|
1
|
Sartor RB: Therapeutic manipulation of the
enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel diseases: antibiotics,
probiotics, and prebiotics. Gastroenterology. 126:1620–1633. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duchman R, Kaiser I, Hermann E, et al:
Tolerance exists towards resident intestinal flora but is broken in
active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Clin Exp Immunol.
102:448–455. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Podolsky DK: Inflammatory bowel disease. N
Engl J Med. 347:417–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Prantera C and Scribano ML: Antibiotics
and probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: why, when, and how.
Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 25:329–333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sandborn WJ and Feagan BG: Review article:
mild to moderate Crohn’s disease – defining the basis for a new
treatment algorithm. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 18:263–277. 2003.
|
|
6
|
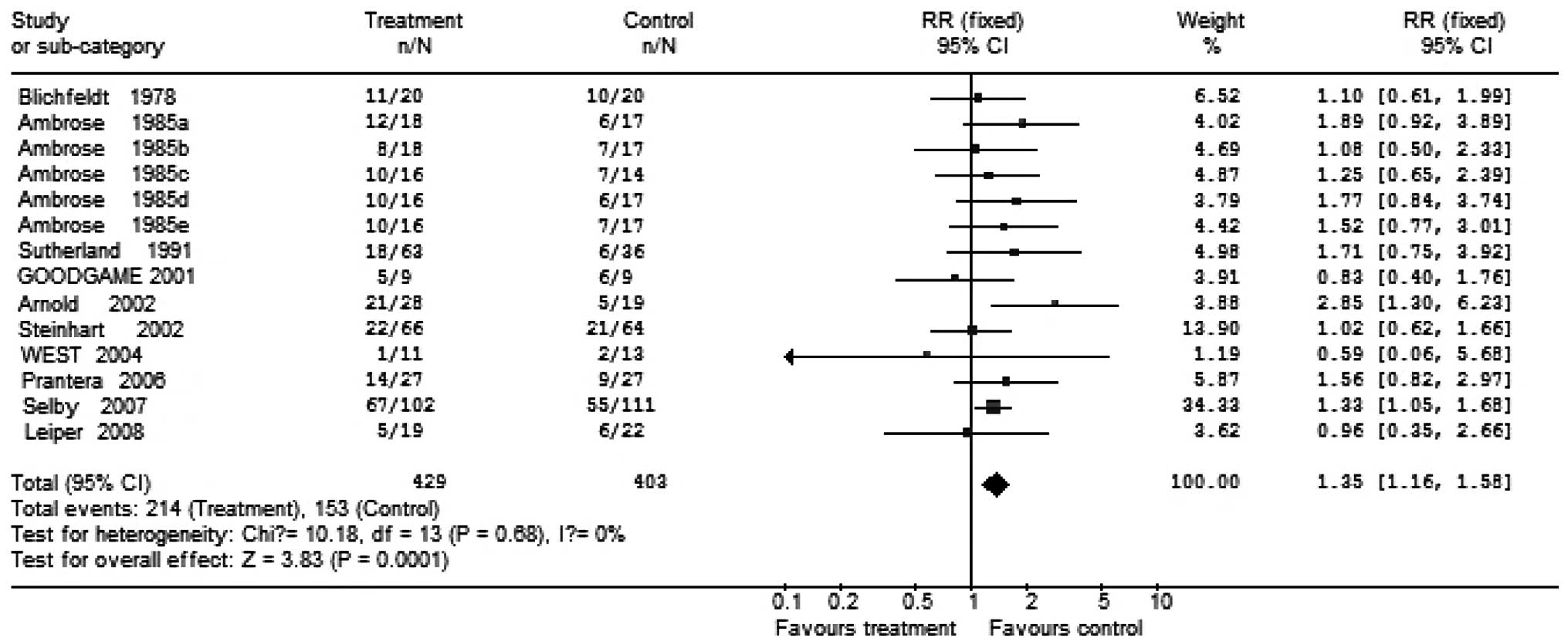
Sutherland L, Singleton J, Sessions J,
Hanauer S, Krawitt E, Rankin G, Summers R, Mekhjian H, Greenberger
N and Kelly M: Double blind, placebo controlled trial of
metronidazole in Crohn’s disease. Gut. 32:1071–1075. 1991.
|
|
7
|
Steinhart AH, Feagan BG, Wong CJ,
Vandervoort M, Mikolainis S, Croitoru K, Seidman E, Leddin DJ,
Bitton A, Drouin E, et al: Combined budesonide and antibiotic
therapy for active Crohn’s disease: a randomized controlled trial.
Gastroenterology. 123:33–40. 2002.
|
|
8
|
Prantera C, Lochs H, Campieri M, Scribano
ML, Sturniolo GC, Castiglione F and Cottone M: Antibiotic treatment
of Crohn’s disease: results of a multicentre, double blind,
randomized, placebo-controlled trial with rifaximin. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 23:1117–1125. 2006.
|
|
9
|
Arnold GL, Beaves MR, Pryjdun VO and Mook
WJ: Preliminary study of ciprofloxacin in active Crohn’s disease.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 8:10–15. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
West RL, van der Woude CJ, Hansen BE, et
al: Clinical and endosonographic effect of ciprofloxacin on the
treatment of perianal fistulae in Crohn’s disease with infliximab:
a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.
20:1329–1336. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leiper K, Martin K, Ellis A, et al:
Clinical trial: randomized study of clarithromycin versus placebo
in active Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 27:1233–1239.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Goodgame RW, Kimball K, Akram S, Ike E, Ou
CN, Sutton F and Graham D: Randomized controlled trial of
clarithromycin and ethambutol in the treatment of Crohn’s disease.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 15:1861–1866. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blichfeldt P, Blomhoff JP, Myhre E and
Gjone E: Metronidazole in Crohn’s disease. A double blind
cross-over clinical trial. Scand J Gastroenterol. 13:123–127.
1978.
|
|
14
|
Ambrose NS, Allan RN, Keighley MR, et al:
Antibiotic therapy for treatment in relapse of intestinal Crohn’s
disease. A prospective randomized study. Dis Colon Rectum.
28:81–85. 1985.
|
|
15
|
Selby W, Pavli P, Crotty B, et al:
Two-year combination antibiotic therapy with clarithromycin,
rifabutin, and clofazimine for Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology.
132:2313–2319. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Colombel JF, Lémann M, Cassagnou M, et al:
A controlled trial comparing ciprofloxacin and mesalamine for the
treatment of active Crohn’s disease. Groupe d’Etudes Therapeutiques
des Affections Inflammatoires Digestives (GETAID). Am J
Gastroenterol. 94:674–678. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cho JH and Weaver CT: The genetics of
inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 133:1327–1339. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kobayashi KS, Chamaillard M, Ogura Y, et
al: Nod2-dependent regulation of innate and adaptive immunity in
the intestinal tract. Science. 307:731–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barnich N and Darfeuille-Michaud A:
Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli and Crohn’s disease. Curr
Opin Gastroenterol. 23:16–20. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Issa M, Vijayapal A, Graham MB, et al:
Impact of Clostridium difficile on inflammatory bowel
disease. Clin Gastronterol Hepatol. 5:345–351. 2007.
|
|
21
|
Greenbloom SL, Steinhart AH and Greenberg
GR: Combination ciprofloxacin and metronidazole for active Crohn’s
disease. Can J Gastroenterol. 12:53–56. 1998.
|
|
22
|
Carter MJ, Lobo AJ, Travis SP, et al:
Guidelines for the management of inflammatory bowel disease in
adults. Gut. 53(Suppl 5): V1–V16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gilat T, Suissa A, Leichtman G, et al: A
comparative study of metronidazole and sulfasalazine in active, not
severe, ulcerative colitis. An Israeli multicenter trial. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 9:415–417. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
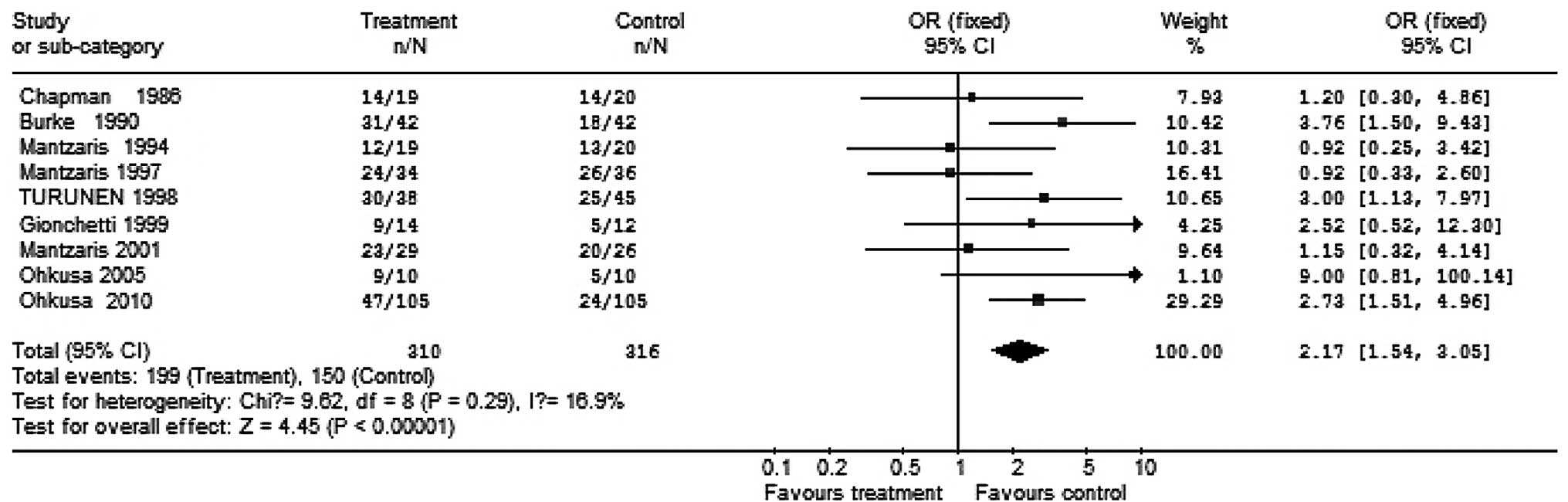
Chapman RW, Selby WS and Jewell DP:
Controlled trial of intravenous metronidazole as an adjunct to
corticosteroids in severe ulcerative colitis. Gut. 27:1210–1212.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mantzaris GJ, Archavlis E, Christoforidis
P, et al: A prospective randomized controlled trial of oral
ciprofloxacin in acute ulcerative colitis. Am J Gastroenterol.
92:454–456. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mantzaris GJ, Petraki K, Archavlis E, et
al: A prospective randomized controlled trial of intravenous
ciprofloxacin as an adjunct to corticosteroids in acute, severe
ulcerative colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 36:971–974. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mantzaris GJ, Hatzis A, Kontogiannis P and
Triadaphyllou G: Intravenous tobramycin and metronidazole as an
adjunct to corticosteroids in acute, severe ulcerative colitis. Am
J Gastroenterol. 89:43–46. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Burke DA, Axon AT, Clayden SA, et al: The
efficacy of tobramycin in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 4:123–129. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gionchetti P, Rizzello F, Ferrieri A, et
al: Rifaximin in patients with moderate or severe ulcerative
colitis refractory to steroid-treatment: a double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Dig Dis Sci. 44:1220–1221. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Turunen U, Färkkilä MA, Hakala K, et al:
Long-term treatment of ulcerative colitis with ciprofloxacin: a
prospective, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
Gastroenterology. 115:1072–1078. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ohkusa T, Nomura T, Terai T, et al:
Effectiveness of antibiotic combination therapy in patients with
active ulcerative colitis: a randomized, controlled pilot trial
with long-term follow-up. Scand J Gastroenterol. 40:1334–1342.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ohkusa T, Kato K, Terao S, et al: Newly
developed antibiotic combination therapy for ulcerative colitis: a
double-blind placebo-controlled multicenter trial. Am J
Gastroenterol. 105:1820–1829. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|