|
1.
|
Light RW: Pleural effusions. Med Clin
North Am. 95:1055–1070. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Bennett R and Maskell N: Management of
malignant pleural effusions. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 11:296–300.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
McGrath EE and Anderson PB: Diagnosis of
pleural effusion: a systematic approach. Am J Crit Care.
20:119–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Lombardi G, Zustovich F, Nicoletto MO,
Donach M, Artioli G and Pastorelli D: Diagnosis and treatment of
malignant pleural effusion: a systematic literature review and new
approaches. Am J Clin Oncol. 33:420–423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Shen YC, Liu MQ, Wan C, Chen L, Wang T and
Wen FQ: Diagnostic accuracy of vascular endothelial growth factor
for malignant pleural effusion. Exp Ther Med. March 14–2012.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
6.
|
Shi HZ, Liang QL, Jiang J, Qin XJ and Yang
HB: Diagnostic value of carcinoembryonic antigen in malignant
pleural effusion: a meta-analysis. Respirology. 13:518–527. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Liang QL, Shi HZ, Qin XJ, Liang XD, Jiang
J and Yang HB: Diagnostic accuracy of tumour markers for malignant
pleural effusion: a meta-analysis. Thorax. 63:35–41. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Zvereva MI, Shcherbakova DM and Dontsova
OA: Telomerase: structure, functions, and activity regulation.
Biochemistry (Mosc). 75:1563–1583. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Rhyu MS: Telomeres, telomerase, and
immortality. J Natl Cancer Inst. 87:884–894. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Chen CH and Chen RJ: Prevalence of
telomerase activity in human cancer. J Formos Med Assoc.
110:275–289. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Ouellette MM, Wright WE and Shay JW:
Targeting telomerase-expressing cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med.
15:1433–1442. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Heaphy CM and Meeker AK: The potential
utility of telomere-related markers for cancer diagnosis. J Cell
Mol Med. 15:1227–1238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Tangkijvanich P, Tresukosol D,
Sampatanukul P, et al: Telomerase assay for differentiating between
malignancy-related and nonmalignant ascites. Clin Cancer Res.
5:2470–2475. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Braunschweig R, Yan P, Guilleret I, et al:
Detection of malignant effusions: comparison of a telomerase assay
and cytologic examination. Diagn Cytopathol. 24:174–180. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group: Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 6:e10000972009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Leeflang MM, Deeks JJ, Gatsonis C and
Bossuyt PM; Cochrane Diagnostic Test Accuracy Working Group:
Systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy. Ann Intern Med.
149:889–897. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Whiting PF, Weswood ME, Rutjes AW, Reitsma
JB, Bossuyt PN and Kleijnen J: Evaluation of QUADAS, a tool for the
quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. BMC Med Res
Methodol. 6:92006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Devillé WL, Buntinx F, Bouter LM, et al:
Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: didactic
guidelines. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2:92002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Moses LE, Shapiro D and Littenberg B:
Combining independent studies of a diagnostic test into a summary
ROC curve: data-analytic approaches and some additional
considerations. Stat Med. 12:1293–1316. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P and Irwig L: The
performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size
effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was
assessed. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:882–893. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
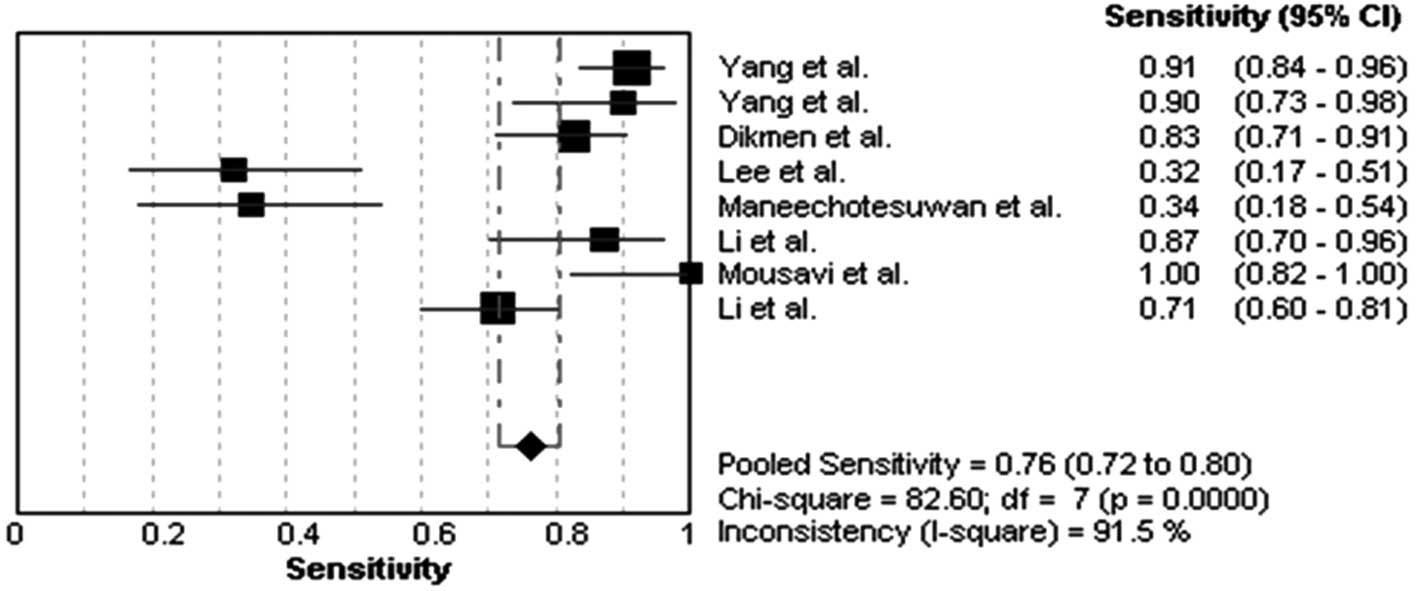
Yang CT, Lee MH, Lan RS and Chen JK:
Telomerase activity in pleural effusions: diagnostic significance.
J Clin Oncol. 16:567–573. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Yang Z and Xie C: Comparison of the
diagnostic value of telomerase activity with CEA level in benign
and malignant pleural effusions. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi.
24:201–203. 2001.(In Chinese).
|
|
23.
|
Dikmen G, Dikmen E, Kara M, Sahin E, Doğan
P and Ozdemir N: Diagnostic implications of telomerase activity in
pleural effusions. Eur Respir J. 22:422–426. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Lee WY: Limitations of detection of
malignancy in pleural effusions using ELISA-based TRAP assay:
comparison with cytological examination. Cytopathology. 16:227–232.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Maneechotesuwan K, Lertworawiwat A,
Tscheikuna J and Wamanuttajinda V: Comparison of telomerase
activity between malignant and tuberculous pleural effusions. J Med
Assoc Thai. 89(Suppl 5): S46–54. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Li GB, Wang M, Guo S, Lü Y and Wang W:
Value of combined pleural effusion testing of telomerase and CEA
for differential diagnosis of malignant and nonmalignant pleural
effusion. Chin J Cancer Prev Treat. 15:299–300. 318:2008.
|
|
27.
|
Mousavi SA, Bahari R and Karimi MA:
Comparison of telomerase activity in malignant and benign pleural
effusions. Tanaffos. 8:17–23. 2009.
|
|
28.
|
Li H, Fu J, Xiu Y and Zhou Q: Diagnostic
significance of combining telomerase activity with CYFRA21-1 level
in differentiating malignant pleural effusion caused by lung cancer
from benign pleural effusion. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 13:652–654.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
29.
|
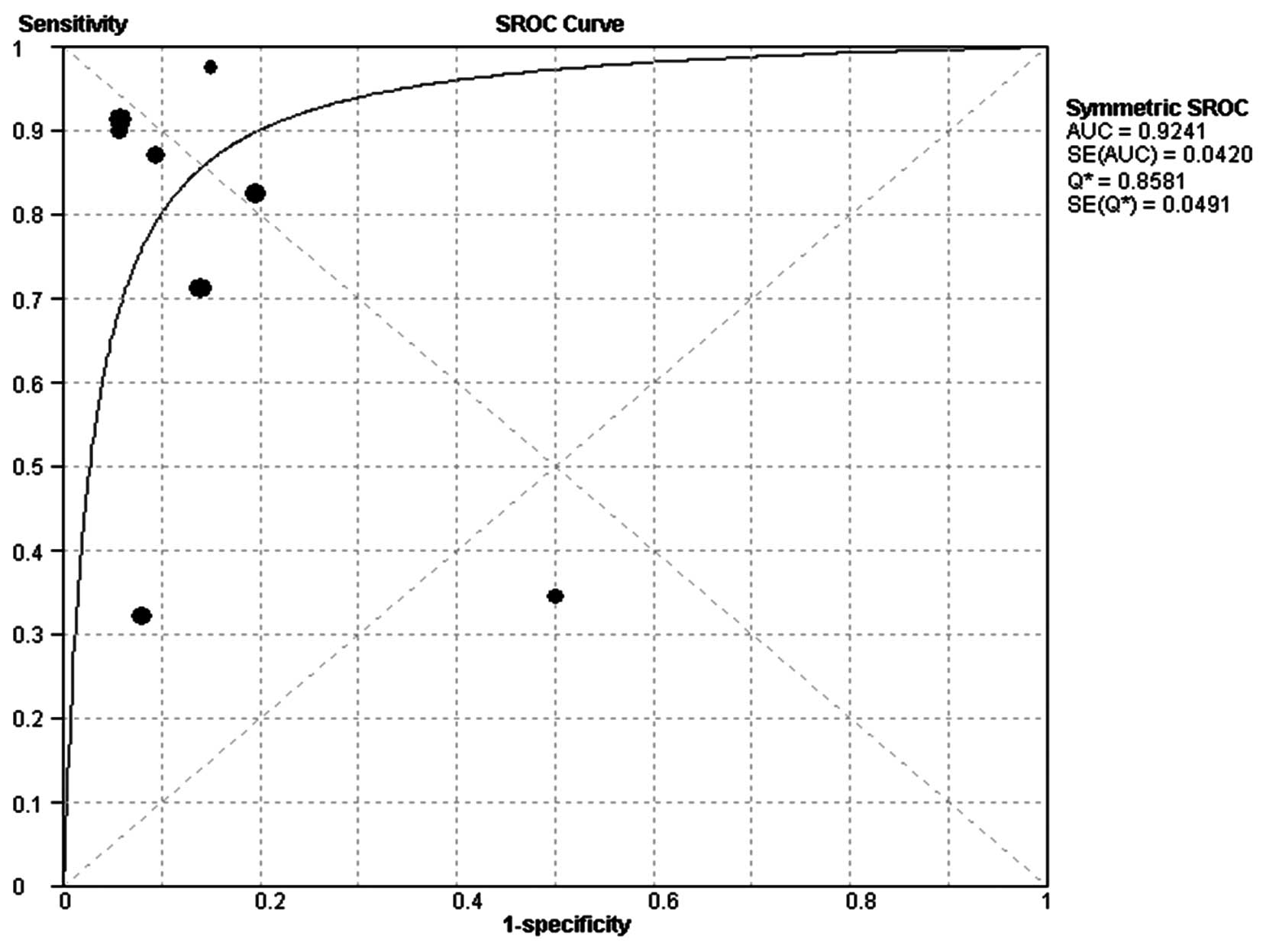
Walter SD: Properties of the summary
receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve for diagnostic test
data. Stat Med. 21:1237–1256. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Jones CM and Athanasiou T: Summary
receiver operating characteristic curve analysis techniques in the
evaluation of diagnostic tests. Ann Thorac Surg. 79:16–20. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
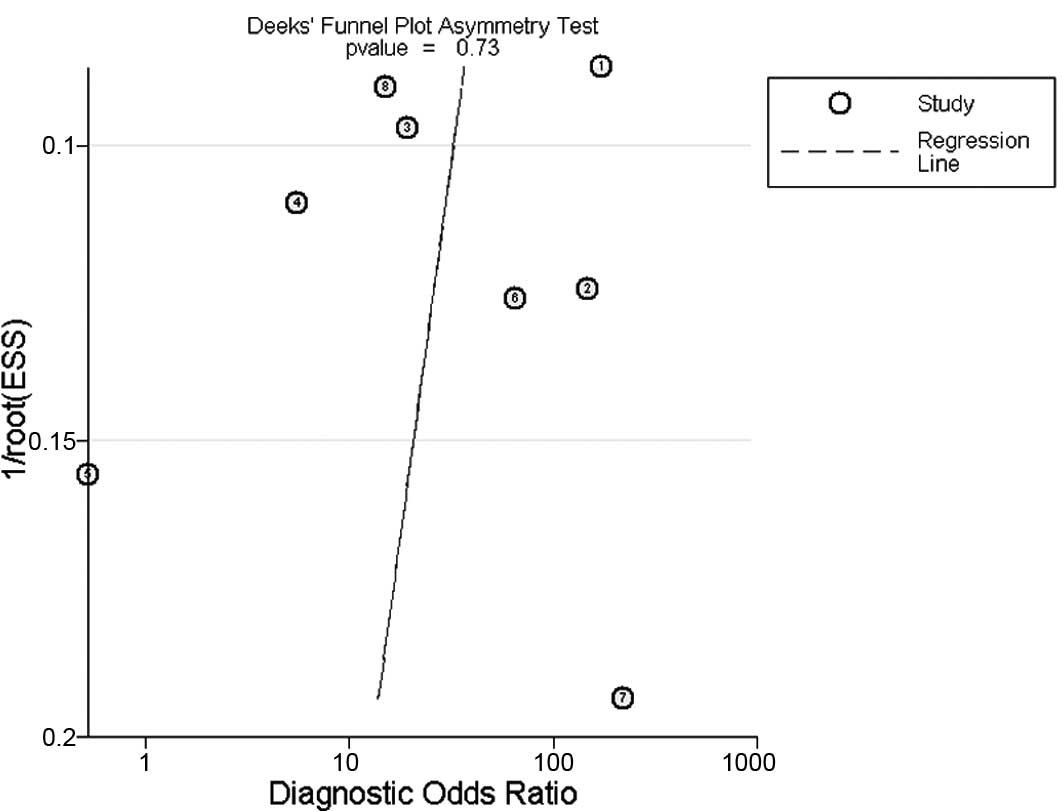
Glas AS, Lijmer JG, Prins MH, Bonsel GJ
and Bossuyt PM: The diagnostic odds ratio: a single indicator of
test performance. J Clin Epidemiol. 56:1129–1135. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Stengel D, Bauwens K, Sehouli J,
Ekkernkamp A and Porzsolt F: A likelihood ratio approach to
meta-analysis of diagnostic studies. J Med Screen. 10:47–51. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Hansson M, Zendehrokh N, Ohyashiki J, et
al: Telomerase activity in effusions: a comparison between telomere
repeat amplification protocol in situ and conventional telomere
repeat amplification protocol assay. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
132:1896–1902. 2008.
|
|
34.
|
Dejmek A, Yahata N, Ohyashiki K, et al: In
situ telomerase activity in pleural effusions: a promising marker
for malignancy. Diagn Cytopathol. 24:11–15. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Song F, Khan KS, Dinnes J and Sutton AJ:
Asymmetric funnel plots and publication bias in meta-analyses of
diagnostic accuracy. Int J Epidemiol. 31:88–95. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|