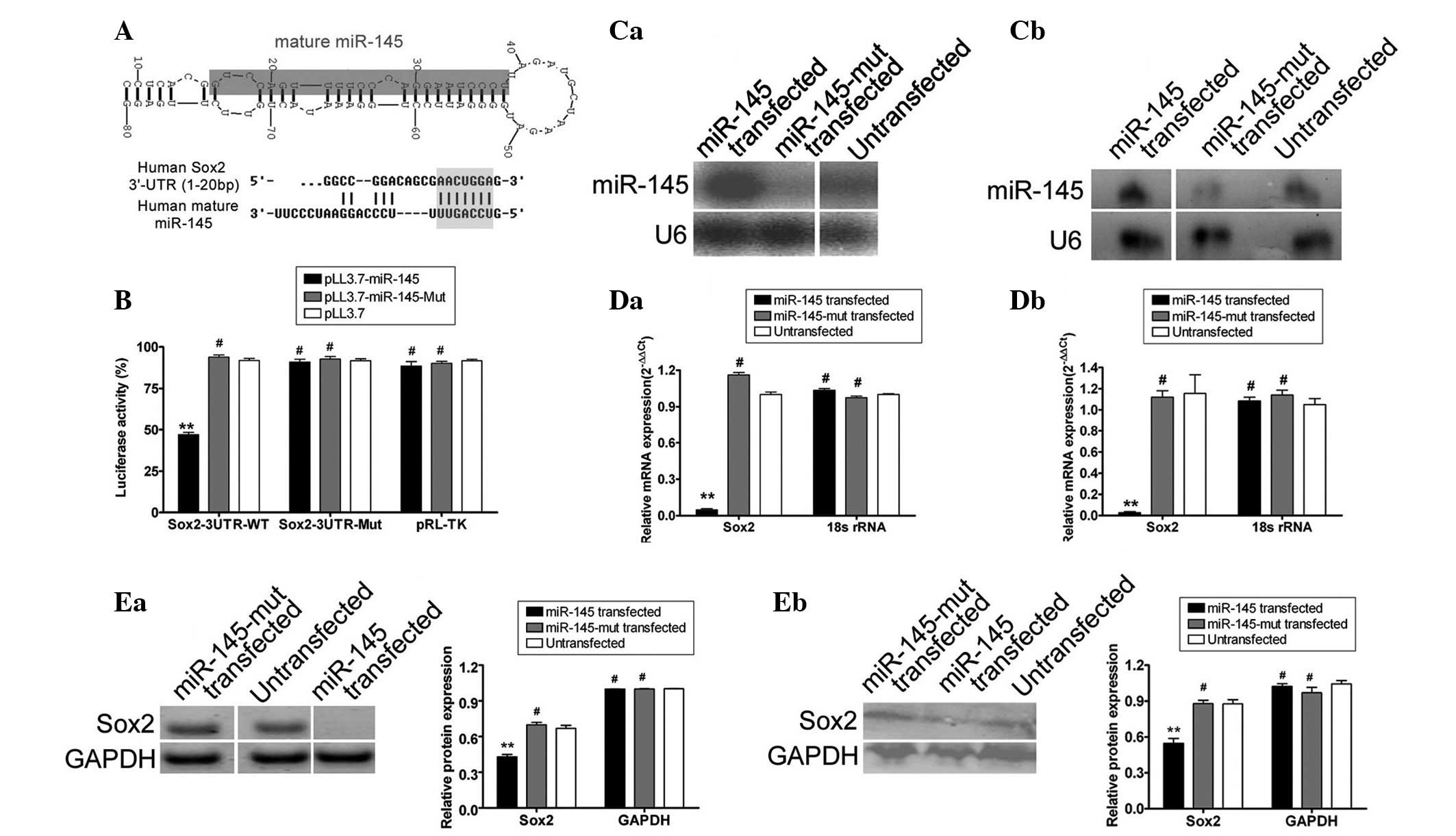
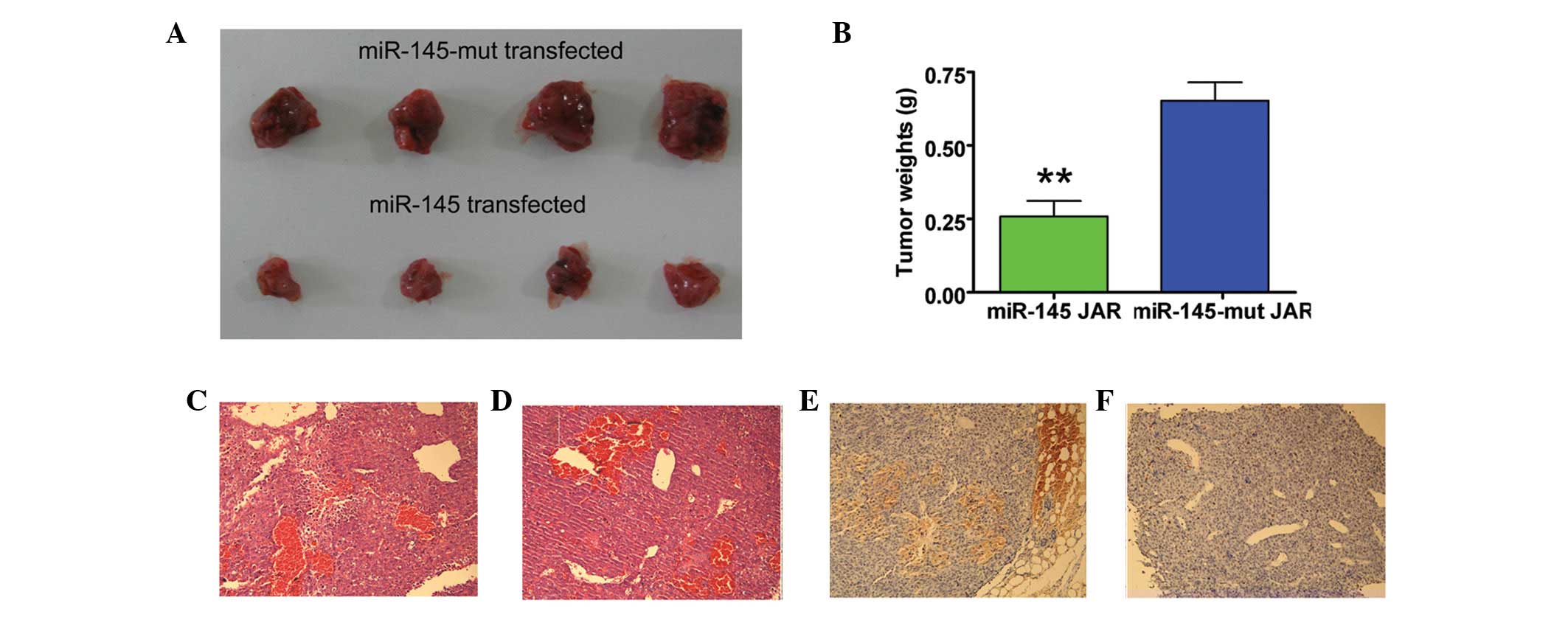
|
1
|
Bagley RG, Ren Y, Kurtzberg L, et al:
Human choriocarcinomas: placental growth factor-dependent
preclinical. Int J Oncol. 40:479–486. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Monzo M, Navarro A, Bandres E, et al:
Overlapping expression of microRNAs in human embryonic colon and
colorectal cancer. Cell Res. 18:823–833. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim VN and Nam JW: Genomics of microRNA.
Trends Genet. 22:165–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hatfield SD, Shcherbata HR, Fischer KA,
Nakahara K, Carthew RW and Ruohola-Baker H: Stem cell division is
regulated by the microRNA pathway. Nature. 435:974–978. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eder M and Scherr M: MicroRNA and lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 352:2446–2448. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, et al: A
MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 353:1793–1801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Houbaviy HB, Murray MF and Sharp PA:
Embryonic stem cell-specific MicroRNAs. Dev Cell. 5:351–358. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lanza G, Ferracin M, Gafà R, et al:
mRNA/microRNA gene expression profile in microsatellite unstable
colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 6:542007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–436.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bandrés E, Cubedo E, Agirre X, et al:
Identification by Real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs
differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral
tissues. Mol Cancer. 5:292006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al: A
microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer
gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Liu T, Huang Y and Liu J:
microRNA-182 inhibits the proliferation and invasion of human lung
adenocarcinoma cells through its effect on human cortical
actin-associated protein. Int J Mol Med. 28:381–388.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chao A, Tsai CL, Wei PC, et al: Decreased
expression of microRNA-199b increases protein levels of SET
(protein phosphatase 2A inhibitor) in human choriocarcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 291:99–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B and
Rigoutsos I: MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions
modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature.
455:1124–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chew JL, Loh YH, Zhang W, et al:
Reciprocal transcriptional regulation of Pou5f1 and Sox2 via the
Oct4/Sox2 complex in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol.
25:6031–6046. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fong H, Hohenstein KA and Donovan PJ:
Regulation of self-renewal and pluripotency by Sox2 in human
embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 26:1931–1938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson
JA and Kosik KS: MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and
represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell.
137:647–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li AS, Siu MK, Zhang H, et al:
Hypermethylation of SOX2 gene in hydatidiform mole and
choriocarcinoma. Reprod Sci. 15:735–744. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakatsugawa M, Takahashi A, Hirohashi Y,
et al: SOX2 is over-expressed in stem-like cells of human lung
adenocarcinoma and augments the tumorigenicity. Lab Invest.
91:1796–1804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu T, Cheng W, Huang Y, Huang Q, Jiang L
and Guo L: Human amniotic epithelial cell feeder layers maintain
human iPS cell pluripotency via inhibited endogenous microRNA-145
and increased Sox2 expression. Exp Cell Res. 318:424–434. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eis PS, Tam W, Sun L, et al: Accumulation
of miR-155 and BIC RNA in human B cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 102:3627–3632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Chao T, Li R, et al: MicroRNA-128
inhibits glioma cells proliferation by targeting transcription
factor E2F3a. J Mol Med (Berl). 87:43–51. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheng W, Liu T, Jiang F, et al:
microRNA-155 regulates angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in
umbilical vein endothelial cells from severely pre-eclamptic
pregnant women. Int J Mol Med. 27:393–399. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang F, Liu T, He Y, et al: MiR-125b
promotes proliferation and migration of type II endometrial
carcinoma cells through targeting TP53INP1 tumor suppressor in
vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 11:4252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Carro MS, Lim WK, Alvarez MJ, et al: The
transcriptional network for mesenchymal transformation of brain
tumours. Nature. 463:318–325. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kluiver J, Haralambieva E, de Jong D, et
al: Lack of BIC and microRNA miR-155 expression in primary cases of
Burkitt lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 45:147–153. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Martin MM, Lee EJ, Buckenberger JA,
Schmittgen TD and Elton TS: MicroRNA-155 regulates human
angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in fibroblasts. J Biol
Chem. 281:18277–18284. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|