|
1.
|
Van Belzen N, Dinjens WN, Diesveld MP, et
al: A novel gene which is up-regulated during colon epithelial cell
differentiation and down-regulated in colorectal neoplasms. Lab
Invest. 77:85–92. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kurdistani SK, Arizti P, Reimer CL, Sugrue
MM, Aaronson SA and Lee SW: Inhibition of tumor cell growth by
RTP/rit42 and its responsiveness to p53 and DNA damage. Cancer Res.
58:4439–4444. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Zhou D, Salnikow K and Costa M: Cap43, a
novel gene specifically induced by Ni2+ compounds.
Cancer Res. 58:2182–2189. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Okuda T and Kondoh H: Identification of
new genes Ndr2 and Ndr3 which are related to Ndr1/RTP/Drg1 but show
distinct tissue specificity and response to N-myc. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 266:208–215. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
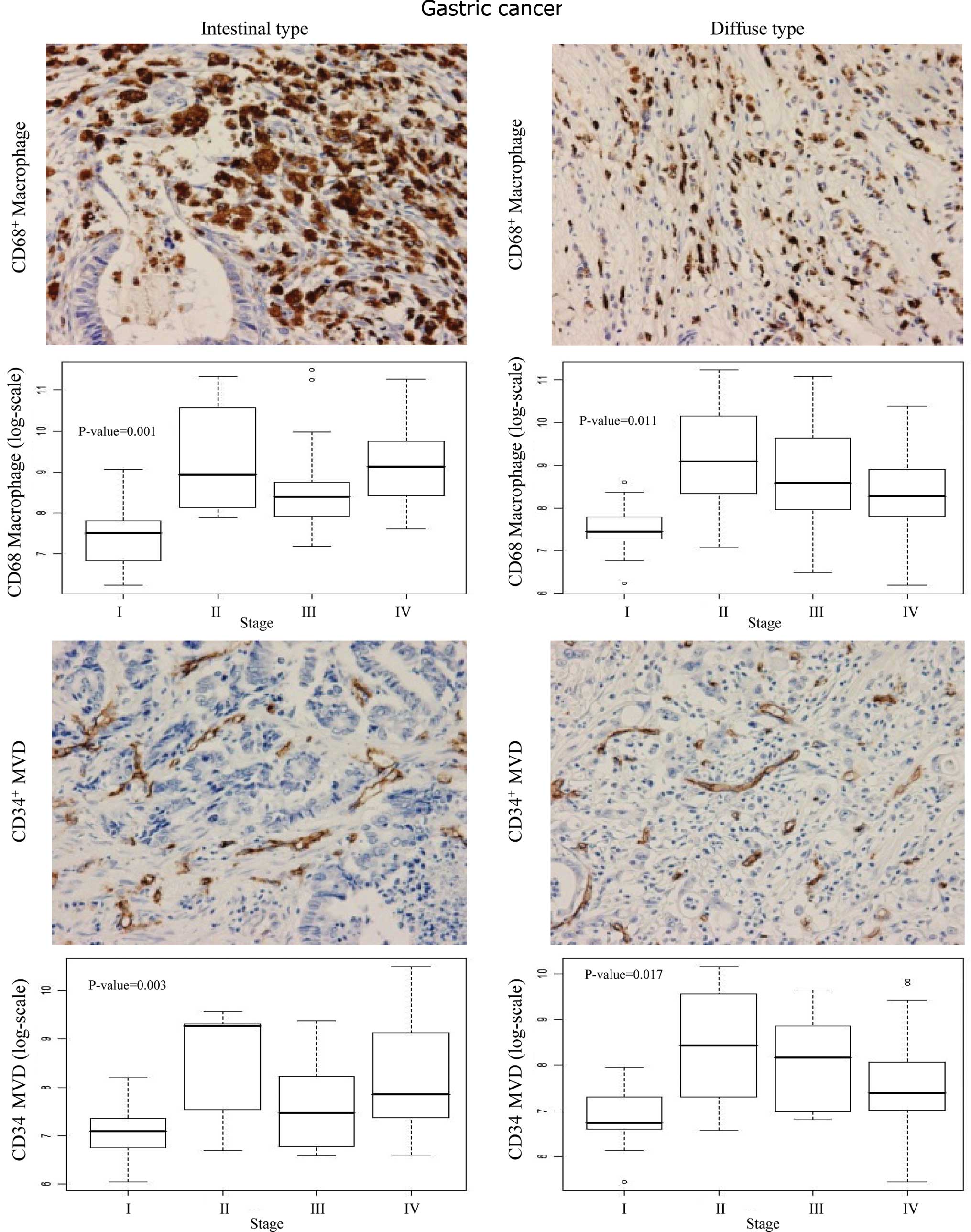
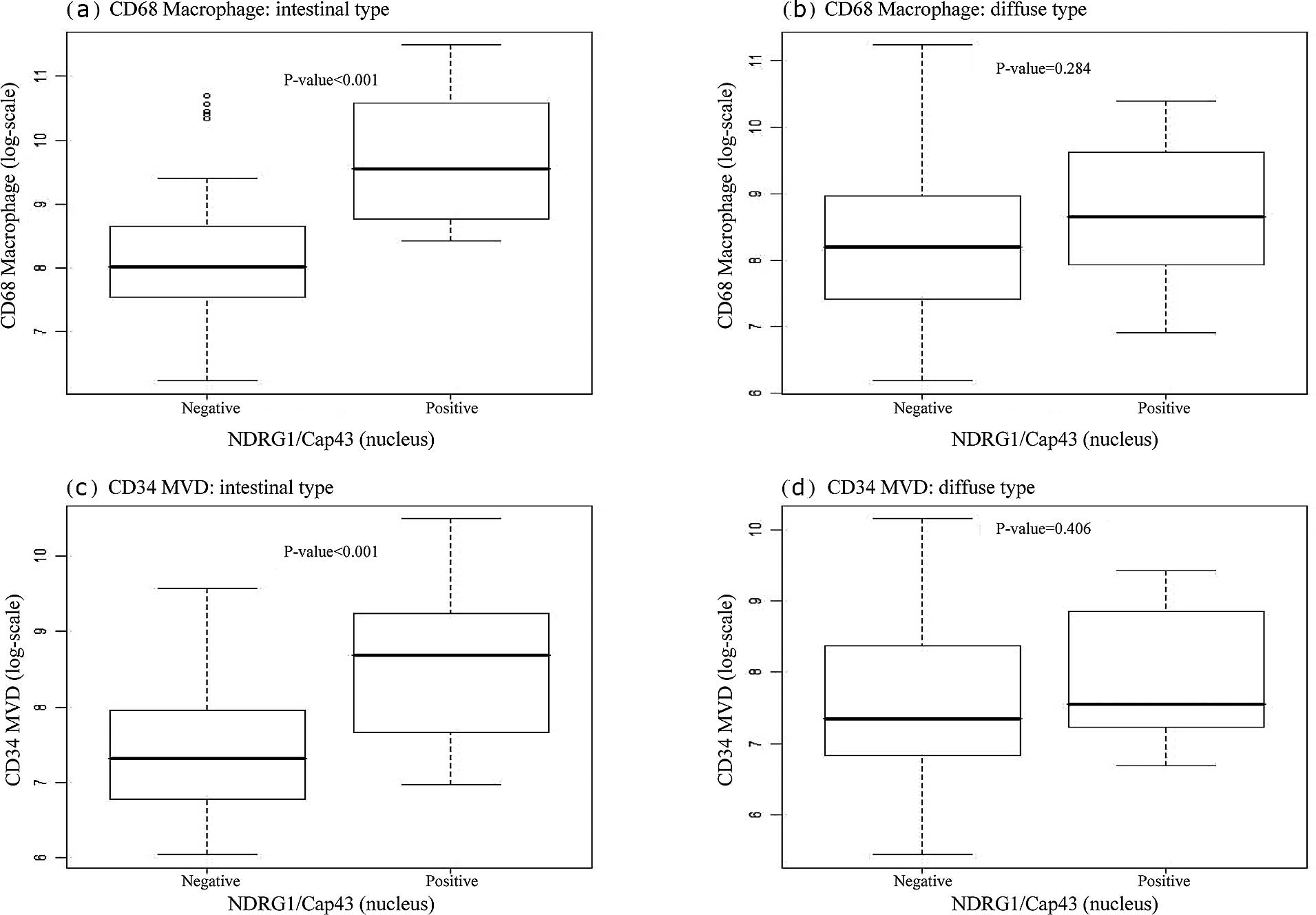
|
Shimono A, Okuda T and Kondoh H:
N-myc-dependent repression of ndr1, a gene identified by direct
subtraction of whole mouse embryo cDNAs between wild type and N-myc
mutant. Mech Dev. 83:39–52. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
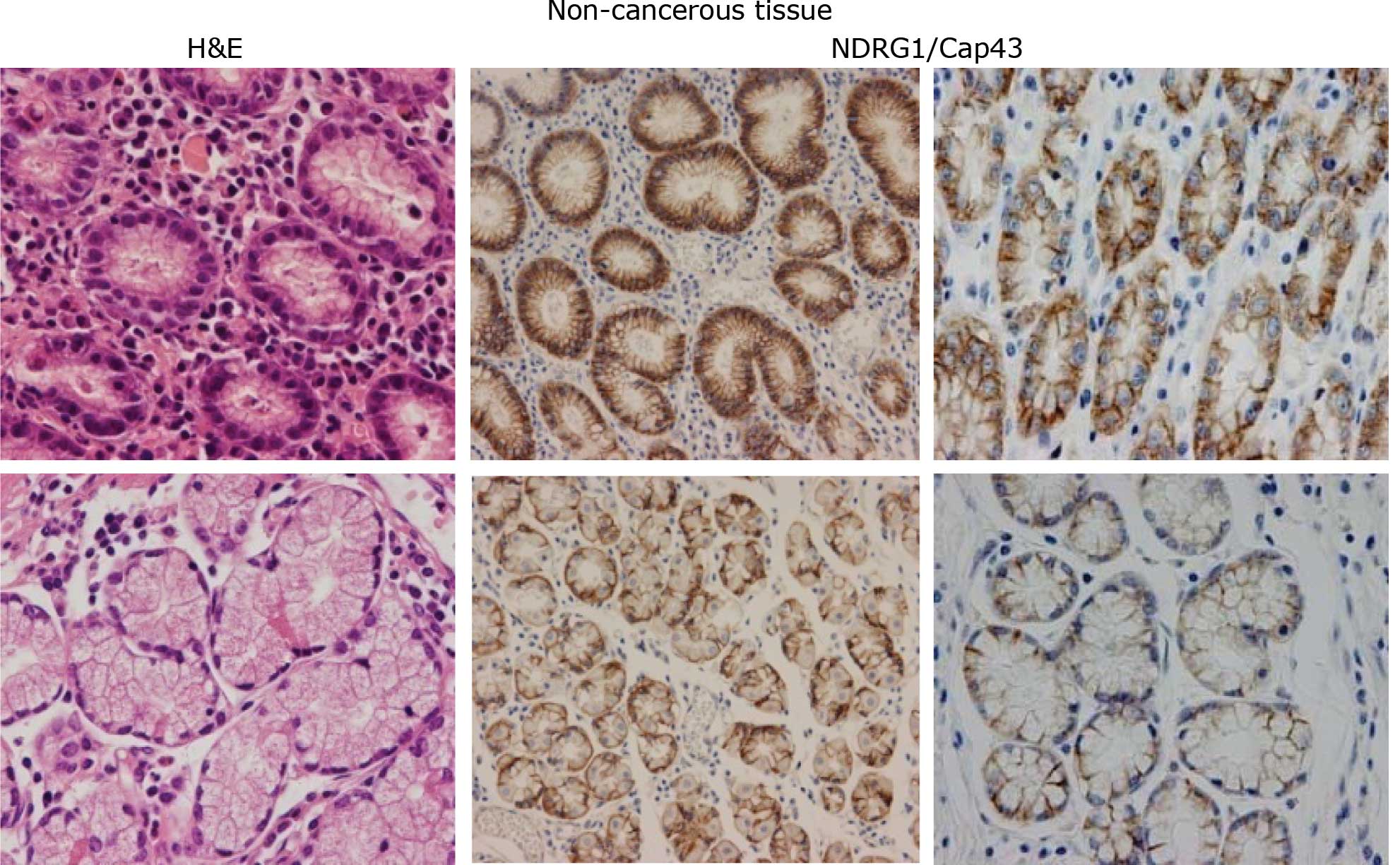
|
6.
|
Qu X, Zhai Y, Wei H, et al:
Characterization and expression of three novel
differentiation-related genes belong to the human NDRG gene family.
Mol Cell Biochem. 229:35–44. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Guan RJ, Ford HL, Fu Y, Li Y, Shaw LM and
Pardee AB: Drg-1 as a differentiation-related, putative metastatic
suppressor gene in human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 60:749–755.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Bandyopadhyay S, Pai SK, Gross SC, et al:
The Drg-1 gene suppresses tumor metastasis in prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 63:1731–1736. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Angst E, Sibold S, Tiffon C, et al:
Cellular differentiation determines the expression of the
hypoxia-inducible protein NDRG1 in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer.
95:307–313. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Fotovati A, Fujii T, Yamaguchi M, et al:
17Beta-estradiol induces down-regulation of Cap43/NDRG1/Drg-1, a
putative differentiation-related and metastasis suppressor gene, in
human breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3010–3018. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Maruyama Y, Ono M, Kawahara A, et al:
Tumor growth suppression in pancreatic cancer by a putative
metastasis suppressor gene Cap43/NDRG1/Drg-1 through modulation of
angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 66:6233–6242. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Ando T, Ishiguro H, Kimura M, et al:
Decreased expression of NDRG1 is correlated with tumor progression
and poor prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 19:454–458. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Fukahori S, Yano H, Tsuneoka M, et al:
Immunohistochemical expressions of Cap43 and Mina53 proteins in
neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 42:1831–1840. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Koshiji M, Kumamoto K, Morimura K, et al:
Correlation of N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 expression with
clinical outcomes of colorectal cancer patients of different
race/ethnicity. World J Gastroenterol. 13:2803–2810.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Song YS, Oda Y, Hori M, et al: N-myc
downstream regulated gene1/Cap43 may play an important role in
malignant progression of prostate cancer, in its close association
with E-cadherin. Human Pathol. 41:214–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Shah MA, Kemeny N, Hummer A, et al: Drg1
expression in 131 colorectal liver metastases: correlation with
clinical variables and patient outcomes. Clin Cancer Res.
11:3296–3302. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Chua MS, Sun H, Cheung ST, et al:
Overexpression of NDRG1 is an indicator of poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 20:76–83. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Nishio S, Ushijima K, Tsuda N, et al:
Cap43/NDRG1/Drg-1 is a molecular target for angiogenesis and a
prognostic indicator in cervical adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett.
264:36–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Sohda M, Mochida Y, Kato H, et al:
Overexpression of Cap43 is associated with malignant status of
esophageal cancer. Anticancer Res. 29:965–970. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kovacevic Z, Fu D and Richardson DR: The
iron-regulated metastasis suppressor, Ndrg-1: identification of
novel molecular targets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1783:1981–1992.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Hosoi F, Izumi H, Kawahara A, et al: N-myc
downstream regulated gene 1/Cap43 suppresses tumor growth and
angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer through attenuation of IKKbeta
expression. Cancer Res. 69:4983–4991. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Murakami Y, Hosoi F, Izumi H, et al:
Identification of sites subjected to serine/threonine
phosphorylation by SGK1 affecting N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1
(NDRG1)/Cap43-dependent suppression of angiogenic CXC chemokine
expression in human pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophysical
Res Commun. 396:376–381. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P and Sica A:
Tumour-associated macrophages as a prototypic type II polarised
phagocyte population: role in tumour progression. Eur J Cancer.
40:1660–1667. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Pollard JW: Tumour-educated macrophages
promote tumour progression and metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:71–78.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Ono M: Molecular links between tumor
angiogenesis and inflammation: inflammatory stimuli of macrophages
and cancer cells as targets for therapeutic strategy. Cancer Sci.
99:1501–1506. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Lin EY and Pollard JW: Tumor-associated
macrophages press the angiogenic switch in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 67:5064–5066. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Sica A and Bronte V: Altered macrophage
differentiation and immune dysfunction in tumor development. J Clin
Invest. 117:1155–1166. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Lewis CE and Pollard JW: Distinct role of
macrophages in different tumor microenvironments. Cancer Res.
66:605–612. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Nakao S, Kuwano T, Tsutsumi-Miyahara C, et
al: Infiltration of COX-2-expressing macrophages is a prerequisite
for IL-1 beta-induced neovascularization and tumor growth. J Clin
Invest. 115:2979–2991. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Kimura YN, Watari K, Fotovati A, et al:
Inflammatory stimuli from macrophages and cancer cells
synergistically promote tumor growth and angiogenesis. Cancer Sci.
98:2009–2018. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Hiraoka K, Zenmyo M, Watari K, et al:
Inhibition of bone and muscle metastases of lung cancer cells by a
decrease in the number of monocytes/macrophages. Cancer Sci.
99:1595–1602. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Lauren P: The two histological main types
of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type
carcinoma: an attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta
Pathol Microbiol Scand. 64:31–49. 1965.
|
|
33.
|
Kawahara A, Hattori S, Akiba J, et al:
Infiltration of thymidine phosphorylase-positive macrophages is
closely associated with tumor angiogenesis and survival in
intestinal type gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 24:405–415. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Rothman KJ and Greenland S: Modern
Epidemiology. 3rd edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;
Philadelphia: 1998
|
|
35.
|
Wakisaka Y, Furuta A, Masuda K, Morikawa
W, Kuwano M and Iwaki T: Cellular distribution of NDRG1 protein in
the rat kidney and brain during normal postnatal development. J
Histochem Cytochem. 51:1515–1525. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Lachat P, Shaw P, Gebhard S, van Belzen N,
Chaubert P and Bosman FT: Expression of NDRG1, a
differentiation-related gene, in human tissues. Histochem Cell
Biol. 118:399–408. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Sibold S, Roh V, Keogh A, et al: Hypoxia
increases cytoplasmic expression of NDRG1, but is insufficient for
its membrane localization in human hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS
Lett. 581:989–994. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38.
|
Maehara Y, Kabashima A, Koga T, et al:
Vascular invasion and potential for tumor angiogenesis and
metastasis in gastric carcinoma. Surgery. 128:408–416. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Inagaki Y, Tang W, Xu HL, et al:
Localization of N-myc downstream-regulated gene 1 in gastric cancer
tissue. Dig Liver Dis. 41:96–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Kovacevic Z and Richardson DR: The
metastasis suppressor, Ndrg-1: a new ally in the fight against
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 27:2355–2366. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Rutherford MN, Bayly GR, Matthews BP, et
al: The leukemogenic transcription factor E2a-Pbx1 induces
expression of the putative N-myc and p53 target gene NDRG1 in Ba/F3
cells. Leukemia. 15:362–370. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42.
|
Stein S, Thomas EK, Herzog B, et al: NDRG1
is necessary for p53-dependent apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
279:48930–48940. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|