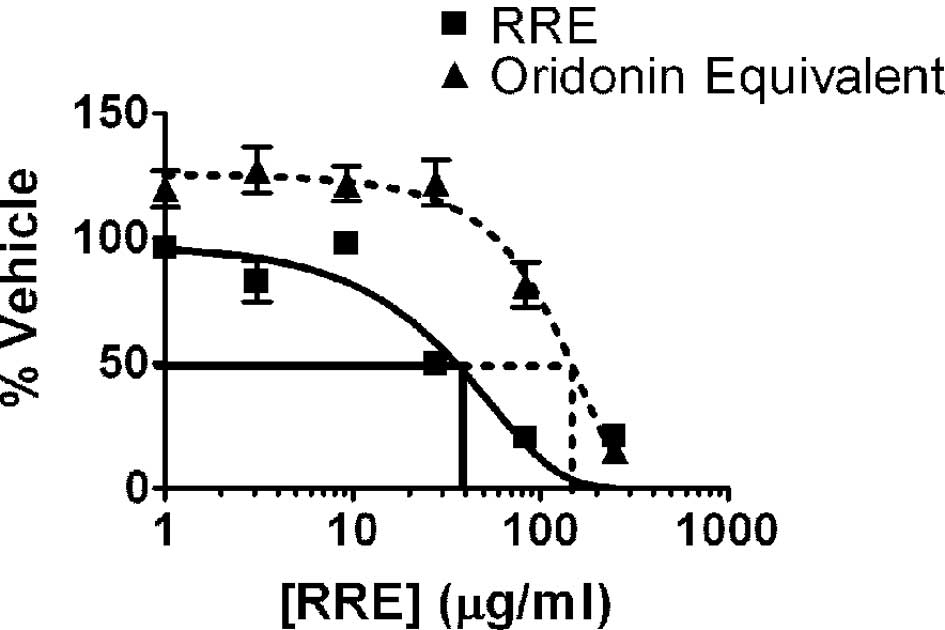
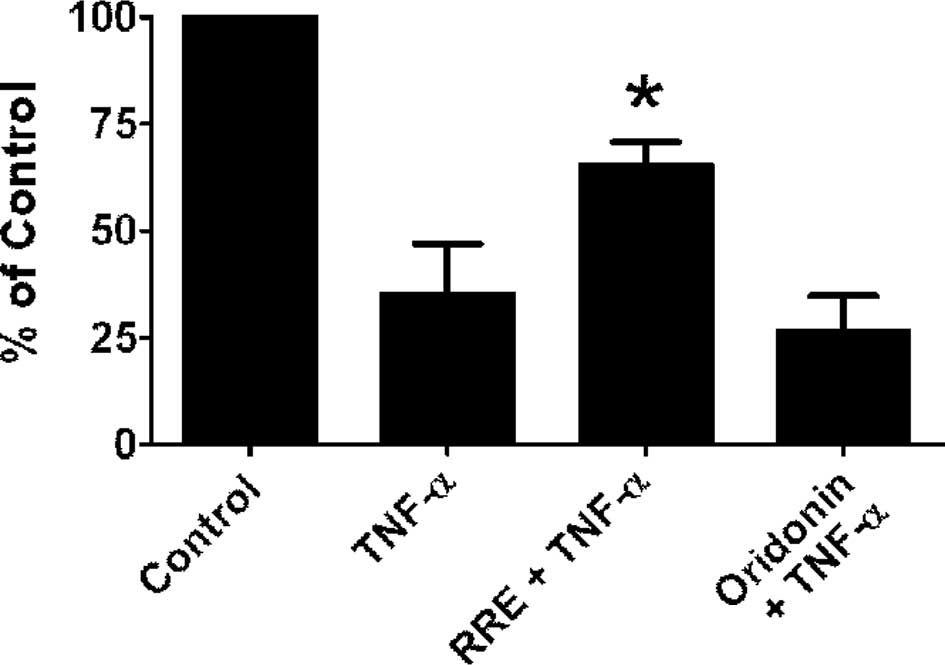
|
1.
|
National Policy on Traditional Medicine
and Regulation of Herbal Medicines: Report of a WHO Global Survery.
WHO Press; Geneva: 2005
|
|
2.
|
Hong MY, Seeram NP, Zhang Y and Heber D:
Chinese red yeast rice versus lovastatin effects on prostate cancer
cells with and without androgen receptor overexpression. J Med
Food. 11:657–666. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Hong MY, Seeram NP, Zhang Y and Heber D:
Anticancer effects of Chinese red yeast rice versus monacolin K
alone on colon cancer cells. J Nutr Biochem. 19:448–458. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Li Z, Seeram NP, Lee R, Thames G, Minutti
C, Wang HJ and Heber D: Plasma clearance of lovastatin versus
chinese red yeast rice in healthy volunteers. J Altern Complement
Med. 11:1031–1038. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Heber D, Yip I, Ashley JM, Elashoff DA,
Elashoff RM and Go VL: Cholesterol-lowering effects of a
proprietary Chinese red-yeast-rice dietary supplement. Am J Clin
Nutr. 69:231–236. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Halbert SC, French B, Gordon RY, Farrar
JT, Schmitz K, Morris PB, Thompson PD, Rader DJ and Becker DJ:
Tolerability of red yeast rice (2,400 mg twice daily) versus
pravastatin (20 mg twice daily) in patients with previous statin
intolerance. Am J Cardiol. 105:198–204. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Seeram NP, Adams LS, Hardy ML and Heber D:
Total cranberry extract versus its phytochemical constituents:
antiproliferative and synergistic effects against human tumor cell
lines. J Agric Food Chem. 52:2512–2517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Seeram NP, Adams LS, Henning SM, Niu Y,
Zhang Y, Nair MG and Heber D: In vitro antiproliferative, apoptotic
and antioxidant activities of punicalagin, ellagic acid and a total
pomegranate tannin extract are enhanced in combination with other
polyphenols as found in pomegranate juice. J Nutr Biochem.
16:360–367. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Henning SM, Niu Y, Liu Y, Lee NH, Hara Y,
Thames GD, Minutti RR, Carpenter CL, Wang H and Heber D:
Bioavailability and antioxidant effect of epigallocatechin gallate
administered in purified form versus as green tea extract in
healthy individuals. J Nutr Biochem. 16:610–616. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Adams LS, Seeram NP, Hardy ML, Carpenter C
and Heber D: Analysis of the interactions of botanical extract
combinations against the viability of prostate cancer cell lines.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 3:117–124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ikezoe T, Chen SS, Tong XJ, Heber D,
Taguchi H and Koeffler HP: Oridonin induces growth inhibition and
apoptosis of a variety of human cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
23:1187–1193. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Hsieh TC, Wijeratne EK, Liang JY,
Gunatilaka AL and Wu JM: Differential control of growth, cell cycle
progression, and expression of NF-kappaB in human breast cancer
cells MCF-7, MCF-10A, and MDA-MB-231 by ponicidin and oridonin,
diterpenoids from the chinese herb Rabdosia rubescens.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 337:224–231. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Sartippour MR, Seeram NP, Heber D, Hardy
M, Norris A, Lu Q, Zhang L, Lu M, Rao JY and Brooks MN: Rabdosia
rubescens inhibits breast cancer growth and angiogenesis. Int J
Oncol. 26:121–127. 2005.
|
|
14.
|
Ikezoe T, Yang Y, Bandobashi K, Saito T,
Takemoto S, Machida H, Togitani K, Koeffler HP and Taguchi H:
Oridonin, a diterpenoid purified from Rabdosia rubescens,
inhibits the proliferation of cells from lymphoid malignancies in
association with blockade of the NF-kappa B signal pathways. Mol
Cancer Ther. 4:578–586. 2005.
|
|
15.
|
Hu HZ, Yang YB, Xu XD, Shen HW, Shu YM,
Ren Z, Li XM, Shen HM and Zeng HT: Oridonin induces apoptosis via
PI3K/Akt pathway in cervical carcinoma HeLa cell line. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 28:1819–1826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ren KK, Wang HZ, Xie LP, Chen DW, Liu X,
Sun J, Nie YC and Zhang RQ: The effects of oridonin on cell growth,
cell cycle, cell migration and differentiation in melanoma cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 103:176–180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Wang HJ, Li D, Yang FY, Tashiro S, Onodera
S and Ikejima T: Oridonin induces human melanoma A375-S2 cell death
partially through inhibiting insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
signaling. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 10:787–798. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Zhang CL, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Oridonin induced A375-S2 cell apoptosis via
bax-regulated caspase pathway activation, dependent on the
cytochrome c/caspase-9 apoptosome. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 6:127–138.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Chen S, Gao J, Halicka HD, Huang X,
Traganos F and Darzynkiewicz Z: The cytostatic and cytotoxic
effects of oridonin (Rubescenin), a diterpenoid from Rabdosia
rubescens, on tumor cells of different lineage. Int J Oncol.
26:579–588. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Wu D, Tashiro S, Onodera S
and Ikejima T: NF-kappa B facilitates oridonin-induced apoptosis
and autophagy in HT1080 cells through a p53-mediated pathway. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 489:25–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Zhang CL, Wu LJ, Zuo HJ, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Cytochrome c release from oridonin-treated
apoptotic A375-S2 cells is dependent on p53 and extracellular
signal-regulated kinase activation. J Pharmacol Sci. 96:155–163.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Liu YQ, You S, Tashiro S, Onodera S and
Ikejima T: Activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, protein kinase
C, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase is required for
oridonin-enhanced phagocytosis of apoptotic bodies in human
macrophage-like U937 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 98:361–371. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Wagner H and Ulrich-Merzenich G: Synergy
research: approaching a new generation of phytopharmaceuticals.
Phytomedicine. 16:97–110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Ulrich-Merzenich G, Panek D, Zeitler H,
Wagner H and Vetter H: New perspectives for synergy research with
‘omic’ technologies. Phytomedicine. 16:495–508. 2009.
|