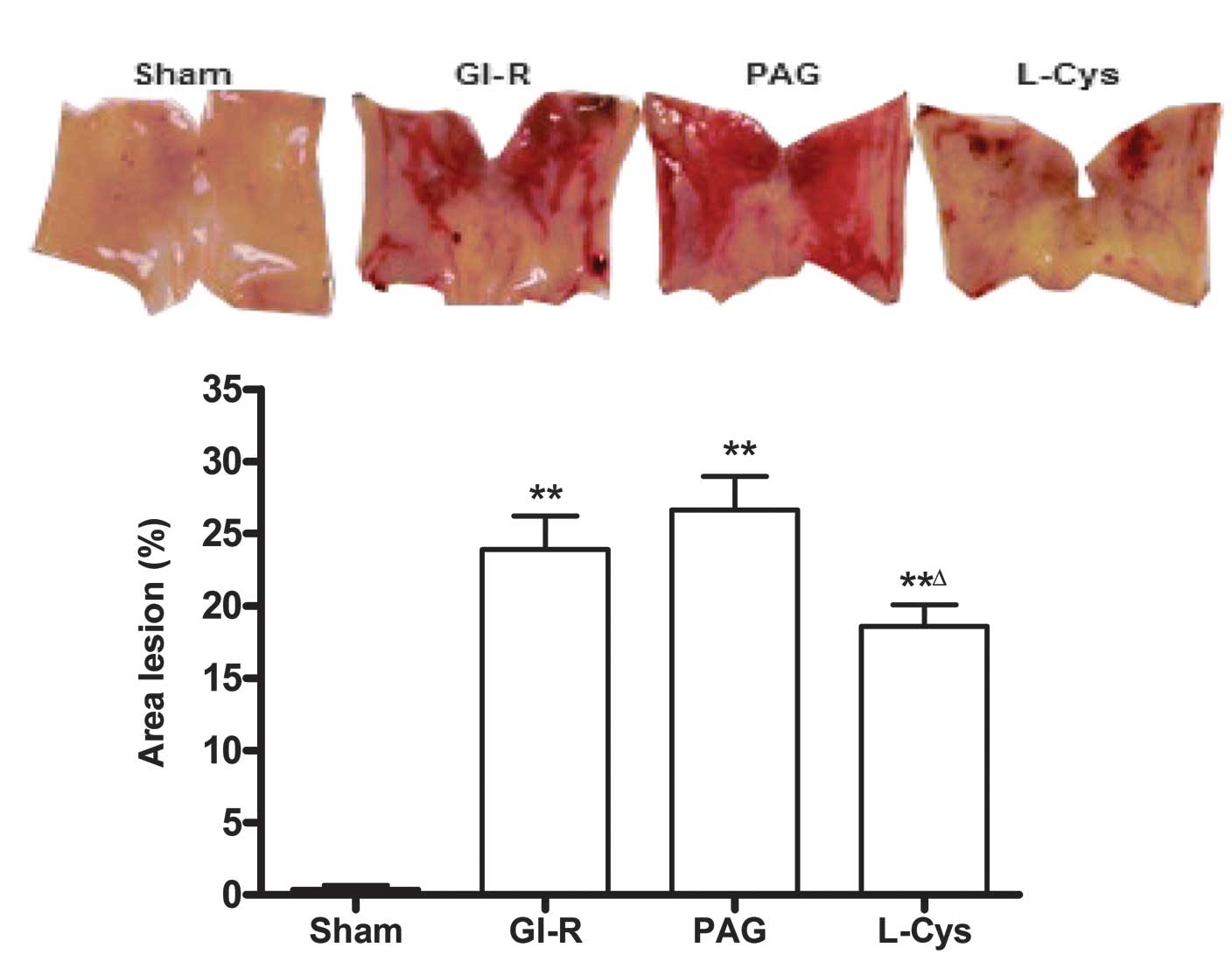
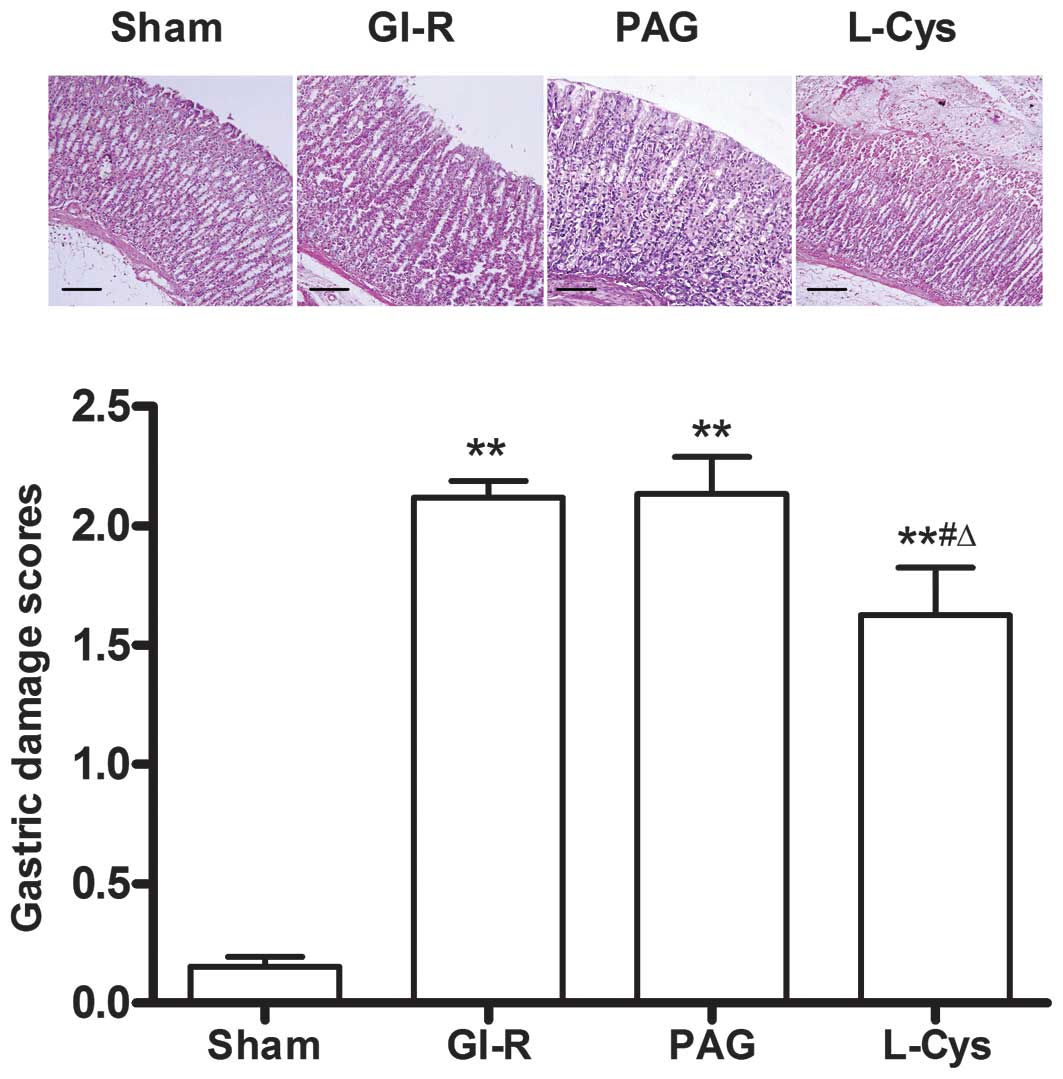
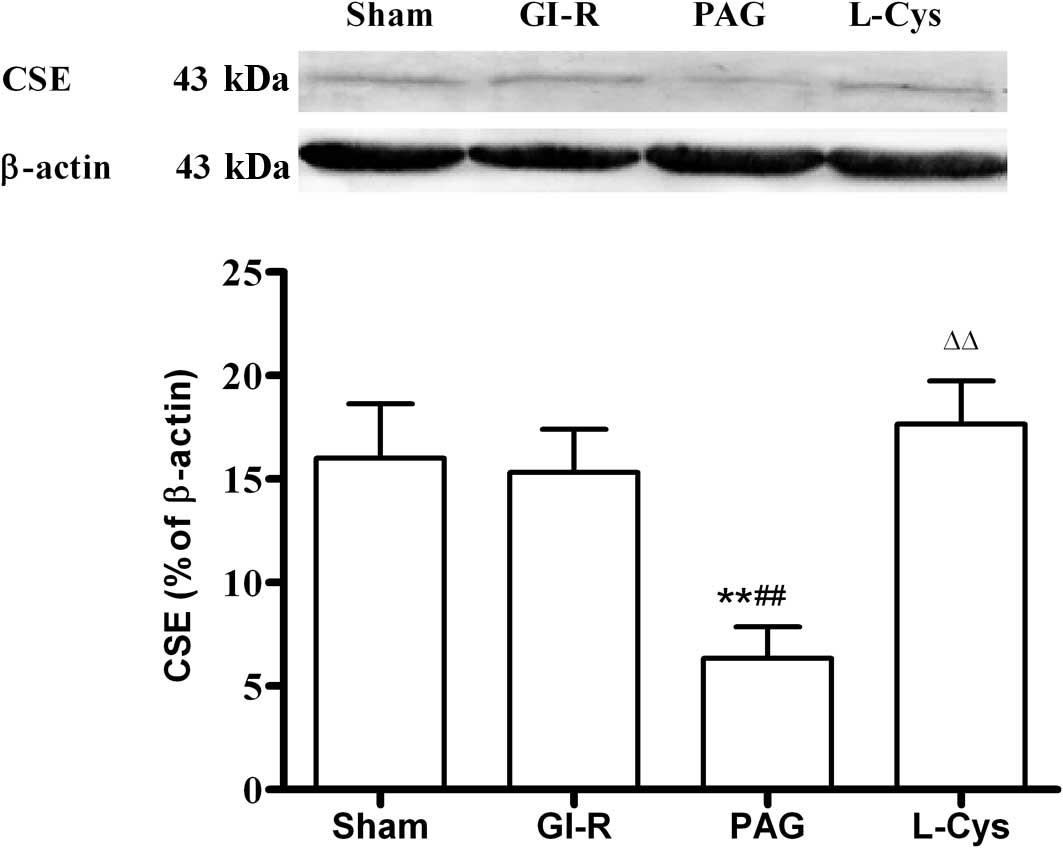
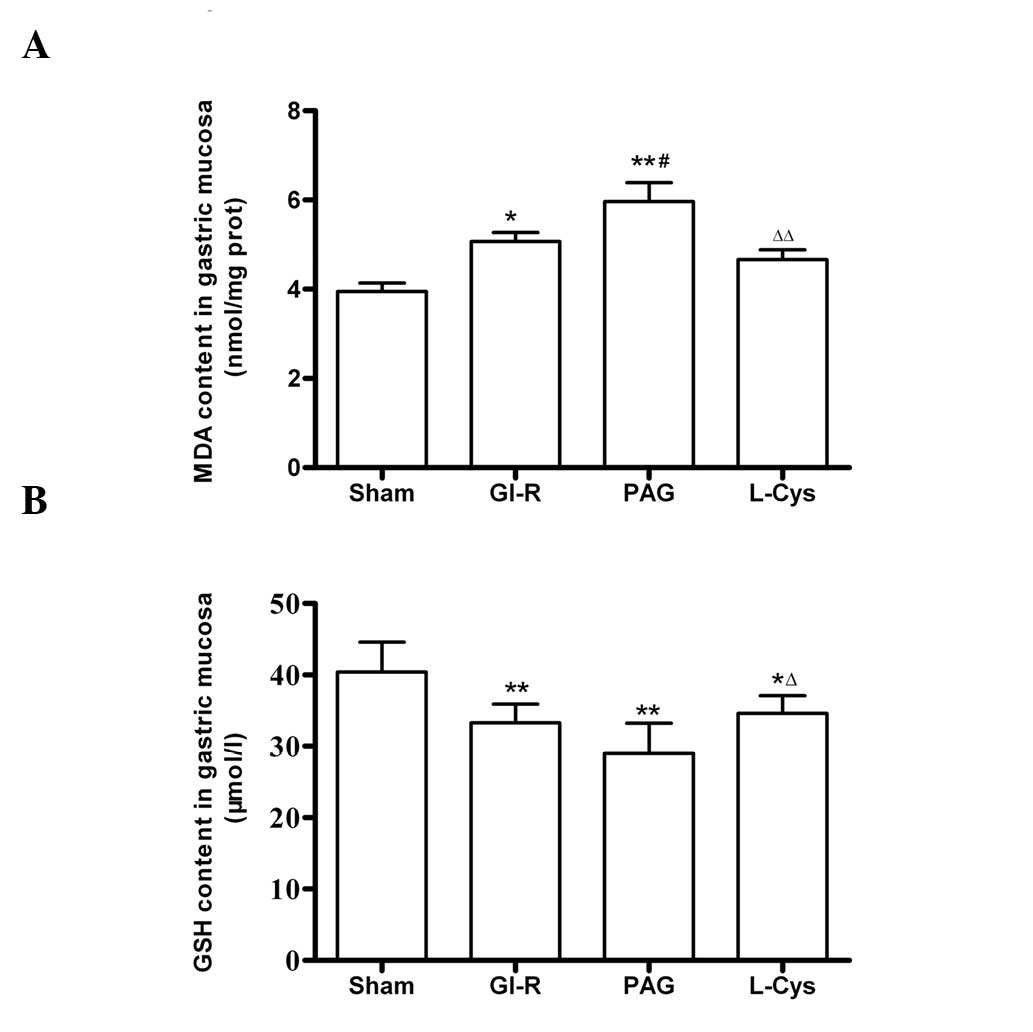
|
1.
|
Gross GJ and Auchampach JA: Reperfusion
injury: does it exist? J Mol Cell Cardiol. 42:12–18. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Wang R: Two’s company, three’s a crowd:
can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter?
FASEB J. 16:1792–1798. 2002.
|
|
3.
|
Tokuda K, Kida K, Marutani E, Crimi E,
Bougaki M, Khatri A, Kimura H and Ichinose F: Inhaled hydrogen
sulfide prevents endotoxin-induced systemic inflammation and
improves survival by altering sulfide metabolism in mice. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 17:11–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Jiang LH, Luo X, He W, Huang XX and Cheng
TT: Effects of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on apoptosis proteins and
oxidative stress in the hippocampus of rats undergoing heroin
withdrawal. Arch Pharm Res. 34:2155–2162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Whiteman M, Armstrong JS, Chu SH, Jia-Ling
S, Wong BS, Cheung NS, Halliwell B and Moore PK: The novel
neuro-modulator hydrogen sulfide: an endogenous peroxynitrite
‘scavenger’? J Neurochem. 90:765–768. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Sivarajah A, McDonald MC and Thiemermann
C: The production of hydrogen sulfide limits myocardial ischemia
and reperfusion injury and contributes to the cardioprotective
effects of preconditioning with endotoxin, but not ischemia in the
rat. Shock. 26:154–161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Tay AS, Hu LF, Lu M, Wong PT and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide protects neurons against hypoxic injury via
stimulation of ATP-sensitive potassium channel/protein kinase
C/extra-cellular signal-regulated kinase/heat shock protein 90
pathway. Neuroscience. 167:277–286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Kang K, Zhao M, Jiang H, Tan G, Pan S and
Sun X: Role of hydrogen sulfide in hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Liver Transpl.
15:1306–1314. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Fu Z, Liu X, Geng B, Fang L and Tang C:
Hydrogen sulfide protects rat lung from ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Life Sci. 82:1196–1202. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Mard SA, Neisi N, Solgi G, Hassanpour M,
Darbor M and Maleki M: Gastroprotective effect of NaHS against
mucosal lesions induced by ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat. Dig
Dis Sci. 57:1496–1503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Wada K, Kamisaki Y, Kitano M, Kishimoto Y,
Nakamoto K and Itoh T: A new gastric ulcer model induced by
ischemia-reperfusion in the rat: role of leukocytes on ulceration
in rat stomach. Life Sci. 59:PL295–PL301. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Pan TT, Feng ZN, Lee SW, Moore PK and Bian
JS: Endogenous hydrogen sulfide contributes to the cardioprotection
by metabolic inhibition preconditioning in the rat ventricular
myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 40:119–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Masuda E, Kawano S, Nagano K, Tsuji S,
Takei Y, Hayashi N, Tsujii M, Oshita M, Michida T, Kobayashi I, et
al: Role of endogenous endothelin in pathogenesis of
ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Am J Physiol.
265:G474–G481. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Kwiecień S, Brzozowski T and Konturek SJ:
Effects of reactive oxygen species action on gastric mucosa in
various models of mucosal injury. J Physiol Pharmacol. 53:39–50.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Andrews FJ, Malcontenti-Wilson C and
O’Brien PE: Polymorphonuclear leukocyte infiltration into gastric
mucosa after ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol. 266:G48–G54.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Wada K, Kamisaki Y, Ohkura T, Kanda G,
Nakamoto K, Kishimoto Y, Ashida K and Itoh T: Direct measurement of
nitric oxide release in gastric mucosa during ischemia-reperfusion
in rats. Am J Physiol. 274:G465–G471. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Ishii M, Shimizu S, Nawata S, Kiuchi Y and
Yamamoto T: Involvement of reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide
in gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: protective effect
of tetrahydrobiopterin. Dig Dis Sci. 45:93–98. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Itoh M and Guth PH: Role of oxygen-derived
free radicals in hemorrhagic shock-induced gastric lesions in the
rat. Gastroenterology. 88:1162–1167. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
El Eter E, Hagar HH, Al-Tuwaijiri A and
Arafa M: Nuclear factor-kappaB inhibition by
pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate attenuates gastric ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 83:483–492.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Kimura Y, Dargusch R, Schubert D and
Kimura H: Hydrogen sulfide protects HT22 neuronal cells from
oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal. 8:661–670. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kimura Y and Kimura H: Hydrogen sulfide
protects neurons from oxidative stress. FASEB J. 18:1165–1167.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Zhang Z, Huang H, Liu P, Tang C and Wang
J: Hydrogen sulfide contributes to cardioprotection during
ischemia-reperfusion injury by opening K ATP channels. Can J
Physiol Pharmacol. 85:1248–1253. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Elsey DJ, Fowkes RC and Baxter GF:
L-cysteine stimulates hydrogen sulfide synthesis in myocardium
associated with attenuation of ischmia-reperfusion injury. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 15:53–59. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Tyagi N, Moshal KS, Sen U, Vacek TP, Kumar
M, Hughes WM Jr, Kundu S and Tyagi SC: H2S protects
against methionine-induced oxidative stress in brain endothelial
cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 11:25–33. 2009.
|
|
25.
|
Zhu YZ, Wang ZJ, Ho P, Loke YY, Zhu YC,
Huang SH, Tan CS, Whiteman M, Lu J and Moore PK: Hydrogen sulfide
and its possible roles in myocardial ischemia in experimental rats.
J Appl Physiol. 102:261–268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Pompella A, Visvikis A, Paolicchi A, De
Tata V and Casini AF: The changing faces of glutathione, a cellular
protagonist. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:1499–1503. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Liu H, Bai XB, Shi S and Cao YX: Hydrogen
sulfide protects from intestinal ischaemia-reperfusion injury in
rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 61:207–212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Margaritis EV, Yanni AE, Agrogiannis G,
Liarakos N, Pantopoulou A, Vlachos I, Papachristodoulou A,
Korkolopoulou P, Patsouris E, Kostakis M, Perrea DN and Kostakis A:
Effects of oral administration of l-arginine, l-NAME and
allopurinol on intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Life
Sci. 88:1070–1076. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Wang T, Leng YF and Zhang Y, Xue X, Kang
YQ and Zhang Y: Oxidative stress and hypoxia-induced factor 1alpha
expression in gastric ischemia. World J Gastroenterol.
17:1915–1922. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Yonezawa D, Sekiguchi F, Miyamoto M,
Taniguchi E, Honjo M, Masuko T, Nishikawa H and Kawabata A: A
protective role of hydrogen sulfide against oxidative stress in rat
gastric mucosal epithelium. Toxicology. 241:11–18. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|