|
1
|
Adeyemi BF, Olusanya AA and Lawoyin JO:
Oral squamous cell carcinoma, socioeconomic status and history of
exposure to alcohol and tobacco. J Natl Med Assoc. 103:498–502.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li L, Psoter WJ, Buxó CJ, Elias A,
Cuadrado L and Morse DE: Smoking and drinking in relation to oral
potentially malignant disorders in Puerto Rico: a case-control
study. BMC Cancer. 11:3242011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin WJ, Jiang RS, Wu SH, Chen FJ and Liu
SA: Smoking, alcohol, and betel quid and oral cancer: a prospective
cohort study. J Oncol. 2011:5259762011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhuo W, Wang Y, Zhuo X, et al: CYP1A1 and
GSTM1 polymorphisms and oral cancer risk: association studies via
evidence-based meta-analyses. Cancer Invest. 27:86–95. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhuo XL, Li Q, Zhou Y, et al: Study on
TP53 codon 72 polymorphisms with oral carcinoma susceptibility.
Arch Med Res. 40:625–634. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou C, Zhou Y, Li J, et al: The Arg194Trp
polymorphism in the X-ray repair cross-complementing group 1 gene
as a potential risk factor of oral cancer: a meta-analysis. Tohoku
J Exp Med. 219:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Niu Y, Hu Y, Wu M, et al: CYP2E1 Rsa I/Pst
I polymorphism contributes to oral cancer susceptibility: a
meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 39:607–612. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Witzel II, Koh LF and Perkins ND:
Regulation of cyclin D1 gene expression. Biochem Soc Trans.
38:217–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reis-Filho JS, Savage K, Lambros MB, et
al: Cyclin D1 protein overexpression and CCND1 amplification in
breast carcinomas: an immunohistochemical and chromogenic in
situ hybridisation analysis. Mod Pathol. 19:999–1009. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kumar H, Vandana R and Kumar G:
Immunohistochemical expression of cyclin D1 in ameloblastomas and
adenomatoid odontogenic tumors. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol.
15:283–287. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kaminagakura E, Werneck da Cunha I, Soares
FA, Nishimoto IN and Kowalski LP: CCND1 amplification and protein
overexpression in oral squamous cell carcinoma of young patients.
Head Neck. 33:1413–1419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saini SS and Klein MA: Targeting Cyclin D1
in non-small cell lung cancer and mesothelioma cells by antisense
oligonucleotides. Anticancer Res. 31:3683–3690. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Musgrove EA, Caldon CE, Barraclough J,
Stone A and Sutherland RL: Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:558–572. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pabalan N, Bapat B, Sung L, Jarjanazi H,
Francisco-Pabalan O and Ozcelik H: Cyclin D1 Pro241Pro
(CCND1-G870A) polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk
in human populations: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 17:2773–2781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Betticher DC, Thatcher N, Altermatt HJ,
Hoban P, Ryder WD and Heighway J: Alternate splicing produces a
novel cyclin D1 transcript. Oncogene. 11:1005–1011. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Solomon DA, Wang Y, Fox SR, et al: Cyclin
D1 splice variants. Differential effects on localization, RB
phosphorylation, and cellular transformation. J Biol Chem.
278:30339–30347. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sathyan KM, Nalinakumari KR, Abraham T and
Kannan S: CCND1 polymorphisms (A870G and C1722G) modulate its
protein expression and survival in oral carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
44:689–697. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rydzanicz M, Golusinski P,
Mielcarek-Kuchta D, Golusinski W and Szyfter K: Cyclin D1 gene
(CCND1) polymorphism and the risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the
larynx. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 263:43–48. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
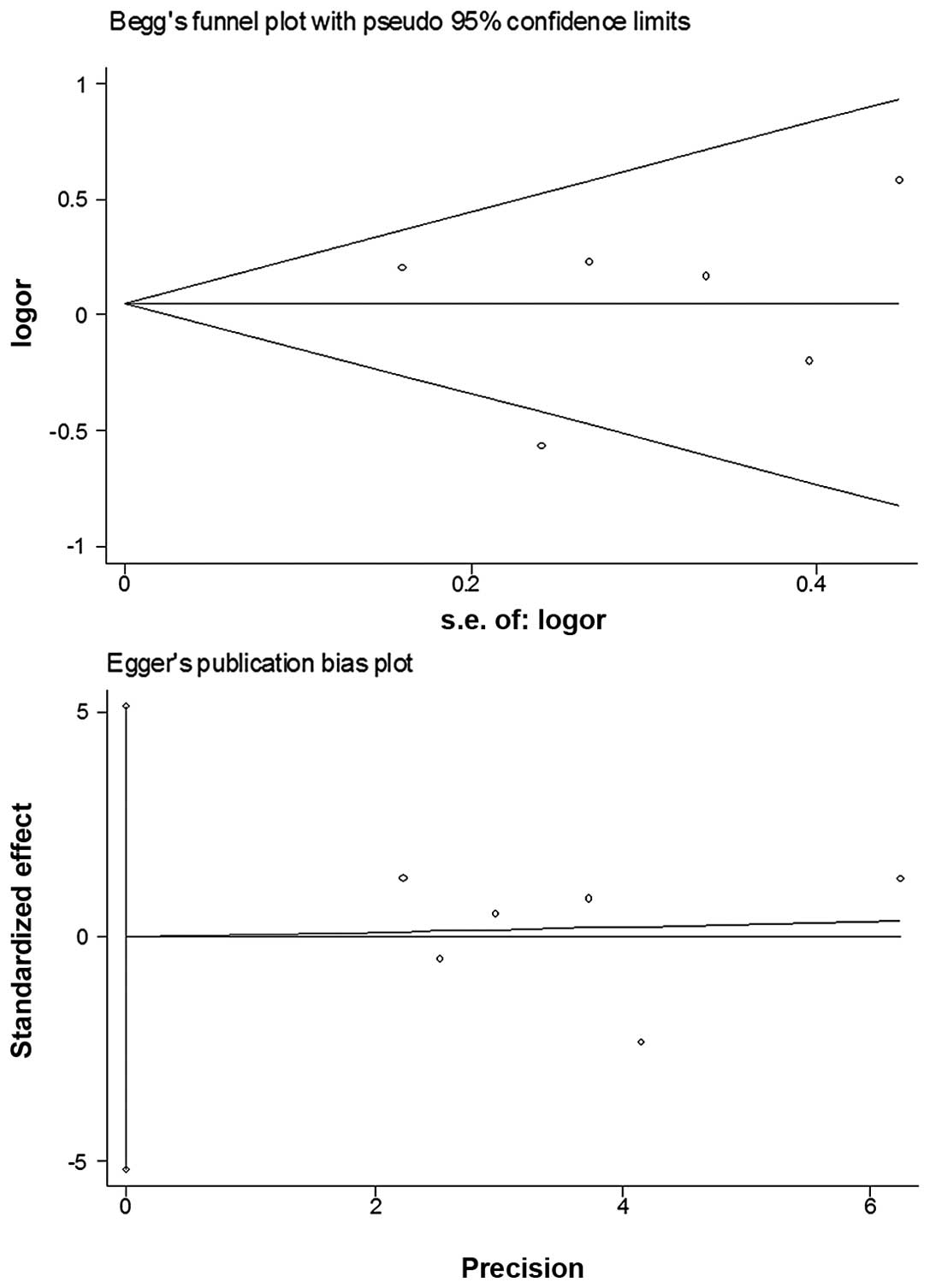
Munafò MR, Clark TG and Flint J: Assessing
publication bias in genetic association studies: evidence from a
recent meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 129:39–44. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nishimoto IN, Pinheiro NA, Rogatto SR, et
al: Cyclin D1 gene polymorphism as a risk factor for squamous cell
carcinoma of the upper aerodigestive system in non-alcoholics. Oral
Oncol. 40:604–610. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Izzo JG, Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Liu DD,
et al: Cyclin D1 genotype, response to biochemoprevention, and
progression rate to upper aerodigestive tract cancer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 95:198–205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taniyama Y, Takeuchi S and Kuroda Y:
Genetic polymorphisms and oral cancer. J UOEH. 32:221–236.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Henriksson E, Baldetorp B, Borg A, et al:
p53 mutation and cyclin D1 amplification correlate with cisplatin
sensitivity in xenografted human squamous cell carcinomas from head
and neck. Acta Oncol. 45:300–305. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu HS, Lu HH, Lui MT, et al: Detection of
copy number amplification of cyclin D1 (CCND1) and cortactin (CTTN)
in oral carcinoma and oral brushed samples from areca chewers. Oral
Oncol. 45:1032–1036. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kuropkat C, Venkatesan TK, Caldarelli DD,
et al: Abnormalities of molecular regulators of proliferation and
apoptosis in carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx. Auris
Nasus Larynx. 29:165–174. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sartor M, Steingrimsdottir H, Elamin F, et
al: Role of p16/MTS1, cyclin D1 and RB in primary oral cancer and
oral cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 80:79–86. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu J, Gimenez-Conti IB, Cunningham JE, et
al: Alterations of p53, cyclin D1, Rb, and H-ras in human oral
carcinomas related to tobacco use. Cancer. 83:204–212. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsai MH, Tsai CW, Tsou YA, Hua CH, Hsu CF
and Bau DT: Significant association of cyclin D1 single nucleotide
polymorphisms with oral cancer in Taiwan. Anticancer Res.
31:227–231. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
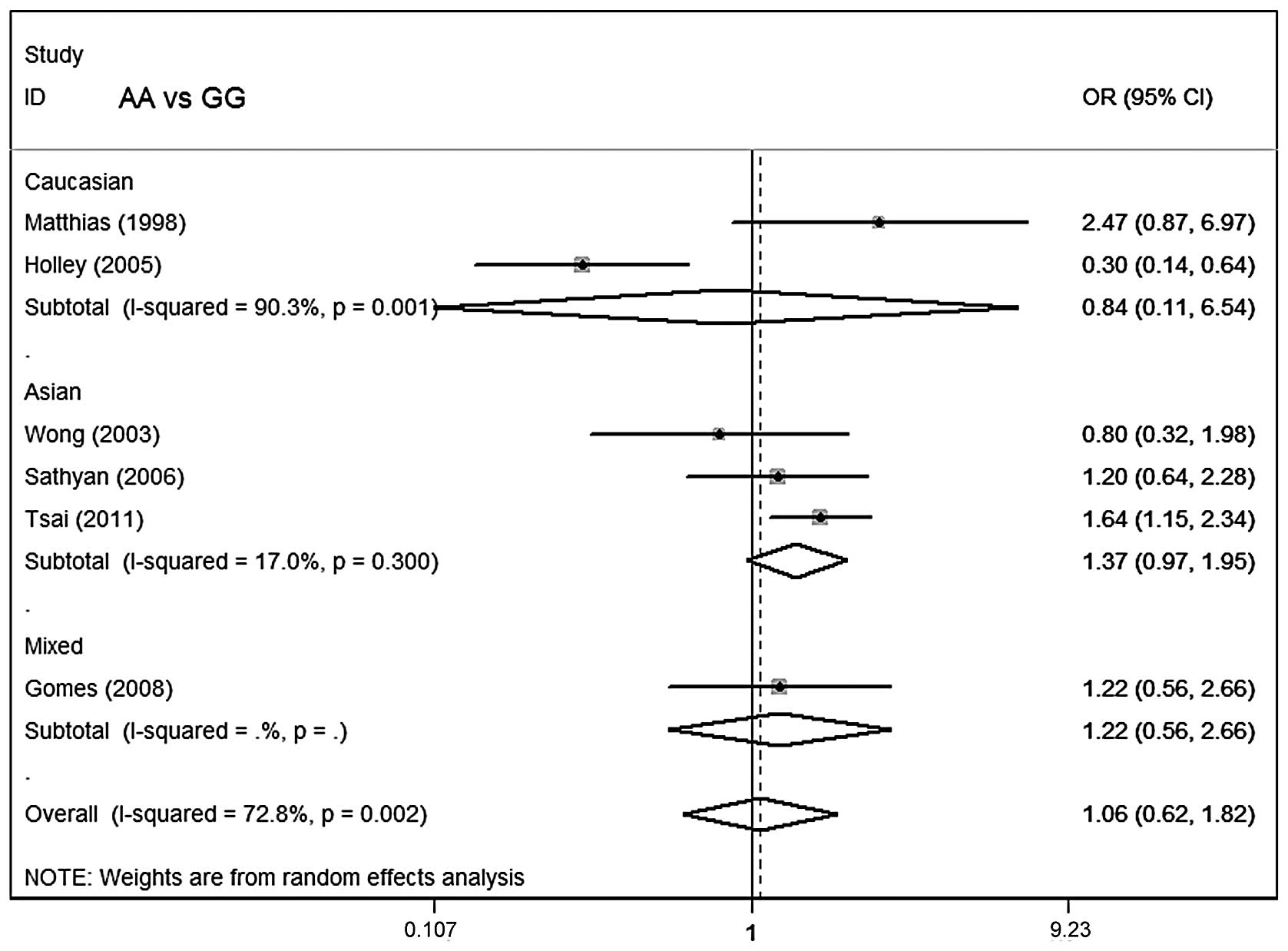
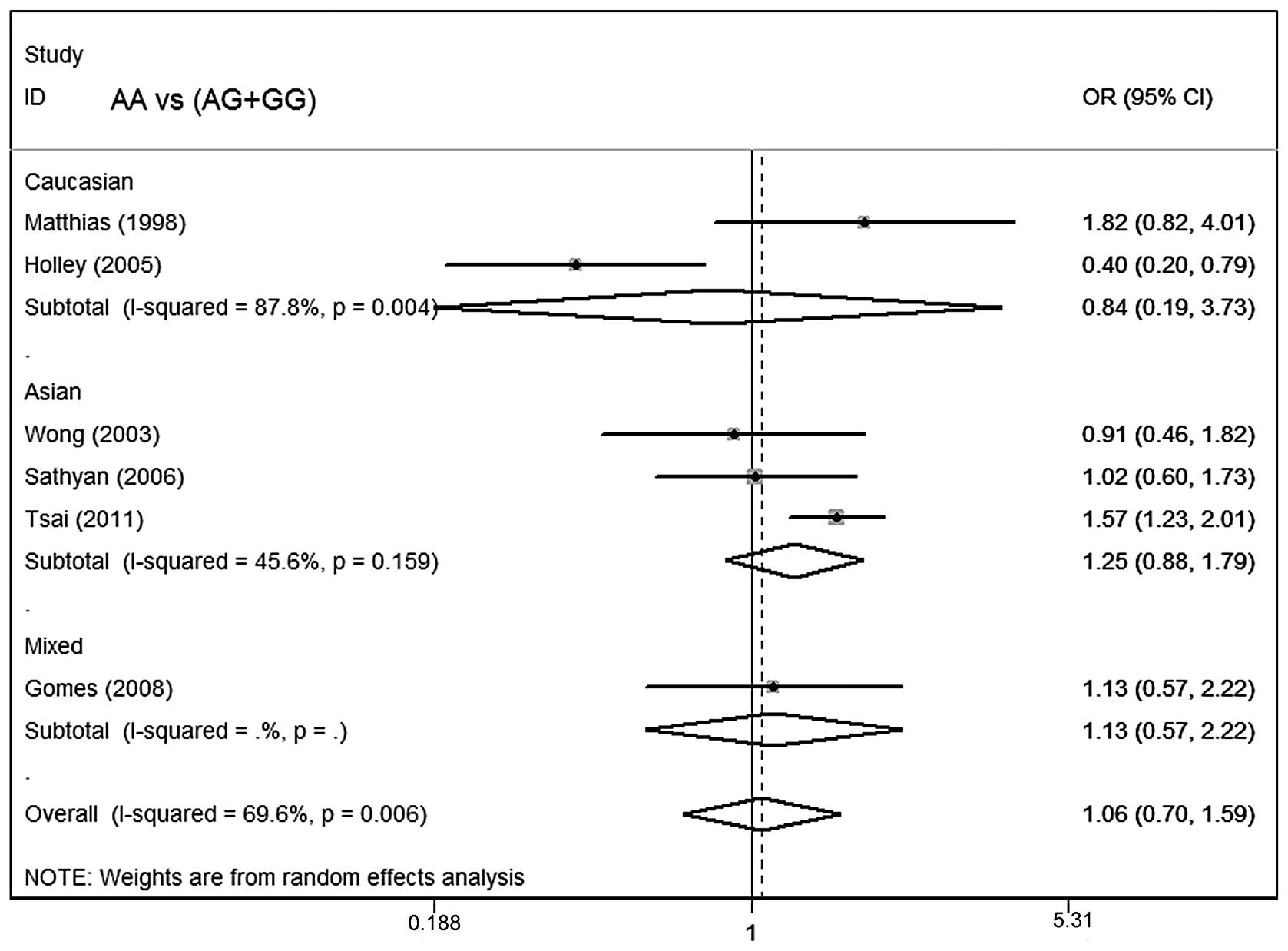
Gomes CC, Drummond SN, Guimarães AL,
Andrade CI, Mesquita RA and Gomez RS: P21/WAF1 and cyclin D1
variants and oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Oral Pathol Med.
37:151–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sathyan KM, Nalinakumari KR, Abraham T and
Kannan S: Influence of single nucleotide polymorphisms in H-Ras and
cyclin D1 genes on oral cancer susceptibility. Oral Oncol.
42:607–613. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Holley SL, Matthias C, Jahnke V, Fryer AA,
Strange RC and Hoban PR: Association of cyclin D1 polymorphism with
increased susceptibility to oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral
Oncol. 41:156–160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wong YK, Lin SC, Chang CS, et al: Cyclin
D1 genotype in areca-associated oral squamous cell carcinoma. J
Oral Pathol Med. 32:265–270. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matthias C, Branigan K, Jahnke V, et al:
Polymorphism within the cyclin D1 gene is associated with prognosis
in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin
Cancer Res. 4:2411–2418. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thakkinstian A, McElduff P, D’Este C,
Duffy D and Attia J: A method for meta-analysis of molecular
association studies. Stat Med. 24:1291–1306. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen C, Sun H, Sun D, et al: Polymorphisms
of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and breast cancer risk: a
meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 126:763–770. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang LQ, Wang J, Shang JQ, et al: Cyclin
D1 G870A polymorphism and colorectal cancer susceptibility: a
meta-analysis of 20 populations. Int J Colorectal Dis.
26:1249–1255. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sergentanis TN and Economopoulos KP:
Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a
meta-analysis comprising 9,911 cases and 11,171 controls. Mol Biol
Rep. 38:4955–4963. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yuan L, Gu X, Shao J, Wang M, Zhu Q and
Zhang Z: Cyclin D1 G870A polymorphism is associated with risk and
clinicopathologic characteristics of bladder cancer. DNA Cell Biol.
29:611–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ni J, Wang M, Wang M, Fu S, Zhou D, Zhang
Z and Han S: CCND1 G870A polymorphism and cervical cancer risk: a
case-control study and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
137:489–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang C, Wang Z, Yu J, Wu Y, Zhu Z and Chen
N: CCND1 G870A polymorphism and risk for head and neck cancer: a
meta-analysis. Med Oncol. 28:1319–1324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsia TC, Liu CJ, Lin CH, et al:
Interaction of CCND1 genotype and smoking habit in Taiwan lung
cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 31:3601–3605. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gautschi O, Hugli B, Ziegler A, et al:
Cyclin D1 (CCND1) A870G gene polymorphism modulates smoking-induced
lung cancer risk and response to platinum-based chemotherapy in
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. Lung Cancer.
51:303–311. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|