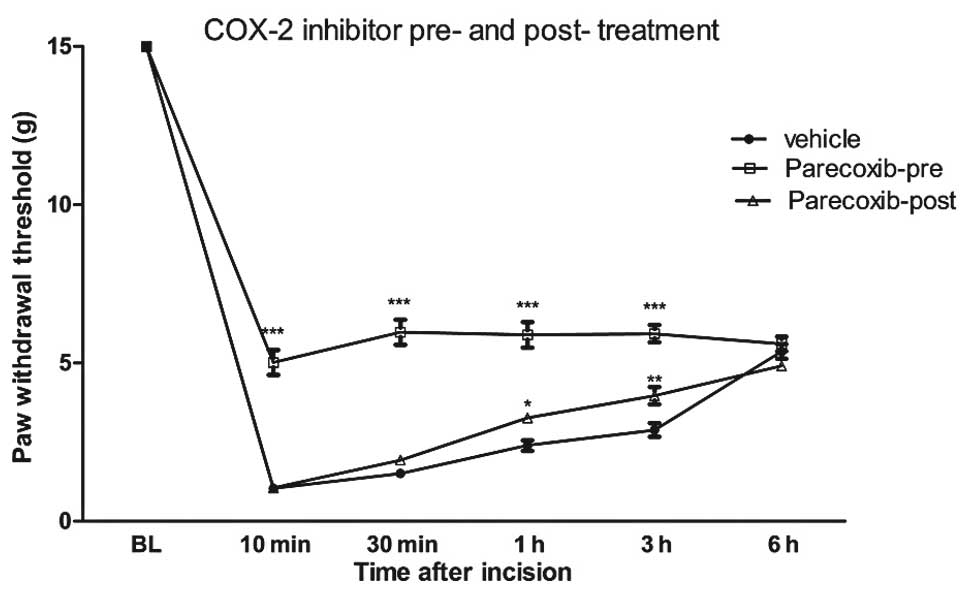
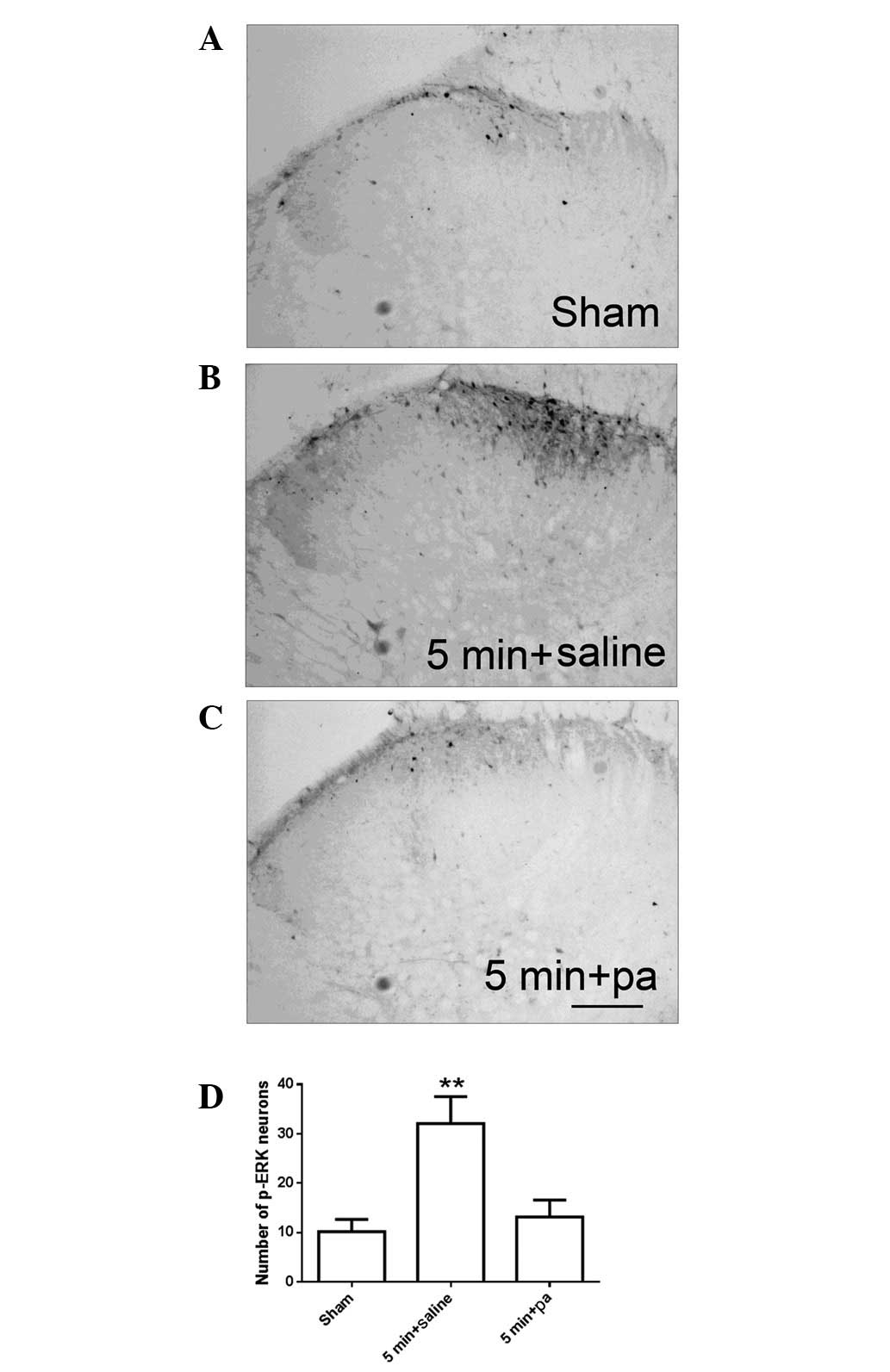
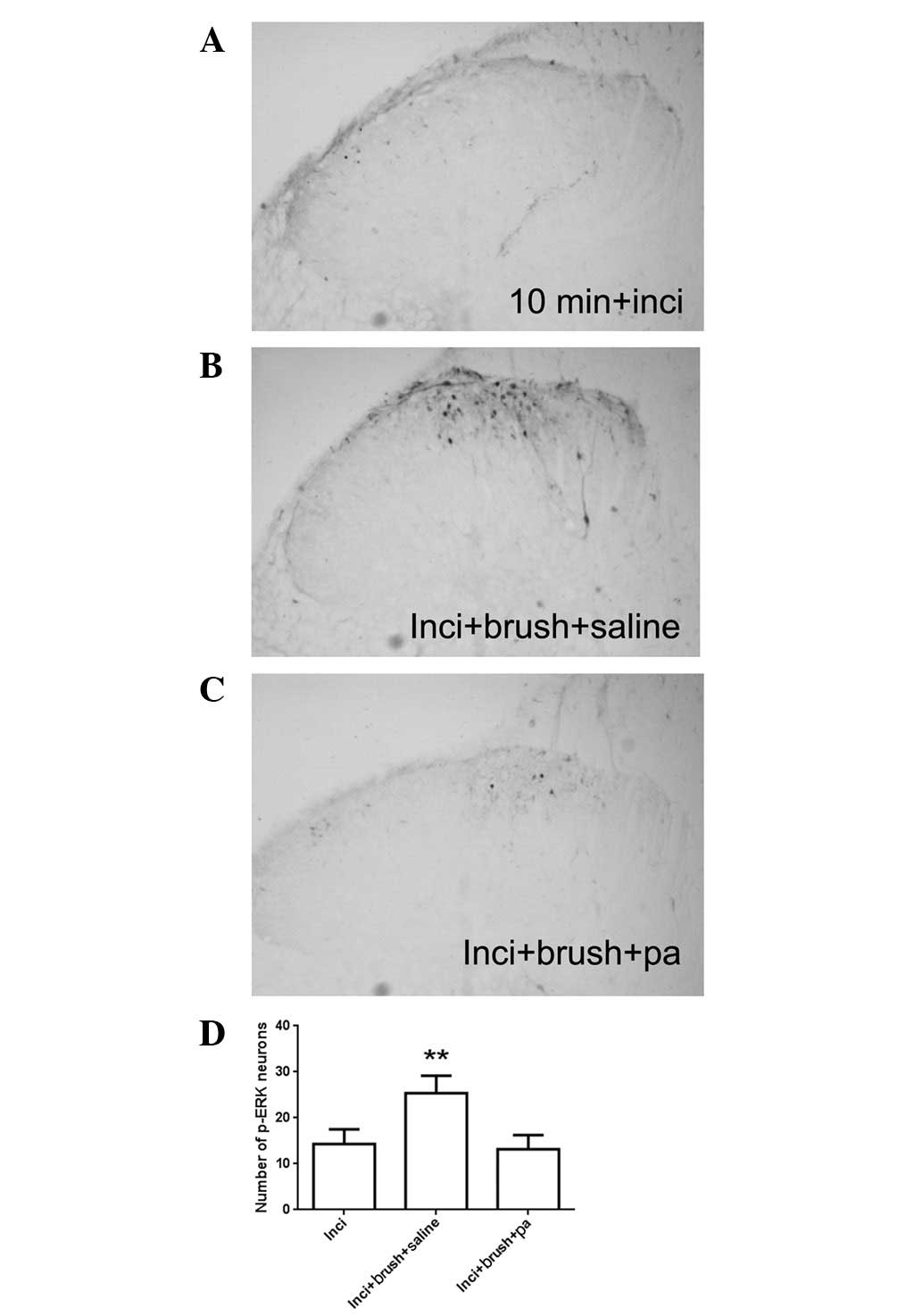
|
1.
|
Costantini R, Affaitati G, Fabrizio A and
Giamberardino MA: Controlling pain in the post-operative setting.
Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 49:116–127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Wu CL and Raja SN: Treatment of acute
postoperative pain. Lancet. 377:2215–2225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Lloyd R, Derry S, Moore RA and McQuay HJ:
Intravenous or intramuscular parecoxib for acute postoperative pain
in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2:CD0047712009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Myles PS and Power I: Clinical update:
postoperative analgesia. Lancet. 369:810–812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Langford RM, Joshi GP, Gan TJ, Mattera MS,
Chen WH, Revicki DA, Chen C and Zlateva G: Reduction in
opioid-related adverse events and improvement in function with
parecoxib followed by valdecoxib treatment after non-cardiac
surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
parallel-group trial. Clin Drug Investig. 29:577–590. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Samad TA, Moore KA, Sapirstein A, Billet
S, Allchorne A, Poole S and Woolf CJ: Interleukin-1β-mediated
induction of Cox-2 in the CNS contributes to inflammatory pain
hypersensitivity. Nature. 410:471–475. 2001.
|
|
7.
|
Yaksh TL, Dirig DM, Conway CM, Svensson C,
Luo ZD and Isakson PC: The acute antihyperalgesic action of
nonsteroidal, anti-inflammatory drugs and release of spinal
prostaglandin E2 is mediated by the inhibition of constitutive
spinal cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) but not COX-1. J Neurosci.
21:5847–5853. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Zhu X, Conklin DR and Eisenach JC:
Preoperative inhibition of cyclooxygenase-1 in the spinal cord
reduces postoperative pain. Anesth Analg. 100:1390–1393. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
McCrory C and Fitzgerald D: Spinal
prostaglandin formation and pain perception following thoracotomy:
a role for cyclooxygenase-2. Chest. 125:1321–1327. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Reuben SS, Buvanendran A, Kroin JS and
Steinberg RB: Postoperative modulation of central nervous system
prostaglandin E2 by cyclooxygenase inhibitors after vascular
surgery. Anesthesiology. 104:411–416. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Ji RR, Befort K, Brenner GJ and Woolf CJ:
ERK MAP kinase activation in superficial spinal cord neurons
induces prodynorphin and NK-1 upregulation and contributes to
persistent inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. J Neurosci.
22:478–485. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Zhuang ZY, Gerner P, Woolf CJ and Ji RR:
ERK is sequentially activated in neurons, microglia, and astrocytes
by spinal nerve ligation and contributes to mechanical allodynia in
this neuropathic pain model. Pain. 114:149–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Shi XD, Fu D, Xu JM, Zhang YL and Dai RP:
Activation of spinal ERK1/2 contributes to mechanical allodynia in
rat model of postoperative pain. Mol Med Rep. 7:1661–1665.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP and Gebhart
GF: Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain. Pain.
64:493–501. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM
and Yaksh TL: Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the
rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 53:55–63. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Li CQ, Xu JM, Liu D, Zhang JY and Dai RP:
Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) contributes to the pain
hypersensitivity following surgical incision in the rats. Mol Pain.
4:272008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Kroin JS, Buvanendran A, Watts DE, Saha C
and Tuman KJ: Upregulation of cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral
prostaglandin E2 in a rat postoperative pain model. Anesth Analg.
103:334–343. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Pham-Marcou TA, Beloeil H, Sun X, Gentili
M, Yaici D, Benoit G, Benhamou D and Mazoit JX: Antinociceptive
effect of resveratrol in carrageenan-evoked hyperalgesia in rats:
prolonged effect related to COX-2 expression impairment. Pain.
140:274–283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Obata K and Noguchi K: MAPK activation in
nociceptive neurons and pain hypersensitivity. Life Sci.
74:2643–2653. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Bhave G and Gereau RW IV:
Posttranslational mechanisms of peripheral sensitization. J
Neurobiol. 61:88–106. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21.
|
Obata K, Yamanaka H, Kobayashi K, Dai Y,
Mizushima T, Katsura H, Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A and Noguchi K: Role
of mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in injured and
intact primary afferent neurons for mechanical and heat
hypersensitivity after spinal nerve ligation. J Neurosci.
24:10211–10222. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22.
|
Ji RR, Baba H, Brenner GJ and Woolf CJ:
Nociceptive-specific activation of ERK in spinal neurons
contributes to pain hypersensitivity. Nat Neurosci. 2:1114–1119.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Pogatzki-Zahn EM and Zahn PK: From
preemptive to preventive analgesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol.
19:551–555. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Katz J, Clarke H and Seltzer Z: Review
article: Preventive analgesia: quo vadimus? Anesth Analg.
113:1242–1253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Dahl JB and Kehlet H: Preventive
analgesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 24:331–338. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|