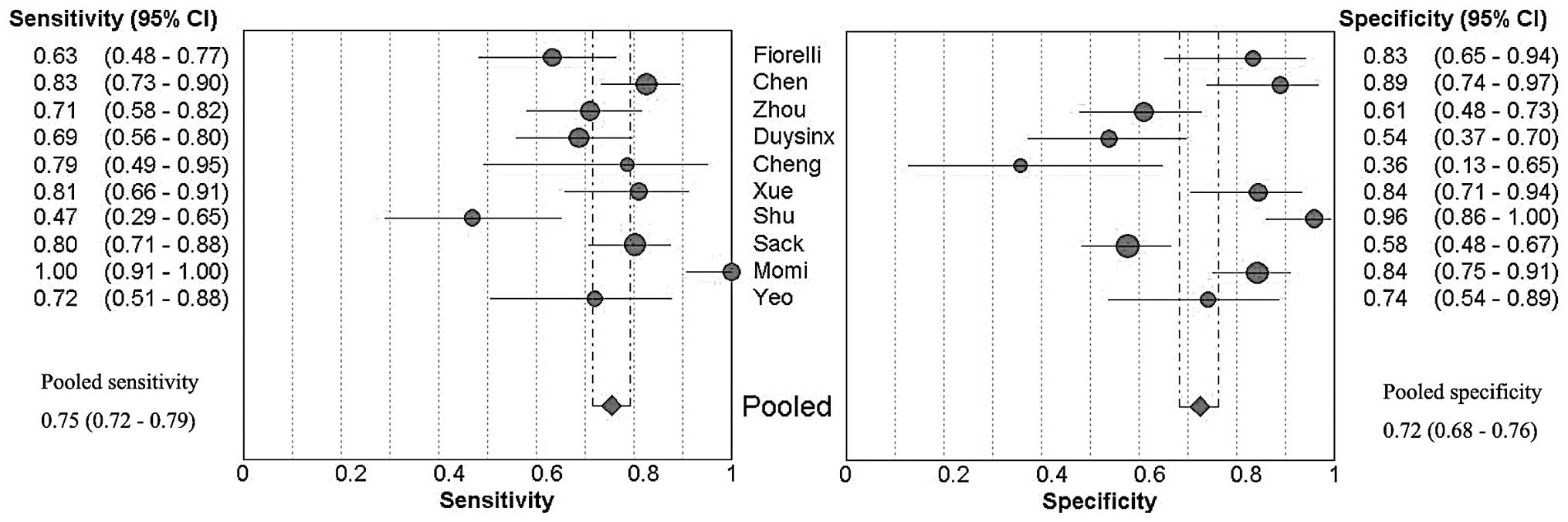
|
1.
|
McGrath EE and Anderson PB: Diagnosis of
pleural effusion: a systematic approach. Am J Crit Care.
20:119–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Bennett R and Maskell N: Management of
malignant pleural effusions. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 11:296–300.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Prakash UB and Reiman HM: Comparison of
needle biopsy with cytologic analysis for the evaluation of pleural
effusion: analysis of 414 cases. Mayo Clin Proc. 60:158–164. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Lombardi G, Zustovich F, Nicoletto MO,
Donach M, Artioli G and Pastorelli D: Diagnosis and treatment of
malignant pleural effusion: a systematic literature review and new
approaches. Am J Clin Oncol. 33:420–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Shi HZ, Liang QL, Jiang J, Qin XJ and Yang
HB: Diagnostic value of carcinoembryonic antigen in malignant
pleural effusion: a meta-analysis. Respirology. 13:518–527. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Liang QL, Shi HZ, Qin XJ, Liang XD, Jiang
J and Yang HB: Diagnostic accuracy of tumour markers for malignant
pleural effusion: a meta-analysis. Thorax. 63:35–41. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Senger DR, Van de Water L, Brown LF, et
al: Vascular permeability factor (VPF, VEGF) in tumor biology.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 12:303–324. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Berse B, Brown LF, Van de Water L, Dvorak
HF and Senger DR: Vascular permeability factor (vascular
endothelial growth factor) gene is expressed differentially in
normal tissues, macrophages, and tumors. Mol Biol Cell. 3:211–220.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Zebrowski BK, Yano S, Liu W, Shaheen RM,
Hicklin DJ, Putnam JB Jr and Ellis LM: Vascular endothelial growth
factor levels and induction of permeability in malignant pleural
effusions. Clin Cancer Res. 5:3364–3368. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Kraft A, Weindel K, Ochs A, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor in the sera and effusions of
patients with malignant and nonmalignant disease. Cancer.
85:178–187. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ishimoto O, Saijo Y, Narumi K, et al: High
level of vascular endothelial growth factor in hemorrhagic pleural
effusion of cancer. Oncology. 63:70–75. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Lim SC, Jung SI, Kim YC and Park KO:
Vascular endothelial growth factor in malignant and tuberculous
pleural effusions. J Korean Med Sci. 15:279–283. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Hamed EA, El-Noweihi AM, Mohamed AZ and
Mahmoud A: Vasoactive mediators (VEGF and TNF-alpha) in patients
with malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions. Respirology.
9:81–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Kishiro I, Kato S, Fuse D, Yoshida T,
Machida S and Kaneko N: Clinical significance of vascular
endothelial growth factor in patients with primary lung cancer.
Respirology. 7:93–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, et al:
Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic
accuracy: the STARD initiative. Standards for Reporting of
Diagnostic Accuracy. Clin Chem. 49:1–6. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt
PM and Kleijnen J: The development of QUADAS: a tool for the
quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in
systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 3:252003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Jones CM, Ashrafian H, Skapinakis P, Arora
S, Darzi A, Dimopoulos K and Athanasiou T: Diagnostic accuracy
meta-analysis: a review of the basic principles of interpretation
and application. Int J Cardiol. 140:138–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Moses LE, Shapiro D and Littenberg B:
Combining independent studies of a diagnostic test into a summary
ROC curve: data-analytic approaches and some additional
considerations. Stat Med. 12:1293–1316. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lijmer JG, Bossuyt PM and Heisterkamp SH:
Exploring sources of heterogeneity in systematic reviews of
diagnostic tests. Stat Med. 21:1525–1537. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Koniari I, Koletti B and Apostolakis E:
Vascular endothelial growth factor with tumour growth factor-beta,
endostatin, proteinases or cytokines might be useful for
differential diagnosis of pleural effusions. Interact Cardiovasc
Thorac Surg. 12:424–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Kiropoulos TS, Kostikas K and
Gourgoulianis KI: Vascular endothelial growth factor levels in
pleural fluid and serum of patients with tuberculous pleural
effusions. Chest. 128:4682005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Economidou F, Antoniou KM, Soufla G, et
al: Role of VEGF-stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha/CXCL12 axis in
pleural effusion of lung cancer. J Recept Signal Transduct Res.
30:154–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Kotyza J, Havel D, Vrzalová J, Kulda V and
Pesek M: Diagnostic and prognostic significance of inflammatory
markers in lung cancer-associated pleural effusions. Int J Biol
Markers. 25:12–20. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Bunatova K, Obermajer N, Kotyza J, Pesek M
and Kos J: Levels of cathepsins S and H in pleural fluids of
inflammatory and neoplastic origin. Int J Biol Markers. 24:47–51.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Economidou F, Antoniou KM, Tzanakis N,
Sfiridaki K, Siafakas NM and Schiza SE: Angiogenic molecule Tie-2
and VEGF in the pathogenesis of pleural effusions. Respir Med.
102:774–779. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Atanackovic D, Cao Y, Kim JW, et al: The
local cytokine and chemokine milieu within malignant effusions.
Tumour Biol. 29:93–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Tomimoto H, Yano S, Muguruma H, Kakiuchi S
and Sone S: Levels of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 1 are elevated in the exudative pleural effusions. J Med
Invest. 54:146–153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Daniil ZD, Zintzaras E, Kiropoulos T,
Papaioannou AI, Koutsokera A, Kastanis A and Gourgoulianis KI:
Discrimination of exudative pleural effusions based on multiple
biological parameters. Eur Respir J. 30:957–964. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Yeh HH, Lai WW, Chen HH, Liu HS and Su WC:
Autocrine IL-6-induced Stat3 activation contributes to the
pathogenesis of lung adenocarcinoma and malignant pleural effusion.
Oncogene. 25:4300–4309. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Kalomenidis I, Kollintza A, Sigala I,
Papapetropoulos A, Papiris S, Light RW and Roussos C:
Angiopoietin-2 levels are elevated in exudative pleural effusions.
Chest. 129:1259–1266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Ruiz E, Alemán C, Alegre J, et al:
Angiogenic factors and angiogenesis inhibitors in exudative pleural
effusions. Lung. 183:185–195. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Jin HY, Lee KS, Jin SM and Lee YC:
Vascular endothelial growth factor correlates with matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in the pleural effusion. Respir Med.
98:115–122. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Davidson B, Vintman L, Zcharia E, et al:
Heparanase and basic fibroblast growth factor are co-expressed in
malignant mesothelioma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 21:469–476. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
van Hensbergen Y, Broxterman HJ,
Hanemaaijer R, et al: Soluble aminopeptidase N/CD13 in malignant
and nonmalignant effusions and intratumoral fluid. Clin Cancer Res.
8:3747–3754. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
J Strizzi L, Catalano A, Vianale G, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor in
human malignant mesothelioma. J Pathol. 193:468–475.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Verheul HM, Hoekman K, Jorna AS, Smit EF
and Pinedo HM: Targeting vascular endothelial growth factor
blockade: ascites and pleural effusion formation. Oncologist.
5(Suppl 1): 45–50. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Cheng D, Lee YC, Rogers JT, Perkett EA,
Moyers JP, Rodriguez RM and Light RW: Vascular endothelial growth
factor level correlates with transforming growth factor-beta
isoform levels in pleural effusions. Chest. 118:1747–1753. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39.
|
Yanagawa H, Takeuchi E, Suzuki Y, Ohmoto
Y, Bando H and Sone S: Vascular endothelial growth factor in
malignant pleural effusion associated with lung cancer. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 48:396–400. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Thickett DR, Armstrong L and Millar AB:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in inflammatory and
malignant pleural effusions. Thorax. 54:707–710. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Cheng D, Rodriguez RM, Perkett EA, Rogers
J, Bienvenu G, Lappalainen U and Light RW: Vascular endothelial
growth factor in pleural fluid. Chest. 116:760–765. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Yeo KT, Wang HH, Nagy JA, et al: Vascular
permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) in guinea
pig and human tumor and inflammatory effusions. Cancer Res.
53:2912–2918. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Momi H, Matsuyama W, Inoue K, Kawabata M,
Arimura K, Fukunaga H and Osame M: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and proinflammatory cytokines in pleural effusions. Respir
Med. 96:817–822. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Sack U, Hoffmann M, Zhao XJ, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor in pleural effusions of
different origin. Eur Respir J. 25:600–604. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45.
|
Shu J, Sun G, Liu H and Liu J: Clinical
utility of vascular endothelial growth factor in diagnosing
malignant pleural effusions. Acta Oncol. 46:1004–1011. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Xue K, Xiong S and Xiong W: Clinical value
of vascular endothelial growth factor combined with
interferon-gamma in diagnosing malignant pleural effusion and
tuberculous pleural effusion. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 27:495–497. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47.
|
Cheng M, Chen Y, Yu X, Tian Z and Wei H:
Diagnostic utility of LunX mRNA in peripheral blood and pleural
fluid in patients with primary non-small cell lung cancer. BMC
Cancer. 8:1562008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Duysinx BC, Corhay JL, Hubin L, Nguyen D,
Henket M and Louis R: Diagnostic value of interleukine-6,
transforming growth factor-beta 1 and vascular endothelial growth
factor in malignant pleural effusions. Respir Med. 102:1708–1714.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Zhou WB, Bai M and Jin Y: Diagnostic value
of vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin in malignant
pleural effusions. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 13:381–386.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50.
|
Chen Y, Liang B, Zhao YJ, Wang SC, Fan YB
and Wu GP: Transcription expression and clinical significance of
vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA and endostatin mRNA in
pleural effusions of patients with lung cancer. Diagn Cytopathol.
Oct. 26–2010, (E-pub ahead of print). View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51.
|
Fiorelli A, Vicidomini G, Di Domenico M,
et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor in pleural fluid for
differential diagnosis of benign and malignant origin and its
clinical applications. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 12:420–424.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52.
|
Glas AS, Lijmer JG, Prins MH, Bonsel GJ
and Bossuyt PM: The diagnostic odds ratio: a single indicator of
test performance. J Clin Epidemiol. 56:1129–1135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|