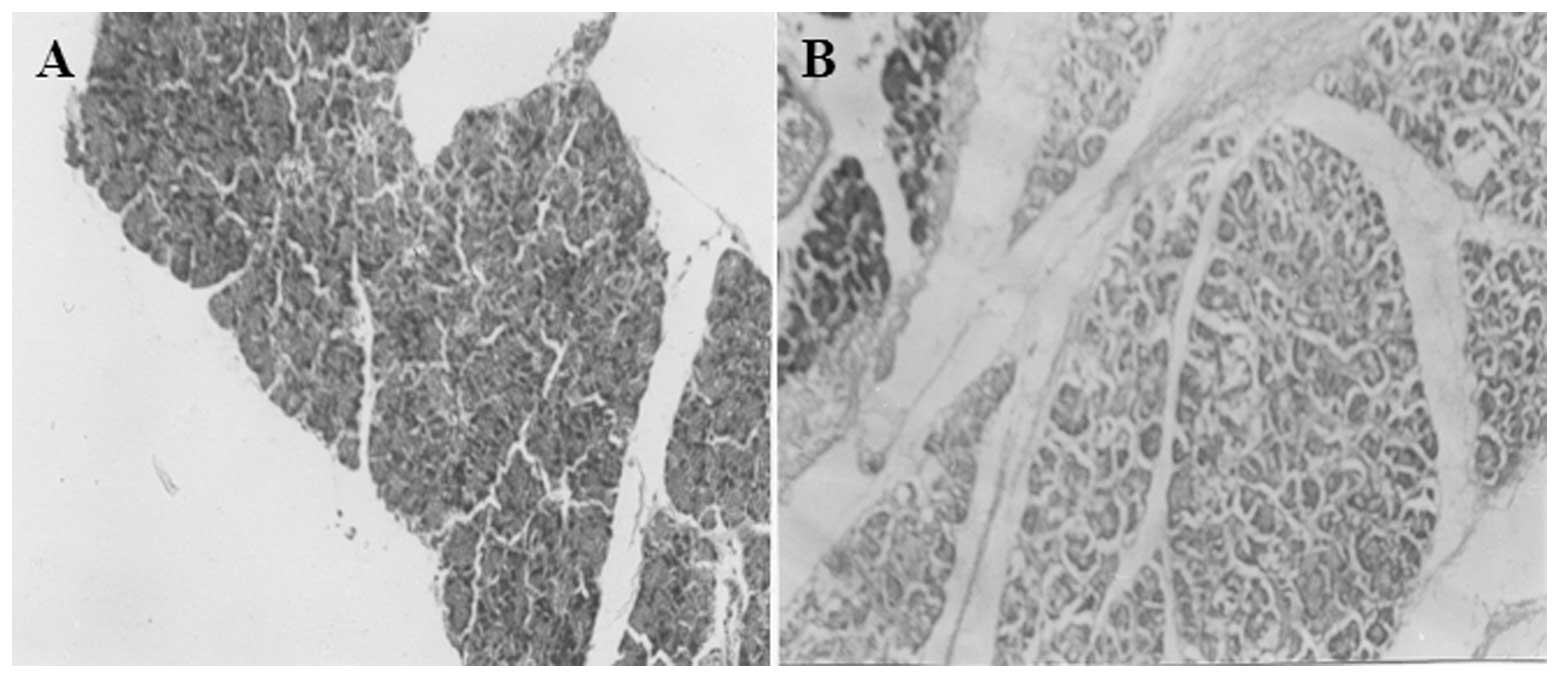
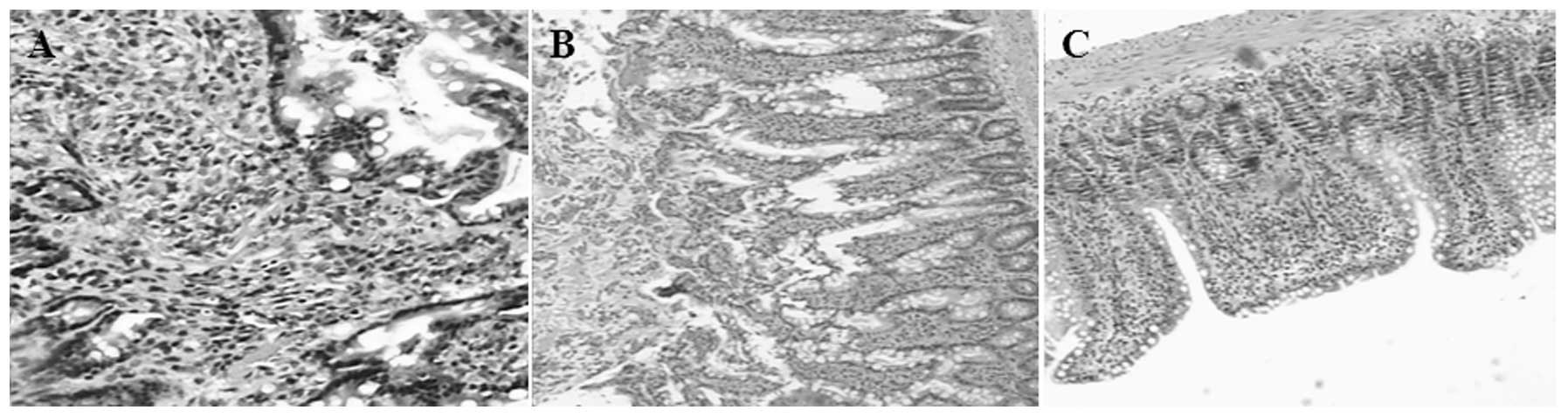
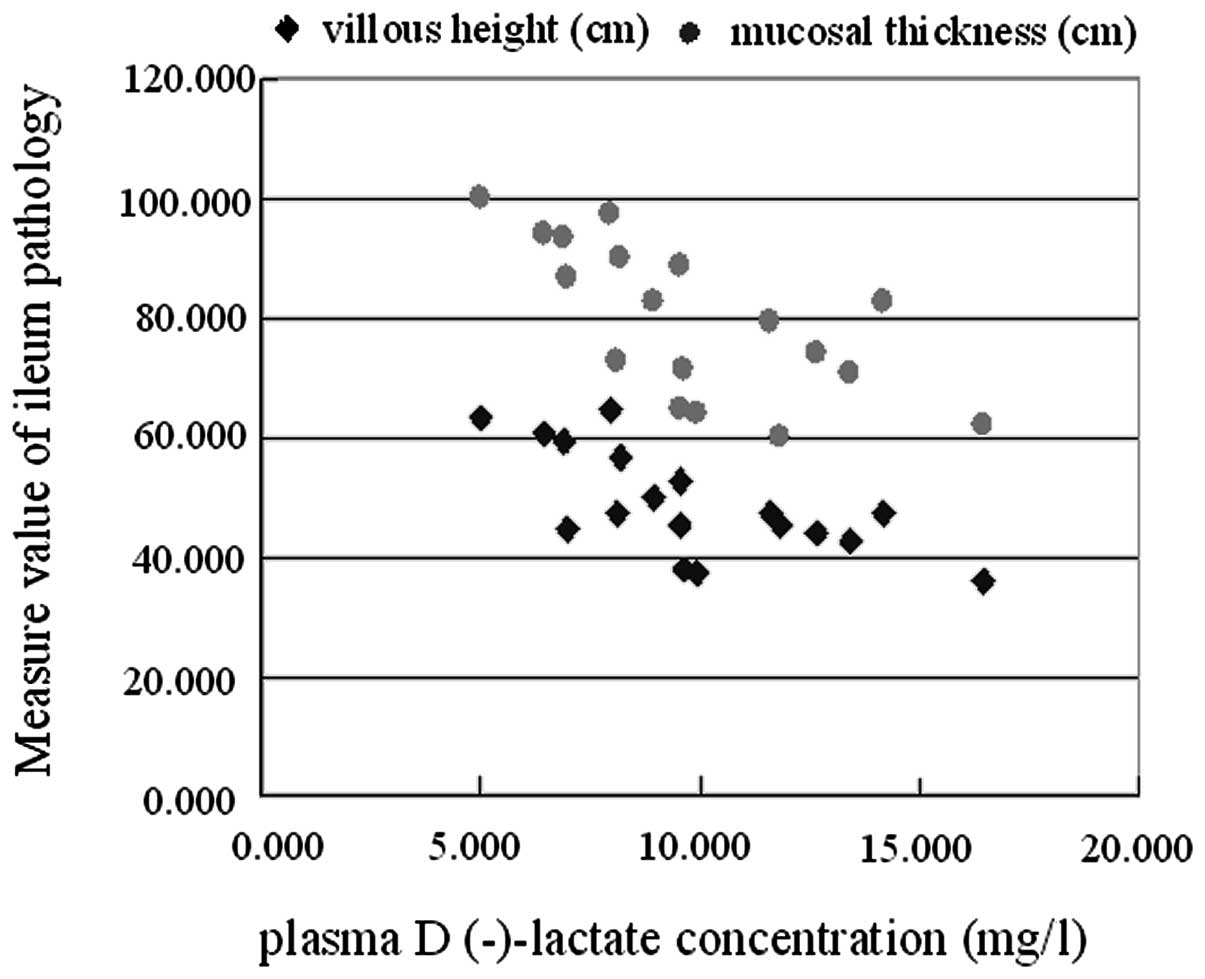
|
1.
|
Hong W, Ma BJ and Cai D: New progress of
diagnosis and treatment of acute pancreatitis. J Hepatopancreatobil
Surg. 3:1652001.(In Chinese).
|
|
2.
|
Ammori BJ: Role of the gut in the course
of severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 26:122–129. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Jin C, Ni QX, Zhang QH, Xiang Y, Zhang N
and Zhang YL: An experimental study on the immunoregulatory effect
of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F in rats with acute
necrotizing pancreatitis. Chin J Gen Surg. 15:283–285. 2000.(In
Chinese).
|
|
4.
|
Brandt B, Siegel A, Waters G and Bloch MH:
Spectrophotometic assay for D-(-)-lactate in plasma. Anal Biochem.
102:39–46. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Schmidt J, Rattner DW, Lewandrowski K, et
al: A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy.
Ann Surg. 215:44–56. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Kazantsev GB, Hecht DW, Rao R, et al:
Plasmid labeling confirms bacterial translocation in pancreatitis.
Am J Surg. 167:201–206. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Nettelbladt CG, Katouli M, Bark T,
Svenberg T, Möllby R and Ljungqvist O: Evidence of bacterial
translocation in fatal hemorrhagic pancreatitis. J Trauma.
48:314–315. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Cicalese L, Sahai A, Sileri P, et al:
Acute pancreatitis and bacterial translocation. Dig Dis Sci.
46:1127–1132. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lemaire LC, van Lanschot JJ, Stoutenbeek
CP, van Deventer SJ, Wells CL and Gouma DJ: Bacterial translocation
in multiple organ failure: cause or epiphenomenona still unproven.
Br J Surg. 84:1340–1350. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Ogawa M: Acute pancreatitis and cytokines:
‘second attack’ by septic complication leads to organ failure.
Pancreas. 16:312–315. 1998.
|
|
11.
|
Ding LA, Li JS, Li YS, Zhu NT, Liu FN and
Tan L: Intestinal barrier damage caused by trauma and
lipopolysaccharide. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2373–2378.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Murry J, Gonze D, Nowak R and Cobb CF:
Serum D-(-)-lactate levels as an aid to diagnosing acute intestinal
ischemia. Am J Surg. 167:575–578. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Sun XQ, Fu XB, Zhang R, et al: Plasma
D-lactate levels as a useful marker of increased intestinal
permeability after severe injuries. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu
Yi Xue. 12:476–478. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
14.
|
Ammori BJ, Leeder PC, King RF, et al:
Early increase in intestinal permeability in patients with severe
acute pancreatitis: correlation with endotoxemia, organ failure,
and mortality. J Gastrointest Surg. 3:252–262. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Wang XP, Wang BX, Wu JX, et al: Bacterial
translocation from gut in acute necrotizing pancreatitis:
beneficial effect of growth hormone. Chung Hua Hsiao Hua Tsa Chih.
20:171–174. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
16.
|
Cao M, Sun RQ, Wu DJ, et al: The research
progression of Chinese drug Tripterygium wilfordii hook.f.
Chinese Patent Medicine. 18:40–42. 1996.(In Chinese).
|
|
17.
|
Chang DM, Chang WY, Kuo SY and Chang ML:
The effects of traditional antirheumatic herbal medicines on immune
response cells. J Rheumatol. 24:436–441. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Zhao G, Vaszar LT, Qiu DV, Shi LF and Kao
PN: Anti-inflammatory effects of triptolide in human bronchial
epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
279:L958–L966. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Bao J and Dai SM: A Chinese herb
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F in the treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis: mechanism, efficacy, and safety. Rheumatol Int.
31:1123–1129. 2011.
|
|
20.
|
Wang GM and Bao MS: The experiment
research of therapeutic alliance using Salvia miltiorrhiza
bunge and Tripterygium wilfordii hook f multiglycosides in
acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Journal of Shanxi Medical
University. 35:15–17. 2004.(In Chinese).
|