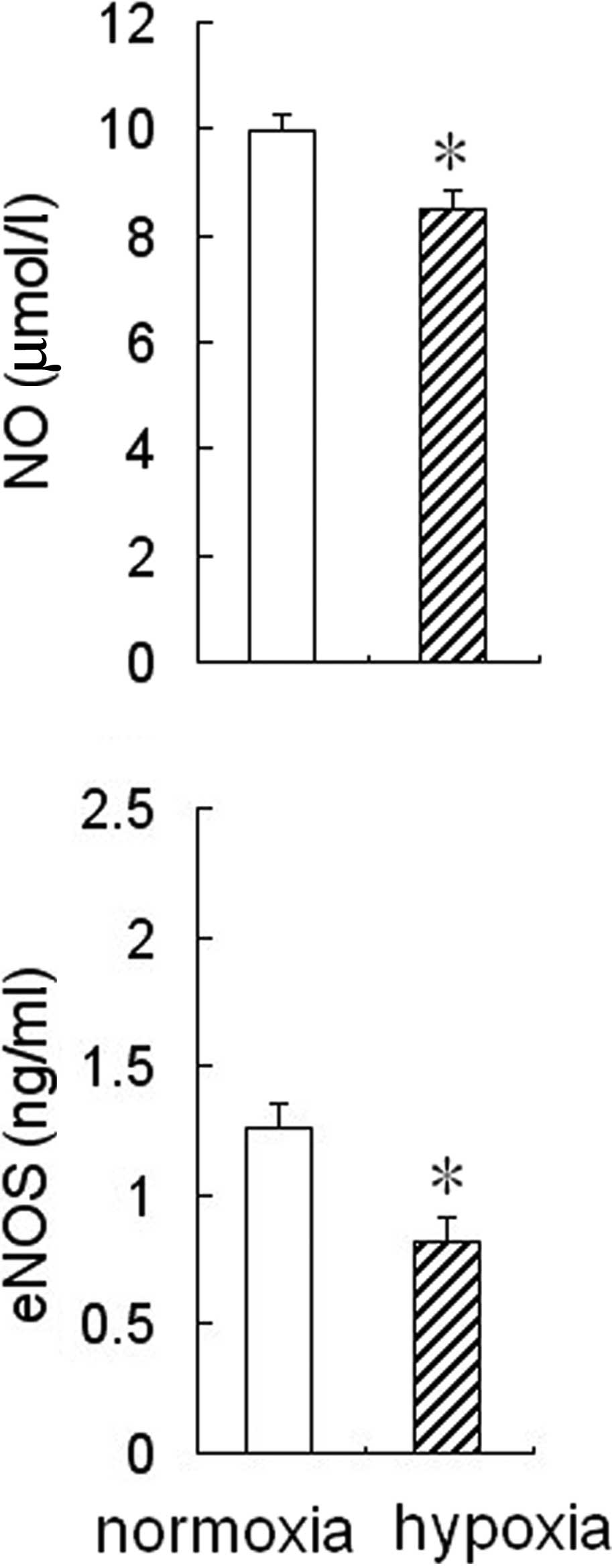
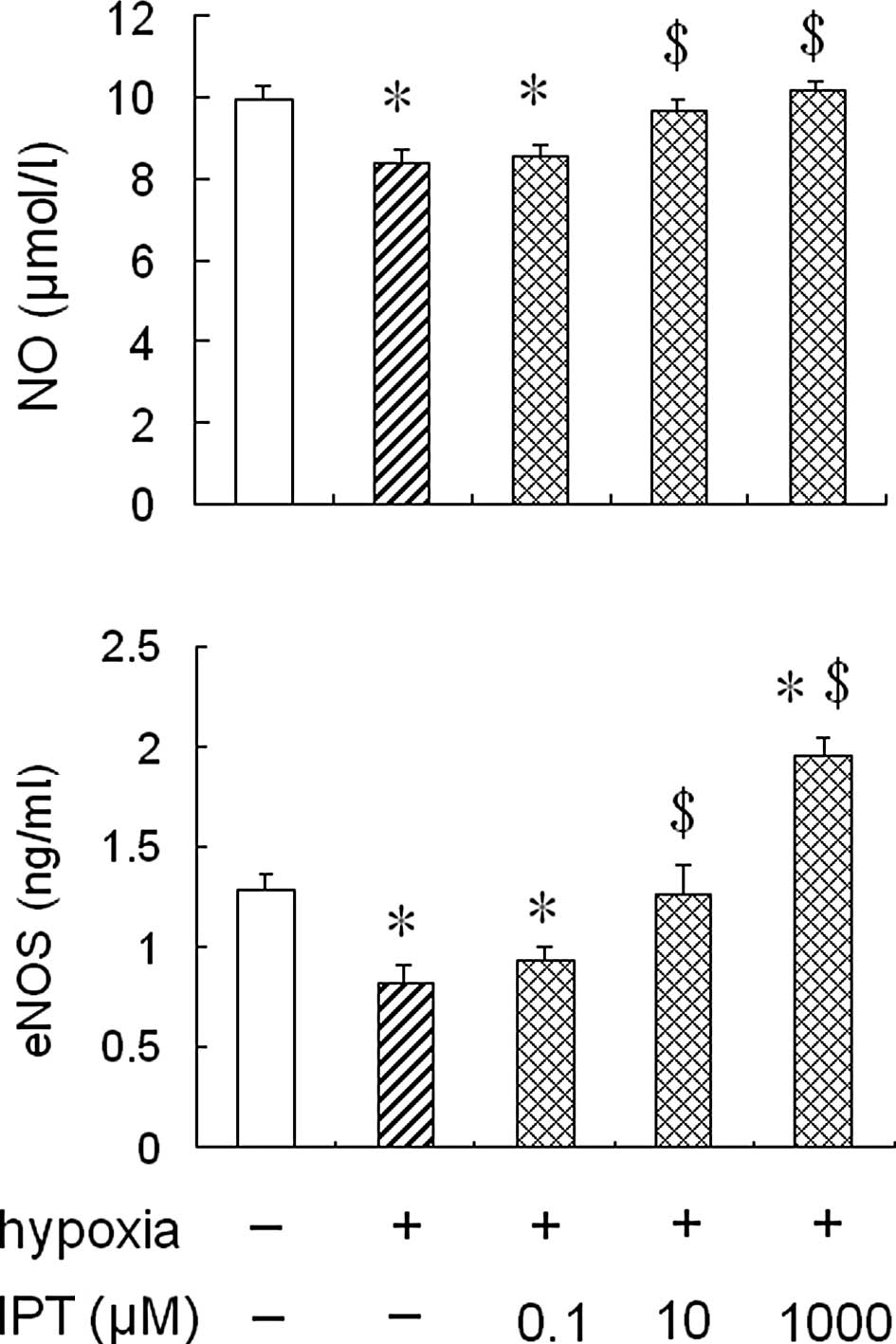
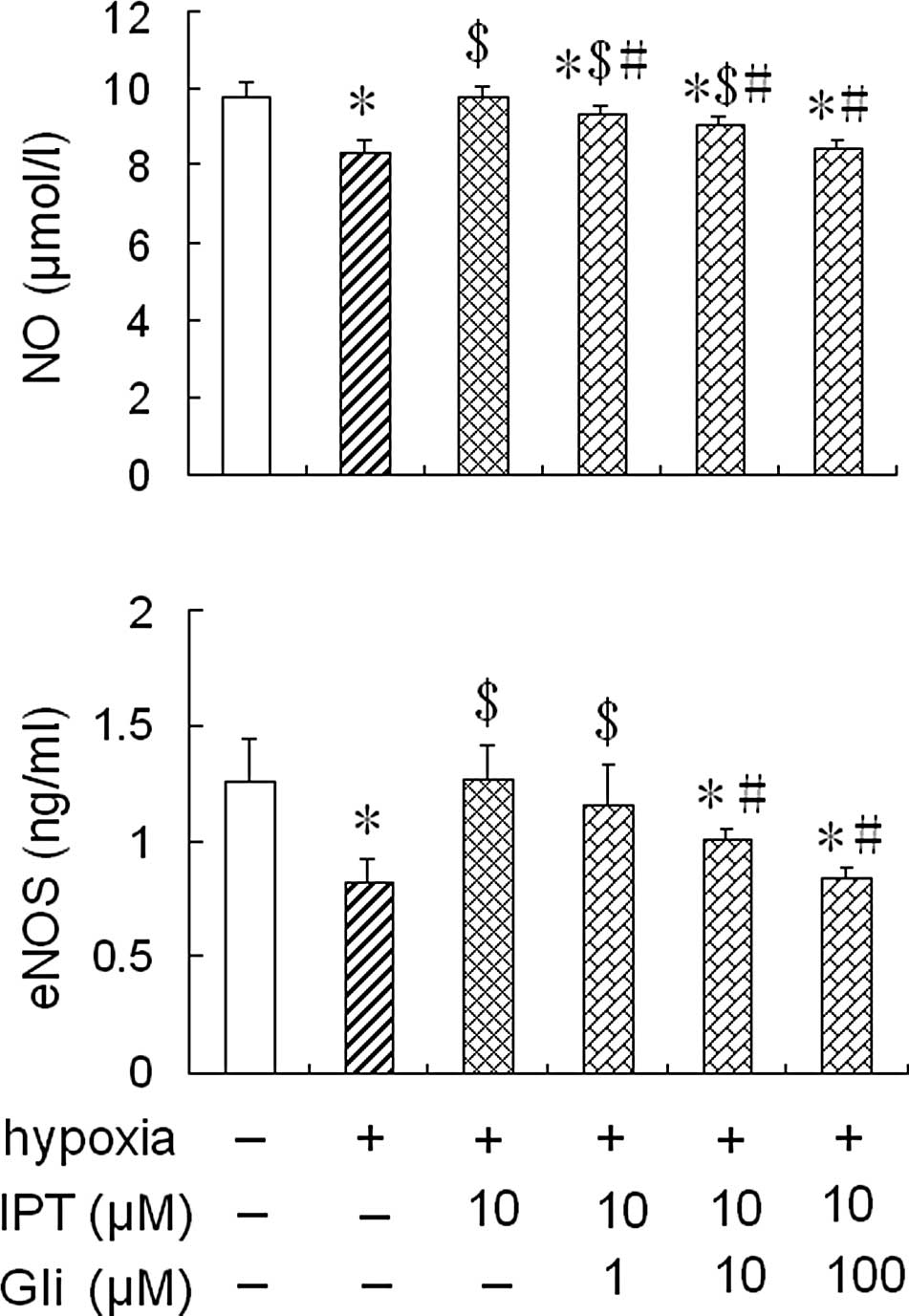
|
1.
|
Y ZhuS ZhangW XieQ LiY ZhouH WangIptakalim
inhibited endothelin-1-induced proliferation of human pulmonary
arterial smooth muscle cells through the activation of KATP
channelVascul Pharmacol489299200810.1016/j.vph.2008.01.001
|
|
2.
|
FA KlokMV HuismanEpidemiology and
management of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertensionNeth J
Med68347351201020876914
|
|
3.
|
MM HoeperDefinition, classification, and
epidemiology of pulmonary arterial hypertensionSemin Respir Crit
Care Med30369375200910.1055/s-0029-123330619634076
|
|
4.
|
B AlanS NalbantgilGenetic, cellular and
molecular mechanisms of pulmonary arterial hypertensionAnadolu
Kardiyol Derg10Suppl 1913201010.5152/akd.2010.114
|
|
5.
|
J BauersachsJD WidderEndothelial
dysfunction in heart failurePharmacol Rep601191262008
|
|
6.
|
D JanigroGA WestEL GordonHR
WinnATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat aorta and brain
microvascular endothelial cellsAm J
Physiol265C812C82119938214038
|
|
7.
|
M ShiraiJT PearsonA ShimouchiChanges in
functional and histological distributions of nitric oxide synthase
caused by chronic hypoxia in rat small pulmonary arteriesBr J
Pharmacol139899910200310.1038/sj.bjp.0705312
|
|
8.
|
S ChatterjeeAB Al-MehdiI LevitanT
StevensAB FisherShear stress increases expression of a KATP channel
in rat and bovine pulmonary vascular endothelial cellsAm J Physiol
Cell Physiol285C959C967200310.1152/ajpcell.00511.200212826604
|
|
9.
|
LF HuS WangXR ShiATP-sensitive potassium
channel opener iptakalim protected against the cytotoxicity of
MPP+ on SH-SY5Y cells by decreasing extracellular
glutamate levelJ
Neurochem9415701579200510.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03306.x16000145
|
|
10.
|
N MisakiX MaoYF LinIptakalim, a vascular
ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel opener, closes rat
pancreatic beta-cell KATP channels and increases insulin releaseJ
Pharmacol Exp Ther322871878200710.1124/jpet.107.12112917522344
|
|
11.
|
W XieH WangH WangG HuEffects of iptakalim
hydrochloride, a novel KATP channel opener, on pulmonary vascular
remodeling in hypoxic ratsLife
Sci7520652076200410.1016/j.lfs.2004.03.03115312751
|
|
12.
|
H WangC LongZ DuanC ShiG JiaY ZhangA new
ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener protects endothelial
function in cultured aortic endothelial cellsCardiovasc
Res73497503200710.1016/j.cardiores.2006.10.00717116295
|
|
13.
|
AR WhortonDB SimondsCA
PiantadosiRegulation of nitric oxide synthesis by oxygen in
vascular endothelial cellsAm J Physiol2721161116619979227518
|
|
14.
|
JK LiaoJJ ZuluetaFS YuHB PengCG CotePM
HassounRegulation of bovine endothelial constitutive nitric oxide
synthase by oxygenJ Clin
Invest9626612666199510.1172/JCI1183328675632
|
|
15.
|
UA ArnetA McMillanJL DinermanB
BallermannCJ LowensteinRegulation of endothelial nitric-oxide
synthase during hypoxiaJ Biol
Chem2711506915073199610.1074/jbc.271.25.150698663208
|
|
16.
|
JK LiaoRho-kinase mediates hypoxia-induced
downregulation of endothelial nitric oxide
synthaseCirculation1065762200210.1161/01.CIR.0000020682.73694.AB12093770
|
|
17.
|
LP McQuillanGK LeungPA MarsdenSK KostykS
KourembanasHypoxia inhibits expression of eNOS via transcriptional
and posttranscriptional mechanismsAm J
Physiol2671921192719947526714
|
|
18.
|
MW PhelanDV FallerHypoxia decreases
constitutive nitric oxide synthase transcript and protein in
cultured endothelial cellsJ Cell
Physiol167469476199610.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199606)167:3%3C469::AID-JCP11%3E3.0.CO;2-%238655601
|
|
19.
|
JX ChenB MeyrickHypoxia increases Hsp90
binding to eNOS via PI3K-Akt in porcine coronary artery
endotheliumLab
Invest84182190200410.1038/labinvest.370002714661033
|
|
20.
|
JM JusticeMA TannerPR MyersEndothelial
cell regulation of nitric oxide production during hypoxia in
coronary microvessels and epicardial arteriesJ Cell
Physiol182359365200010.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(200003)182:3%3C359::AID-JCP6%3E3.0.CO;2-310653602
|
|
21.
|
HY SohnF KrotzT GloeDifferential
regulation of xanthine and NAD(P)H oxidase by hypoxia in human
umbilical vein endothelial cellsRole of nitric oxide and adenosine
Cardiovasc Res58638646200312798437
|
|
22.
|
XP XuJS PollockMA TannerPR MyersHypoxia
activates nitric oxide synthase and stimulates nitric oxide
production in porcine coronary resistance arteriolar endothelial
cellsCardiovasc Res30841847199510.1016/0008-6363(95)00117-4
|
|
23.
|
L OstergaardE StankeviciusMR
AndersenDiminished NO release in chronic hypoxic human endothelial
cellsAm J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol29328942903200710.1152/ajpheart.01230.200617720765
|
|
24.
|
S TaddeiA VirdisL GhiadoniI SudanoA
SalvettiEffects of antihypertensive drugs on endothelial
dysfunction: clinical
implicationsDrugs62265284200210.2165/00003495-200262020-0000311817973
|
|
25.
|
A GiaidD SalehReduced expression of
endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the lungs of patients with
pulmonary hypertensionN Engl J
Med333214221199510.1056/NEJM1995072733304037540722
|
|
26.
|
L KuoJD ChancellorAdenosine potentiates
flow-induced dilation of coronary arterioles by activating KATP
channels in endotheliumAm J Physiol6954154919957653618
|
|
27.
|
M Mederos y SchnitzlerC DerstJ DautR
Preisig-MüllerATP-sensitive potassium channels in capillaries
isolated from guinea-pig heartJ Physiol525307317200010835035
|
|
28.
|
H WangPharmacological characteristics of
the novel antihypertensive drug, iptakalim hydrochloride, and its
molecular mechanismsDrug Dev Res586568200310.1002/ddr.10132
|
|
29.
|
H XueYL ZhangGS LiuH WangA new
ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener protects the kidney from
hypertensive damage in spontaneously hypertensive ratsJ Pharmacol
Exp Ther315501509200510.1124/jpet.105.08972216051697
|
|
30.
|
H WangYL ZhangXC TangHS FengG HuTargeting
ischemic stroke with a novel opener of ATP-sensitive potassium
channels in the brainMol
Pharmacol6611601168200410.1124/mol.104.00317815304552
|