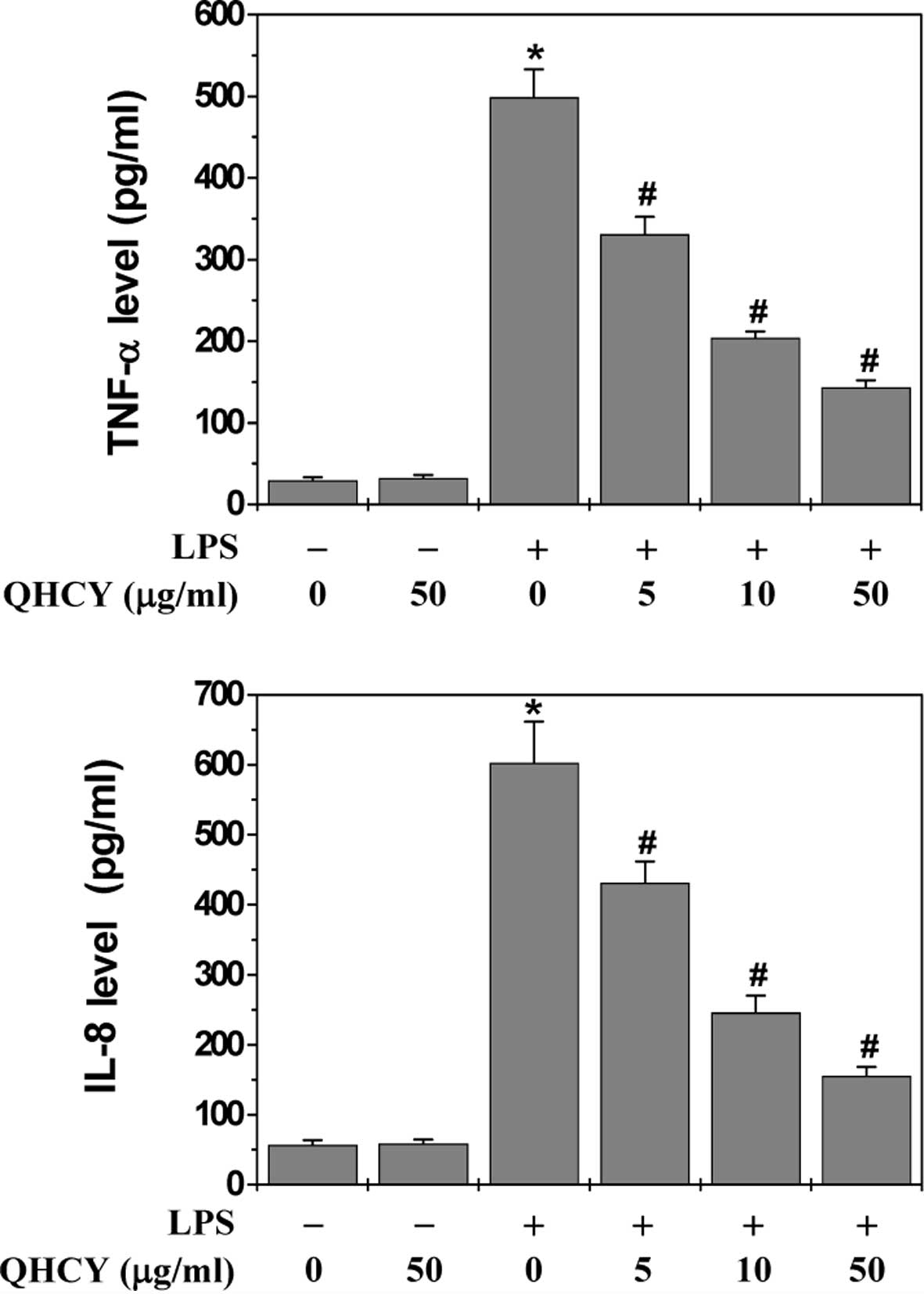
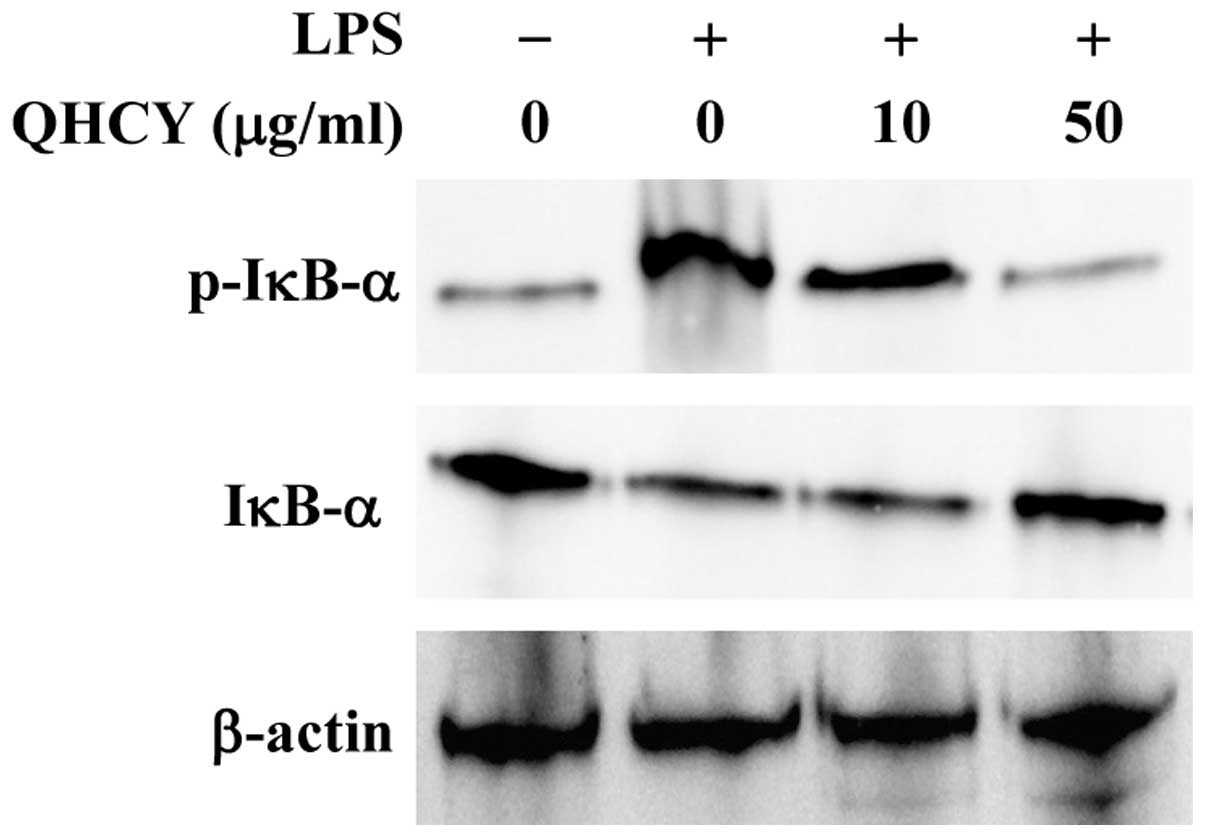
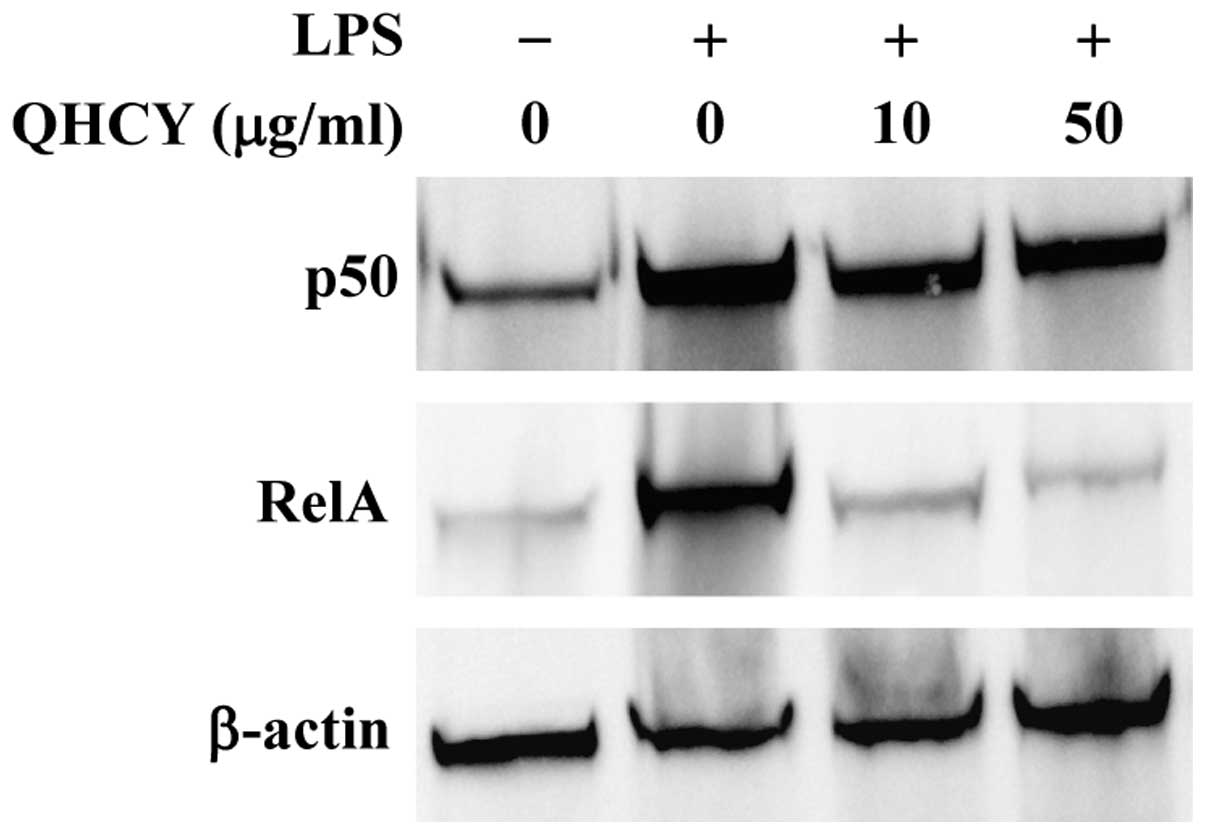
|
1.
|
Rezaie A, Parker RD and Abdollahi M:
Oxidative stress and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease: an
epiphenomenon or the cause? Dig Dis Sci. 52:2015–2021. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Podolsky DK: Inflammatory bowel disease. N
Engl J Med. 347:417–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Odashima M, Otaka M, Jin M, et al:
Successful treatment of refractory duodenal Crohn’s disease with
infliximab. Dig Dis Sci. 52:31–32. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Treasure J: Herbal medicine and cancer: an
introductory overview. Semin Oncol Nurs. 21:177–183. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Stickel F and Schuppan D: Herbal medicine
in the treatment of liver diseases. Dig Liver Dis. 39:293–304.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Langmead L and Rampton DS: Review article:
complementary and alternative therapies for inflammatory bowel
disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23:341–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Bensoussan M, Jovenin N, Garcia B, et al:
Complementary and alternative medicine use by patients with
inflammatory bowel disease: results from a postal survey.
Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 30:14–23. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Caradonna L, Amati L, Magrone T,
Pellegrino M, Jirillo E and Caccavo D: Enteric bacteria,
lipopolysaccharides and related cytokines in inflammatory bowel
disease: biological and clinical significance. J Endotoxin Res.
6:205–214. 2000.
|
|
9.
|
Böcker U, Yezerskyy O, Feick P, et al:
Responsiveness of intestinal epithelial cell lines to
lipopolysaccharide is correlated with Toll-like receptor 4 but not
Toll-like receptor 2 or CD14 expression. Int J Colorectal Dis.
18:25–32. 2003.
|
|
10.
|
Bruewer M, Utech M, Ivanov AI, Hopkins AM,
Parkos CA and Nusrat A: Interferon-gamma induces internalization of
epithelial tight junction proteins via a macropinocytosis-like
process. FASEB J. 19:923–933. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Schreiber S, Nikolaus S and Hampe J:
Activation of nuclear factor kappa B inflammatory bowel disease.
Gut. 42:477–484. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Andresen L, Jørgensen VL, Perner A, Hansen
A, Eugen-Olsen J and Rask-Madsen J: Activation of nuclear factor
kappaB in colonic mucosa from patients with collagenous and
ulcerative colitis. Gut. 54:503–509. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Lakatos PL, Fischer S, Lakatos L, et al:
Current concept on the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel
disease-crosstalk between genetic and microbial factors: pathogenic
bacteria and altered bacterial sensing or changes in mucosal
integrity take ‘toll’? World J Gastroenterol. 12:1829–1841.
2006.
|
|
14.
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Snape WJ Jr and Kao HW: Role of
inflammatory mediators in colonic smooth muscle function in
ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 33(Suppl 3): 65S–70S. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Neuman MG: Immune dysfunction in
inflammatory bowel disease. Transl Res. 149:173–186. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Eckmann L, Jung HC, Schürer-Maly C, Panja
A, Morzycka-Wroblewska E and Kagnoff MF: Differential cytokine
expression by human intestinal epithelial cell lines: regulated
expression of interleukin 8. Gastroenterol. 105:1689–1697.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Wang D, DuBois RN and Richmond A: The role
of chemokines in intestinal inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 9:688–696. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Brynskov J, Foegh P, Pedersen G, et al:
Tumour necrosis factor alpha converting enzyme (TACE) activity in
the colonic mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease.
Gut. 51:37–43. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Wang XY and Tian DL: Etiological and
pathological characteristics of ulcerative colitis and TCM
differentiation and treatment. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao.
30:554–559. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
21.
|
Gong YP, Liu W, Ma GT, et al: Randomized
control study of ‘Qingchang Suppository’ on ulcerative colitis.
Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao. 21:33–36. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
22.
|
Fu NL and Huang JY: Progress of clinical
research of traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of
ulcerative colitis. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
40:501–503. 1999.(In Chinese).
|
|
23.
|
Li QG: An idea about treatment of
ulcerative colitis by TCM methods. Beijing Zhong Yi. 23:149–150.
2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
24.
|
Wang CH, Gao WY, Li YF, et al: Study of
Fufangkushen colon-release capsule on ulcerative colitis of
endo-retention of damp heat type. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za
Zhi. 18:13–15. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
25.
|
Chen JT, Ke X, Fu XY, et al: The clinical
study of heat-clearing and damp-drying on the treatment of
damp-heat ulcerative colitis. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xiao Hua
Za Zhi. 17:256–257. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
26.
|
Kawai T and Akira S: TLR signaling. Cell
Death Differ. 13:816–825. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Johnson GB, Brunn GJ, Kodaira Y and Platt
JL: Receptor-mediated monitoring of tissue well-being via detection
of soluble heparan sulfate by Toll-like receptor 4. J Immunol.
168:5233–5239. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Lehnardt S, Schott E and Trimbuch T: A
vicious cycle involving release of heat shock protein 60 from
injured cells and activation of Toll-like receptor 4 mediates
neurodegeneration in the CNS. J Neurosci. 28:2320–2331. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Smiley ST, King JA and Hancock WW:
Fibrinogen stimulates macrophage chemokine secretion through
Toll-like receptor 4. J Immunol. 167:2887–2894. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|