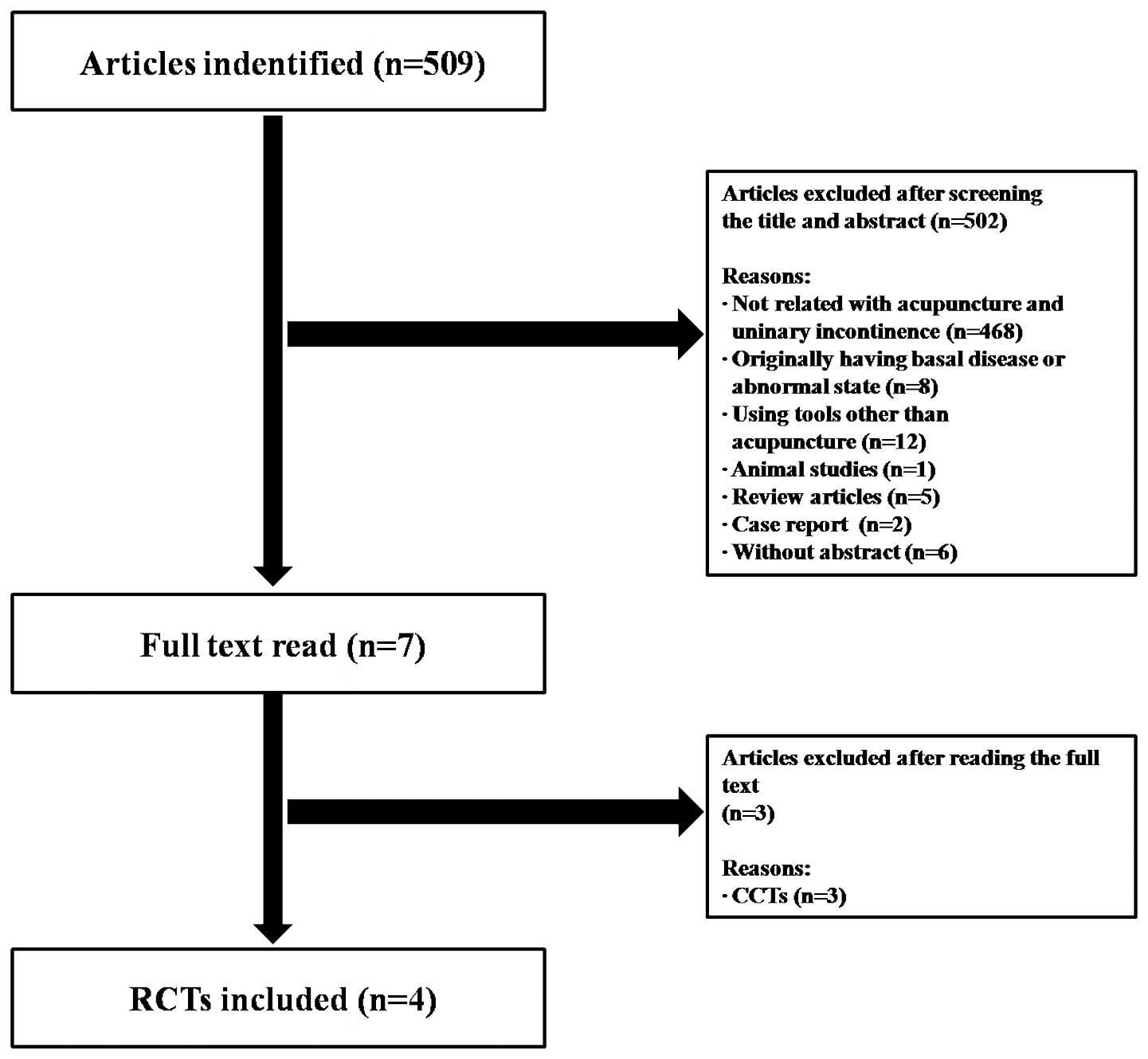
|
1
|
Nygaard IE and Heit M: Stress urinary
incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 104:607–620. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abrams P, Cadozo L, Fall M, et al;
Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence
Society. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract
dysfunction: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the
International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn. 21:167–178.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Robinson D: Patholophysiology of female
lower urinary tract dysfunction. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am.
25:747–756. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Philip T, Shah PJ and Worth PH:
Acupuncture in the treatment of bladder instability. Br J Urol.
61:490–493. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chang PL: Urodynamic studies in
acupuncture in women with frequency, urgency, and dysuria. J Urol.
140:563–566. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bergström K, Carlsson C, Lindholm C and
Widengren R: Improvement of urge- and mixed-type incontinence after
acupuncture treatment among elderly women - a pilot study. J Auton
Nerv Syst. 79:173–180. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Honjo H, Kitakoji H, Kawakita K, et al:
Acupuncture for urinary incontinence in patients with chronic
spinal cord injury. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi. 89:665–669.
1998.(In Japanese).
|
|
8
|
Kelleher C, Filshie J, Khullar V and
Cardozo L: Acupuncture and the treatment of irritative bladder
symptoms. Acupunct Med. 12:9–12. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Knardahl S, Elam M, Olausson B and Wallin
BG: Sympathetic nerve activity after acupuncture in humans. Pain.
75:19–25. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rajaofetra N, Passagia JG, Marlier L, et
al: Serotoninergic, noradrenergic, and peptidergic innervation of
Onuf’s nucleus of normal and transected spinal cords of baboons
(Papio papio). J Comp Neurol. 318:1–17. 1992.
|
|
11
|
Minni B, Capozza N, Creti G, De Gennaro M,
Caione P and Bischko J: Bladder instability and enuresis treated by
acupuncture and electro-therapeutics: early urodynamic
observations. Acupunct Electrother Res. 15:19–25. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nakamura M, Sakurai T, Tsujimoto Y and
Tada Y: Bladder inhibition by electrical stimulation of the
perianal skin. Urol Int. 41:62–63. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sato A, Sato Y, Shimada F and Torigata Y:
Changes in vesical function produced by cutaneous stimulation in
rats. Brain Res. 94:465–474. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chartier-Kastler EJ, Ruud Bosch JL,
Perrigot M, et al: Long-term results of sacral nerve stimulation
(S3) for the treatment of neurogenic refractory urge incontinence
related to detrusor hyperreflexia. J Urol. 164:1476–1480. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang H, Wang PJ, Zeng HW and Zhao XH:
Central mechanism of electric-acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) for
gastric mucous membrane protection with FMRI. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za
Zhi. 90:1458–1462. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Anderson S and Lundeberg T: Acupuncture -
from empiricism to science: functional background to acupuncture
effects in pain and disease. Med Hypotheses. 45:271–281. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Itoh K, Minakawa Y and Kitakoji H: Effect
of acupuncture depth on muscle pain. Chin Med. 6:242001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Silca ML, Silva JR and Prado WA: The
antinociceptive effect of electroacupuncture at different depths of
acupoints and under the needling surface. Chin Med. 7:32012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Itoh K, Katsumi Y and Kitakoji H: Trigger
point acupuncture treatment of chronic low back pain in elderly
patients - a blinded RCT. Acupunct Med. 22:170–177. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Itoh K, Okada K and Kawakita K: A proposed
experimental model of myofascial trigger points in human muscle
after slow eccectric exercise. Acupunct Med. 22:2–12. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Engberg S, Cohen S and Sereika SM: The
efficacy of acupuncture in treating urge and mixed incontinence in
women: a pilot study. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 36:661–670.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Emmons SL and Otto L: Acupuncture for
overactive bladder: a randomized controlled trial. Obstet Gynecol.
106:138–143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chang KK, Wong TK, Wong TH, Leung AW and
Chung JW: Effect of acupressure in treating urodynamic stress
incontinence: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Chin Med.
39:1139–1159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Azevedo RF, Cbiari BM, Okada DM and
Onishi ET: Impact of acupuncture on otoacoustic emissions in
patients with tinnitus. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 73:599–607.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Okada DM, Onishi ET, Chami FI, Borin A,
Cassola N and Guerreiro VM: Acupuncture for tinnitus immediate
relief. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 72:182–186. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hansen PE, Hansen JH and Bentzen O:
Acupuncture treatment of chronic unilateral tinnitus - a
double-blind cross-over trial. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci.
7:325–329. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vilholm OJ, Møller K and Jørgensen K:
Effect of traditional Chinese acupuncture on severe tinnitus: a
double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical investigation with open
therapeutic control. Br J Audiol. 32:197–204. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jeon SW, Kim KS and Nam HJ: Long-term
effect of acupuncture for treatment of tinnitus: a randomized,
patient- and assessor-blind, sham-acupuncture-controlled, pilot
trial. J Alter Complement Med. 18:693–699. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang K, Bugge J and Bugge S: A randomised,
placebo-controlled trial of manual and electrical acupuncture for
the treatment of tinnitus. Complement Ther Med. 18:249–255. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Marks NJ, Emery P and Onisiphorou C: A
controlled trial of acupuncture in tinnitus. J Laryngol Otol.
98:1103–1109. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ezzo J, Berman B, Hadhazy VA, Jadad AR,
Lao L and Singh BB: Is acupuncture effective for the treatment of
chronic pain? A systemic review. Pain. 86:217–225. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zaslawski CJ, Cobbin D, Lidums E and
Petocz P: The impact of site specificity and needle manipulation on
changes to pain pressure threshold following manual acupuncture: a
controlled study. Complement Ther Med. 11:11–21. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Loke YK, Derry S and Aronson JK: A
comparison of three different sources of data in assessing the
frequencies of adverse reactions to amiodarone. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 57:616–621. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Loke YK and Derry S: Reporting of adverse
drug reactions in randomised controlled trials - a systematic
survey. BMC Clin Pharmacol. 1:32001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|