lal A, Shi L and Su TP: Benzomorphan and non-benzomorphan
agonists differentially alter sigma-1 receptor quaternary
structure, as does types of cellular stress. Cell Mol Life Sci.
81(14)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hung Y, Chung CC, Chen YC, Kao YH, Lin WS,
Chen SA and Chen YJ: Klotho modulates pro-fibrotic activities in
human atrial fibroblasts through inhibition of phospholipase C
signaling and suppression of store-operated calcium entry.
Biomedicines. 10(1574)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu Z, Wu X, Wang Q, Li Z, Liu X, Sheng X,
Zhu H, Zhang M, Xu J, Feng X, et al: CD73-Adenosine A1R Axis
regulates the activation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells
through the PLC-IP3-Ca2+/DAG-PKC signaling pathway.
Front Pharmacol. 13(922885)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ishikawa J, Ohga K, Yoshino T, Takezawa R,
Ichikawa A, Kubota H and Yamada T: A pyrazole derivative, YM-58483,
potently inhibits store-operated sustained Ca2+ influx
and IL-2 production in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 170:4441–4449.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shideman CR, Reinardy JL and Thayer SA:
gamma-Secretase activity modulates store-operated Ca2+
entry into rat sensory neurons. Neurosci Lett. 451:124–128.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cuoghi A, Caiazzo M, Bellei E, Monari E,
Bergamini S, Palladino G, Ozben T and Tomasi A: Quantification of
p-cresol sulphate in human plasma by selected reaction monitoring.
Anal Bioanal Chem. 404:2097–2104. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|