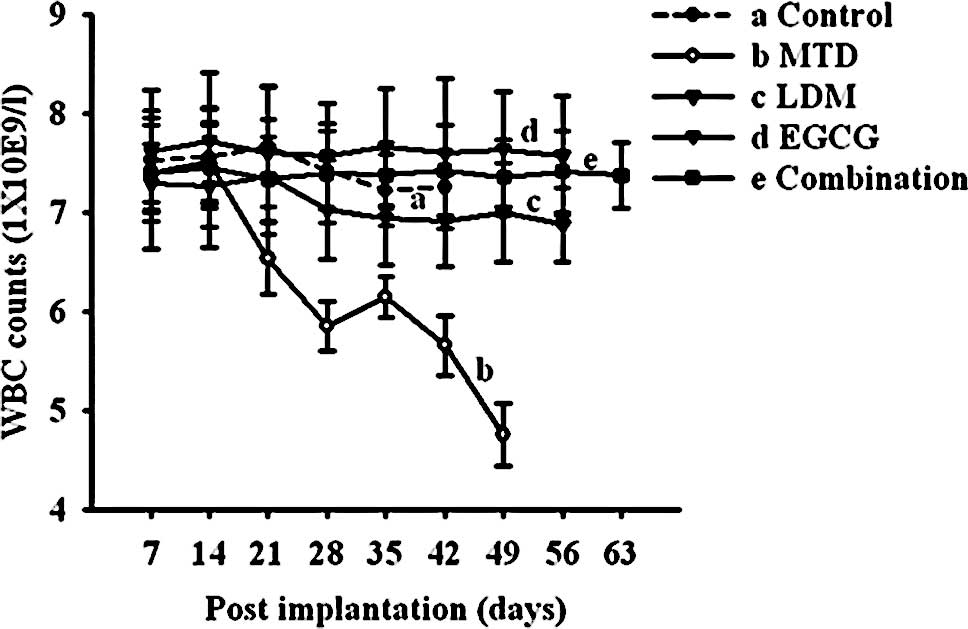
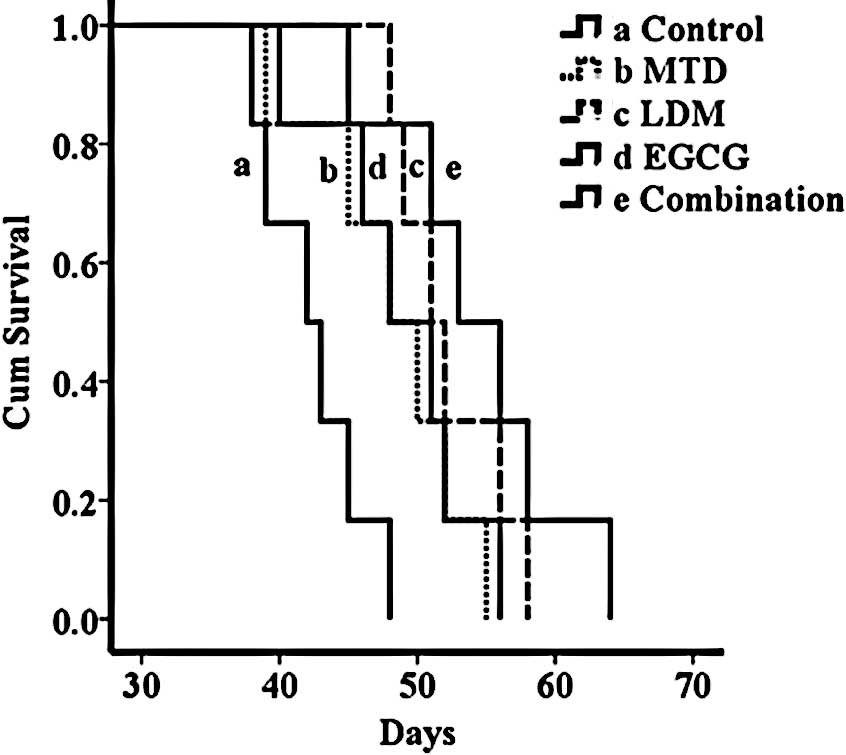
|
1.
|
Albert A: New drugs in the treatment of
gastric tumors. Clin Transl Oncol. 10:256–261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Orlando L, Cardillo A, Rocca A, et al:
Prolonged clinical benefit with metronomic chemotherapy in patients
with metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 17:961–967. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Scharovsky OG, Mainetti LE and Rozados VR:
Metronomic chemotherapy is changing the paradigm that more is
better. Curr Oncol. 16:7–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Tham CK, Choo SP and Poon DY: Capecitabine
with radiation is an effective adjuvant therapy in gastric cancers.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:3709–3715. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bergers G and Hanahan D: Combining
antiangiogenic agents with metronomic chemotherapy enhances
efficacy against late-stage pancreatic islet carcinomas in mice.
Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 67:293–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Garcia AA, Hirte H, Fleming G, et al:
Phase II clinical trial of bevacizumab and low-dose metronomic oral
cyclophosphamide in recurrent ovarian cancer: a trial of the
California, Chicago, and Princess Margaret Hospital phase II
consortia. J Clin Oncol. 26:76–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, et al:
Continuous low-dose therapy with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2
antibody induces sustained tumor regression without overt toxicity.
J Clin Invest. 105:R15–R24. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Khan N, Afaq F, Saleem M, Ahmad N and
Mukhtar H: Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea
polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res.
66:2500–2505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Neuhaus T, Pabst S, Stier S, et al:
Inhibition of the vascular-endothelial growth factor-induced
intracellular signaling and mitogenesis of human endothelial cells
by epigallocatechin-3 gallate. Eur J Pharmacol. 483:223–227. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10.
|
Fassina G, Vene R, Morini M, et al:
Mechanisms of inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and vascular tumor
growth by epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Clin Cancer Res.
10:4865–4873. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Bocci G, Falcone A, Fioravanti A, et al:
Antiangiogenic and anticolorectal cancer effects of metronomic
irinotecan chemotherapy alone and in combination with semaxinib. Br
J Cancer. 98:1619–1629. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Liu TG, Huang Y, Cui D, et al: Inhibitory
effect of ginsenoside Rg3 combined with gemcitabine on angiogenesis
and growth of lung cancer in mice statistical analysis. BMC Cancer.
9:2502009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kamat AA, Kim TJ, Landen CN, et al:
Metronomic chemotherapy enhances the efficacy of antivascular
therapy in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 67:281–288. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Kerbel RS and Kamen BA: The
anti-angiogenic basis of metronomic chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:423–436. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Benelli R, Monteghirfo S, Balbi C, Barboro
P and Ferrari N: Novel antivascular efficacy of metronomic
docetaxel therapy in prostate cancer: hnRNP K as a player. Int J
Cancer. 124:2989–2996. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bocci G, Nicolaou KC and Kerbel RS:
Protracted low-dose effects on human endothelial cell proliferation
and survival in vitro reveal a selective antiangiogenic window for
various chemotherapeutic drugs. Cancer Res. 62:6938–6943.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Zhang M, Tao W, Pan S, Sun X and Jiang H:
Low-dose metronomic chemotherapy of paclitaxel synergizes with
cetuximab to suppress human colon cancer xenografts. Anticancer
Drugs. 20:355–363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Zhang Q, Kang X and Zhao W: Antiangiogenic
effect of low-dose cyclophosphamide combined with ginsenoside Rg3
on Lewis lung carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 342:824–828.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Kerbel RS: Inhibition of tumor
angiogenesis as a strategy to circumvent acquired resistance to
anticancer therapeutic agents. Bioessays. 13:31–36. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Castilla MA, Caramelo C, Gazapo RM, et al:
Role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in endothelial
cell protection against cytotoxic agents. Life Sci. 67:1003–1013.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Ma YP, Yang Y, Zhang S, et al: Efficient
inhibition of lung cancer in murine model by plasmid-encoding VEGF
short hairpin RNA in combination with low-dose DDP. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 29:562010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Machado DE, Berardo PT, Palmero CY, et al:
Higher expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and
its receptor VEGFR-2 (Flk-1) and metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in a
rat model of peritoneal endometriosis is similar to cancer
diseases. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 29:42010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Magnon C, Galaup A, Rouffiac V, et al:
Dynamic assessment of antiangiogenic therapy by monitoring both
tumoral vascularization and tissue degeneration. Gene Ther.
14:108–117. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Raspollini MR, Castiglione F, Garbini F,
et al: Correlation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression
with tumor microdensity vessels and with vascular endothelial
growth factor expression in ovarian carcinoma. Int J Surg Pathol.
13:135–142. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Ji Y, Hayashi K, Amoh Y, et al: The
camptothecin derivative CPT-11 inhibits angiogenesis in a
dual-color imageable orthotopic metastatic nude mouse model of
human colon cancer. Anticancer Res. 27:713–718. 2007.
|
|
26.
|
Mei Y, Qian F, Wei D and Liu J: Reversal
of cancer multidrug resistance by green tea polyphenols. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 56:1307–1314. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Domingo DS, Camouse MM, Hsia AH, et al:
Anti-angiogenic effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in human
skin. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 3:705–709. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Donà M, Dell'Aica I, Calabrese F, et al:
Neutrophil restraint by green tea: inhibition of inflammation,
associated angiogenesis, and pulmonary fibrosis. J Immunol.
15:4335–4341. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Zhu BH, Zhan WH, Li ZR, et al:
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits growth of gastric cancer by
reducing VEGF production and angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol.
13:1162–1169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Lang M, Henson R, Braconi C and Patel T:
Epigallocatechin-gallate modulates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis
in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. Liver Int. 29:670–677. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|