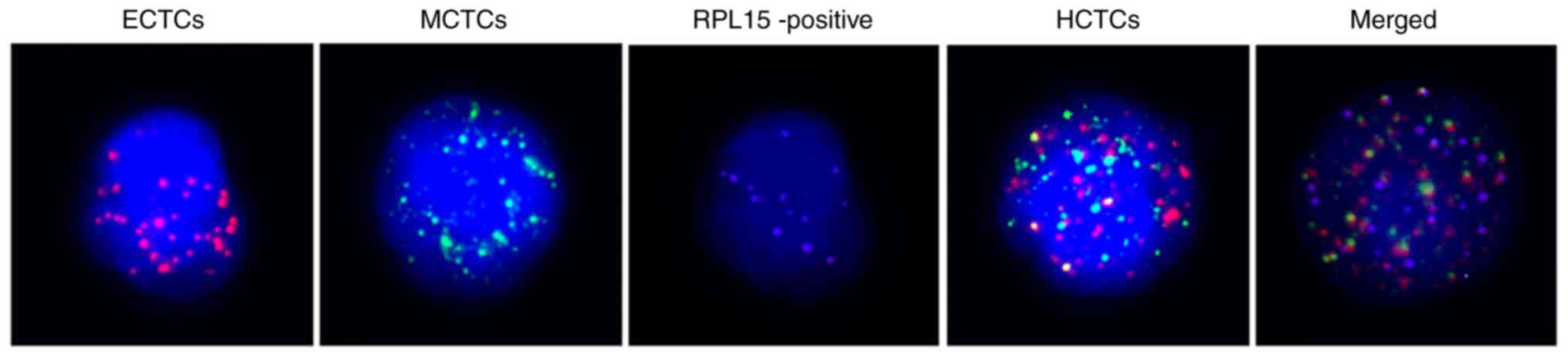
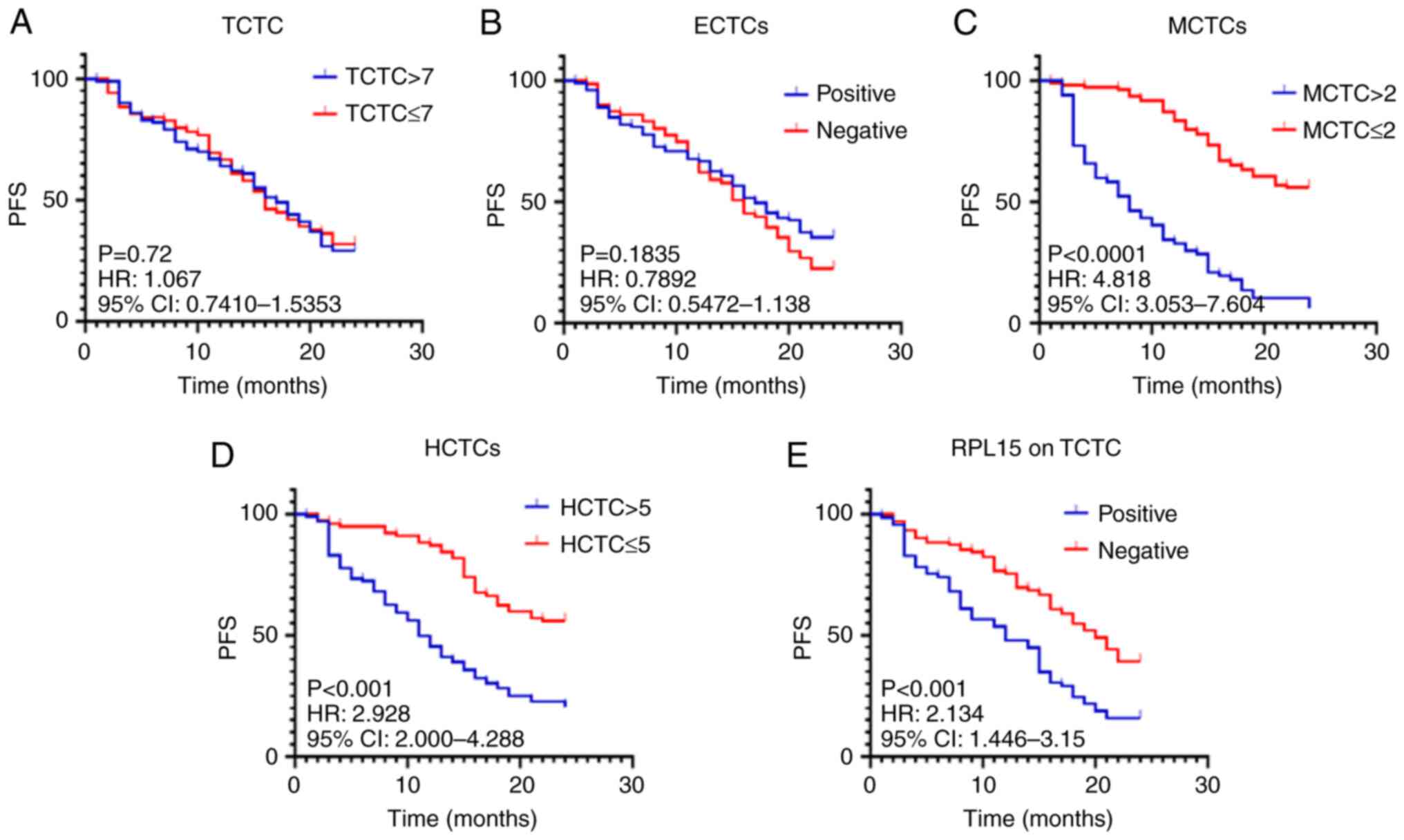
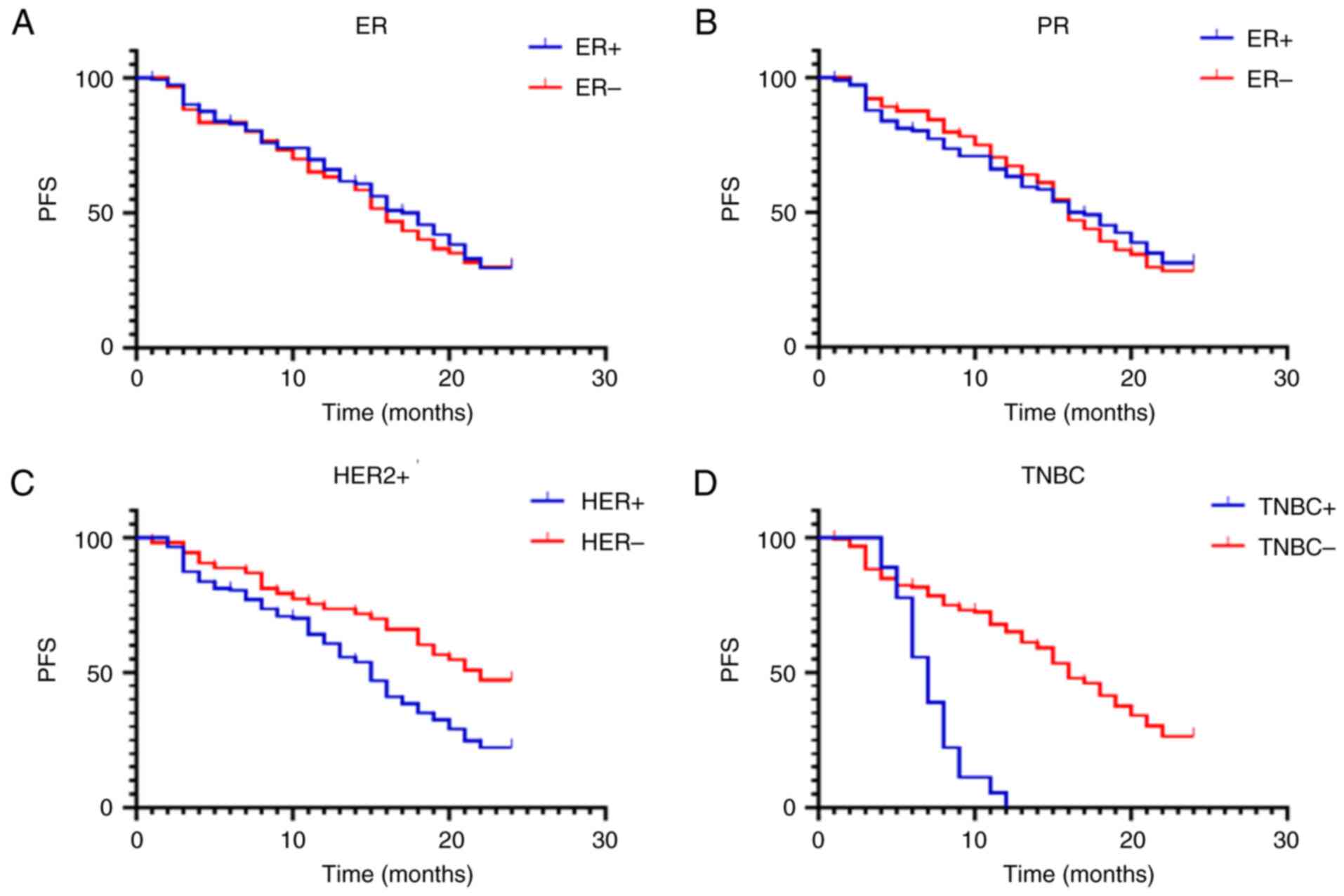
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Xia C,
Zuo T, Yang Z, Zou X and He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in
China, 2013. Cancer Lett. 401:63–71. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Balasubramanian R, Rolph R, Morgan C and
Hamed H: Genetics of breast cancer: Management strategies and
risk-reducing surgery. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 80:720–725.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Laversanne M, Brewster
DH, Gombe Mbalawa C, Kohler B, Piñeros M, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Swaminathan R, Antoni S, et al: Cancer incidence in five
continents: Inclusion criteria, highlights from volume X and the
global status of cancer registration. Int J Cancer. 137:2060–2071.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in
Breast Cancer. Breast cancer and breastfeeding: collaborative
reanalysis of individual data from 47 epidemiological studies in 30
countries, including 50302 women with breast cancer and 96973 women
without the disease. Lancet. 360:187–195. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gage M, Wattendorf D and Henry LR:
Translational advances regarding hereditary breast cancer
syndromes. J Surg Oncol. 105:444–451. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Oeffinger KC, Fontham ET, Etzioni R,
Herzig A, Michaelson JS, Shih YC, Walter LC, Church TR, Flowers CR,
LaMonte SJ, et al: Breast cancer screening for women at average
risk: 2015 Guideline update from the American cancer society. JAMA.
314:1599–1614. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fleshner L, Lagree A, Shiner A, Alera MA,
Bielecki M, Grant R, Kiss A, Krzyzanowska MK, Cheng I, Tran WT and
Gandhi S: Drivers of emergency department use among oncology
patients in the era of novel cancer therapeutics: A systematic
review. Oncologist. 28:1020–1033. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Egelston CA, Guo W, Yost SE, Ge X, Lee JS,
Frankel PH, Cui Y, Ruel C, Schmolze D, Murga M, et al:
Immunogenicity and efficacy of pembrolizumab and doxorubicin in a
phase I trial for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast
cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 72:3013–3027. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao J, Li GY, Lu XY, Zhu LR and Gao Q:
Landscape of m6A RNA methylation regulators in liver
cancer and its therapeutic implications. Front Pharmacol.
15(1376005)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Du C, Wu X, He M, Zhang Y, Zhang R and
Dong CM: Polymeric photothermal agents for cancer therapy: Recent
progress and clinical potential. J Mater Chem B. 9:1478–1490.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kumar V, Garg V and Dureja H:
Nanomedicine-based approaches for delivery of herbal compounds.
Tradit Med Res. 7(48)2022.
|
|
14
|
Gao Z, Zheng S, Kamei K and Tian C: Recent
progress in cancer therapy based on the combination of ferroptosis
with photodynamic therapy. Acta Mater Med. 1:411–426. 2022.
|
|
15
|
Huober J and Thurlimann B: The role of
combination chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with
metastatic breast cancer. Breast Care (Basel). 4:367–372.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cohen EN, Jayachandran G, Moore RG,
Cristofanilli M, Lang JE, Khoury JD, Press MF, Kim KK, Khazan N,
Zhang Q, et al: A multi-center clinical study to harvest and
characterize circulating tumor cells from patients with metastatic
breast cancer using the Parsortix® PC1 system. Cancers
(Basel). 14(5238)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yu M, Bardia A, Wittner BS, Stott SL, Smas
ME, Ting DT, Isakoff SJ, Ciciliano JC, Wells MN, Shah AM, et al:
Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in
epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science. 339:580–584.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fina E: Signatures of breast cancer
progression in the blood: What could be learned from circulating
tumor cell transcriptomes. Cancers (Basel). 14(5668)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li J, Liao Y, Ran Y, Wang G, Wu W, Qiu Y,
Liu J, Wen N, Jing T, Wang H and Zhang S: Evaluation of sensitivity
and specificity of CanPatrol™ technology for detection
of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small cell lung
cance. BMC Pulm Med. 20(274)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ho KH, Huang TW, Shih CM, Lee YT, Liu AJ,
Chen PH and Chen KC: Glycolysis-associated lncRNAs identify a
subgroup of cancer patients with poor prognoses and a
high-infiltration immune microenvironment. BMC Med.
19(59)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lu H, Li Z, Liu L, Tao Y, Zhou Y, Mao X,
Zhu A, Wu H and Zheng X: A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic
roles of RAD51 in human tumors. Adv Gut Microbiome Res.
2022(1591377)2022.
|
|
22
|
Mäurer M, Schott D, Pizon M, Drozdz S,
Wendt T, Wittig A and Pachmann K: Increased circulating epithelial
tumor cells (CETC/CTC) over the course of adjuvant radiotherapy is
a predictor of less favorable outcome in patients with early-stage
breast cancer. Curr Oncol. 30:261–273. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cristofanilli M, Budd GT, Ellis MJ,
Stopeck A, Matera J, Miller MC, Reuben JM, Doyle GV, Allard WJ,
Terstappen LW and Hayes DF: Circulating tumor cells, disease
progression, and survival in metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J
Med. 351:781–791. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu S, Liu S, Liu Z, Huang J, Pu X, Li J,
Yang D, Deng H, Yang N and Xu J: Classification of circulating
tumor cells by epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers. PLoS One.
10(e0123976)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jung R, Krüger W, Hosch S, Holweg M,
Kröger N, Gutensohn K, Wagener C, Neumaier M and Zander AR:
Specificity of reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction
assays designed for the detection of circulating cancer cells is
influenced by cytokines in vivo and in vitro. Br J Cancer.
78:1194–1198. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Giuliano M, Giordano A, Jackson S, Hess
KR, De Giorgi U, Mego M, Handy BC, Ueno NT, Alvarez RH, De
Laurentiis M, et al: Circulating tumor cells as prognostic and
predictive markers in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving
first-line systemic treatment. Breast Cancer Res.
13(R67)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mego M, Cierna Z, Janega P, Karaba M,
Minarik G, Benca J, Sedlácková T, Sieberova G, Gronesova P,
Manasova D, et al: Relationship between circulating tumor cells and
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in early breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 15(533)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mancheng AD and Ossas U: How does lncrna
regulation impact cancer metastasis. Cancer Insight. 1(6)2022.
|
|
29
|
Riethdorf S, Fritsche H, Müller V, Rau T,
Schindlbeck C, Rack B, Janni W, Coith C, Beck K, Jänicke F, et al:
Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of
patients with metastatic breast cancer: A validation study of the
CellSearch system. Clin Cancer Res. 13:920–928. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Balic M, Dandachi N, Hofmann G, Samonigg
H, Loibner H, Obwaller A, van der Kooi A, Tibbe AG, Doyle GV,
Terstappen LW and Bauernhofer T: Comparison of two methods for
enumerating circulating tumor cells in carcinoma patients.
Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 68:25–30. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cruz I, Ciudad J, Cruz JJ, Ramos M,
Gómez-Alonso A, Adansa JC, Rodríguez C and Orfao A: Evaluation of
multiparameter flow cytometry for the detection of breast cancer
tumor cells in blood samples. Am J Clin Pathol. 123:66–74.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Meng S, Tripathy D, Frenkel EP, Shete S,
Naftalis EZ, Huth JF, Beitsch PD, Leitch M, Hoover S, Euhus D, et
al: Circulating tumor cells in patients with breast cancer
dormancy. Clin Cancer Res. 10:8152–8162. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang J, Ma J, Jin Y, Cheng S, Huang S,
Zhang N and Wang Y: Development and validation for prognostic
nomogram of epithelial ovarian cancer recurrence based on
circulating tumor cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci
Rep. 11(6540)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhou H, Shen H, Xiang F, Yang X, Li R,
Zeng Y and Liu Z: Correlation analysis of the expression of
mesenchymal circulating tumor cells and CD133 with the prognosis of
colorectal cancer. Am J Transl Res. 15:3489–3499. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Rath B, Plangger A, Klameth L, Hochmair M,
Ulsperger E, Boeckx B, Neumayer C and Hamilton G: Small cell lung
cancer: Circulating tumor cell lines and expression of mediators of
angiogenesis and coagulation. Explor Target Antitumor Ther.
4:355–365. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Magri V, Marino L, Nicolazzo C, Gradilone
A, De Renzi G, De Meo M, Gandini O, Sabatini A, Santini D, Cortesi
E and Gazzaniga P: Prognostic role of circulating tumor cell
trajectories in metastatic colorectal cancer. Cells.
12(1172)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen H, Li H, Shi W, Qin H and Zheng L:
The roles of m6A RNA methylation modification in cancer stem cells:
New opportunities for cancer suppression. Cancer Insight.
1(10)2022.
|
|
38
|
Gao T, Mao J, Huang J, Luo F, Lin L, Lian
Y, Bin S, Zhao L and Li S: Prognostic significance of circulating
tumor cell measurement in the peripheral blood of patients with
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clinics (Sao Paulo).
78(100179)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang HT, Bai LY, Wang YT, Lin HJ, Yang HR,
Hsueh PR and Cho DY: Circulating tumor cells positivity provides an
early detection of recurrence of pancreatic cancer. J Formos Med
Assoc. 122:653–655. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ebright RY, Lee S, Wittner BS,
Niederhoffer KL, Nicholson BT, Bardia A, Truesdell S, Wiley DF,
Wesley B, Li S, et al: Deregulation of ribosomal protein expression
and translation promotes breast cancer metastasis. Science.
367:1468–1473. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kenmochi N, Kawaguchi T, Rozen S, Davis E,
Goodman N, Hudson TJ, Tanaka T and Page DC: A map of 75 human
ribosomal protein genes. Genome Res. 8:509–523. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ma Y, Xue H, Wang W, Yuan Y and Liang F:
The miR-567/RPL15/TGF-β/Smad axis inhibits the stem-like properties
and chemo-resistance of gastric cancer cells. Transl Cancer Res.
9:3539–3549. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL and Brierley
JD: AJCC cancer staging manual. 8th edition. New York: Springer,
2017.
|
|
44
|
Tsongalis GJ: Branched DNA technology in
molecular diagnostics. Am J Clin Pathol. 126:448–453.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Allison KH, Harvey
BE, Mangu PB, Bartlett JMS, Bilous M, Ellis IO, Fitzgibbons P,
Hanna W, et al: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in
breast cancer: American society of clinical oncology/college of
American pathologists clinical practice guideline focused update. J
Clin Oncol. 36:2105–2122. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Joseph C, Papadaki A, Althobiti M,
Alsaleem M, Aleskandarany MA and Rakha EA: Breast cancer
intratumour heterogeneity: Current status and clinical
implications. Histopathology. 73:717–731. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ji X, Tian X, Feng S, Zhang L, Wang J, Guo
R, Zhu Y, Yu X, Zhang Y, Du H, et al: Intermittent F-actin
perturbations by magnetic fields inhibit breast cancer metastasis.
Research (Wash DC). 6(0080)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Navin N, Krasnitz A, Rodgers L, Cook K,
Meth J, Kendall J, Riggs M, Eberling Y, Troge J, Grubor V, et al:
Inferring tumor progression from genomic heterogeneity. Genome Res.
20:68–80. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Jiang X, Zhong M, Yu B and Yuan H:
Whole genome sequencing of single-circulating tumor cell
ameliorates unraveling breast cancer heterogeneity. Breast Cancer
(Dove Med Press). 14:505–513. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Dong J, Zhu D, Tang X, Qiu X, Lu D, Li B,
Lin D and Zhou Q: Detection of circulating tumor cell molecular
subtype in pulmonary vein predicting prognosis of stage I-III
non-small cell lung cancer patients. Front Oncol.
9(1139)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Wang X, Ma K, Yang Z, Cui J, He H, Hoffman
AR, Hu JF and Li W: Systematic correlation analyses of circulating
tumor cells with clinical variables and tumor markers in lung
cancer patients. J Cancer. 8:3099–3104. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang Q, Yang C, Zhou J, Wang X, Wu M and
Liu Z: Cloning and characterization of full-length human ribosomal
protein L15 cDNA which was overexpressed in esophageal cancer.
Gene. 263:205–209. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Nindl I, Dang C, Forschner T, Kuban RJ,
Meyer T, Sterry W and Stockfleth E: Identification of
differentially expressed genes in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
by microarray expression profiling. Mol Cancer.
5(30)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yan TT, Fu XL, Li J, Bian YN, Liu DJ, Hua
R, Ren LL, Li CT, Sun YW, Chen HY, et al: Downregulation of RPL15
may predict poor survival and associate with tumor progression in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:37028–37042.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Shi R and Liu Z: RPL15 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of RPs-MDM2-p53
signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 22(150)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Kitai Y: Elucidation of the mechanism of
topotecan-induced antitumor immune activation. Yakugaku Zasshi.
142:911–916. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Japanese).
|
|
58
|
Yamada S, Kitai Y, Tadokoro T, Takahashi
R, Shoji H, Maemoto T, Ishiura M, Muromoto R, Kashiwakura JI, Ishii
KJ, et al: Identification of RPL15 60S ribosomal protein as a novel
topotecan target protein that correlates with DAMP secretion and
antitumor immune activation. J Immunol. 209:171–179.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Feng H, Liu H, Wang Q, Song M, Yang T,
Zheng L, Wu D, Shao X and Shi G: Breast cancer diagnosis and
prognosis using a high b-value non-Gaussian continuous-time
random-walk model. Clin Radiol. 78:e660–e667. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Mai N, Abuhadra N and Jhaveri K:
Molecularly targeted therapies for triple negative breast cancer:
History, advances, and future directions. Clin Breast Cancer.
23:784–799. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Bartsch R and Bergen E: ASCO 2018:
Highlights in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Memo.
11:280–283. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Papadaki MA, Stoupis G, Theodoropoulos PA,
Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V and Agelaki S: Circulating tumor cells
with stemness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition features are
chemoresistant and predictive of poor outcome in metastatic breast
cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:437–447. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Ahn S, Woo JW, Lee K and Park SY: HER2
status in breast cancer: Changes in guidelines and complicating
factors for interpretation. J Pathol Transl Med. 54:34–44.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|