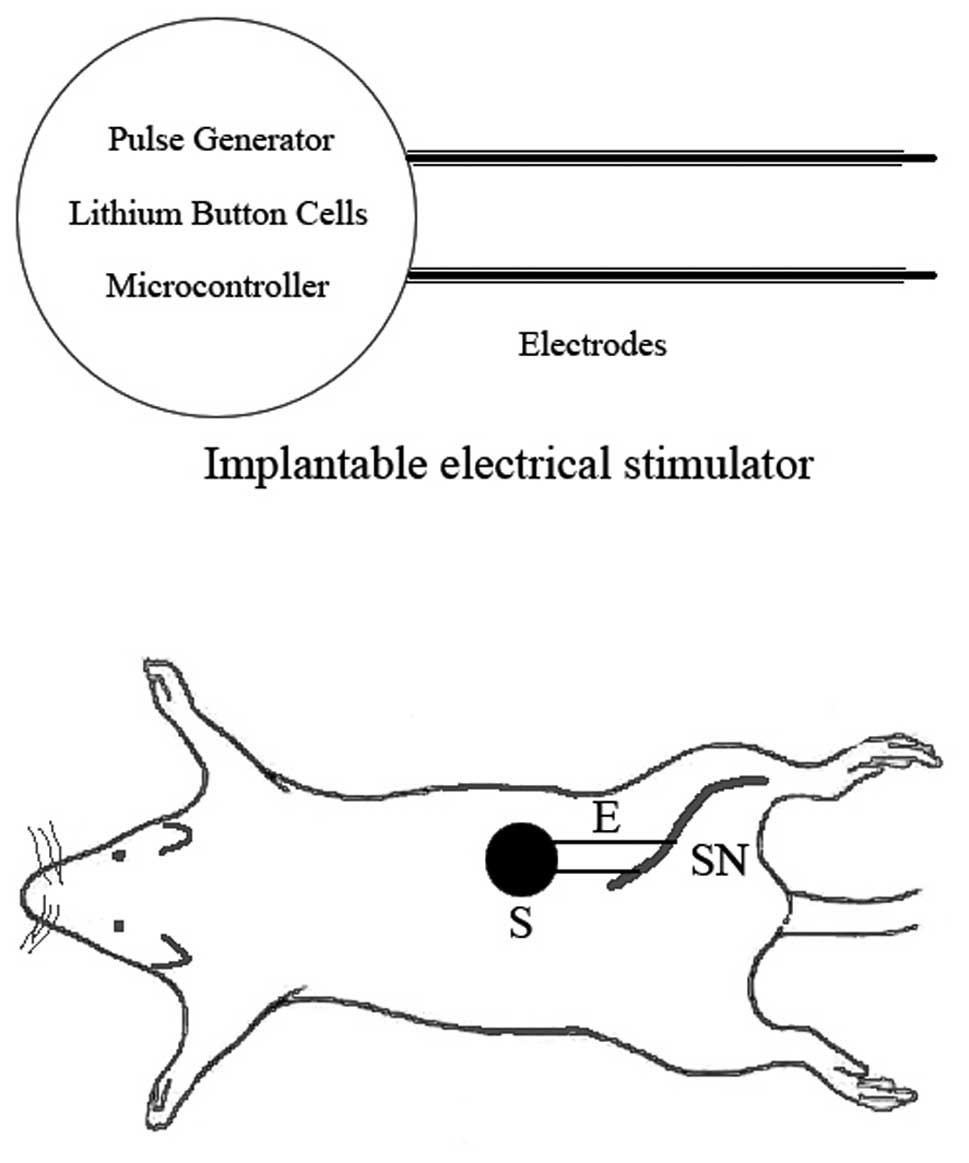
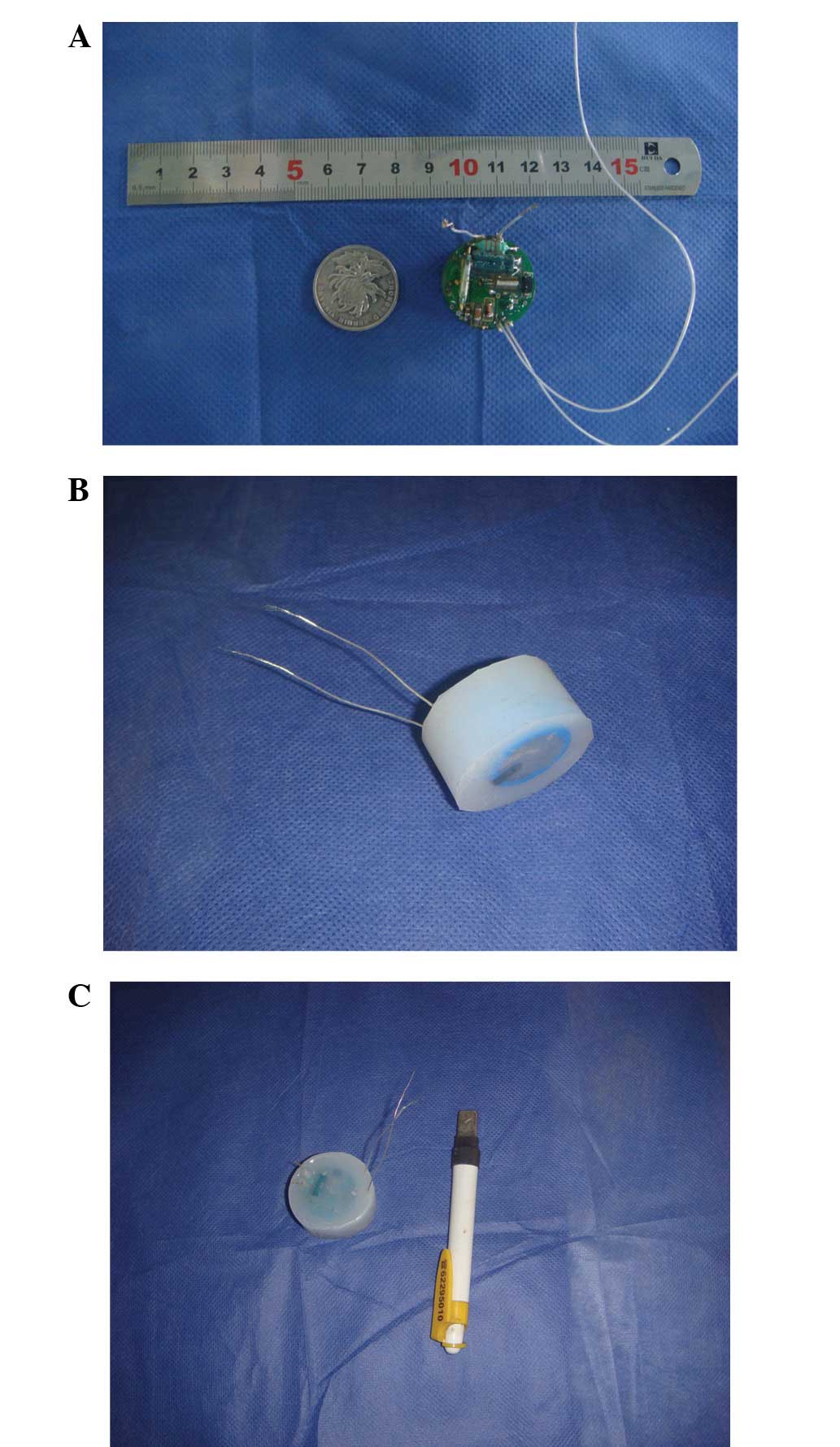
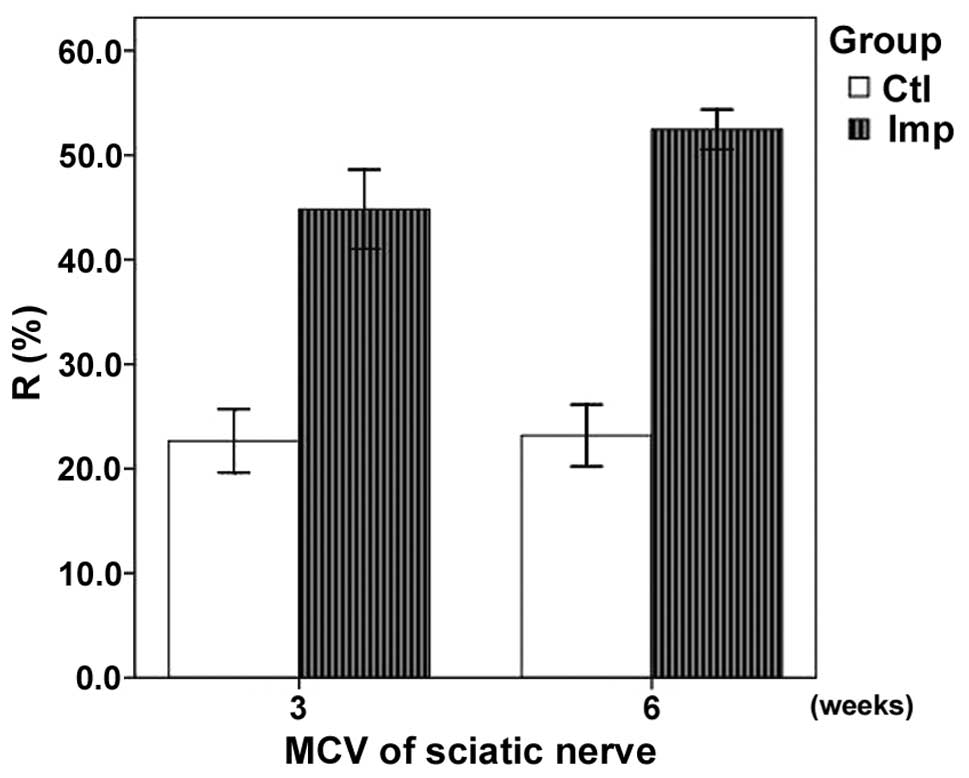
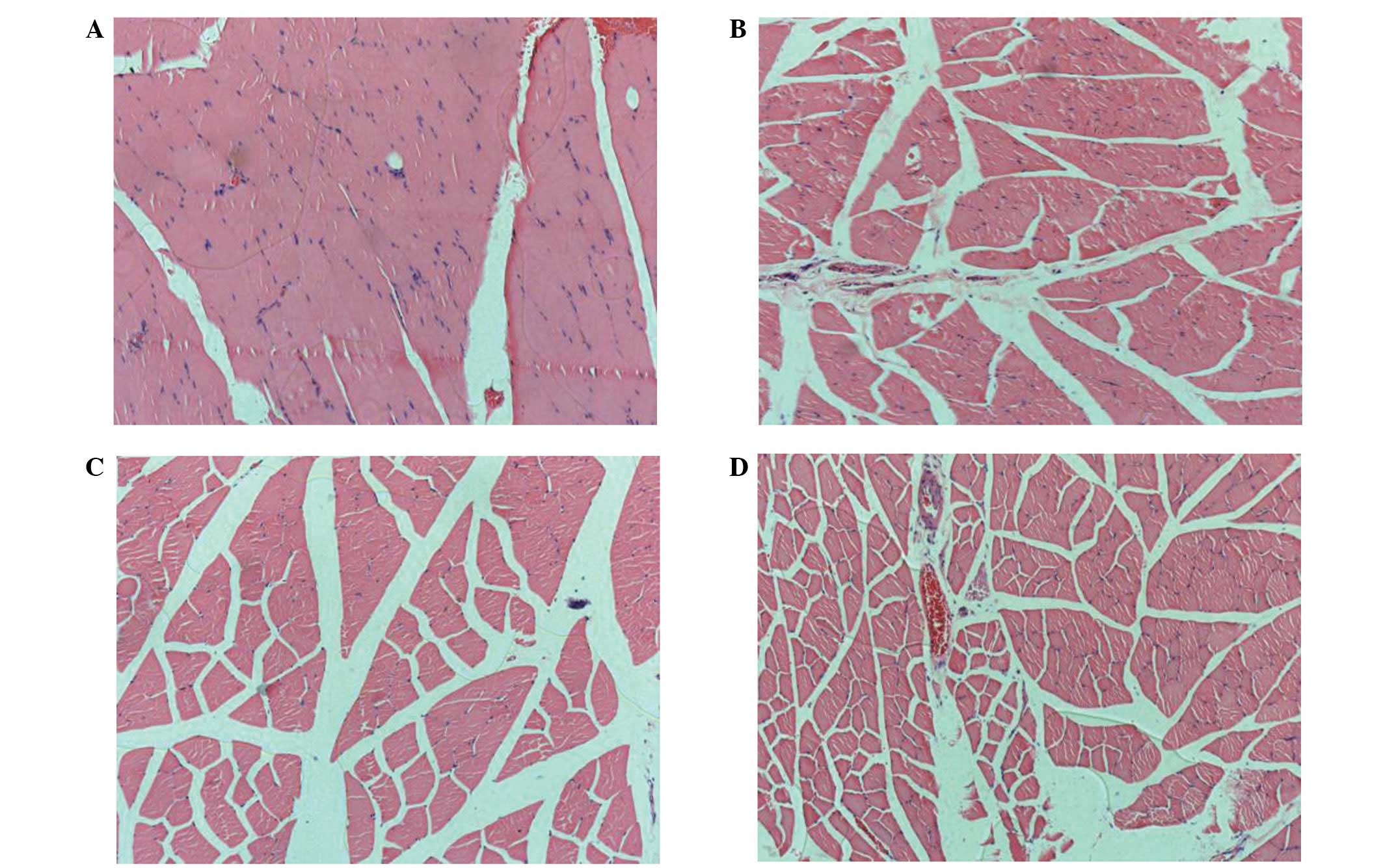
|
1.
|
Al-Majed AA, Neumann CM, Brushart TM and
Gordon T: Brief electrical stimulation promotes the speed and
accuracy of motor axonal regeneration. J Neurosci. 20:2602–2608.
2000.
|
|
2.
|
Brushart TM, Jari R, Verge V, Rohde C and
Gordon T: Electrical stimulation restores the specificity of
sensory axon regeneration. Exp Neurol. 194:221–229. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
English AW, Schwartz G, Meador W, Sabatier
MJ and Mulligan A: Electrical stimulation promotes peripheral axon
regeneration by enhanced neuronal neurotrophin signaling. Dev
Neurobiol. 67:158–172. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Geremia NM, Gordon T, Brushart TM,
Al-Majed AA and Verge VM: Electrical stimulation promotes sensory
neuron regeneration and growth-associated gene expression. Exp
Neurol. 205:347–359. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Yamada M, Tanemura K, Okada S, et al:
Electrical stimulation modulates fate determination of
differentiating embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells. 25:562–570. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Zhang Z, Rouabhia M, Wang Z, et al:
Electrically conductive biodegradable polymer composite for nerve
regeneration: electricity-stimulated neurite outgrowth and axon
regeneration. Artif Organs. 31:13–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Zealear DL, Rodriguez RJ, Kenny T, et al:
Electrical stimulation of a denervated muscle promotes selective
reinnervation by native over foreign motoneurons. J Neurophysiol.
87:2195–2199. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Al-Majed AA, Tam SL and Gordon T:
Electrical stimulation accelerates and enhances expression of
regeneration-associated genes in regenerating rat femoral
motoneurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 24:379–402. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Gordon T, Udina E, Verge VM and de Chaves
EI: Brief electrical stimulation accelerates axon regeneration in
the peripheral nervous system and promotes sensory axon
regeneration in the central nervous system. Motor Control.
13:412–441. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Snapp HA, Fabry DA, Telischi FF, Arheart
KL and Angeli SI: A clinical protocol for predicting outcomes with
an implantable prosthetic device (Baha) in patients with
single-sided deafness. J Am Acad Audiol. 21:654–662. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Yanagihara N, Gyo K, Sato H, Yamanaka E
and Saiki T: Implantable hearing aid in fourteen patients with
mixed deafness. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 458:90–94. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Leclercq JF, Ménasché P, Piwnica A, Coumel
P and Slama R: The implantable automatic defibrillator. Preventive
treatment of sudden death caused by ventricular arrhythmia. Presse
Med. 12:1707–1710. 1983.(In French).
|
|
13.
|
Chiou YH, Luh JJ, Chen SC, Chen YL, Lai JS
and Kuo TS: Patient-driven loop control for hand function
restoration in a non-invasive functional electrical stimulation
system. Disabil Rehabil. 30:1499–1505. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Blomstedt P: Deep-brain stimulation in
Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med. 346:452–453. 2002.
|
|
15.
|
National Institute of Health (NIH): Guide
for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Publication no. 85–23.
The National Academies Press; Washington, D.C: 1996
|
|
16.
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Generation of
neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian
central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1710. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Bain JR, Mackinnon SE and Hunter DA:
Functional evaluation of complete sciatic, peroneal, and posterior
tibial nerve lesions in the rat. Plast Reconstr Surg. 83:129–138.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Lundborg G: A 25-year perspective of
peripheral nerve surgery: evolving neuroscientific concepts and
clinical significance. J Hand Surg Am. 25:391–414. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Naff NJ and Ecklund JM: History of
peripheral nerve surgery techniques. Neurosurg Clin N Am.
12:197–209. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Dvali L and Mackinnon S: Nerve repair,
grafting, and nerve transfers. Clin Plast Surg. 30:203–221. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Zeng X, Zhang L, Sun L, et al: Recovery
from rat sciatic nerve injury in vivo through the use of
differentiated MDSCs in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 5:193–196.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Stieglitz T: Neural prostheses and
functional electrical stimulation. Biomed Tech (Berl). 49:70–71.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Tong KC, Lo SK and Cheing GL: Alternating
frequencies of transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation: does it
produce greater analgesic effects on mechanical and thermal pain
thresholds? Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 88:1344–1349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Malm-Buatsi E, Nepple KG, Boyt MA, Austin
JC and Cooper CS: Efficacy of transcutaneous electrical nerve
stimulation in children with overactive bladder refractory to
pharmacotherapy. Urology. 70:980–983. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Robaina F and Clavo B: Spinal cord
stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke patients: current state
and future directions. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 97:277–282.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Hamid S and Hayek R: Role of electrical
stimulation for rehabilitation and regeneration after spinal cord
injury: an overview. Eur Spine J. 17:1256–1269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Hamani C, Schwalb JM, Rezai AR, Dostrovsky
JO, Davis KD and Lozano AM: Deep brain stimulation for chronic
neuropathic pain: long-term outcome and the incidence of
insertional effect. Pain. 125:188–196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Beer GM, Steurer J and Meyer VE:
Standardizing nerve crushes with a non-serrated clamp. J Reconstr
Microsurg. 17:531–534. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Varejão AS, Cabrita AM, Meek MF, et al:
Functional and morphological assessment of a standardized rat
sciatic nerve crush injury with a non-serrated clamp. J
Neurotrauma. 21:1652–1670. 2004.
|
|
30.
|
Ahlborn P, Schachner M and Irintchev A:
One hour electrical stimulation accelerates functional recovery
after femoral nerve repair. Exp Neurol. 208:137–144. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Baptista AF, Gomes JR, Oliveira JT, Santos
SM, Vannier-Santos MA and Martinez AM: High- and low-frequency
transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation delay sciatic nerve
regeneration after crush lesion in the mouse. J Peripher Nerv Syst.
13:71–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32.
|
Lilly JC, Hughes JR, Alvord EC Jr and
Galkin TW: Brief, noninjurious electric waveform for stimulation of
the brain. Science. 121:468–469. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|