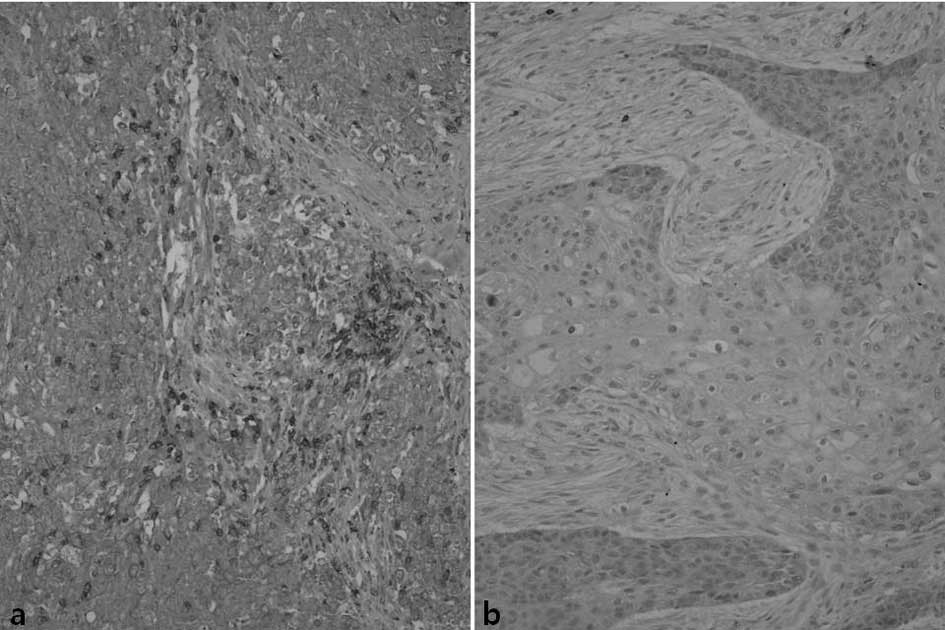
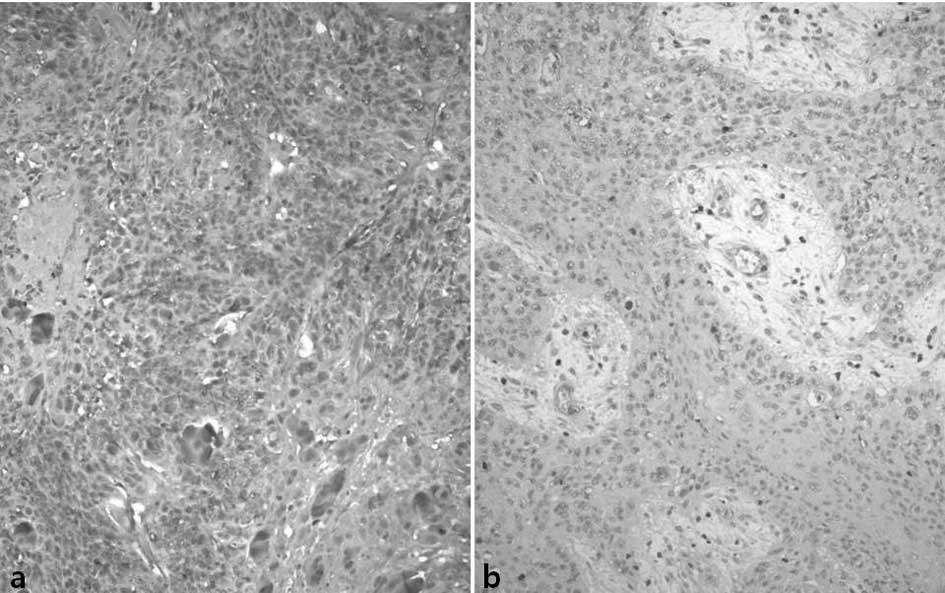
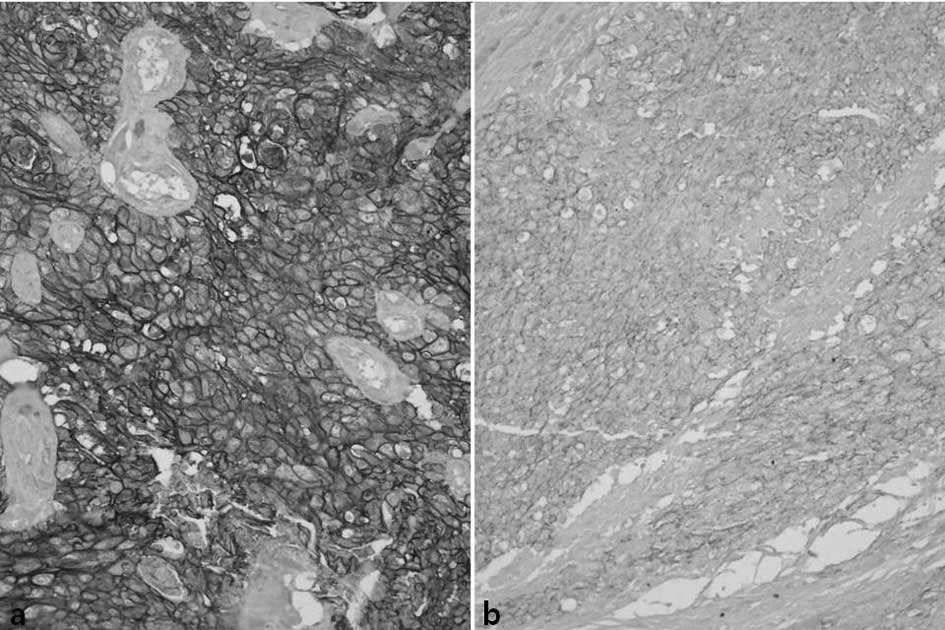
|
1.
|
Zender CA and Petruzzelli GJ: Why do
patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma experience
distant metastases: can they be prevented? Curr Opin Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 2:101–104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Lin DT, Subbaramaiah K, Shah JP,
Dannenberg AJ and Boyle JO: Cyclooxygenase-2: a novel molecular
target for the prevention and treatment of head and neck cancer.
Head Neck. 8:792–799. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP: Inflammation: a driving
force speeds cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle. 15:3267–3273. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Mukhopadhyay P, Ali MA, Nandi A, Carreon
P, Choy H and Saha D: The cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor
down-regulates interleukin-1β-mediated induction of
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer
Res. 66:1758–1766. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Teruel A, Romero M, Cacalano NA, Head C
and Jewett A: Potential contribution of naive immune effectors to
oral tumor resistance: role in synergistic induction of VEGF, IL-6,
and IL-8 secretion. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 57:359–366. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Bancroft CC, Chen Z, Yeh J, Sunwoo JB, Yeh
NT, Jackson S, Jackson C and van Waes C: Effects of pharmacologic
antagonists of epidermal growth factor receptor, PI3K and MEK
signal kinases on NF-κB and AP-1 activation and IL-8 and VEGF
expression in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines.
Int J Cancer. 99:538–548. 2002.
|
|
7.
|
Wolf JS, Chen Z, Dong G, Sunwoo JB,
Bancroft CC, Capo DE, Yeh NT, Mukaida N and van Waes C: IL
(interleukin)-1α promotes nuclear factor-κB and AP-1-induced IL-8
expression, cell survival, and proliferation in head and neck
squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1812–1820. 2001.
|
|
8.
|
Tsai CC, Chen CC, Lin CC, Chen CH, Lin TS
and Shieh TY: Interleukin-1β in oral submucous fibrosis, verrucous
hyperplasia and squamous cell carcinoma tissues. Kaohsiung J Med
Sci. 15:513–519. 1999.
|
|
9.
|
Williams CS, Mann M and DuBois RN: The
role of cyclooxygenases in inflammation, cancer, and development.
Oncogene. 18:7908–7916. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Langenbach R, Loftin CD, Lee C and Tiano
H: Cyclooxygenasedeficient mice. A summary of their characteristics
and susceptibilities to inflammation and carcinogenesis. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 889:52–61. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Callejas NA, Casado M, Diaz-Guerra MJM,
Bosca L and Martin-Sanz P: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 promotes
the release of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in fetal rat
hepatocytes. Hepatology. 33:860–867. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Martin-Sanz P, Callejas NA, Casado M,
Diaz-Guerra MJ and Bosca L: Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in
foetal rat hepatocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide and
pro-inflammatory cytokines. Br J Pharmacol. 125:1313–1319. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Shioiri M, Shida T, Koda K, Oda K, Seike
K, Nishimura M, Takano S and Miyazaki M: Slug expression is an
independent prognostic parameter for poor survival in colorectal
carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer. 19:1816–1822. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Beahrs OH, Henson DE, Hutter RVP and
Kennedy BJ: Manual for Staging for Cancer 4th edition American
Joint Committee on Cancer. JB Lippincott; Philadelphia: pp.
1992
|
|
18.
|
Lim SC, Park SY and Do NY: Correlation of
cyclooxygenase-2 pathway and VEGF expression in head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 10:1073–1079. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kyo S, Sakaguchi J, Ohno S, Mizumoto Y,
Maida Y, Hashimoto M, Nakamura M, Takakura M, Nakajima M, Masutomi
K and Inoue M: High Twist expression is involved in infiltrative
endometrial cancer and affects patient survival. Hum Pathol.
37:431–438. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Barbera MJ, Puig I, Domínguez D,
Julien-Grille S, Guaita-Esteruelas S, Peiró S, Baulida J, Francí C,
Dedhar S, Larue L and García de Herreros A: Regulation of Snail
transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor
cells. Oncogene. 23:7345–7354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM and
Gunduz M: Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated
phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Nat Cell Biol. 6:931–940. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Larue L and Bellacosa A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role
of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/ AKT pathways. Oncogene.
24:7443–7454. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Thompson EW, Newgreen DF and Tarin D:
Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: a role for epithelial-esenchymal
transition? Cancer Res. 65:5991–5995. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Leemans CR, Tiwari R, Nauta JJ, van der
Waal I and Snow GB: Regional lymph node involvement and its
significance in the development of distant metastases in head and
neck carcinoma. Cancer. 71:452–456. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Buckley JG and
Mondin V: General considerations on distant metastases from head
and neck cancer. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 63:189–191.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Brabant G, Hoang-Vu C and Cetin Y:
E-cadherin: a differentiation marker in thyroid malignancies.
Cancer Res. 53:4987–4993. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Naito A, Iwase H, Kuzushima T, Nakamura T
and Kobayashi S: Clinical significance of E-cadherin expression in
thyroid neoplasms. J Surg Oncol. 76:176–180. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Rocha AS, Soares P, Fonseca E,
Cameselle-Teijeiro J, Oliveira MC and Sobrinho-Simoes M: E-cadherin
loss rather than β-catenin alterations is a common feature of
poorly differentiated thyroid carcinomas. Histopathology.
42:580–587. 2003.
|
|
29.
|
Kato N, Tsuchiya T, Tamura G and Motoyama
T: E-cadherin expression in follicular carcinoma of the thyroid.
Pathol Int. 52:13–18. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, Dominguez D,
Monfar M and Baulida J: The transcription factor snail is a
repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells.
Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Yokoyama K, Kamata N, Fujimoto R, Tsutsumi
S, Tomonari M and Taki M: Increased invasion and matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression by Snail-induced mesenchymal
transition in squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Oncol. 22:891–898.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Yang MH, Chang SY, Chiou SH, Liu CJ, Chi
CW, Chen PM, Teng SC and Wu KJ: Overexpression of NBS1 induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and co-expression of NBS1 and
Snail predicts metastasis of head and neck cancer. Oncogene.
26:1459–1467. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Nieto MA, Sargent MG, Wilkinson DG and
Cooke J: Control of cell behavior during vertebrate development by
Slug, a zinc finger gene. Science. 6:835–859. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Hajra KM, Chen DY and Fearon ER: The SLUG
zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 15:1613–1618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Martin TA, Goyal A, Watkins G and Jiang
WG: Expression of the transcription factors snail, slug, and twist
and their clinical significance in human breast cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 12:488–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Uchikado Y, Natsugoe S, Okumura H,
Setoyama T, Matsumoto M, Ishigami S and Aikou T: Slug expression in
the E-cadherin preserved tumors is related to prognosis in patients
with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
11:1174–1180. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
D’Amours D and Jackson SP: The Mre11
complex: at the crossroads of DNA repair and checkpoint signalling.
Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:317–327. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Loercher A, Lee TL and Ricker JL: Nuclear
factor-κB is an important modulator of the altered gene expression
profile and malignant phenotype in squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 64:6511–6523. 2004.
|
|
40.
|
Chiba T and Marusawa H: A novel mechanism
for inflammation-associated carcinogenesis; an important role of
activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) in mutation induction.
J Mol Med. 87:1023–1027. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41.
|
Costa AC, Figueiredo C and Touati E:
Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter.
14(Suppl 1): 15–20. 2009.
|
|
42.
|
Lim SC, Kim SM, Choi JE, Kim CH, Duong HQ,
Han SI and Kang HS: Sodium salicylate switches glucose
depletion-induced necrosis to autophagy and inhibits high mobility
group box protein 1 release in A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 19:1165–1171. 2008.
|
|
43.
|
Boolbol SK, Dannenberg AJ, Chadburn A,
Martucci C, Guo XJ, Ramonetti JT, Abreu-Goris M, Newmark HL, Lipkin
ML, DeCosse JJ and Bertagnolli MM: Cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression
and tumor formation are blocked by sulindac in a murine model of
familial adenomatous polyposis. Cancer Res. 56:2556–2560.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|