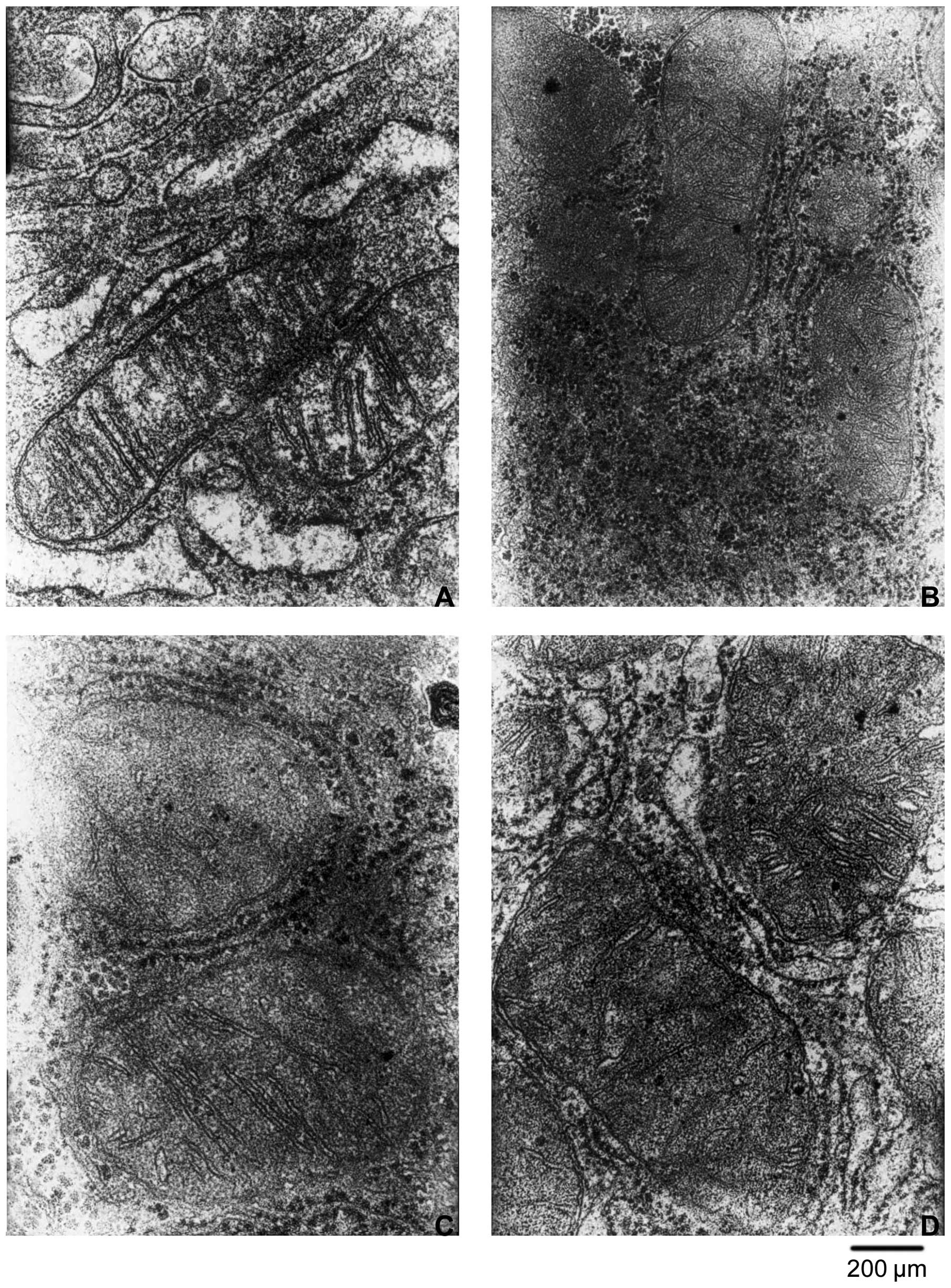
|
1.
|
Guicciardi ME and Gores GJ: Apoptosis: a
mechanism of acute and chronic liver injury. Gut. 54:1024–1033.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Bruix J, Hessheimer AJ, Forner A, Boix L,
Vilana R and Llovet JM: New aspects of diagnosis and therapy of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 25:3848–3856. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Bulteau AL and Bayot A: Mitochondrial
proteases and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1807:595–601. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Li X, Shi ZM, Feng P, Wen ZY and Wang XL:
Effect of Qi-protecting powder (Huqi San) on expression of c-jun,
c-fos and c-myc in diethylnitrosamine-mediated
hepatocarcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 13:4192–4198.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Craddock VM: Effect of a single treatment
with the alkylating carcinogens dimethylnitrosamine,
diethylnitrosamine and methyl methanesulphonate, on liver
regenerating after partial hepatectomy. I Test for induction of
liver carcinomas. Chem Biol Interact. 10:313–321. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
McNeil CM, Sergio CM, Anderson LR, et al:
c-Myc overexpression and endocrine resistance in breast cancer. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 102:147–155. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Chao MP, Majeti R, Weissman IL, Kesari S,
Antony ML and Singh SV: Programmed cell removal: a new obstacle in
the road to developing cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:58–67.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kesari S, Antony ML and Singh SV:
Understanding glioblastoma tumor biology: the potential to improve
current diagnosis and treatments. Semin Oncol. 38(Suppl 4): S2–S10.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Antony ML and Singh SV: Molecular
mechanisms and targets of cancer chemoprevention by garlic-derived
bioactive compound diallyl trisulfide. Indian J Exp Biol.
49:805–816. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Zurawa-Janicka D, Skorko-Glonek J and
Lipinska B: HtrA proteins as targets in therapy of cancer and other
diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:665–679. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Liu J, Yang CF, Wasser S, Shen HM, Tan CE
and Ong CN: Protection of salvia miltiorrhiza against
aflatoxin-B1-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in Fischer 344 rats dual
mechanisms involved. Life Sci. 69:309–326. 2001.
|
|
12.
|
Stennicke HR, Ryan CA and Salvesen GS:
Reprieval from execution: the molecular basis of caspase
inhibition. Trends Biochem Sci. 27:94–101. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Ferreira CG, van der Valk P, Span SW, et
al: Assessment of IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis) proteins as
predictors of response to chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell
lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 12:799–805. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Hofmann HS, Simm A, Hammer A, Silber RE
and Bartling B: Expression of inhibitors of apoptosis (IAP)
proteins in non-small cell human lung cancer. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 128:554–560. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Banares S, et
al: Elevated expression of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4914–4925. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Tamm I, Kornblau SM, Segall H, et al:
Expression and prognostic significance of IAP-family genes in human
cancers and myeloid leukemias. Clin Cancer Res. 6:1796–1803.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS and
Reed JC: X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death
proteases. Nature. 388:300–304. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K,
Salvesen GS and Reed JC: Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis
protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for
caspases. EMBO J. 18:5242–5251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Takahashi R, Deveraux Q, Tamm I, et al: A
single BIR domain of XIAP sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J
Biol Chem. 273:7787–7790. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Yang L, Cao Z, Yan H and Wood WC:
Coexistence of high levels of apoptotic signaling and inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins in human tumor cells: implication for cancer
specific therapy. Cancer Res. 63:6815–6824. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Holcik M, Thompson CS, Yaraghi Z, Lefebvre
CA, MacKenzie AE and Korneluk RG: The hippocampal neurons of
neuronal apoptosis inhibitory protein 1 (NAIP1)-deleted mice
display increased vulnerability to kainic acid-induced injury. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:2286–2290. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23.
|
Harlin H, Reffey SB, Duckett CS, Lindsten
T and Thompson CB: Characterization of XIAP-deficient mice. Mol
Cell Biol. 21:3604–3608. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Okada M, Adachi S, Imai T, et al: A novel
mechanism for imatinib mesylate-induced cell death of
BCR-ABL-positive human leukemic cells: caspase-independent,
necrosis-like programmed cell death mediated by serine protease
activity. Blood. 103:2299–2307. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Reed JC: The Survivin saga goes in vivo. J
Clin Invest. 108:965–969. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|