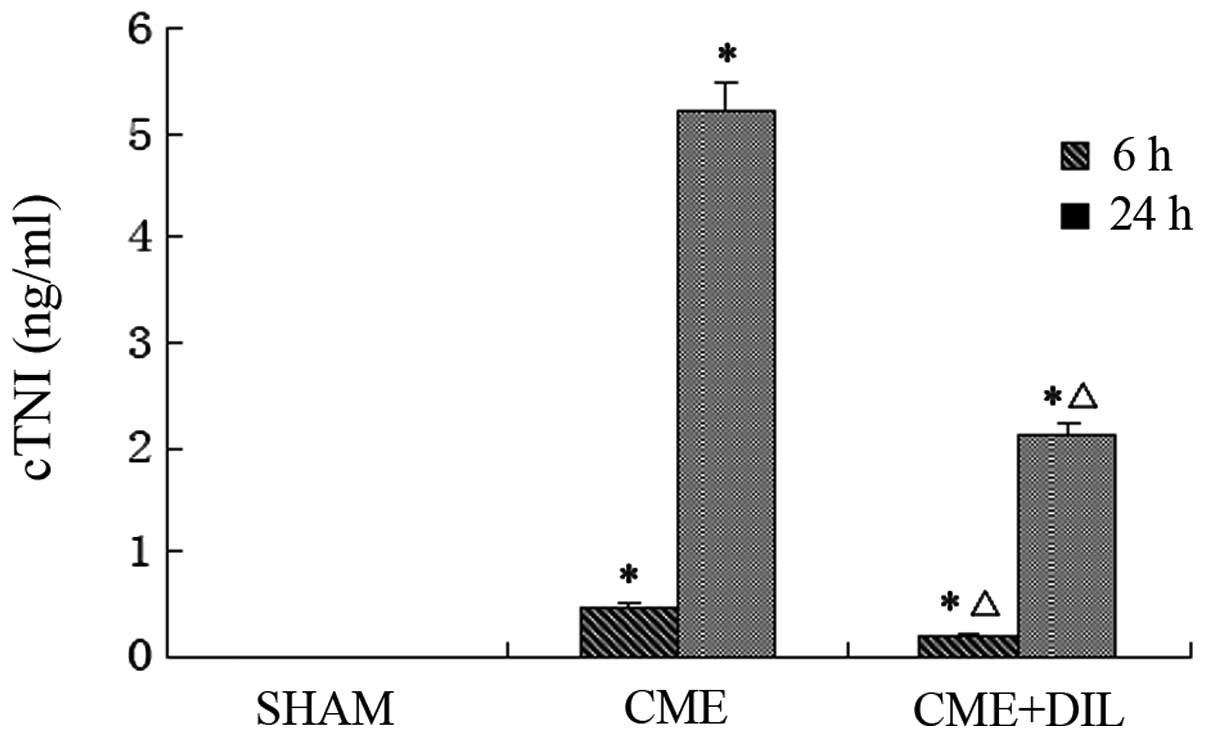
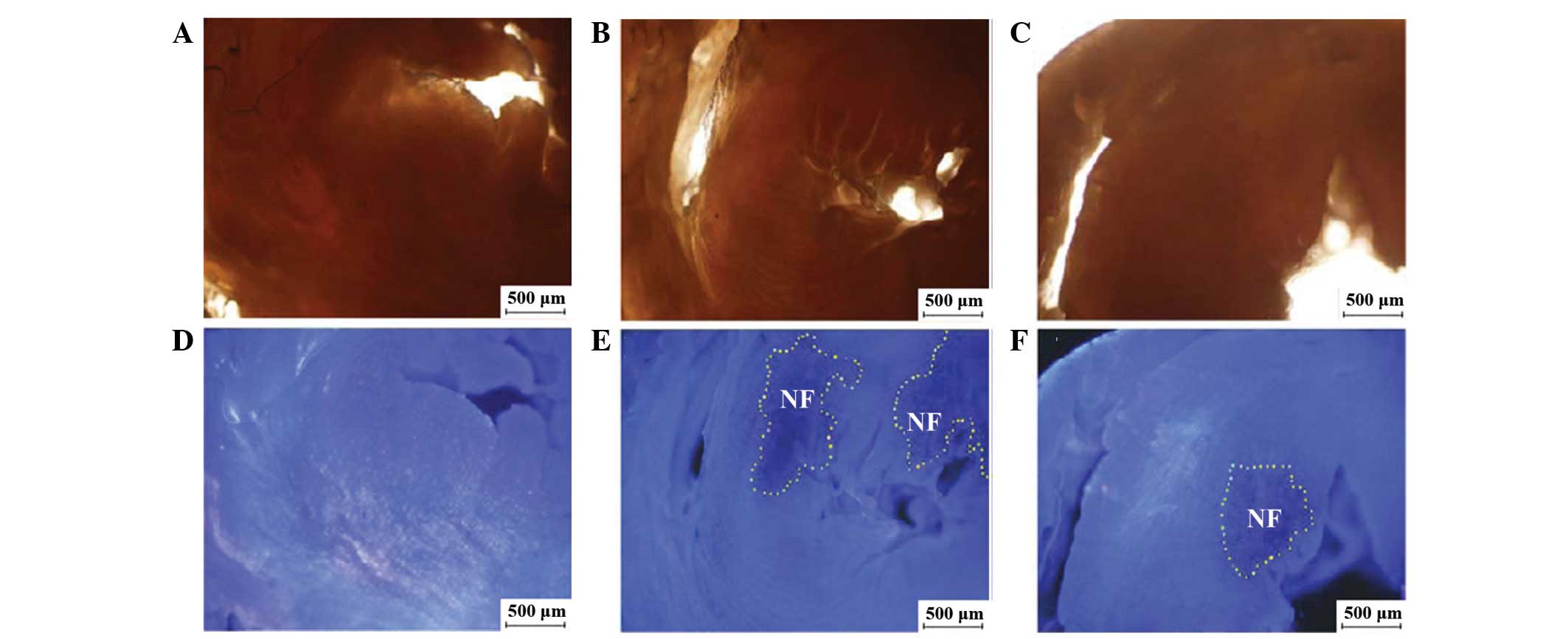
|
1.
|
Abdelmeguid AE, Topol EJ, Whitlow PL, Sapp
SK and Ellis SG: Significance of mild transient release of creatine
kinase-MB fraction after percutaneous coronary interventions.
Circulation. 94:1528–1536. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Califf RM, Abdelmeguid AE, Kuntz RE, et
al: Myonecrosis after revascularization procedures. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 31:241–251. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Herrmann J, Haude M, Lerman A, et al:
Abnormal coronary flow velocity reserve after coronary intervention
is associated with cardiac marker elevation. Circulation.
103:2339–2345. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Mehran R, Dangas G, Mintz GS, et al:
Atherosclerotic plaque burden and CK-MB enzyme elevation after
coronary interventions: intravascular ultrasound study of 2256
patients. Circulation. 101:604–610. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Erbel R and Heusch G: Coronary
microembolization. J Am Coll Cardiol. 36:22–24. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Golino P, Piscione F, Benedict CR, et al:
Local effect of serotonin released during coronary angioplasty. N
Engl J Med. 330:523–528. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Wilson RF, Laxson DD, Lesser JR and White
CW: Intense microvascular constriction after angioplasty of acute
thrombotic coronary arterial lesions. Lancet. 1:807–811. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Piana RN, Paik GY, Moscucci M, et al:
Incidence and treatment of ‘no-reflow’ after percutaneous coronary
intervention. Circulation. 89:2514–2518. 1994.
|
|
9.
|
Gu Y, Bai Y, Wu J, Hu L and Gao B:
Establishment and characterization of an experimental model of
coronary thrombotic microembolism in rats. Am J Pathol.
177:1122–1130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Heusch G, Kleinbongard P, Böse D, et al:
Coronary micro-embolization: from bedside to bench and back to
bedside. Circulation. 120:1822–1836. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Herrmann J: Peri-procedural myocardial
injury: 2005 update. Eur Heart J. 26:2493–2519. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Heusch G, Schulz R, Haude M and Erbel R:
Coronary microembolization. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 37:23–31. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Lee KW and Norell MS: Management of
‘no-reflow’ complicating reperfusion therapy. Acute Card Care.
10:5–14. 2008.
|
|
14.
|
Pasceri V, Patti G and Di Sciascio G:
Prevention of myocardial damage during coronary intervention.
Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 6:77–83. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Valero SJ, Moreno R, Reyes RM, et al:
Pharmacological approach of no-reflow phenomenon related with
percutaneous coronary interventions. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med
Chem. 6:125–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Kleinbongard P, Konorza T, Böse D, et al:
Lessons from human coronary aspirate. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
52:890–896. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Werner GS, Lang K, Kuehnert H and Figulla
HR: Intracoronary verapamil for reversal of no-reflow during
coronary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Catheter
Cardiovasc Interv. 57:444–451. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
McIvor ME, Undemir C, Lawson J and
Reddinger J: Clinical effects and utility of intracoronary
diltiazem. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 35:287–293. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Sütsch G, Oechslin E, Mayer I and Hess OM:
Effect of diltiazem on coronary flow reserve in patients with
microvascular angina. Int J Cardiol. 52:135–143. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Zheng ZF, Pu XQ, Yang TL, et al: Effects
of intracoronary diltiazem on no-reflow phenomenon after emergent
percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute
myocardial infarction. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
31:917–920. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
21.
|
Brown C: Blood collection from the tail of
a rat. Lab Anim (NY). 35:24–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kudo M, Aoyama A, Ichimori S and Fukunaga
N: An animal model of cerebral infarction. Homologous blood clot
emboli in rats. Stroke. 13:505–508. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Grossman W: Pressure measurement.
Grossman’s Cardiac Catheterition, Angiography, and Intervention.
Baim DS: 7th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;
Philadelphia: pp. 139–141. 2006
|
|
24.
|
Genda S, Miura T, Miki T, Ichikawa Y and
Shimamoto K: K(ATP) channel opening is an endogenous mechanism of
protection against the no-reflow phenomenon but its function is
compromised by hypercholesterolemia. J Am Coll Cardiol.
40:1339–1346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Eitzman DT, Bodary PF, Shen Y, et al:
Fabry disease in mice is associated with age-dependent
susceptibility to vascular thrombosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:298–302. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Fujita M, Fujioka Y and Ommura Y:
Histopathological diagnosis of early stages of myocardial
infarction - applications of the improved hematoxylin basic fuchsin
picric acid (HBFP) staining method to human autopsy hearts.
Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 60:313–320. 1985.(In Japanese).
|
|
27.
|
Goldner J: A modification of the Masson
trichrome technique for routine laboratory purposes. Am J Pathol.
14:237–243. 1938.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Blann AD: Plasma von Willebrand factor,
thrombosis, and the endothelium: the first 30 years. Thromb
Haemost. 95:49–55. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
With Notø AT, Bøgeberg Mathiesen E, Amiral
J, Vissac AM and Hansen JB: Endothelial dysfunction and systemic
inflammation in persons with echolucent carotid plaques. Thromb
Haemost. 96:53–59. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Stewart DJ, Kubac G, Costello KB and
Cernacek P: Increased plasma endothelin-1 in the early hours of
acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 18:38–43. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Tønnessen T, Giaid A, Saleh D, Naess PA,
Yanagisawa M and Christensen G: Increased in vivo expression and
production of endothelin-1 by porcine cardiomyocytes subjected to
ischemia. Circ Res. 76:767–772. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Ruggeri ZM: Von Willebrand factor,
platelets and endothelial cell interactions. J Thromb Haemost.
1:1335–1342. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Bonvini RF, Hendiri T and Camenzind E:
Inflammatory response post-myocardial infarction and reperfusion: a
new therapeutic target? Eur Heart J Suppl. 7(Suppl I): I27–I36.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34.
|
Skyschally A, Schulz R, Haude M, Erbel R
and Heusch G: Coronary microembolization: perfusion-contraction
mismatch secondary to myocardial inflammation. Herz. 29:777–781.
2004.(In German).
|
|
35.
|
Dörge H, Neumann T, Behrends M, et al:
Perfusion-contraction mismatch with coronary microvascular
obstruction: role of inflammation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
279:H2587–H2592. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Dörge H, Schulz R, Belosjorow S, et al:
Coronary microembolization: the role of TNF-alpha in contractile
dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 34:51–62. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Triggle DJ and Swamy VC: Calcium
antagonists. Some chemical-pharmacologic aspects. Circ Res.
52:I17–I28. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Kleinbongard P, Heusch G and Schulz R:
TNFalpha in atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and
heart failure. Pharmacol Ther. 127:295–314. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Fleckenstein A: History of calcium
antagonists. Circ Res. 52:I3–I16. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Beltrame JF, Turner SP, Leslie SL, Solomon
P, Freedman SB and Horowitz JD: The angiographic and clinical
benefits of mibefradil in the coronary slow flow phenomenon. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 44:57–62. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Hamm CW and Opie LH: Protection of
infarcting myocardium by slow channel inhibitors. Comparative
effects of verapamil, nifedipine, and diltiazem in the
coronary-ligated, isolated working rat heart. Circ Res.
52:I129–I138. 1983.
|
|
42.
|
Nayler WG, Ferrari R and Williams A:
Protective effect of pretreatment with verapamil, nifedipine and
propranolol on mitochondrial function in the ischemic and
reperfused myocardium. Am J Cardiol. 46:242–248. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Bourdillon PD and Poole-Wilson PA: The
effects of verapamil, quiescence, and cardioplegia on calcium
exchange and mechanical function in ischemic rabbit myocardium.
Circ Res. 50:360–368. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Przyklenk K and Kloner RA: Effect of
verapamil on postischemic ‘stunned’ myocardium: importance of the
timing of treatment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 11:614–623. 1988.
|
|
45.
|
Bush LR, Buja LM, Tilton G, et al: Effects
of propranolol and diltiazem alone and in combination on the
recovery of left ventricular segmental function after temporary
coronary occlusion and long-term reperfusion in conscious dogs.
Circulation. 72:413–430. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46.
|
Higgins AJ and Blackburn KJ: Prevention of
reperfusion damage in working rat hearts by calcium antagonists and
calmodulin antagonists. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 16:427–438. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47.
|
Galiuto L: Optimal therapeutic strategies
in the setting of post-infarct no reflow: the need for a
pathogenetic classification. Heart. 90:123–125. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48.
|
Kleinbongard P, Baars T and Heusch G:
Calcium antagonists in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion - update
2012. Wien Med Wochenschr. 162:302–310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49.
|
Huang Y, Hunyor S, Jiang L, et al:
Remodeling of the chronic severely failing ischemic sheep heart
after coronary microembolization: functional, energetic,
structural, and cellular responses. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 286:2141–2150. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50.
|
Gill RM, Jones BD, Corbly AK, et al:
Exhaustion of the Frank-Starling mechanism in conscious dogs with
heart failure induced by chronic coronary microembolization. Life
Sciences. 79:536–544. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|