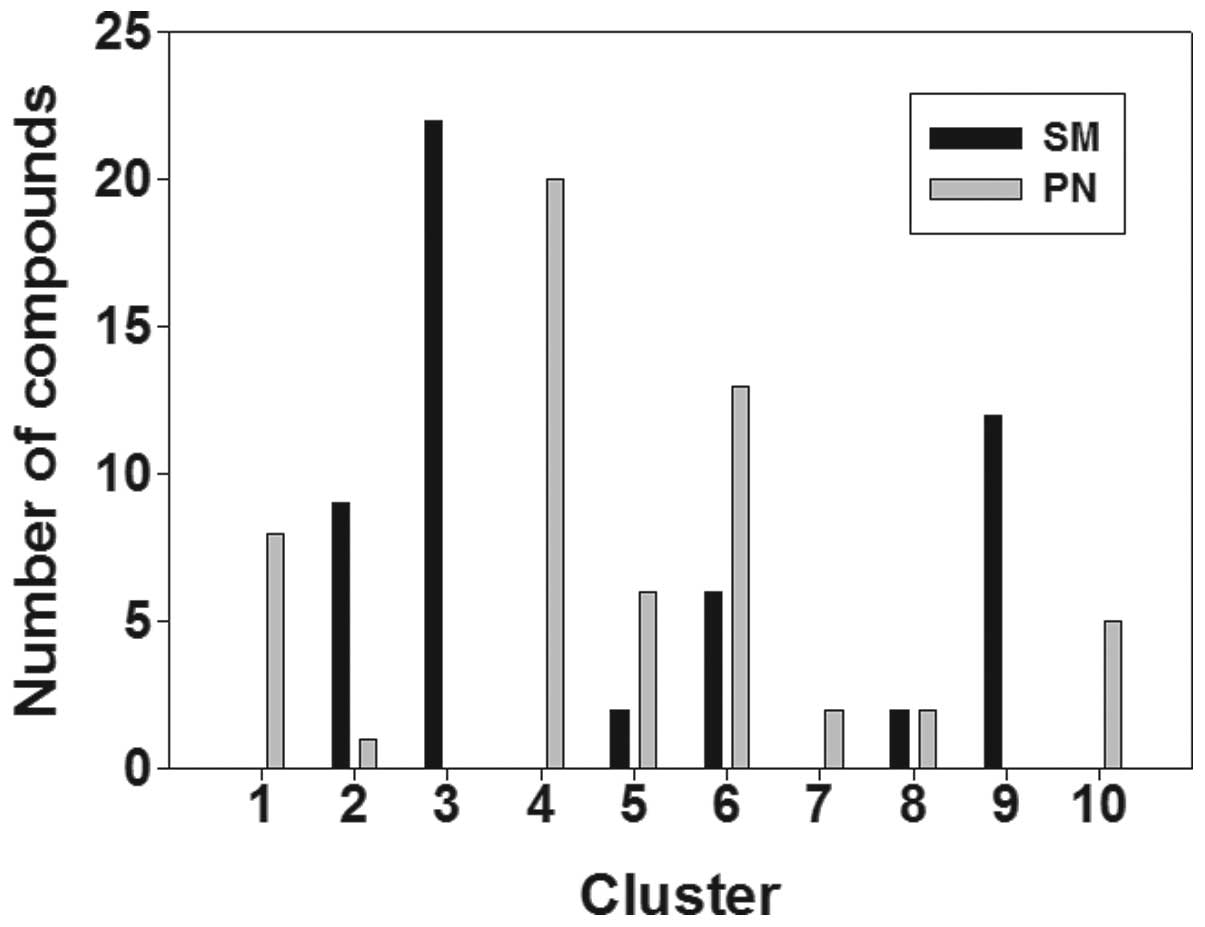
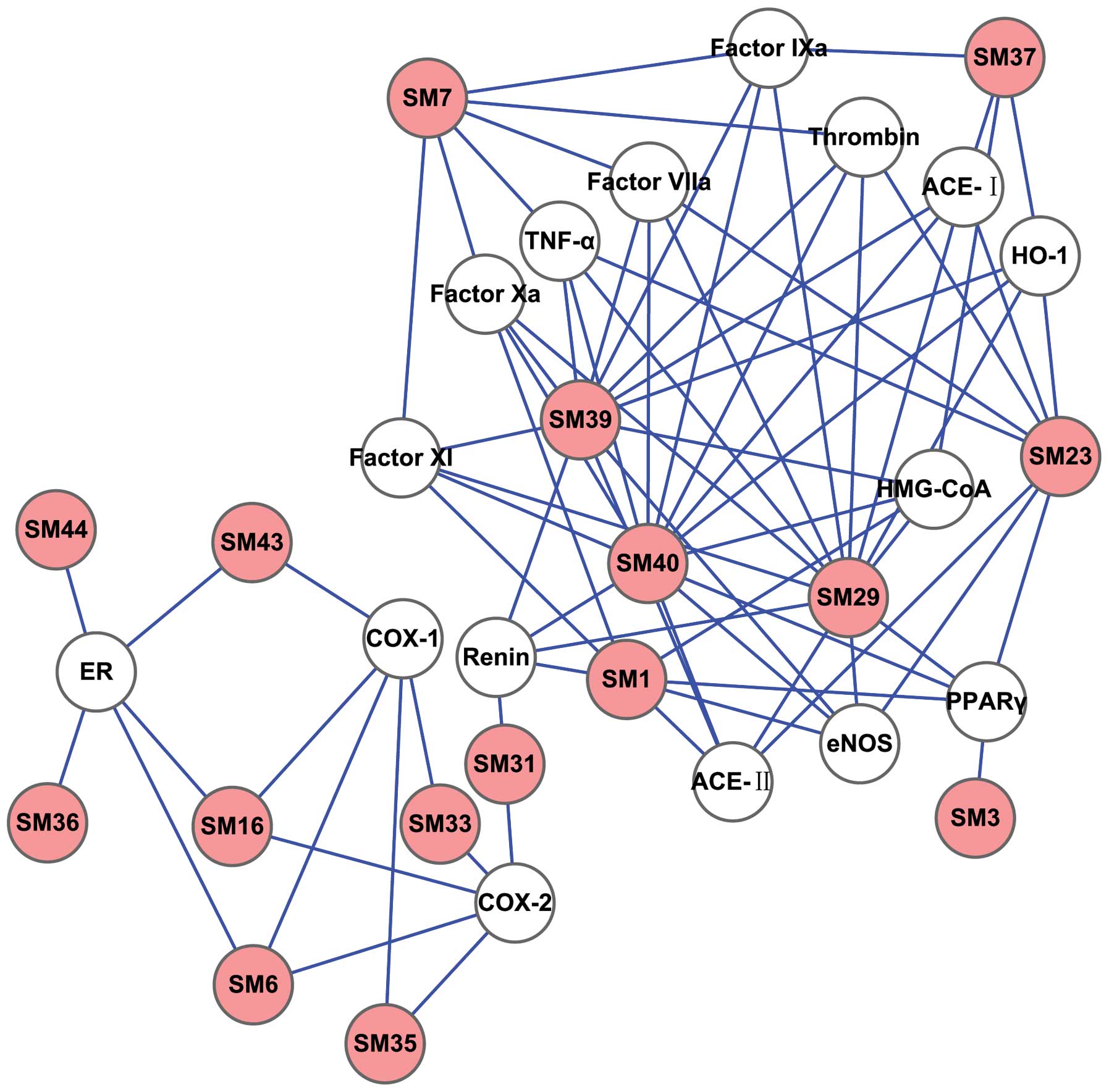
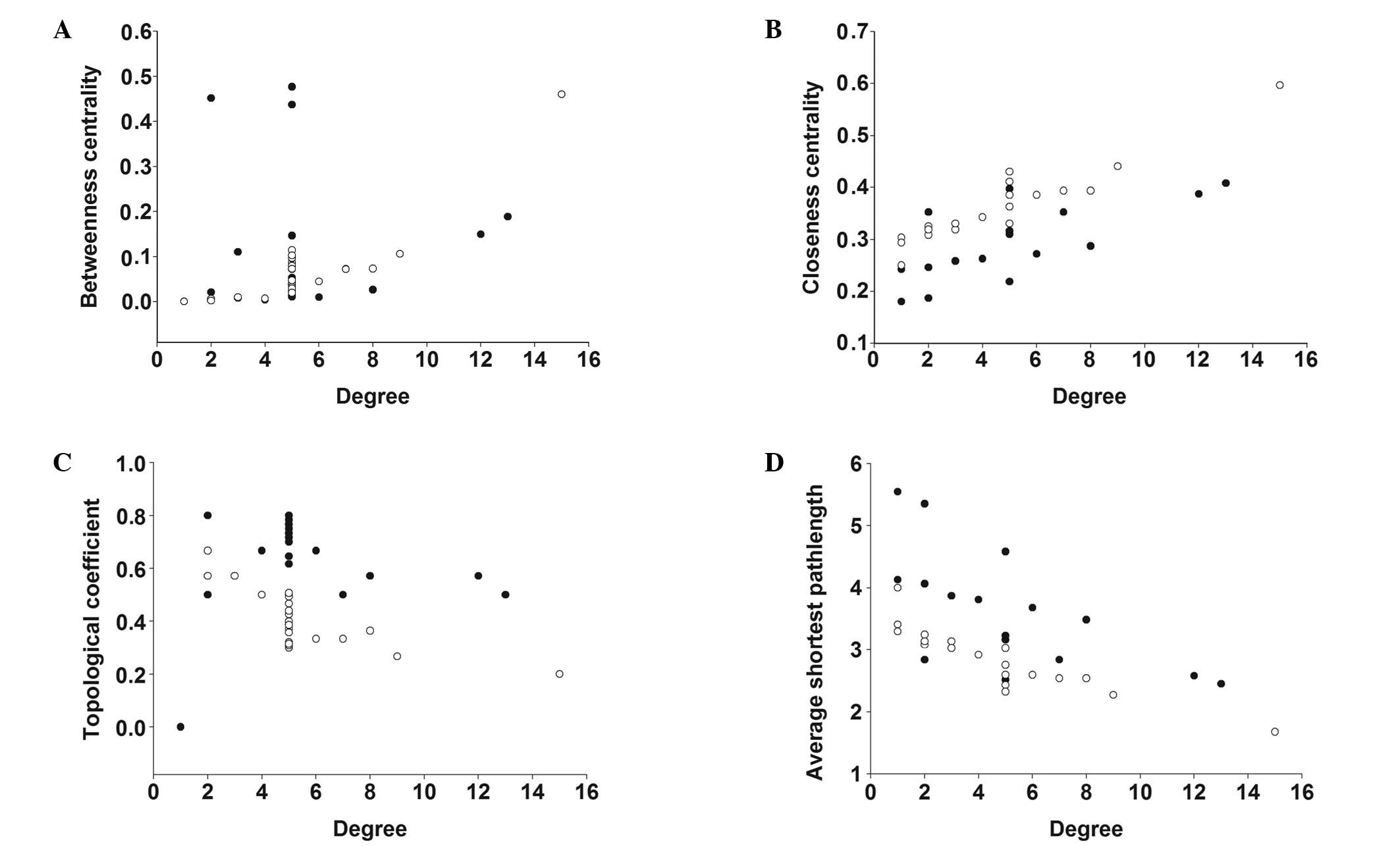
|
1.
|
Alwan A, Armstrong T, Bettcher D, Branca
F, Chisholm D, Ezzati M, Garfield R, MacLean D, Mathers C, Mendis
S, Poznyak V, Riley L, Tang KC and Wild C: Global status report on
noncommunicable diseases 2010. WHO Library
Cataloguingin-Publication Data; Geneva: pp. 100–143. 2011
|
|
2.
|
Li SB: Adverse drug reaction and
prevention of cardiovascular drugs. Hainan Med J. 22(3): 14–19.
2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
3.
|
Toyoshima H, Takahashi K and Akera T: The
impact of side effects on hypertension management: a Japanese
survey. Clin Ther. 19:1458–1469. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Wang S, Hu Y, Tan W, Wu X, Chen R, Cao J,
Chen M and Wang Y: Compatibility art of traditional Chinese
medicine: from the perspective of herb pairs. J Ethnopharmacol.
143:412–423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Frishman WH, Sinatra ST and Moizuddin M:
The use of herbs for treating cardiovascular disease. Semin Integr
Med. 2:23–35. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6.
|
Liang CZ: Focus on the theory of
precaution of disease in Tradition Chinese Medicine from the
function of compound Danshen dripping pill to the heart and blood
vessel’s illness. Chin Arch Trad Chin Med. 26:643–644. 2008.(In
Chinese).
|
|
7.
|
Zheng Q, Peng CC, Shen ML and Yang M:
Study on compatibility of Radix et Rhizoma Salviae
miltiorrhizae and Radix et Rhizoma notoginseng. Chin J Exp Trad
Med Formulae. 15(2): 83–86. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
8.
|
Cheng TO: Cardiovascular effects of
Danshen. Int J Cardiol. 121:9–22. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Zheng CS, Xu XJ, Liu XX and Ye HZ:
Computational pharmacology of Jingzhi Tougu Xiaotong granule in
preventing and treating osteoarthritis. Acta Phys Chim Sin.
26:775–783. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
10.
|
Ma S, Feng C, Zhang X, Dai G, Li C, Cheng
X, Liu P, Ju W and Yu H: The multi-target capabilities of the
compounds in a TCM used to treat sepsis and their in silico
pharmacology. Complement Ther Med. 21:35–41. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Qiao X, Hou T, Zhang W, Guo S and Xu X: A
3D structure database of components from Chinese traditional
medicinal herbs. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 42:481–489. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Zhou JX, Xie GR and Yang XD: Handbook of
the Constituents in Chinese Herb Original Plants. 1st edition.
Chemical Industry Press; Beijing: pp. 1165–1211. 2004
|
|
13.
|
Hassan M, Bielawski JP, Hempel JC and
Waldman M: Optimization and visualization of molecular diversity
and combinatorial libraries. Mol Divers. 2:64–74. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zheng CS, Xu XJ, Ye HZ, Wu GW, Li XH,
Huang SP and Liu XX: Computational approaches for exploring the
potential synergy and polypharmacology of Duhuo Jisheng Decoction
in the therapy of osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 7:1812–1818.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Dobson CM: Chemical space and biology.
Nature. 432:824–828. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Wu DH and Xu XJ: Computational simulation
of benefiting Qi and activating blood mechanism of Traditional
Chinese Medicine. Acta Phys Chim Sin. 25:446–450. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
17.
|
Gu JY, Yuan G, Zhu YH and Xu XJ:
Computational pharmacological studies on cardiovascular disease by
Qishen Yiqi Diwan. Sci China B. 52:1871–1878. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Zheng CS, Ye HZ, Cai LL, Chen JS, Wei LS
and Liu XX: Discussion on multi-component and multi-target pattern
of Liuwei Dihuang pill in the treatment of osteoarthritis on the
basis of computer simulation. J Trad Chin Orthop Traumatol.
25:11–13. 182013.(In Chinese).
|
|
19.
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: new features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW and
Feeney PJ: Experimental and computational approaches to estimate
solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development
settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 46:3–26. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Cooney MT, Dudina A, D’Agostino R and
Graham IM: Cardiovascular risk-estimation systems in primary
prevention: do they differ? Do they make a difference? Can we see
the future? Circulation. 122:300–310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Baur JA and Sinclair DA: Therapeutic
potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 5:493–506. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Hopkins AL: Network pharmacology: the next
paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol. 4:682–690. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Chu Y, Zhang L, Wang XY, Guo JH, Guo ZX
and Ma XH: The effect of Compound Danshen Dripping Pills, a Chinese
herb medicine, on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of
warfarin in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:1457–1461. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Zhu M, Gao L, Li X, Liu Z, Xu C, Yan Y,
Walker E, Jiang W, Su B, Chen X and Lin H: The analysis of the
drug-targets based on the topological properties in the human
protein-protein interaction network. J Drug Target. 17:524–532.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Perez-Vizcaino F and Duarte J: Flavonols
and cardiovascular disease. Mol Aspects Med. 31:478–494. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Ho JH and Hong CY: Salvianolic acid: small
compounds with multiple mechanisms for cardiovascular protection. J
Biomed Sci. 18:302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ji XF and Shi DH: Advances in studies of
baicalin on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular pharmacology. Strait
Pharm J. 18:10–12. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
29.
|
Jiang LP, Nie BM, Lu HM, Gan LJ, Chen HZ
and Lu Y: Inhibitory effect of panaxynol on the proliferation of
rat aortic smooth muscle cell and its mechanisms. Chin Pharmacol
Bull. 21:1313–1319. 2005.(In Chinese).
|