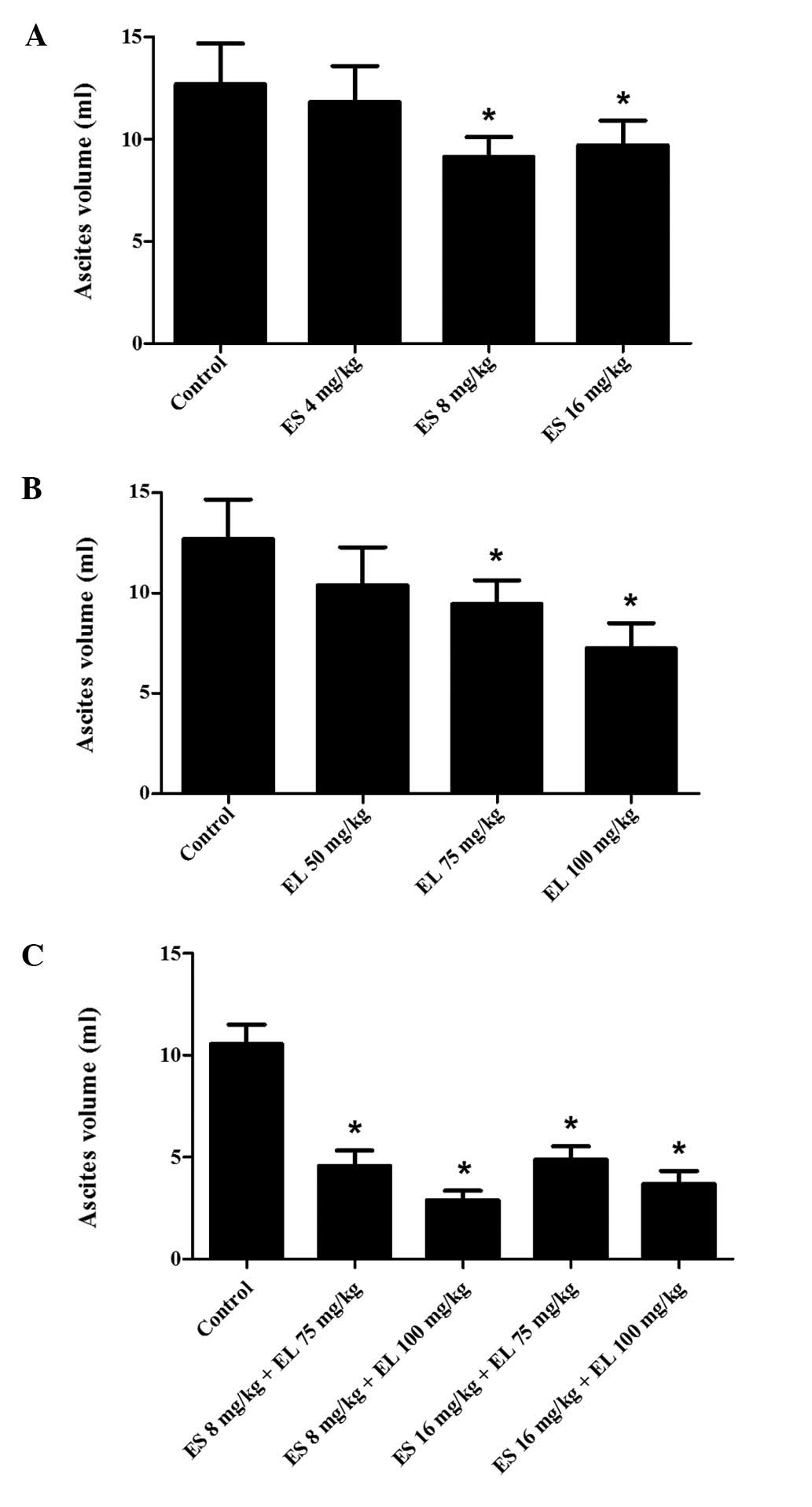
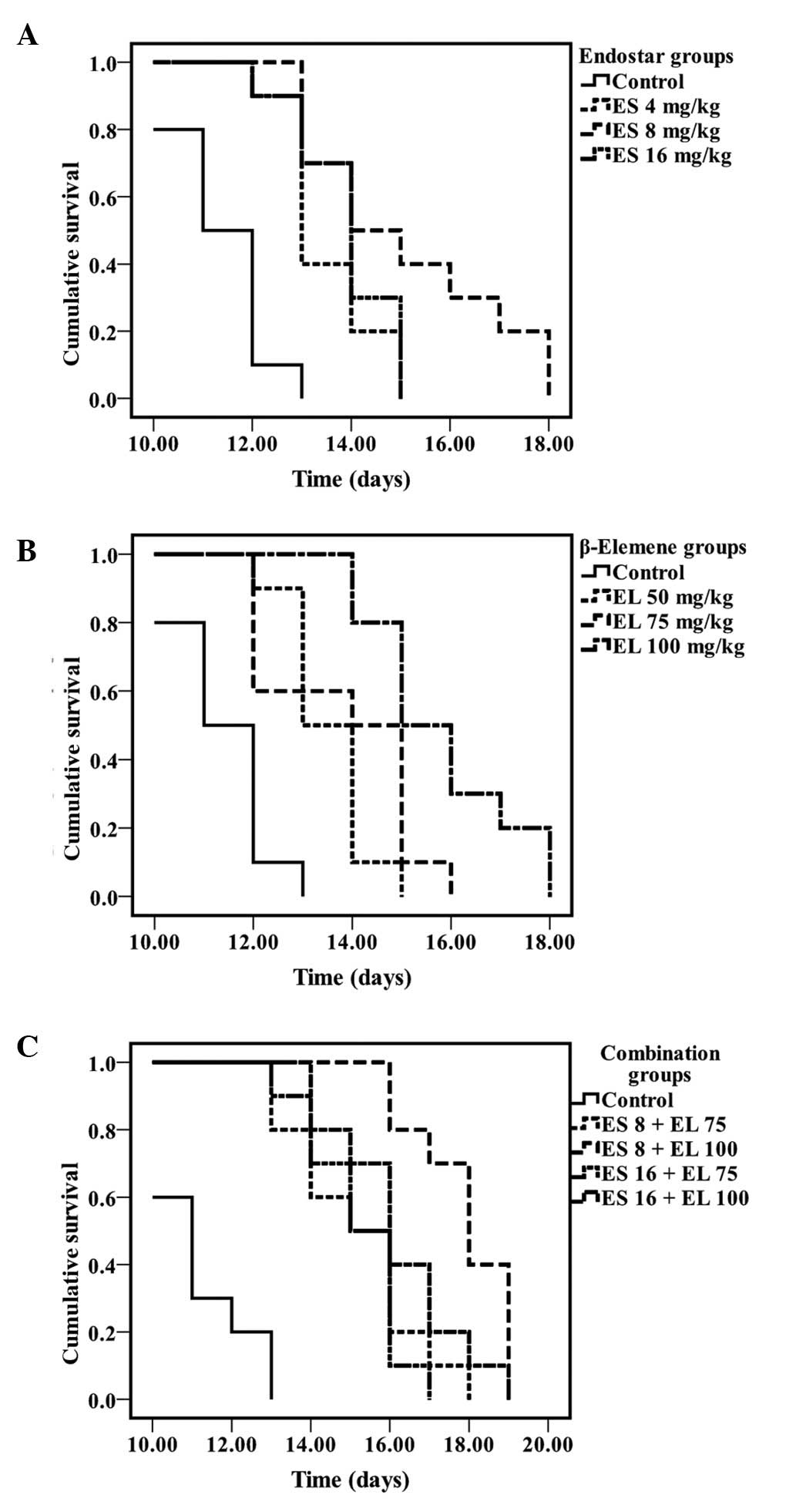
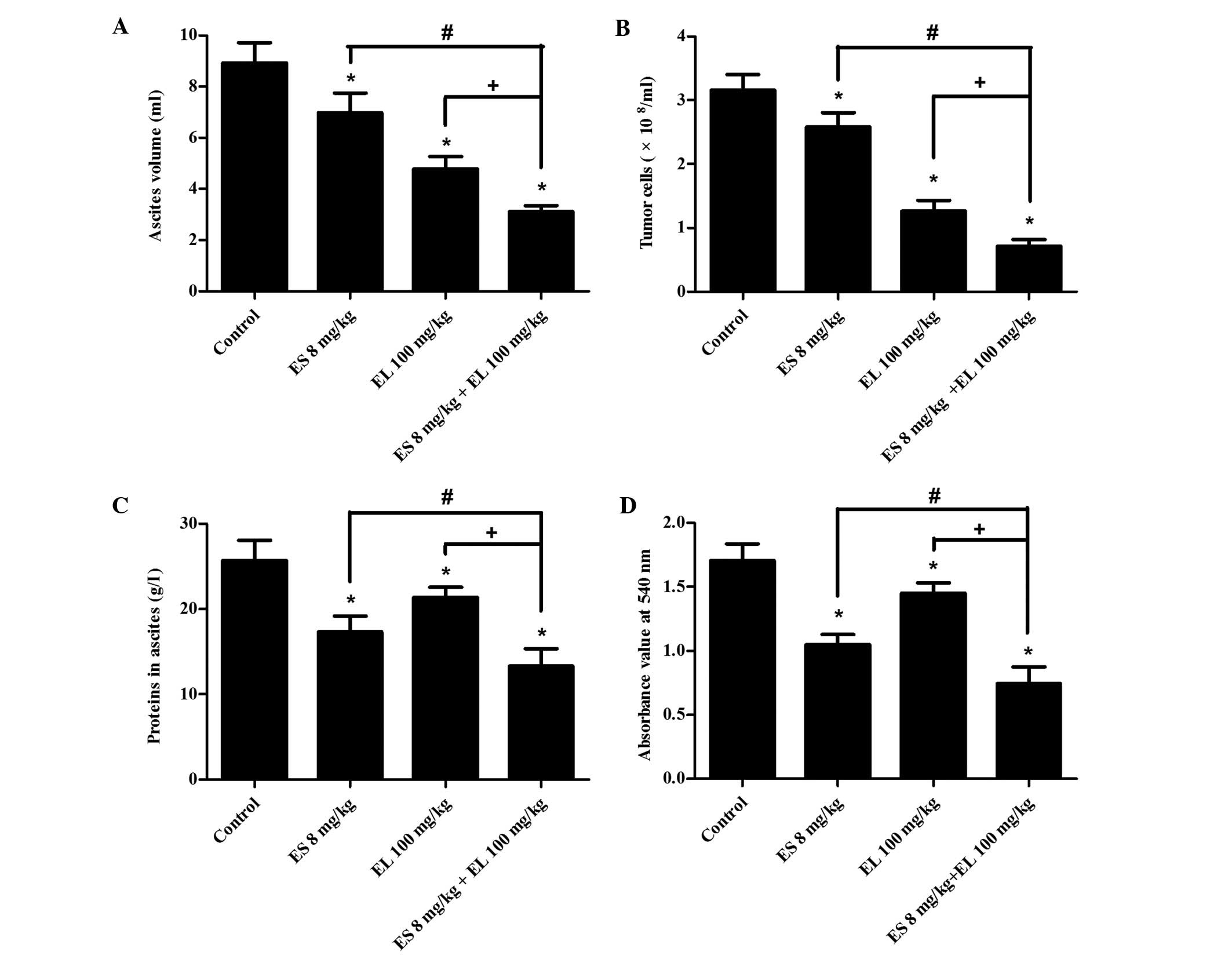
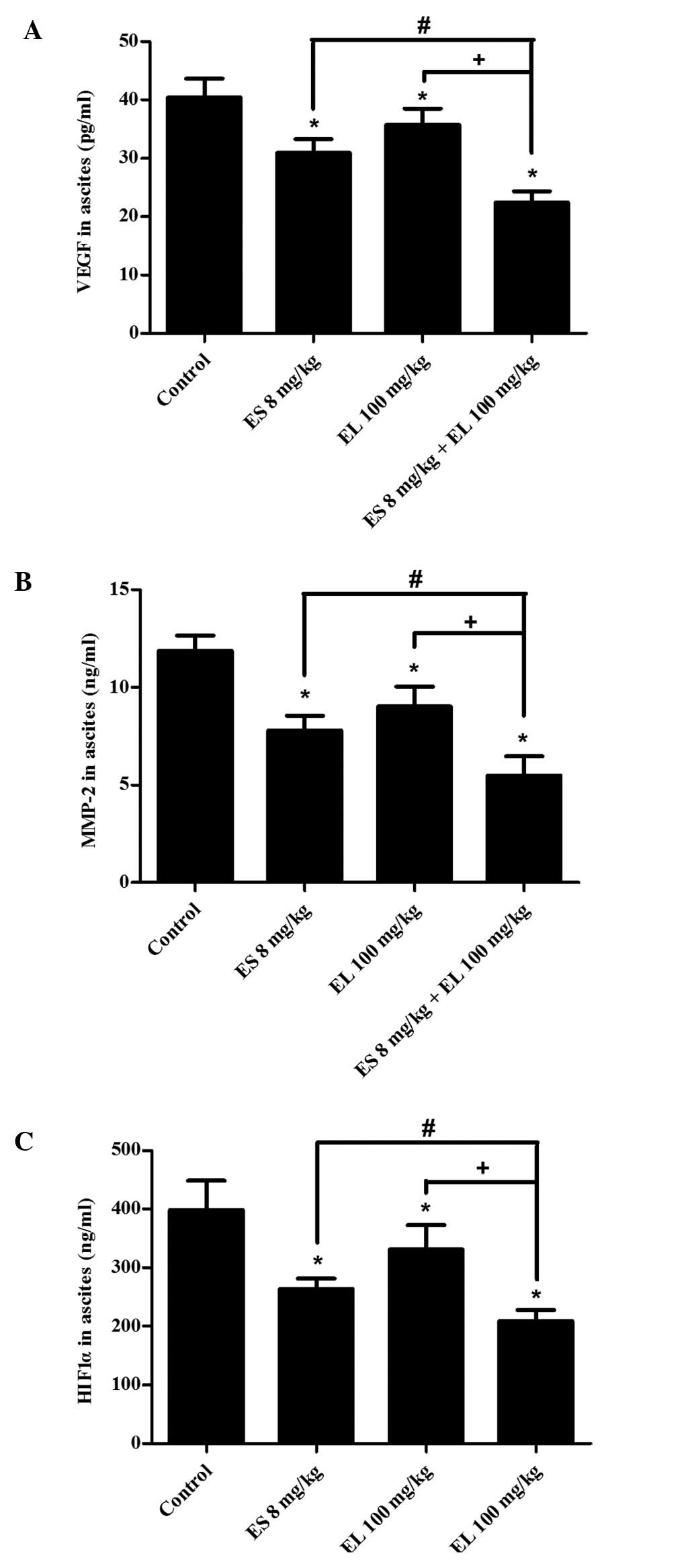
|
1.
|
Garrison RN, Kaelin LD, Galloway RH and
Heuser LS: Malignant ascites: clinical and experimental
observations. Ann Surg. 203:644–651. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Becker G, Galandi D and Blum HE: Malignant
ascites: systematic review and guideline for treatment. Eur J
Cancer. 42:589–597. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Tamsma JT, Keizer HJ and Meinders AE:
Pathogenesis of malignant ascites: Starling's law of capillary
hemodynamics revisited. Ann Oncol. 12:1353–1357. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
O'Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, et al:
Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell. 88:277–285. 1997.
|
|
5.
|
Ling Y, Yang Y, Lu N, et al: Endostar, a
novel recombinant human endostatin, exerts antiangiogenic effect
via blocking VEGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of KDR/Flk-1 of
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 361:79–84. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Wang J, Sun Y, Liu Y, et al: Results of
randomized, multicenter, double-blind phase III trial of
rh-endostatin (YH-16) in treatment of advanced non-small cell lung
cancer patients. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 8:283–290. 2005.(In
Chinese).
|
|
7.
|
Li Y, Huang XE, Yan PW, et al: Efficacy
and safety of endostar combined with chemotherapy in patients with
advanced solid tumors. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:1119–1123.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Jiang Z and Qin S: Study progression of
recombinant human endostatin (Endostar) for the treatment of
malignant serous effusion. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol. 10:435–441.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Li QQ, Wang G, Huang F, et al:
Antineoplastic effect of beta-elemene on prostate cancer cells and
other types of solid tumor cells. J Pharm Pharmacol. 62:1018–1027.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Chen W, Lu Y, Wu J, et al: Beta-elemene
inhibits melanoma growth and metastasis via suppressing vascular
endothelial growth factor-mediated angiogenesis. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 67:799–808. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Zhao J, Li QQ, Zou B, et al: In vitro
combination characterization of the new anticancer plant drug
β-elemene with taxanes against human lung carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
31:241–252. 2007.
|
|
12.
|
Wang J, Zhang H and Sun Y: Phase III
clinical trial of elemenum emulsion in the management of malignant
pleural and peritoneal effusions. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
18:464–467. 1996.(In Chinese).
|
|
13.
|
Kanaoka Y, Maekawa A, Penrose JF, et al:
Attenuated zymosan-induced peritoneal vascular permeability and
IgE-dependent passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in mice lacking
leukotriene C4 synthase. J Biol Chem. 276:22608–22613. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Cao SS and Zhen YS: Potentiation of
antimetabolite antitumor activity in vivo by dipyridamole and
amphotericin B. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 24:181–186. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhang J, Wang X and Lu H: Amifostine
increases cure rate of cisplatin on ascites hepatoma 22 via
selectively protecting renal thioredoxin reductase. Cancer Lett.
260:127–136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, et al:
Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes
accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 219:983–985. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17.
|
Zebrowski BK, Liu W, Ramirez K, et al:
Markedly elevated levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in
malignant ascites. Ann Surg Oncol. 6:373–378. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Luo JC, Toyoda M and Shibuya M:
Differential inhibition of fluid accumulation and tumor growth in
two mouse ascites tumors by an antivascular endothelial growth
factor/permeability factor neutralizing antibody. Cancer Res.
58:2594–2600. 1998.
|
|
19.
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Sun XM, Dong WG, Yu BP, et al: Detection
of type IV collagenase activity in malignant ascites. World J
Gastroenterol. 9:2592–2595. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Hewitson KS, McNeill LA and Schofield CJ:
Modulating the hypoxia-inducible factor signaling pathway:
applications from cardiovascular disease to cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
10:821–833. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Fujiwara S, Nakagawa K, Harada H, et al:
Silencing hypoxiainducible factor-1α inhibits cell migration and
invasion under hypoxic environment in malignant gliomas. Int J
Oncol. 30:793–802. 2007.
|