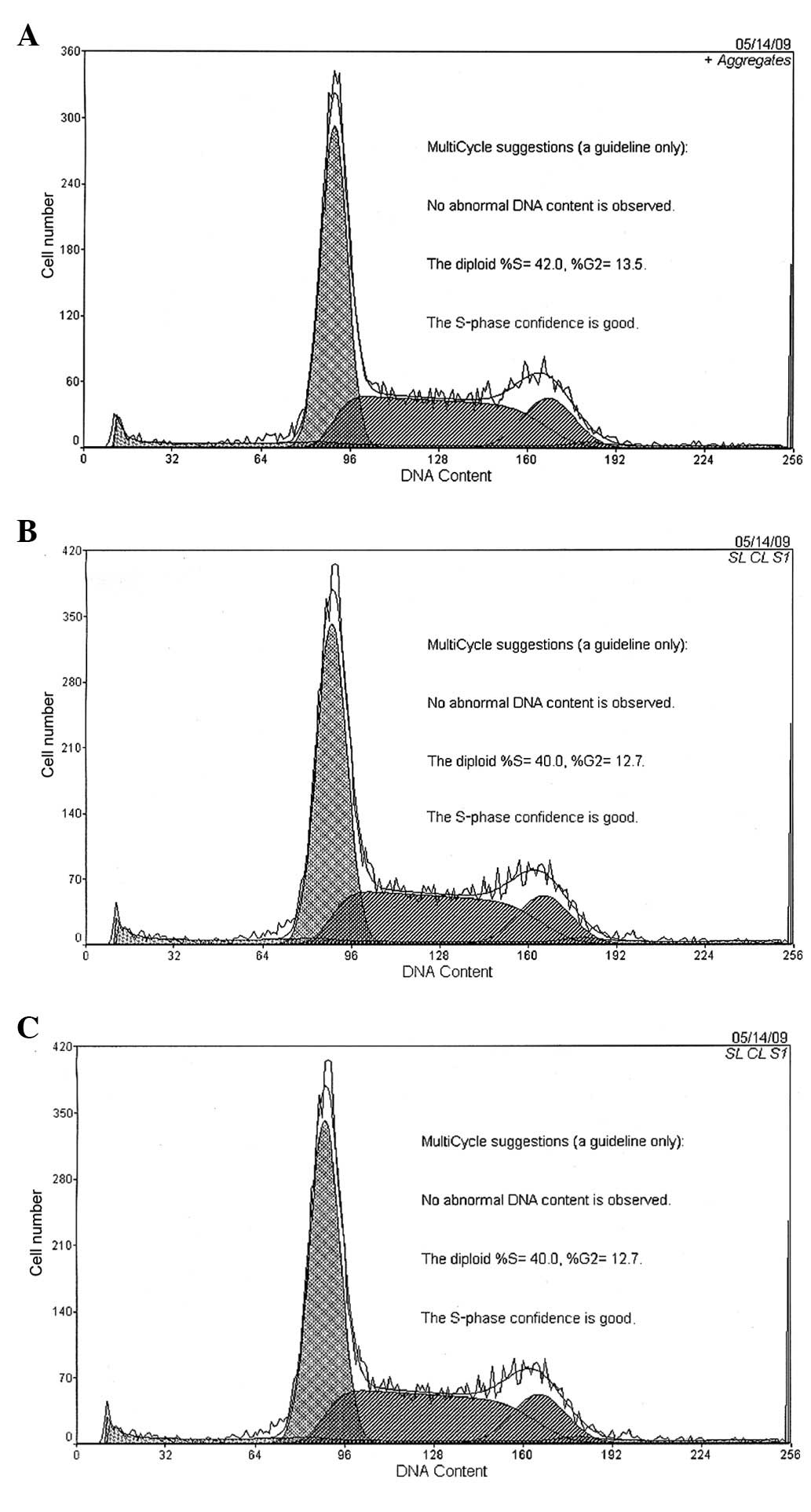
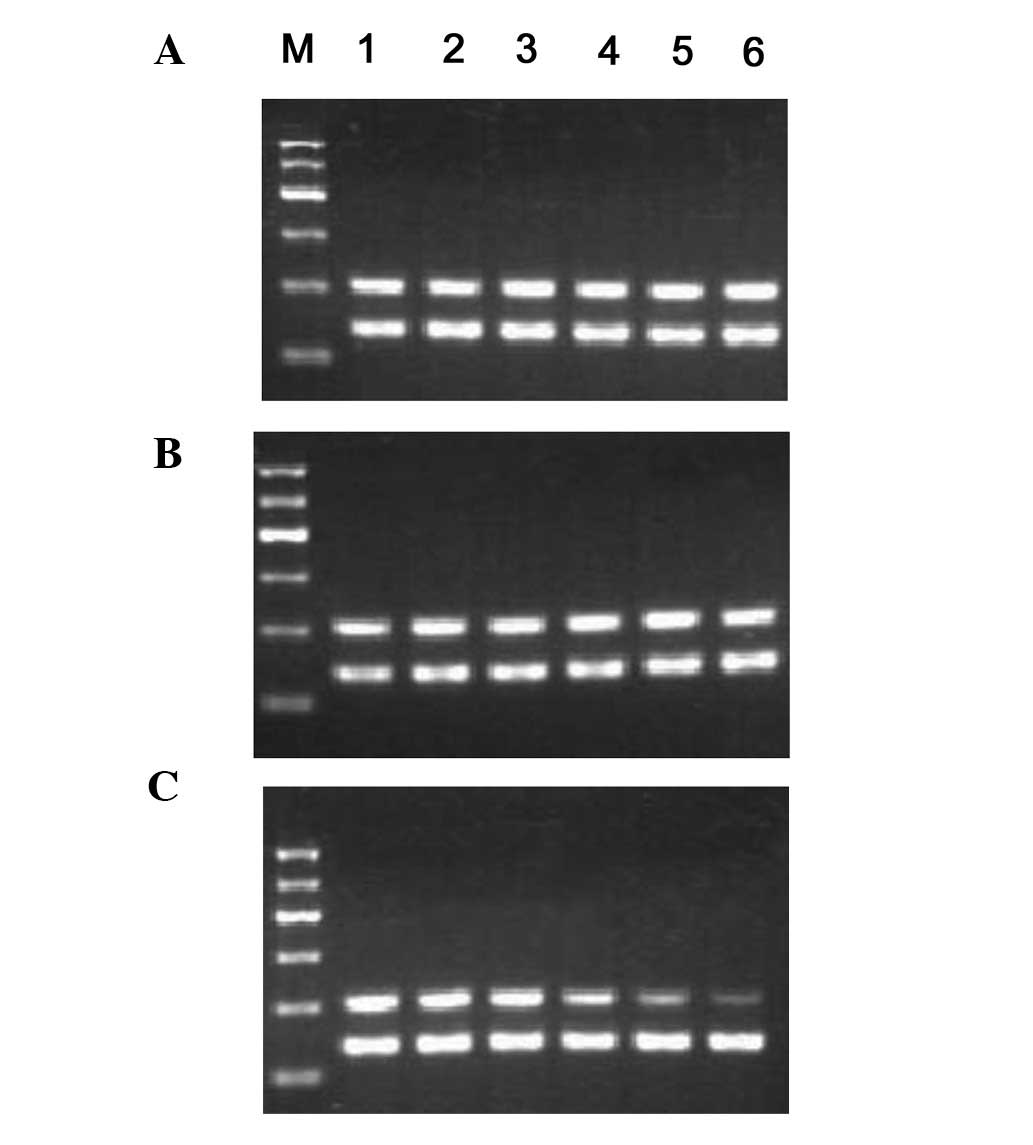
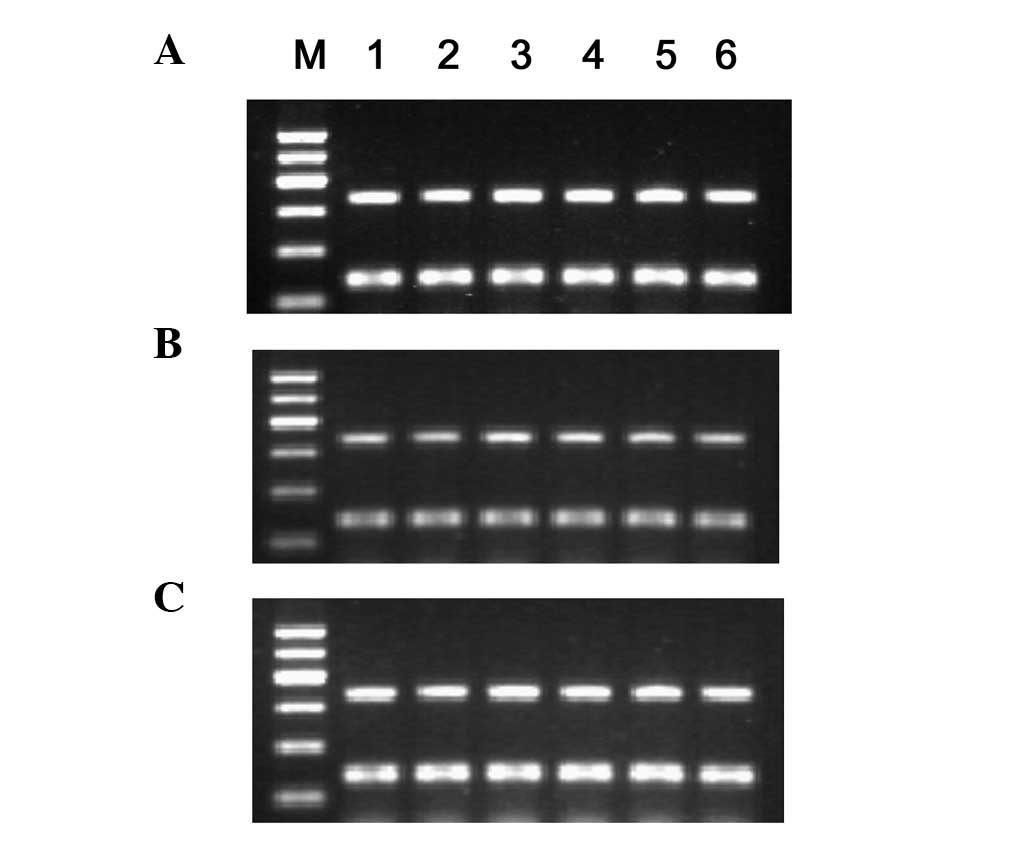
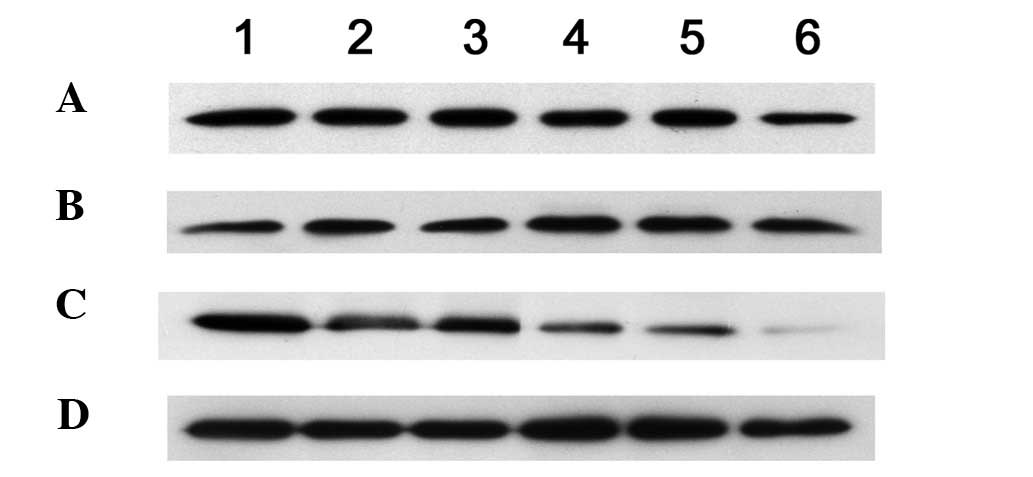
|
1.
|
Friedman SL: Hepatic stellate cells:
protean, multifunctional, and enigmatic cells of the liver. Physiol
Rev. 88:125–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Anderson PAW, Muller-Borer BJ, Esch GL,
Coleman WB, Grisham JW and Malouf NN: Calcium signals induce liver
stem cells to acquire a cardiac phenotype. Cell Cycle. 6:1565–1569.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Iop L, Chiavegato A, Callegari A, et al:
Different cardiovascular potential of adult-and fetal-type
mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of heart cryoinjury. Cell
Transplant. 17:679–694. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lysy PA, Campard D, Smets F, et al:
Persistence of a chimerical phenotype after hepatocyte
differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cell
Prolif. 41:36–58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Polyak K, Lee MH, Erdjument-Bromage H, et
al: Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a
potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell.
78:59–66. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Ishikawa T, Terai S, Urata Y, et al:
Fibroblast growth factor2 facilitates the differentiation of
transplanted bone marrow cells into hepatocytes. Cell Tissue Res.
323:221–231. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Toyoshima H and Hunter T: p27, a novel
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to
p21. Cell. 78:67–74. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Slingerland J and Pagano M: Regulation of
the cdk inhibitor p27 and its deregulation in cancer. J Cell
Physiol. 183:10–17. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Weber JD, Hu W, Jefcoat SC Jr, Raben DM
and Baldassare JJ: Ras-stimulated extracellular signal-related
kinase 1 and RhoA activities coordinate platelet-derived growth
factor-induced G1 progression through the independent regulation of
cyclin D1 and p27. J Biol Chem. 272:32966–32971. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Russo FP, Alison MR, Bigger BW, et al: The
bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis.
Gastroenterology. 130:1807–1821. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Parekkadan B, van Poll D, Megeed Z, et al:
Immunomodulation of activated hepatic stellate cells by mesenchymal
stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 363:247–352. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Shi L, Li G, Wang J, et al: Bone marrow
stromal cells control the growth of hepatic stellate cells in
vitro. Dig Dis Sci. 53:2969–2974. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Cattam P, Hohaus S, Bellacosa A, et al:
Association between Cyclin Dl (CCND1) gene amplification and human
papillomavirus infection in human laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 4:2585–2589. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Calbo J, Parreno M, Sotillo E, et al: Gl
cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase-coordinated phosphorylation of
endogenous pocket proteins differentially regulates their
interactions with E2F4 and E2FI and gene expression. Biol Chem.
277:50–63. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16.
|
Lents NH, Keenan SM, Bellon C and
Baldassare JJ: Stimulation of the Raf/MEK/ERK cascade is necessary
and sufficient for activation and Thr-l60 phosphorylation of a
nuclear-targeted CDK2. Biol Chem. 277:47–69. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Gardner LB, Li Q, Park MS, Flanagan WM,
Semenza GL and Dang CV: Hypoxia inhibits G1/S transition through
regulation of p27 expression. J Biol Chem. 276:7919–7926. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Kuo MY, Hsu HY, Kok SH, et al: Prognostic
role of p27 (Kip1) expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma in
Taiwan. Oral Oncol. 38:172–178. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ridley AJ: Rho proteins and cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 84:13–19. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Hall A: The cytoskeleton and cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:5–14. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Seasholtz TM, Zhang T, Morissette MR,
Howes AL, Yang AH and Brown JH: Increased expression and activity
of RhoA are associated with increased DNA synthesis and reduced
p27(Kip1) expression in the vasculature of hypertensive rats. Circ
Res. 89:488–495. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Mammoto A, Huang S, Moore K, Oh P and
Ingber DE: Role of RhoA, mDia, and ROCK in cell shape-dependent
control of the Skp2-p27kip1 pathway and the G1/S transition.
J Biol Chem. 279:26323–26330. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Besson A, Dowdy SF and Roberts JM: CDK
inhibitors: cell cycle regulators and beyond. Dev Cell. 14:159–169.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Singh SP, Lipman J, Goldman H, et al: Loss
or altered subcellular localization of p27 in Barrett's associated
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 58:1730–1735. 1998.
|
|
25.
|
Yannaki E, Athanasiou E, Xagorari A, et
al: G-CSF-primed hematopoietic stem cells or G-CSF per se
accelerate recovery and improve survival after liver injury,
predominantly by promoting endogenous repair programs. Exp Hematol.
33:108–119. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Oyagi S, Hirose M, Kojima M, et al:
Therapeutic effect of transplanting HGF-treated bone marrow
mesenchymal cells into CCl4-injured rats. J Hepatol. 44:742–748.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Li Y, Chen J, Chen XG, Wang L, et al:
Human marrow stromal cell therapy for stroke in rat: neurotrophins
and functional recovery. Neurology. 59:514–523. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|