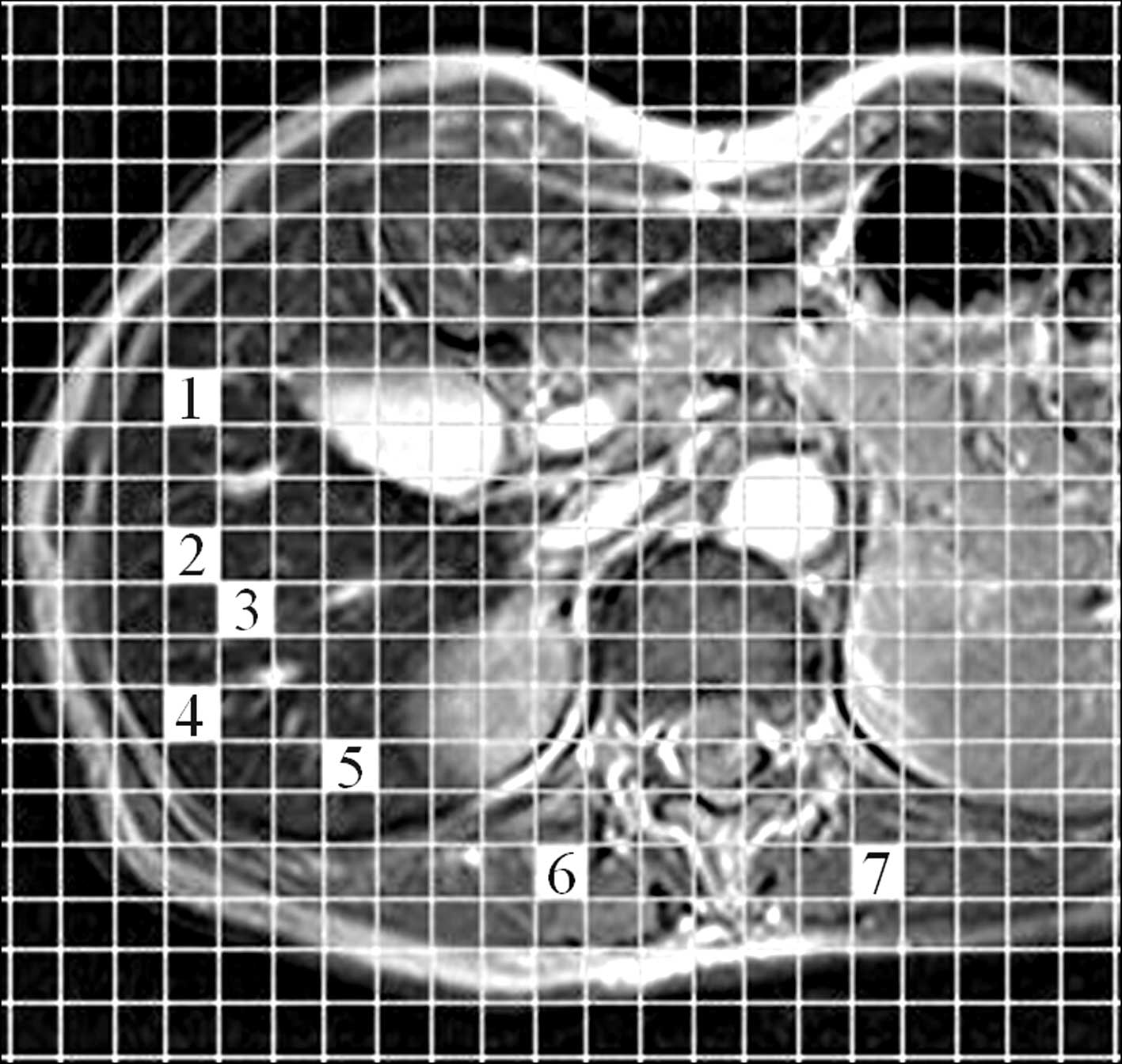
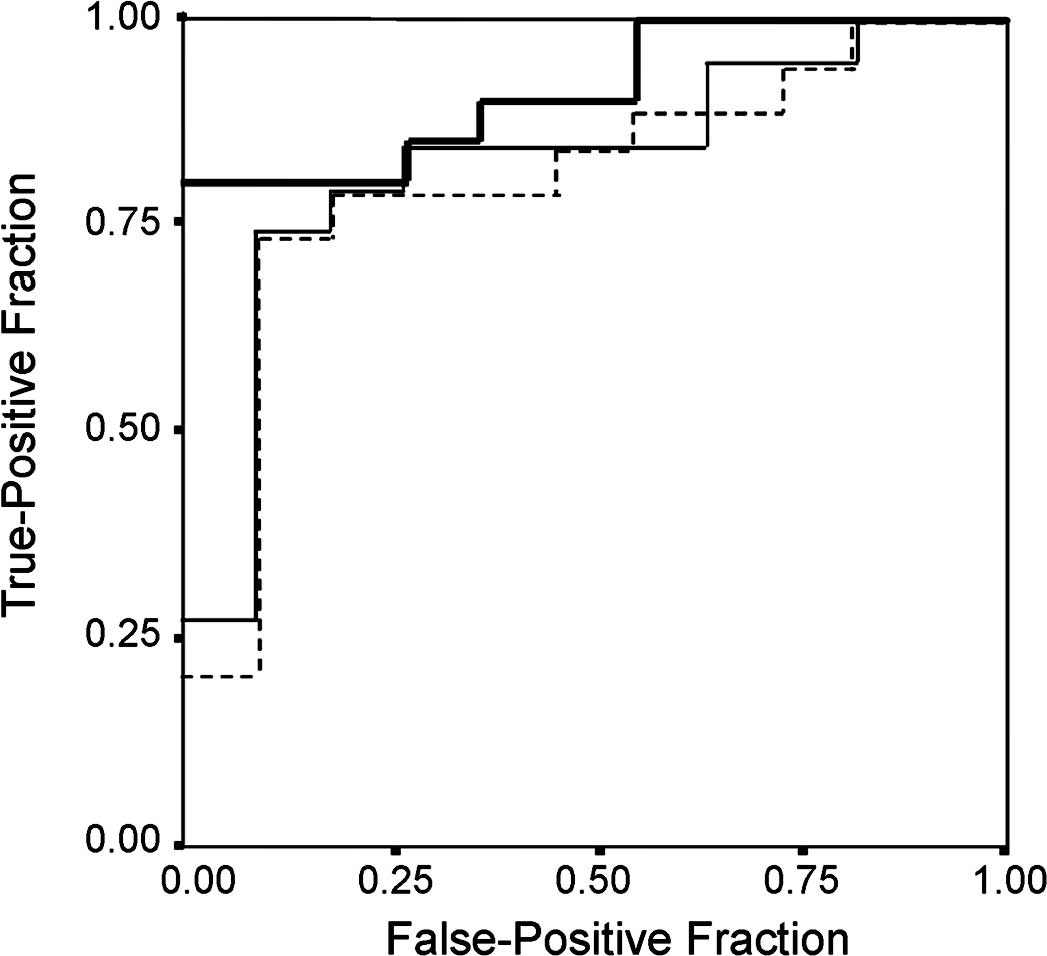
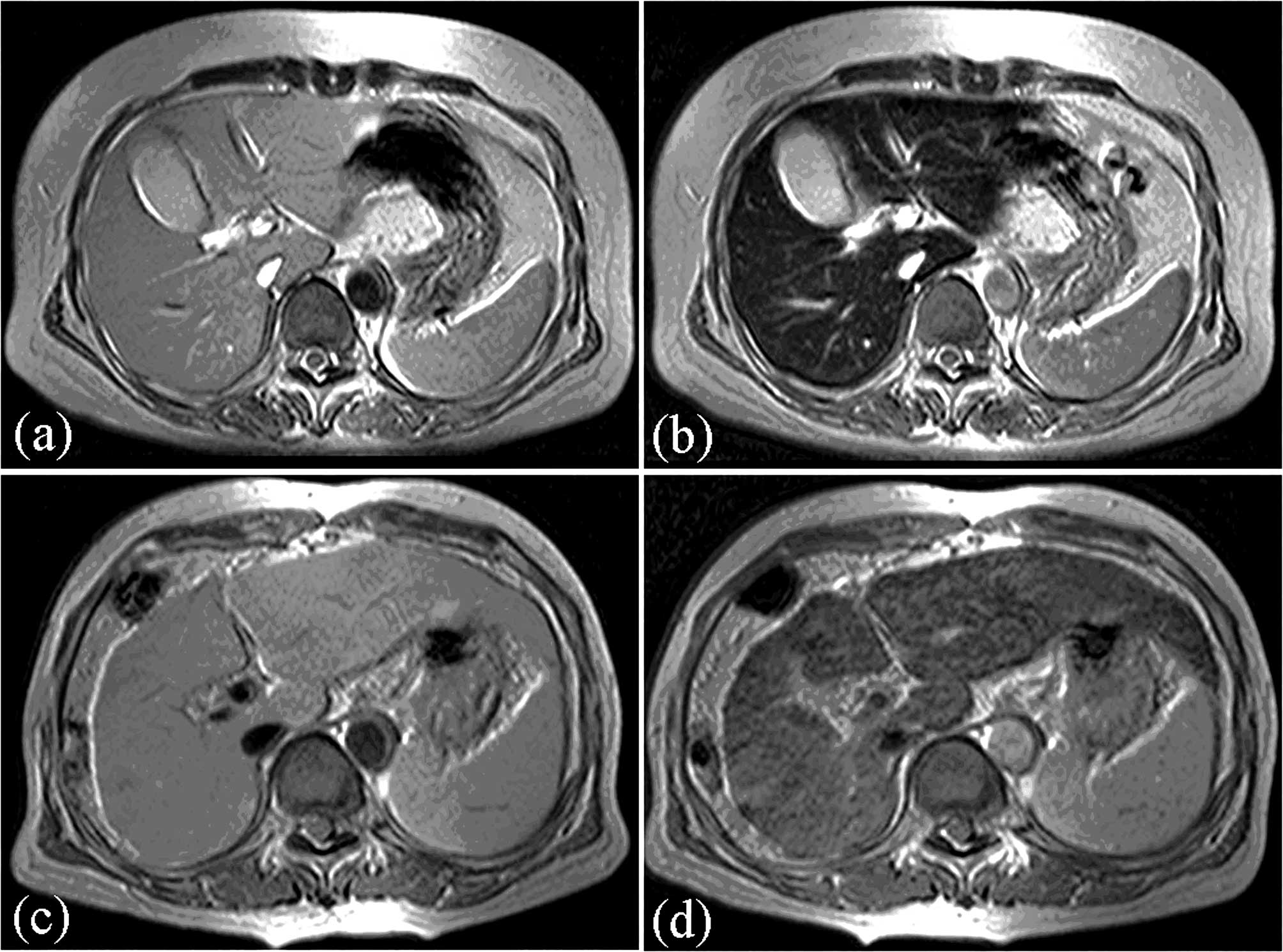
|
1.
|
Child CG and Turcotte JG: Surgery and
portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1:1–85. 1964.
|
|
2.
|
Pugh RNH, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL,
Pietroni MC and Williams R: Transection of the oesophagus for
bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 60:646–649. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Schneider PD: Preoperative assessment of
liver function. Surg Clin North Am. 84:355–373. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Lucey MR, Brown KA, Everson GT, et al:
Minimal criteria for placement of adults on the liver transplant
waiting list. Transplantation. 66:956–962. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Tygstrup N: The galactose elimination
capacity in control subjects and in patients with cirrhosis of the
liver. Acta Med Scand. 175:281–289. 1964. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Hepner GW and Vesell ES: Assessment of
aminopyrine metabolism in man by breath analysis after oral
administration of 14C-aminopyrine. N Engl J Med. 291:134–147.
1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Kawamura H, Kamiyama T, Nakagawa T, et al:
Preoperative evaluation of hepatic functional reserve by converted
ICGR15 calculated from Tc-GSA scintigraphy. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 8:1235–1241. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Moody FG, Rikkers LF and Aldrete JS:
Estimation of the functional reserve of human liver. Ann Surg.
180:592–598. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Yamanaka N, Okamoto E, Kuwata K and Tanaka
N: A multiple regression equation for prediction of posthepatectomy
liver failure. Ann Surg. 200:658–663. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Fujioka H, Kawashita Y, Kamohara Y, et al:
Utility of technetium-99m-labeled-galactosyl human serum albumin
scintigraphy for estimating the hepatic functional reserve. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 28:329–333. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Sasaki N, Shiomi S, Iwata Y, et al:
Clinical usefulness of scintigraphy with 99mTc-galactosyl-human
serum albumin for prognosis of cirrhosis of the liver. J Nucl Med.
40:1652–1656. 1999.
|
|
12.
|
Kawamura E, Shiomi S, Ishizu H, et al:
Natural course of change in hepatic functional reserve in patients
with chronic liver disease evaluated by scintigraphy with GSA.
Hepatol Res. 27:129–135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Shiomi S, Kuroki T, Kuriyama M, et al:
Evaluation of fluminant hepatic failure by scintigraphy with
technetium-99m-GSA. J Nucl Med. 38:79–82. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hakawa SK and Tanaka Y: A quantitative
model of technetium-99m-DTPA-galactosyl-HSA for the assessment of
hepatic blood flow and hepatic binding receptor. J Nucl Med.
32:2233–2240. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Sugai Y, Komatani A, Hosoya T and
Takahashi K: Analysis of the early blood kinetics of 99mTc-GSA and
its verification: new one-compartment model and regression
equation. Nucl Med Commun. 22:773–778. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Sugahara K, Togashi H, Takahashi K, et al:
Separate analysis of asialoglycoprotein receptors in the right and
left hepatic lobes using Tc-GSA SPECT. Hepatology. 38:1401–1409.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Nanashima A, Yamaguchi H, Shibasaki S, et
al: Relationship between indocyanine green test and technetium-99m
galactosyl serum albumin scintigraphy in patients scheduled for
hepatectomy: clinical evaluation and patient outcome. Hepatol Res.
28:184–190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Tonan T, Fujimoto K, Azuma S, et al:
Evaluation of small (< or =2 cm) dysplastic nodules and
well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinomas with
ferucarbotran-enhanced MRI in a 1.0-T MRI unit: utility of
T2-weighted gradient echo sequences with an intermediate-echo time.
Eur J Radiol. 64:133–139. 2007.
|
|
19.
|
Elizondo G, Weissleder R, Stark DD, et al:
Hepatic cirrhosis and hepatitis: MR imaging enhanced with
superparamagnetic iron oxide. Radiology. 174:797–801. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Clement O, Frija G, Chambon C, et al:
Liver tumors in cirrhosis: experimental study with SPIO-enhanced MR
imaging. Radiology. 180:31–36. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kato N, Ihara S, Tsujimoto T and Miyazawa
T: Effect of resovist on rats with different severities of liver
cirrhosis. Invest Radiol. 222:661–666. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Tanimoto A, Yuasa Y, Shinmoto H, et al:
Superparamagnetic iron oxide-mediated hepatic signal intensity
change in patients with and without cirrhosis: pulse sequence
effects and Kupffer cell function. Radiology. 222:661–666. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Hundt W, Petsch R, Heimberger T and Reiser
H: Signal changes in liver and spleen after Endorem administration
in patients with and without liver cirrhosis. Eur Radiol.
10:409–416. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Gandon Y, Olivié D, Guyader D, et al:
Non-invasive assessment of hepatic iron stores by MRI. Lancet.
31:357–362. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Kudo M, Todo A, Ikekubo K, et al:
Functional hepatic imaging with receptor-binding
radiopharmaceutical: clinical potential as a measure of functioning
hepatocyte mass. Gastroenterol Jpn. 26:734–741. 1991.
|
|
26.
|
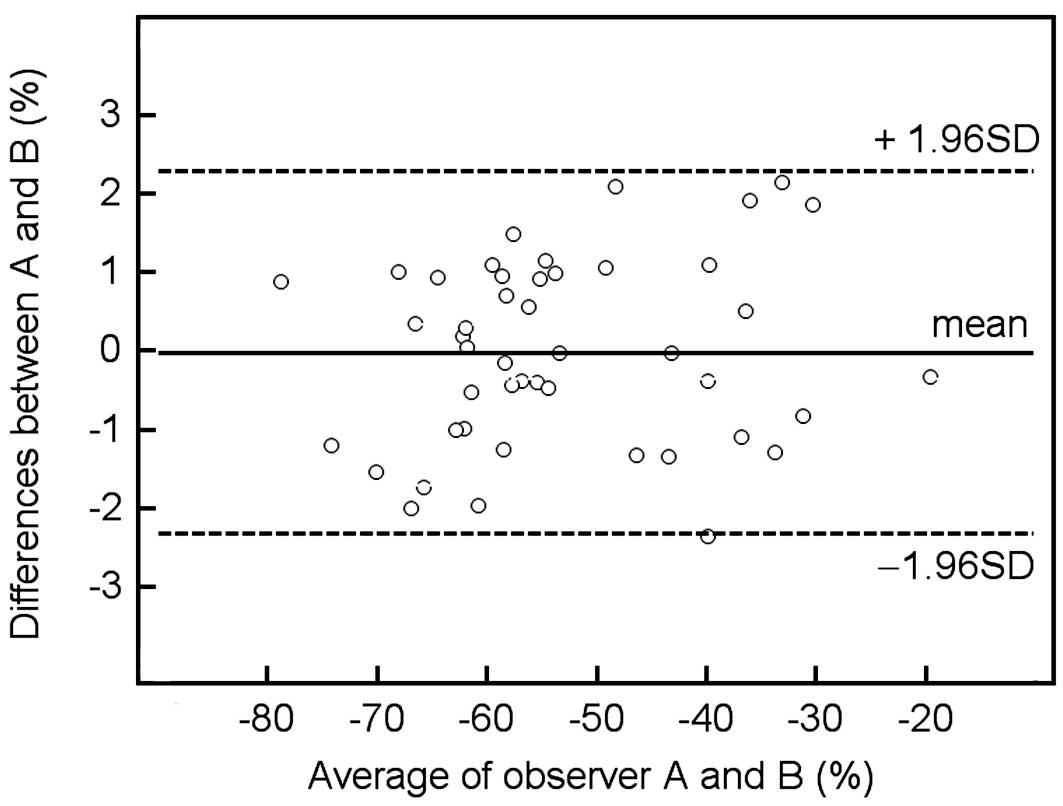
Bland JM and Altman DG: Statistical
methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical
measurement. Lancet. 1:307–310. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Waxman AD: Scintigraphic evaluation of
diffuse hepatic disease. Semin Nucl Med. 12:75–88. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Klingensmith WC III, Fritzberg AR, Zerbe
GO and Koep LJ: Relative role of Tc-99m-diethyl-IDA and
Tc-99m-sulfur colloid in the evaluation of liver function. Clin
Nucl Med. 5:341–346. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Asanuma T, Ono M, Kubota K, et al: Super
paramagnetic iron oxide MRI shows defective Kupffer cell uptake
function in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 59:258–266.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Tsujimoto T, Kawaratani H, Kitazawa T, et
al: Decreased phagocytic activity of Kupffer cells in a rat
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis model. World J Gastroenterol.
14:6036–6043. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Kira T, Tomiguchi S, Kira M, Ohyama Y and
Takahashi M: Quantitative evaluation of the hepatic functional
reserve using technetium-99m DTPA-galactosyl human serum albumin
before and after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Eur
J Nucl Med. 24:1268–1272. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Osada H, Honda N, Takahashi T, et al:
Relationship between (99m)Tc-GSA scintigraphic indices of liver
function reserve and portal circulation in patients with chronic
liver disease. Ann Nucl Med. 21:245–249. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Aguirre DA, Behling CA, Alpert E,
Hassanein TI and Sirlin CB: Liver fibrosis: noninvasive diagnosis
with double contrast material-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology.
239:425–437. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Lucidarme O, Baleston F, Cadi M, et al:
Non-invasive detection of liver fibrosis: Is superparamagnetic iron
oxide particle-enhanced MR imaging a contributive technique? Eur
Radiol. 13:467–474. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Engström-Laurent A, Laurent UB, Lilja K
and Laurent TC: Concentration of sodium hyaluronate in serum. Scand
J Clin Lab Invest. 45:497–504. 1985.
|
|
36.
|
Tsukamoto T, Yamamoto T, Ikebe T, et al:
Serum markers of liver fibrosis and histologic severity of fibrosis
in resected liver. Hepatogastroenterology. 51:777–780.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|