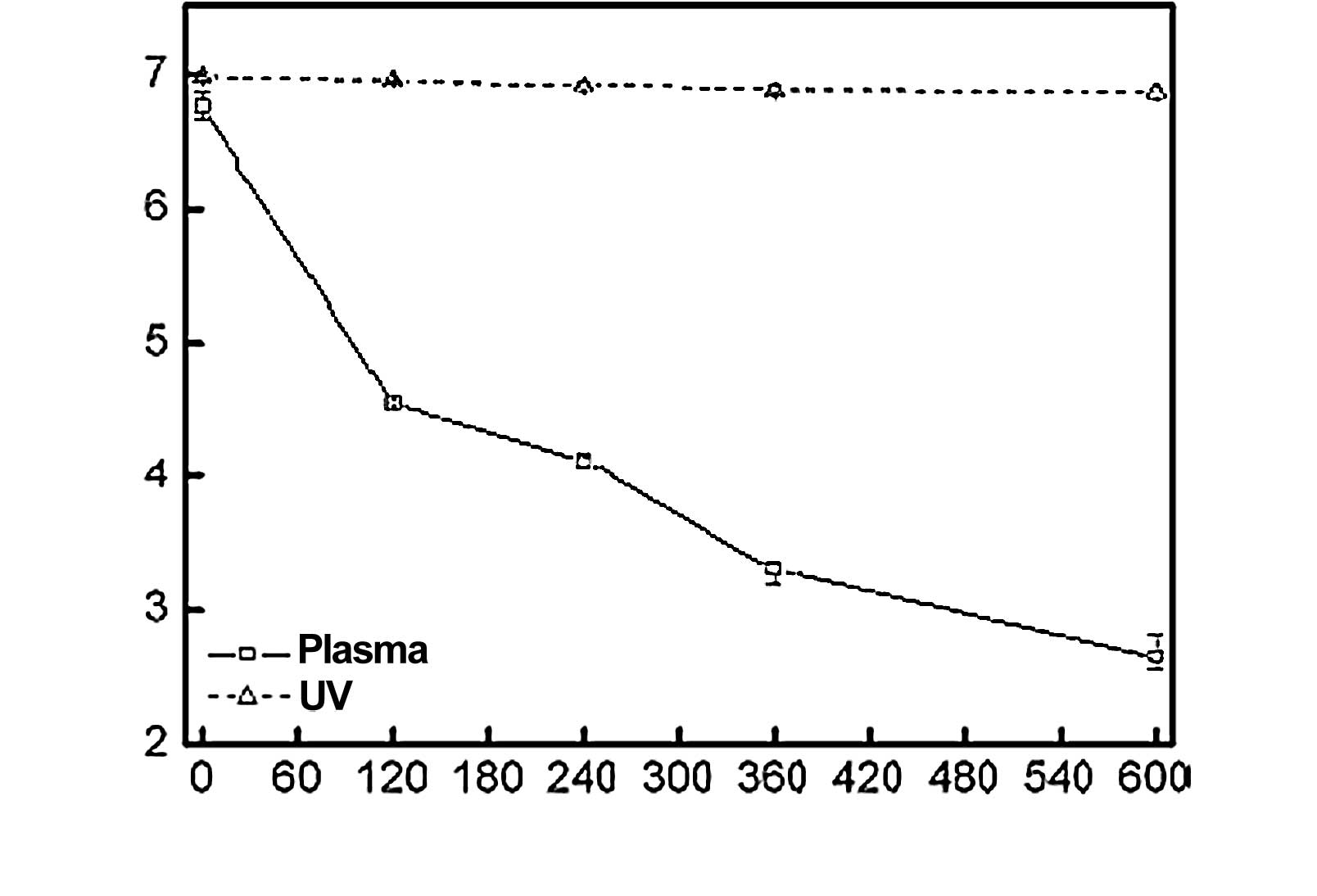
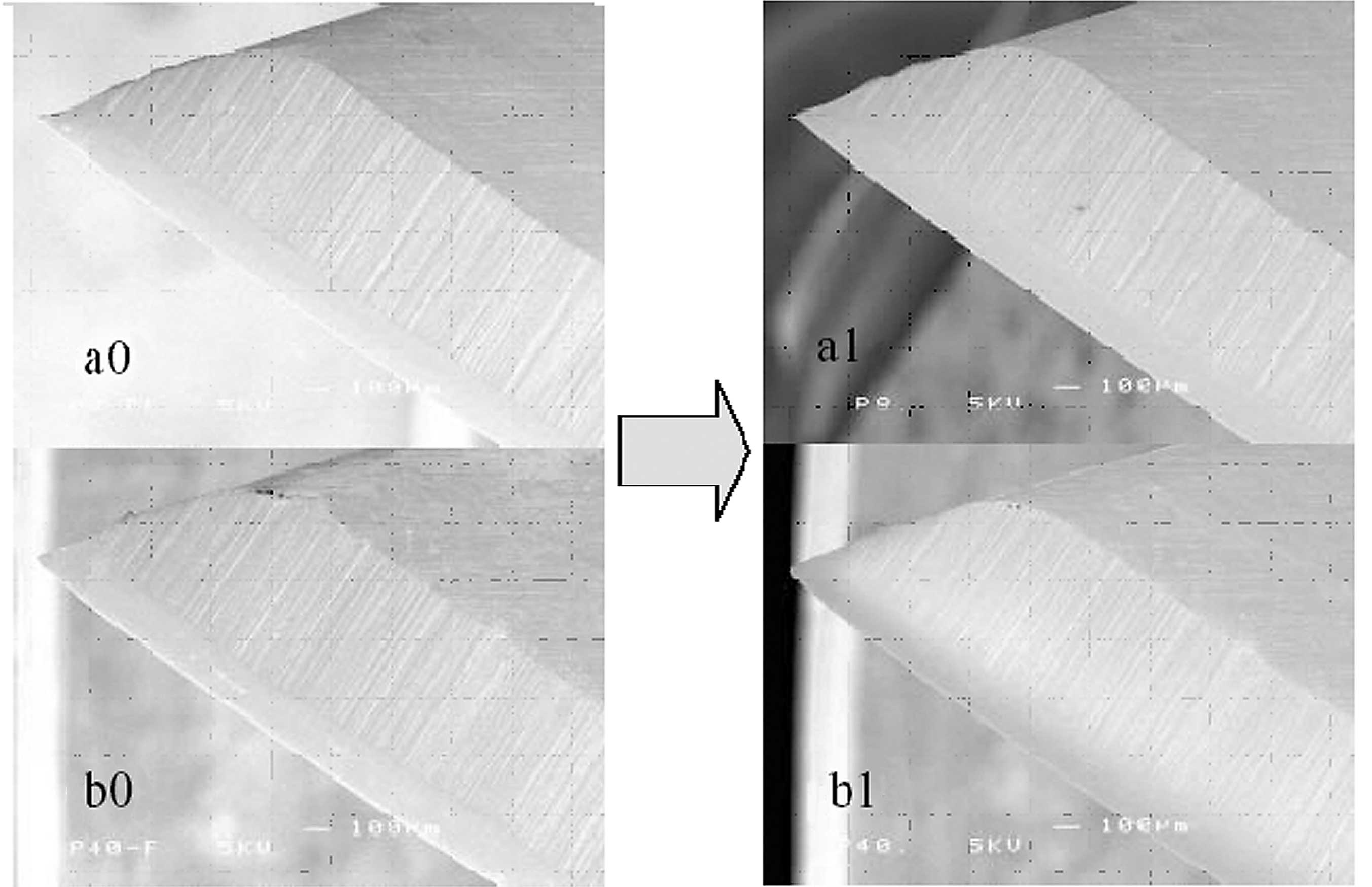
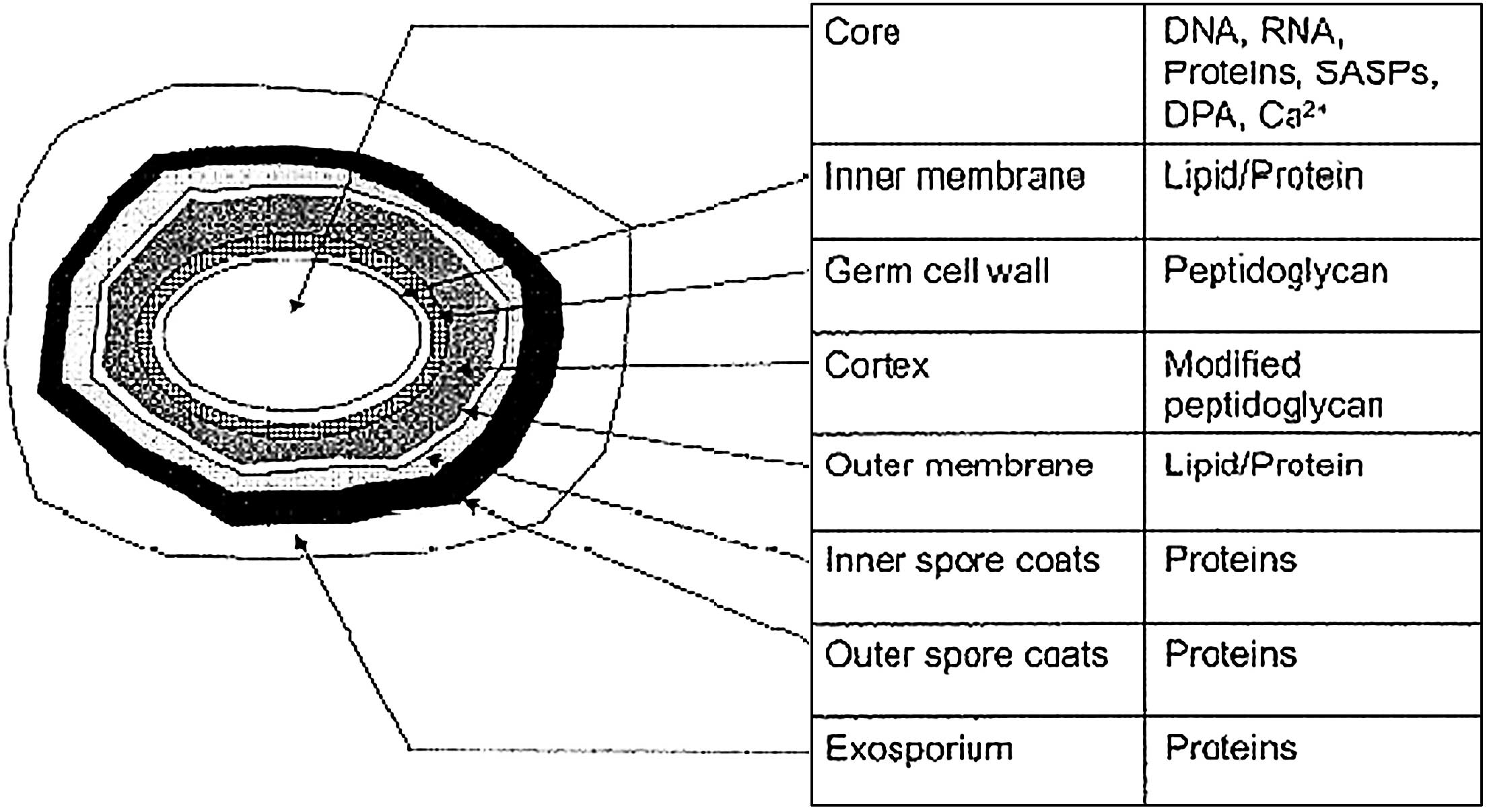
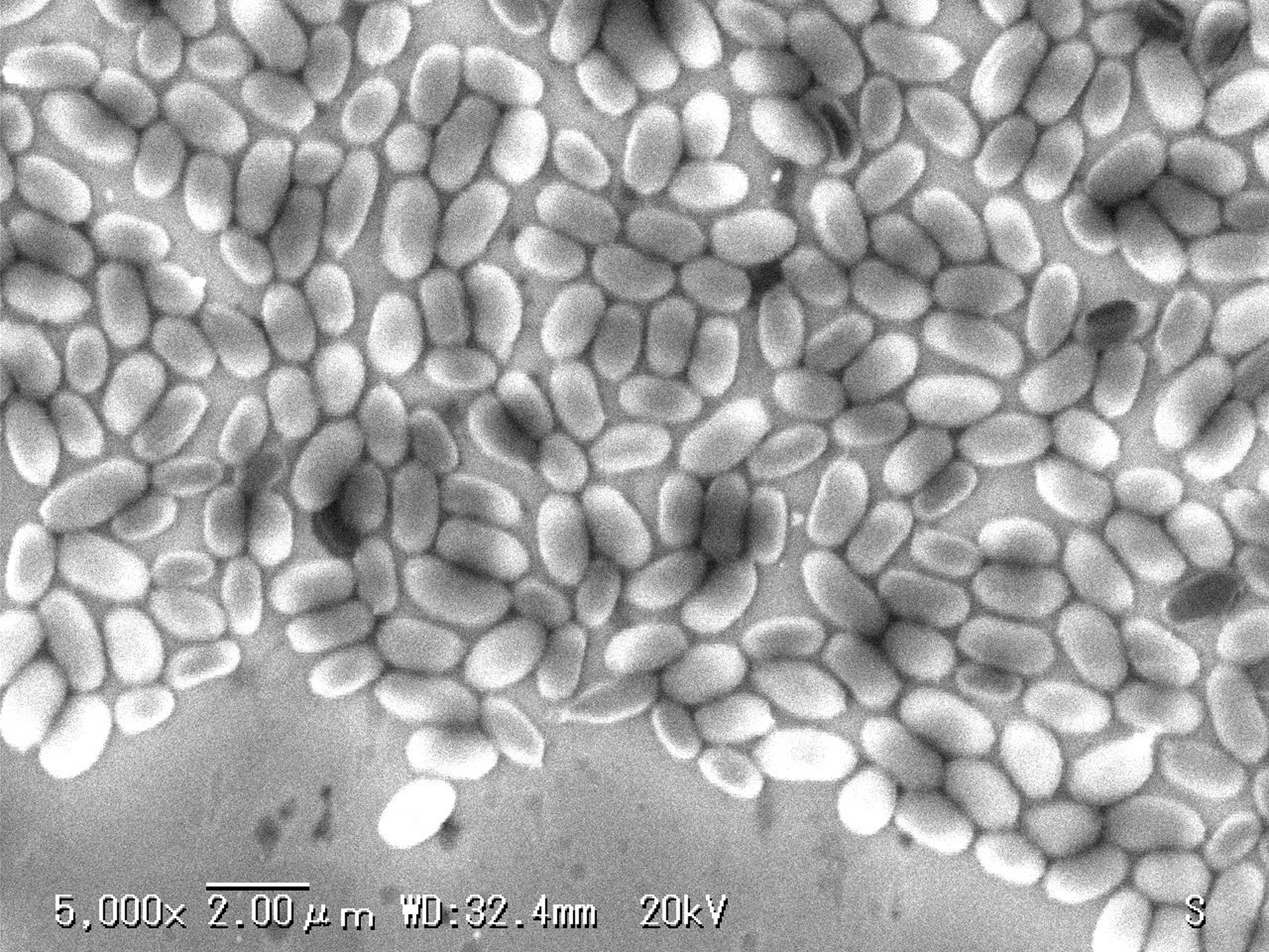
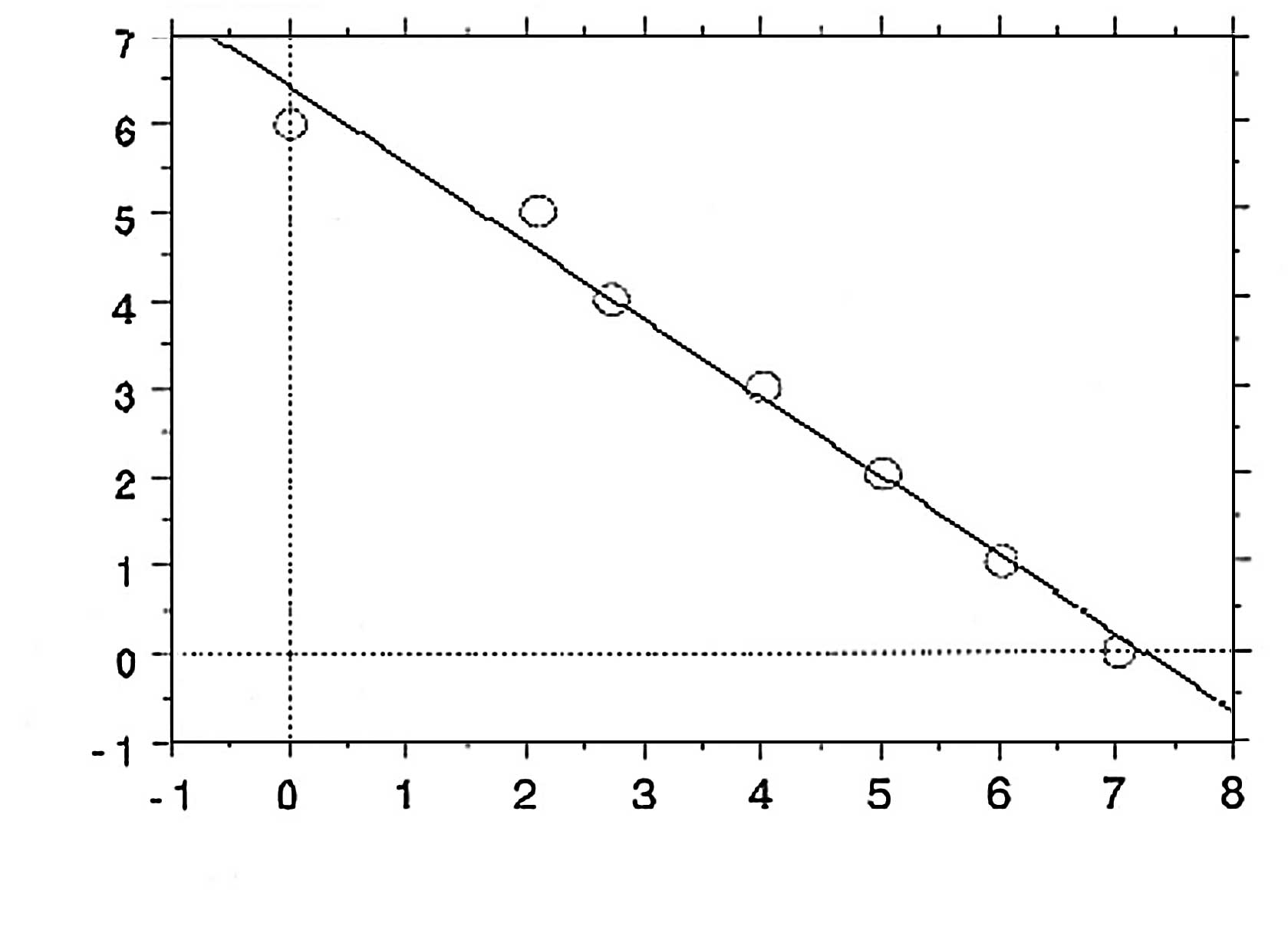
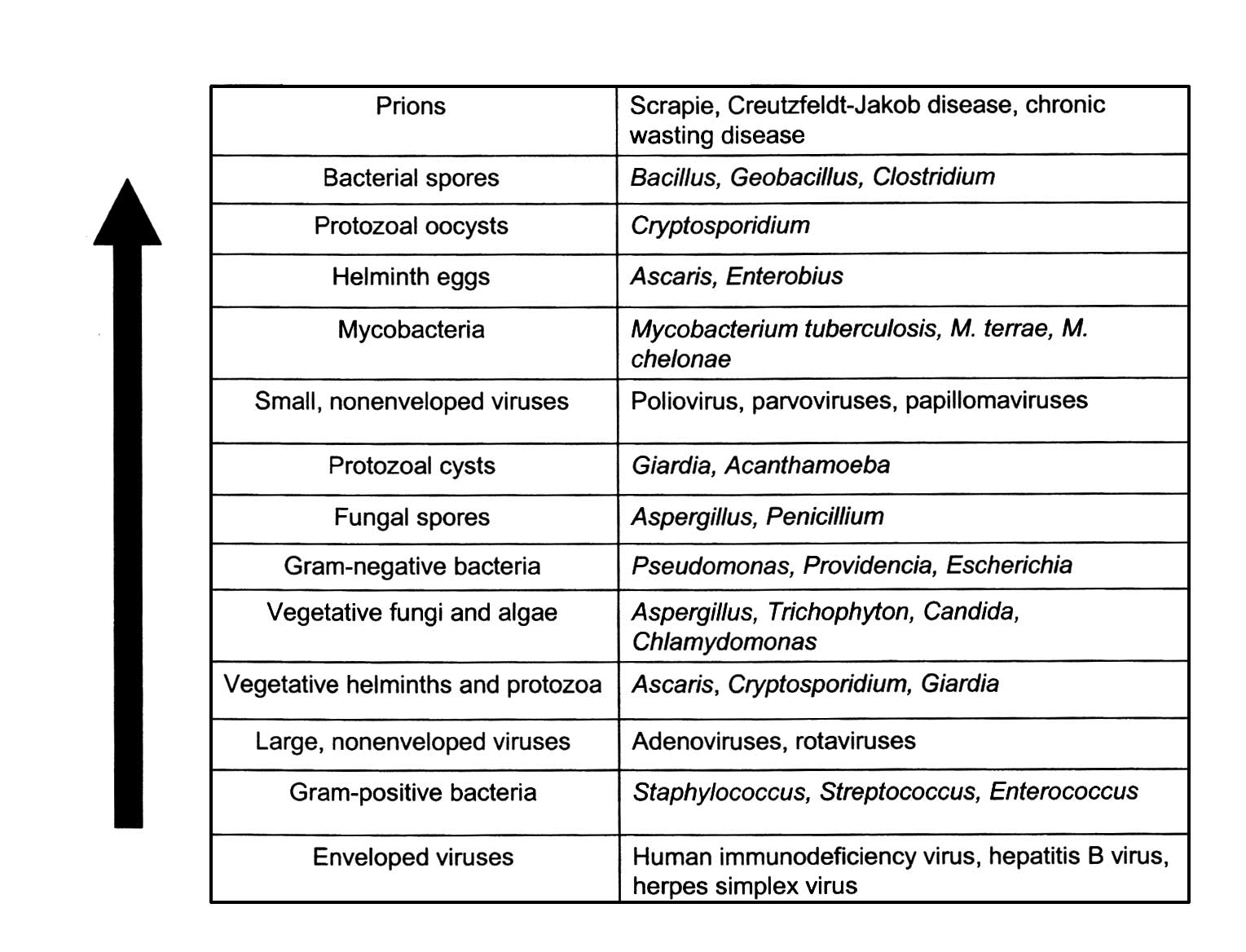
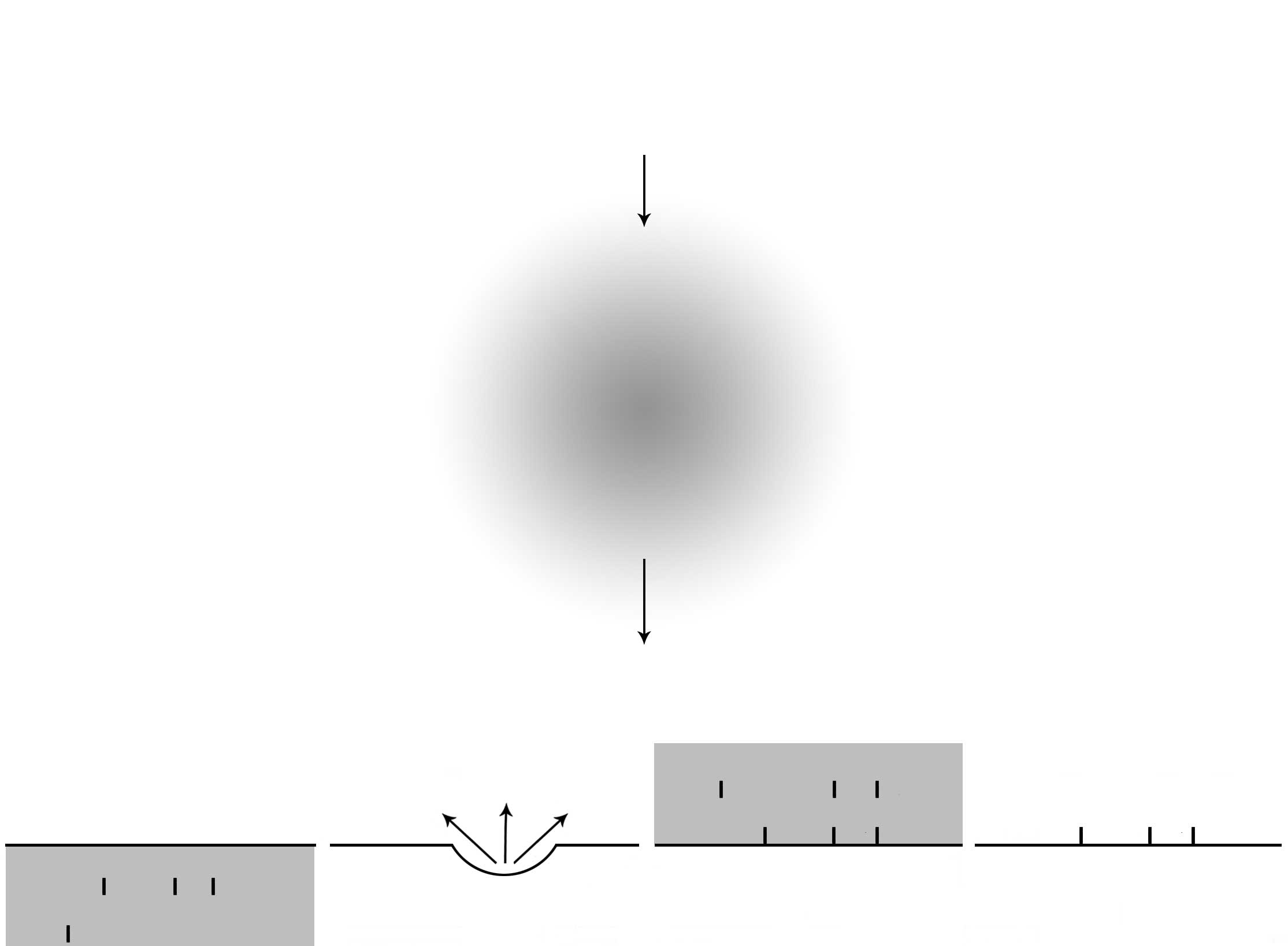
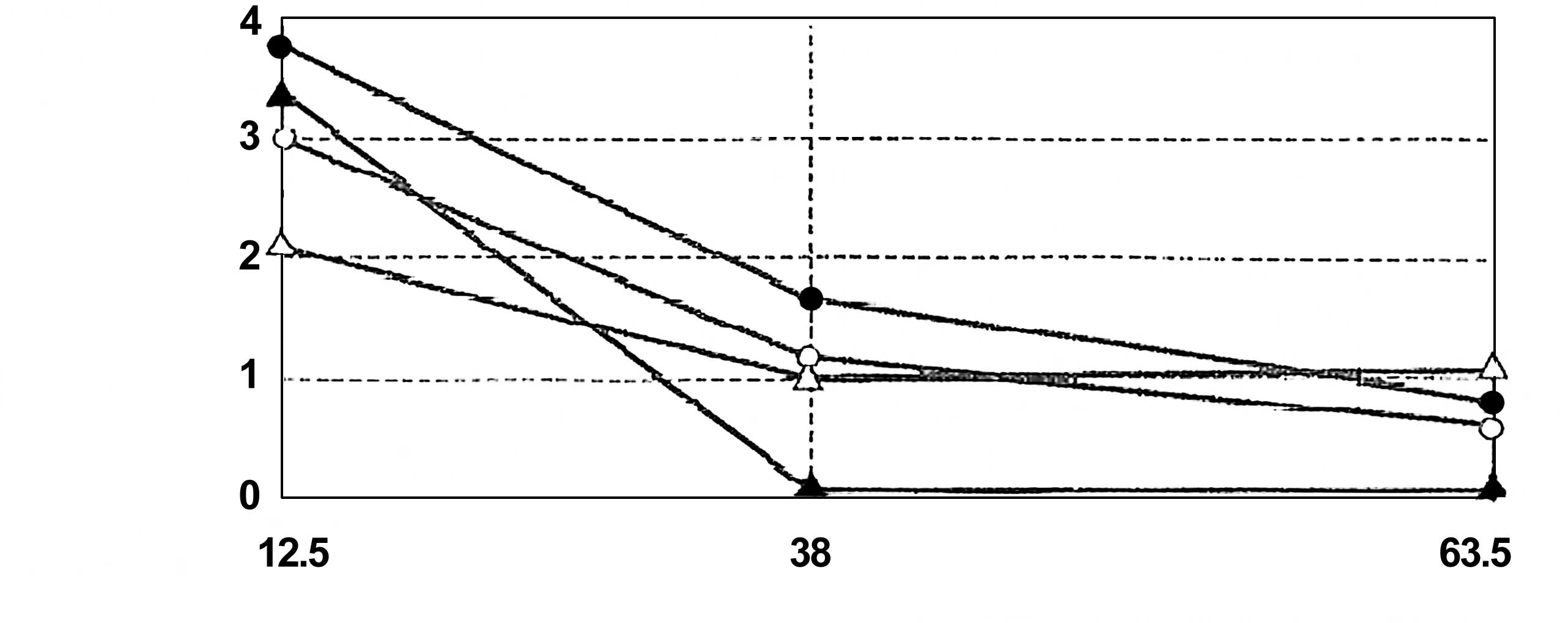
|
1.
|
Shintani H, Shimizu N, Imanishi Y, Sekiya
T, Tamazawa K, Taniguchi A and Kido N: Inactivation of
microorganisms and endotoxins by low temperature nitrogen gas
plasma exposure. Biocontrol Sci. 12:131–143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Krebs MC, Becasse P, Verjat D, et al: Gas
plasma sterilization: relative efficiency of the hydrogen peroxide
phase as compared to that of the plasma phase. Int J Pharm.
160:75–81. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
ISO 14937: 2009, Sterilization of health
care products. General requirements for characterization of a
sterilizing agent and the development, validation and routine
control of a sterilization process for medical devices.
|
|
4.
|
Sato N: Basic approach to plasma
production and control. Advanced Plasma Technology. D'Agostino R,
Favia P, Kawai Y, Ikegami H, Sato N and Arefi-Khonsari F:
Wiley-VCH, Verlag GmbH & Co; Weinheim, Germany: pp. 1–16.
2008
|
|
5.
|
Kylian O, Sasaki T and Rossi F: Plasma
sterilization of Geobacillus stearothermophilus by
O2:N2 RF inductively coupled plasma. Eur Phys
J Appl Phys. 34:139–142. 2006.
|
|
6.
|
Jacobs PT and Lin S-M: Sterilization
processes utilizing low-temperature plasmas. Disinfection,
Sterilization and Preservation. Block SS: Lippincott Williams &
Wilkins; New York: pp. 747–765. 2001
|
|
7.
|
Rossi F, Kylian O and Hasiwa M: Mechanisms
of sterilization and decontamination of surfaces by low-pressure
plasma. Advanced Plasma Technology. D'Agostino R, Favia P, Kawai Y,
Ikegami H, Sato N and Arefi-Khonsari F: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH &
Co; Weinheim, Germany: pp. 319–340. 2008
|
|
8.
|
Rossi F, Kylian O and Hasiwa M:
Decontamination of surfaces by low pressure plasma discharges.
Plasma Process Polym. 3:431–442. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Deng X, Shi J and Kong MG: Physical
mechanisms of inactivation of Bacillus subtilis spores using
cold atmospheric plasmas. IEEE Trans Plasma Sco. 34:1310–1316.
2006.
|
|
10.
|
Kim S-M and Kim J-I: Decomposition of
biological macromolecules by plasma generated with helium and
oxygen. J Microbiol. 44:466–471. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Lee K, Paek K-H, Ju W-T and Lee Y:
Sterilization of bacteria, yeast, and bacterial endospores by
atmospheric-pressure cold plasma using helium and oxygen. J
Microbiol. 44:269–275. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Yu QS, Huang C, Hsieh F-H, Huff H and Duan
Y: Bacterial inactivation using a low-temperature atmospheric
plasma brush sustained with argon gas. J Biomed Mater Res Part B:
Appl Biomater. 80B:211–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Purevdorj D, Igura N, Ariyada O and
Hayakawa I: Effect of feed gas composition of gas charge plasmas on
Bacillus pumillus spore mortality. Lett Appl Microbiol.
37:31–34. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
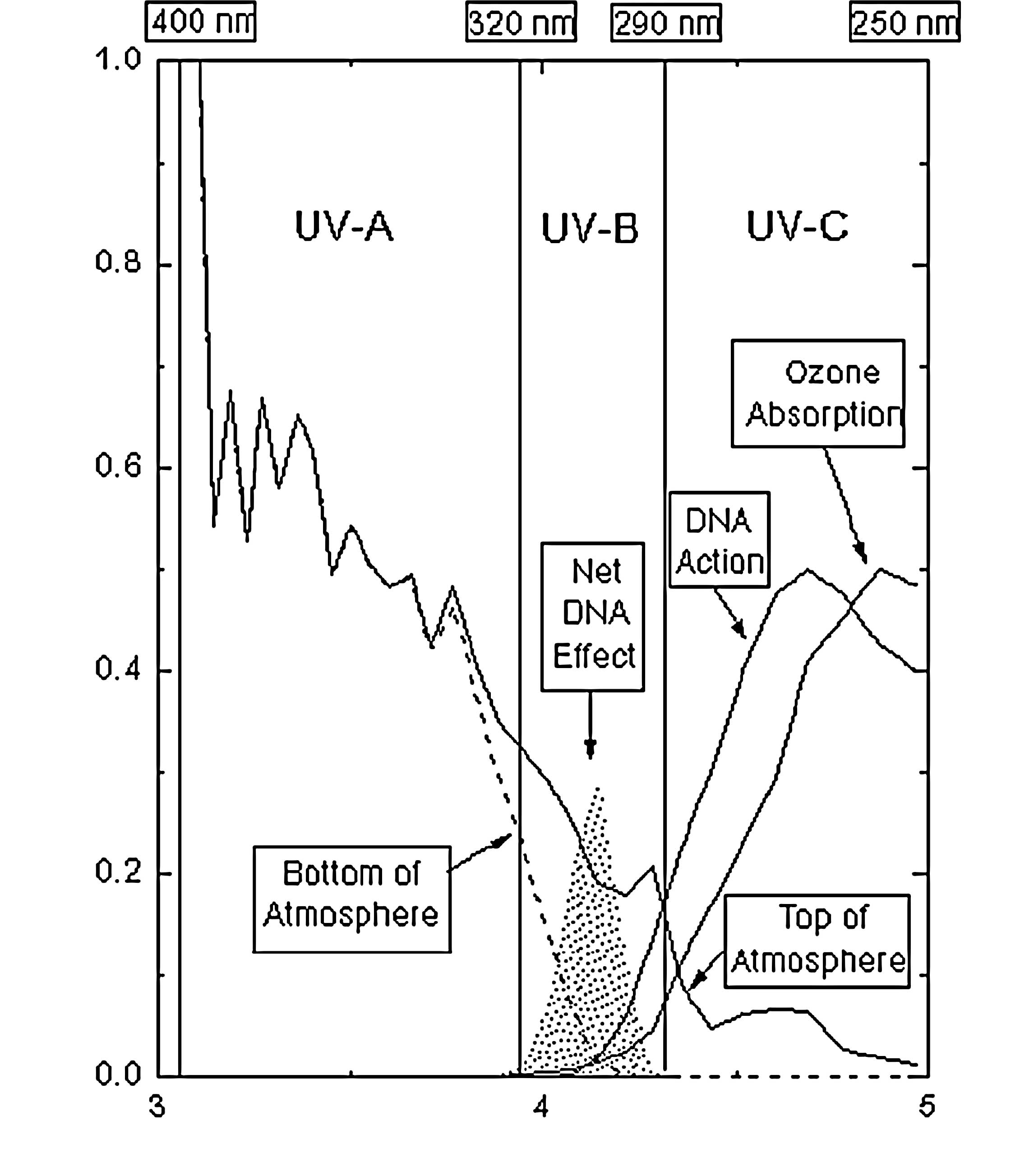
Kinoshita S: Examination of UV and VUV
effect on sterilization. Bohkin Bobai. (In press).
|
|
15.
|
Halfmann H, Bibinov N, Wunderlich J and
Awakowicz P: Correlation between VUV radiation and sterilization
efficiency in a double inductively coupled plasma. In: Presented at
the 28th ICPIG Congress; Prague. pp. 2007
|
|
16.
|
Lerouge S, Fozza AC, Wertheimer MR,
Marchand R and Yahia L: Sterilization by low-pressure plasma: the
role of vacuum-ultraviolet radiation. Plasma Polymers. 5:31–46.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Güçeri S and Fridman A: Plasma Assisted
Decontamination of Biological and Chemical Agents. Springer; The
Netherlands: pp. 2008
|
|
18.
|
McDonnell G: Peroxygens and other forms of
oxygen: their use for effective cleaning, disinfection and
sterilization. New Biocides Development: the Combined Approach of
Chemistry and Microbiology. Zhu PC: Oxford University Press; New
York: pp. 292–308. 2006
|
|
19.
|
Finnegan M, Linley E, Denyer SP, McDonnell
G, Simons C and Maillard J-Y: The mode of action of hydrogen
peroxide and other oxidizing agents: differences in liquid and gas
form. J Pharm Sci. (In press).
|
|
20.
|
McDonnell GE: Antisepsis, Disinfection,
and Sterilization. ASM Press; Washington DC: pp. 33pp. 2822007
|
|
21.
|
Cortezzo DE, Koziol-Dube K, Setlow B and
Setlow P: Treatment with oxidizing agents damages the inner
membrane of spores of Bacillus subtilis and sensitizes
spores to subsequent stress. J Appl Microbiol. 97:838–852. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Setlow P: Spores of bacillus
subtilis: their resistance to and killing by radiation, heat
and chemicals. J Appl Microbiol. 101:514–525. 2006.
|
|
23.
|
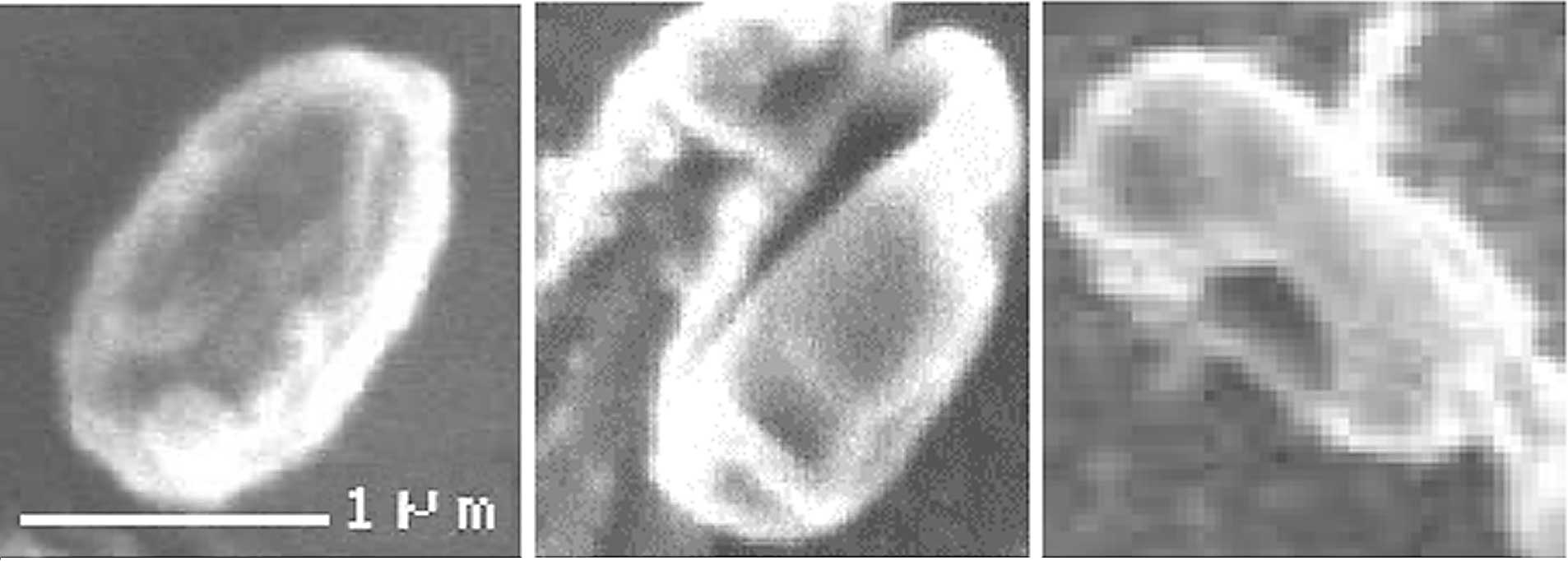
Imae Y, Strominger MB and Strominger J:
Electron microscope studies of conditional spore cortexless mutants
of Bacillus sphaericus. J Bacteriol. 127:1568–1570.
1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
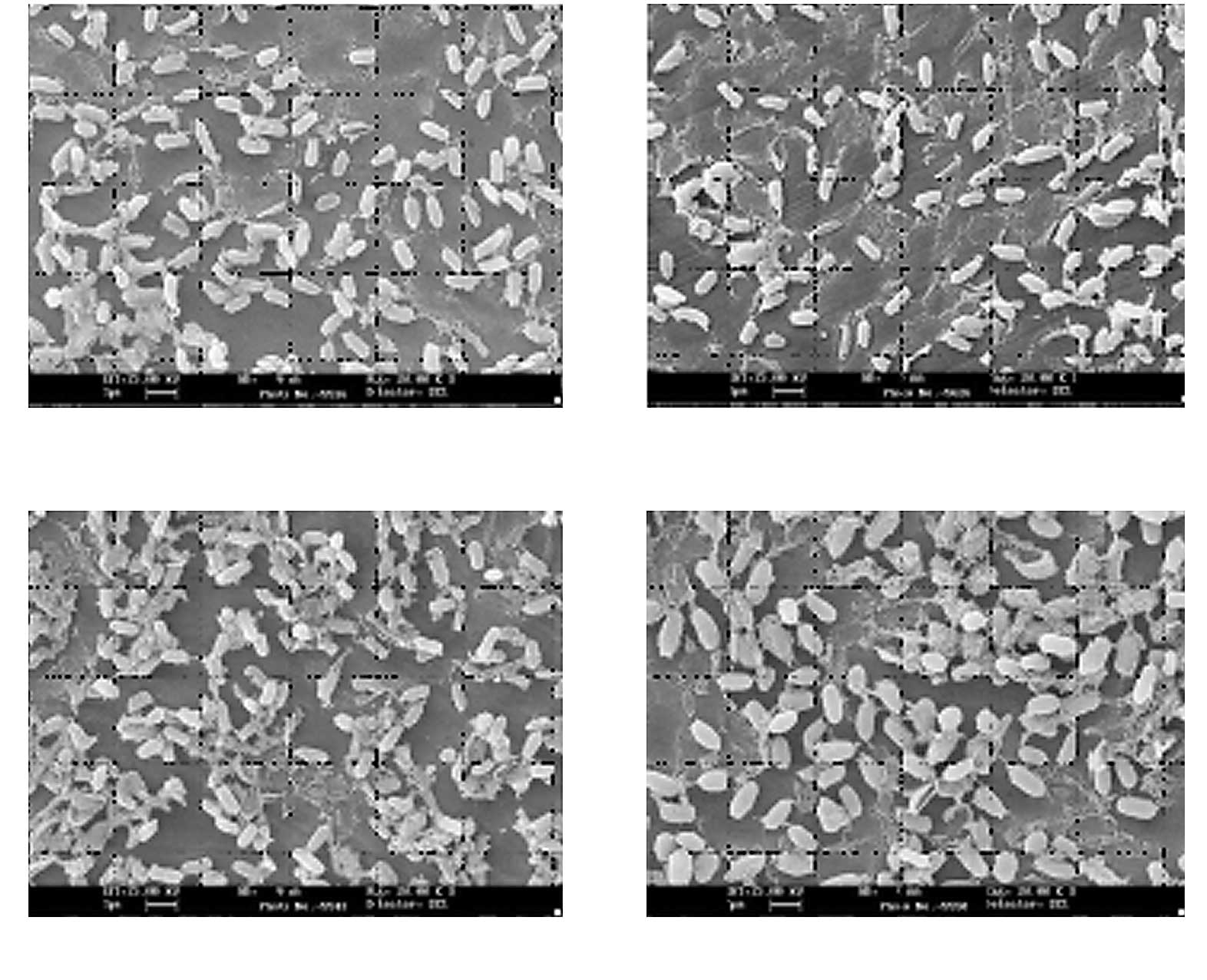
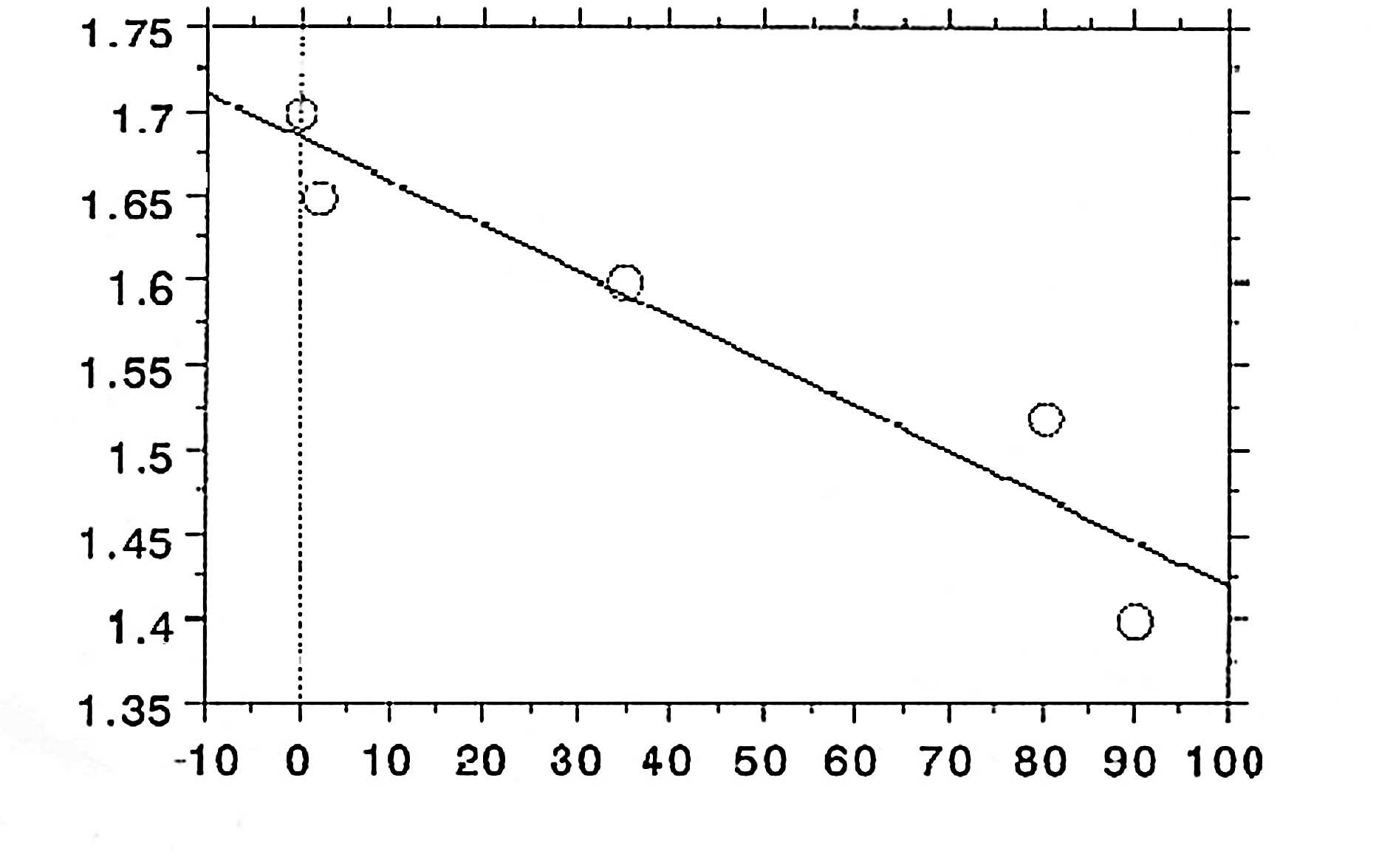
Shintani H and McDonnell G: Inactivation
of microorganisms (spore type and vegetative cells) and the
mechanism by gas plasma. Sterilization and Disinfection by Plasma:
Sterilization Mechanism, Biological and Medical Applications.
Sakudo A and Shintani H: NOVA Science Publishers; New York: (In
press).
|
|
25.
|
Moisan M, Barbeau J, Moreau S, Pelletier
J, Tabrizian M and Yahia LH: Low-temperature sterilization using
gas plasmas: a review of the experiments and an analysis of the
inactivation mechanism. Int J Pharm. 226:1–21. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Joaquin JC, Kwan C, Abramzon N,
Vandervoort K and Breiles-Marino G: Is gas-discharge plasma a new
solution to the old problem of biofilm inactivation? Microbiology.
155:724–732. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Shintani H, Taniai E, Miki A, Kurosu S and
Hayashi F: Comparison of the collecting efficiency of
microbiological air samplers. J Hosp Infect. 56:42–48. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|