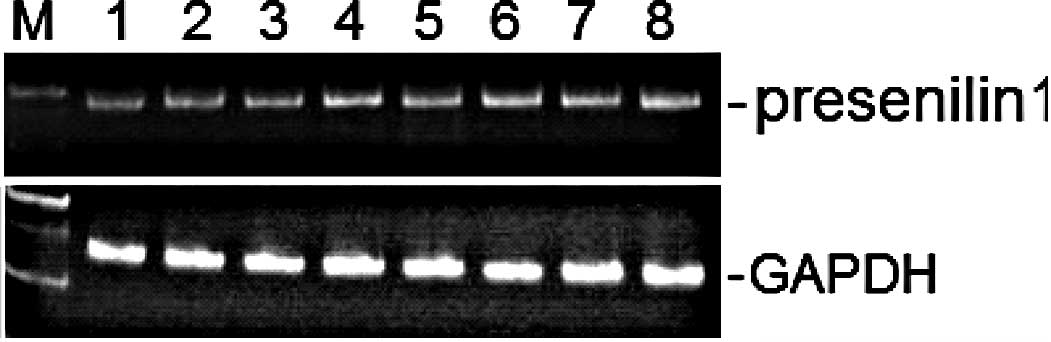
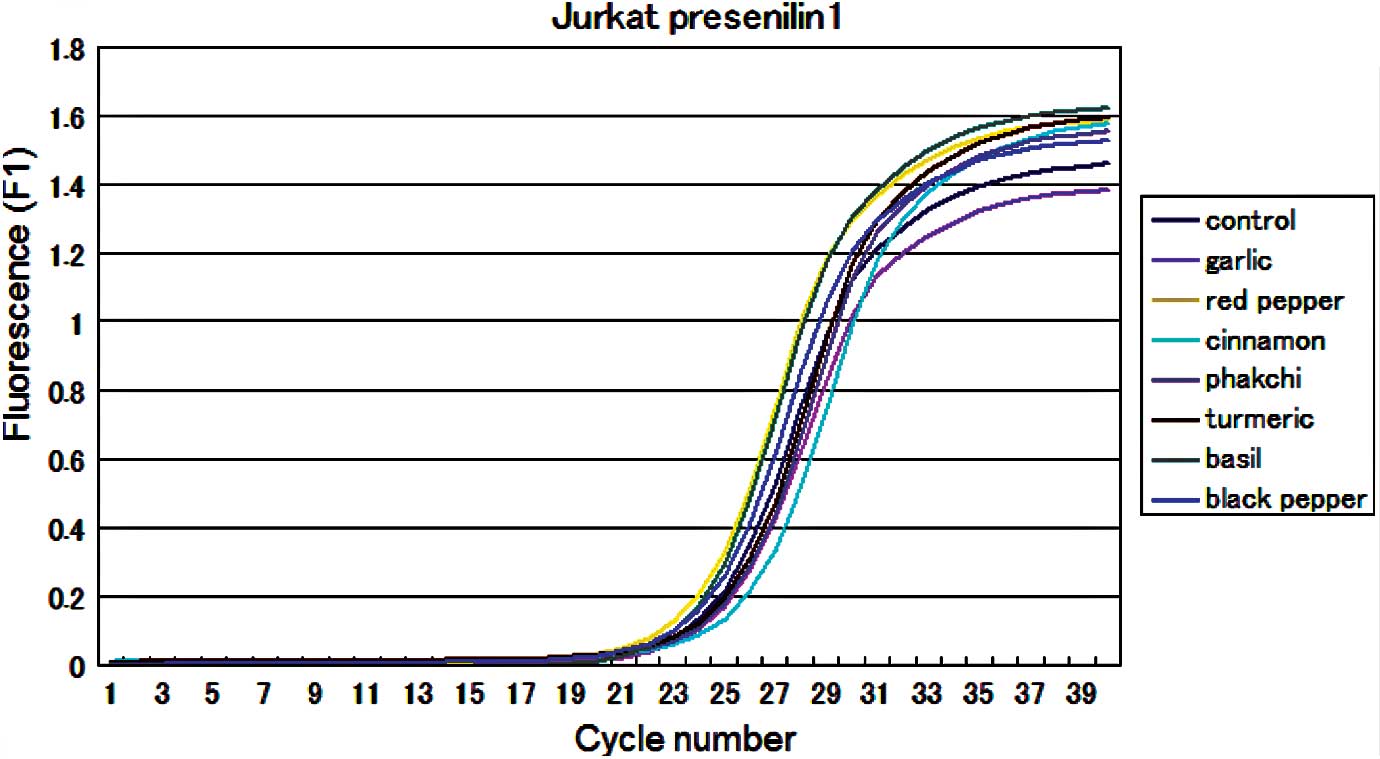
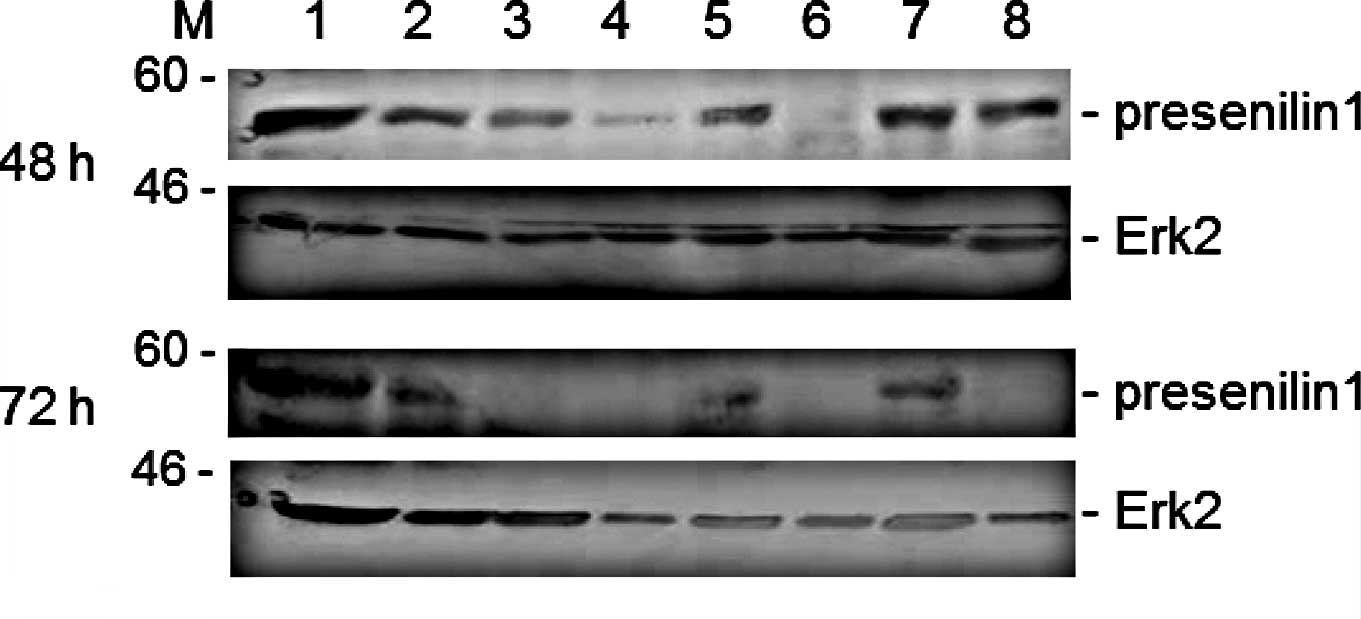
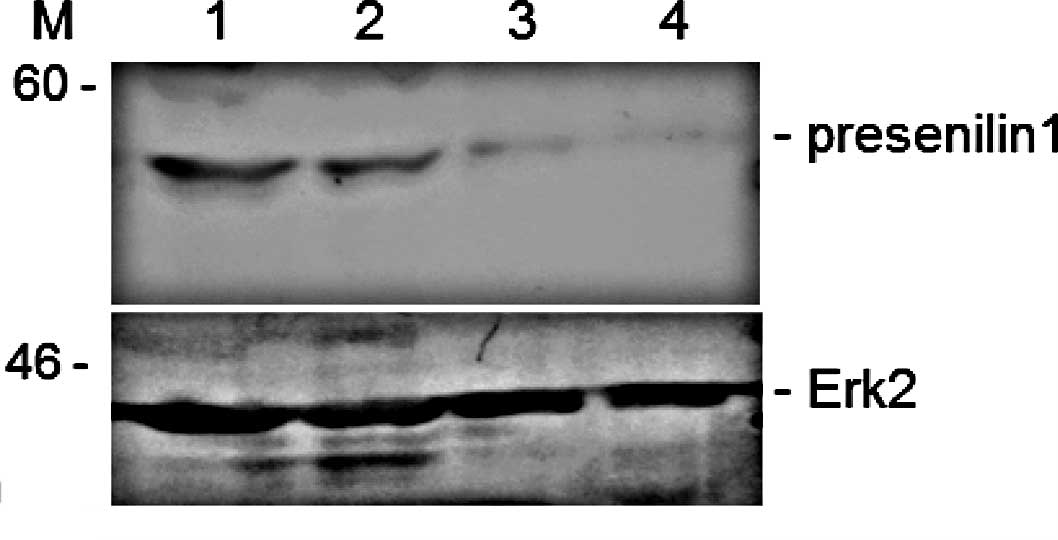
|
1.
|
Bekris LM, Yu CE, Bird TD and Tsuang DW:
Genetics of Alzheimer disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol.
23:213–227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Ittner LM and Götz J: Amyloid-β and tau –
a toxic pas de deux in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci.
12:65–72. 2011.
|
|
3.
|
Woo HN, Baik SH, Park JS, Gwon AR, Yang S,
Yun YK and Jo DG: Secretases as therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's
disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 404:10–15. 2011.
|
|
4.
|
Crews L, Rockenstein E and Masliah E: APP
transgenic modeling of Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms of
neurodegeneration and aberrant neurogenesis. Brain Struct Funct.
214:111–126. 2010.
|
|
5.
|
Al-Mofleh IA: Spices, herbal xenobiotics
and the stomach: friends or foes? World J Gastroenterol.
16:2710–2719. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Wang YJ, Thomas P, Zhong JH, Bi FF,
Kosaraju S, Pollard A, Fenech M and Zhou XF: Consumption of grape
seed extract prevents amyloid-beta deposition and attenuates
inflammation in brain of an Alzheimer's disease mouse. Neurotox
Res. 15:3–14. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Thomas P, Wang YJ, Zhong JH, Kosaraju S,
O'Callaghan NJ, Zhou XF and Fenech M: Grape seed polyphenols and
curcumin reduce genomic instability events in a transgenic mouse
model for Alzheimer's disease. Mutat Res. 661:25–34.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Mei Z, Zhang F, Tao L, Zheng W, Cao Y,
Wang Z, Tang S, Le K, Chen S, Pi R and Liu P: Cryptotanshinone, a
compound from Salvia miltiorrhiza modulates amyloid
precursor protein metabolism and attenuates beta-amyloid deposition
through upregulating alpha-secretase in vivo and in vitro. Neurosci
Lett. 452:90–95. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Kelloff GJ, Crowell JA, Steele VE, Lubet
RA, Malone WA, Boone CW, Kopelovich L, Hawk ET, Lieberman R,
Lawrence JA, Ali I, Viner JL and Sigman CC: Progress in cancer
chemo-prevention: development of diet-derived chemopreventive
agents. J Nutr. 130:S467–S471. 2000.
|
|
10.
|
Ganguli M, Chandra V, Kamboh MI, Johnston
JM, Dodge HH, Thelma BK, Juyal RC, Pandav R, Belle SH and DeKosky
ST: Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer disease: the
Indo-US Cross-National Dementia Study. Arch Neurol. 57:824–830.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Okumura N, Nishimura Y, Yoshida H, Nagata
Y, Kitagishi Y and Matsuda S: Ethanol extract of herb Sage
suppressed the TIMP-1 expression in lymphoid culture cells. Asia J
Sci Technol. 3:64–66. 2010.
|
|
12.
|
Zhang C, Browne A, Child D and Tanzi RE:
Curcumin decreases amyloid-beta peptide levels by attenuating the
maturation of amyloid-beta precursor protein. J Biol Chem.
285:28472–28480. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Garcia-Alloza M, Borrelli LA, Rozkalne A,
Hyman BT and Bacskai BJ: Curcumin labels amyloid pathology in vivo,
disrupts existing plaques, and partially restores distorted
neurites in an Alzheimer mouse model. J Neurochem. 102:1095–1104.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Balasubramanian K: Molecular orbital basis
for yellow curry spice curcumin's prevention of Alzheimer's
disease. J Agric Food Chem. 54:3512–3520. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Viswanathan J, Haapasalo A, Böttcher C, et
al: Alzheimer's disease-associated ubiquilin-1 regulates
presenilin-1 accumulation and aggresome formation. Traffic.
12:330–348. 2011.
|
|
16.
|
Breusing N and Grune T: Regulation of
proteasome-mediated protein degradation during oxidative stress and
aging. Biol Chem. 389:203–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Magini A, Urbanelli L, Ciccarone V,
Tancini B, Polidoro M, Timperio AM, Zolla L, Tedde A, Sorbi S and
Emiliani C: Fibroblasts from PS1-mutated pre-symptomatic subjects
and Alzheimer's disease patients share a unique protein level
profile. J Alzheimers Dis. 21:431–444. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|