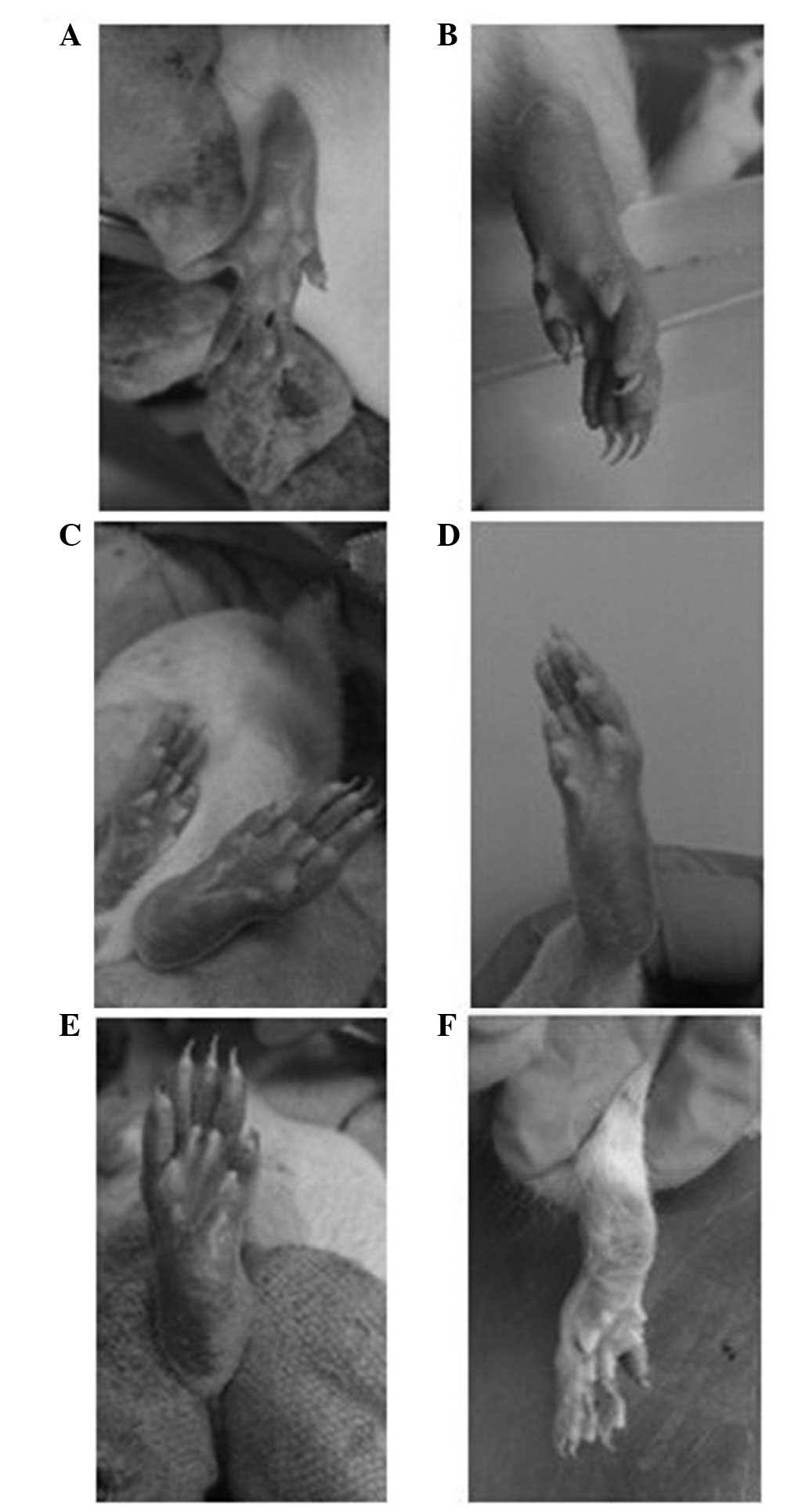
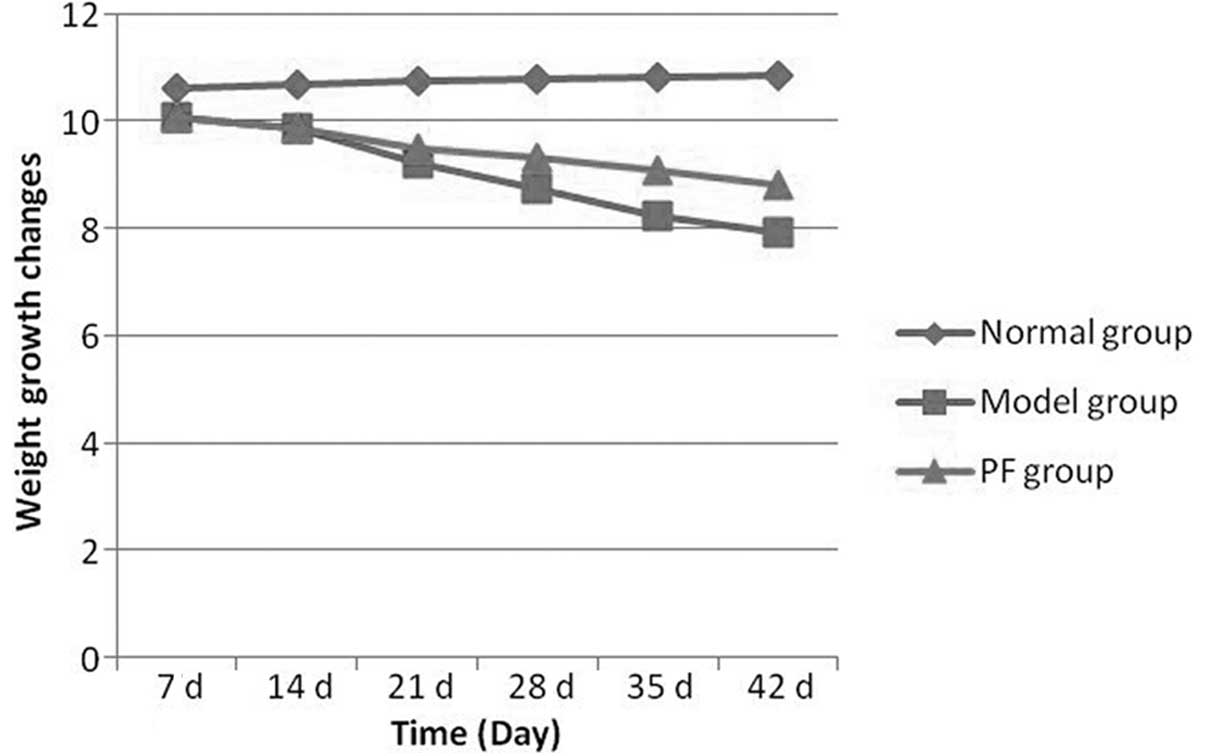
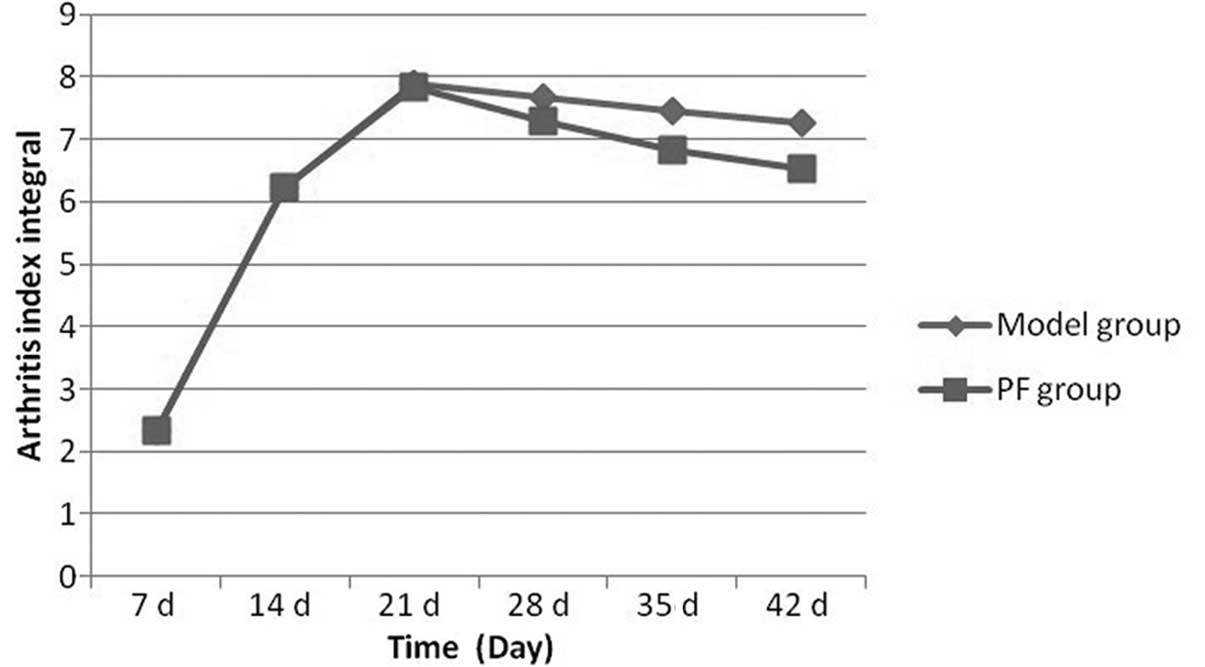
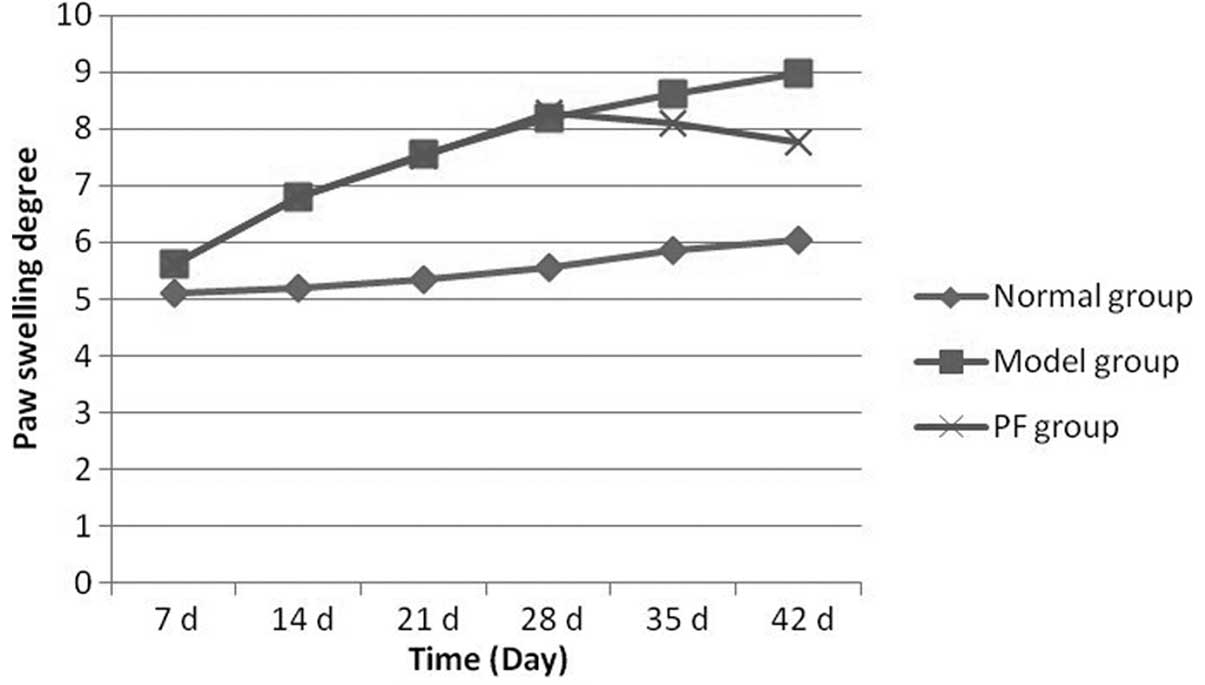
|
1
|
Li RZ: The observation of pathological
manifestations (50 cases) and immunohistochemical (5 cases) of
rheumatoid arthritis. Zhonghua Gu Ke Za Zhi. 1:35–36. 1989.(In
Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Liang Q, Tang T and Zhang H: Clinical
investigation of effects of bizhongxiao decoction (BZX) on
rheumatoid arthritis on active phase. Hunan Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
25:449–452. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Liang QH, Zhang HX and Tang T: The effects
of bizhongxiao decoction (BZX) on T-lymphocyte subsets in the
peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hunan Yi Ke
Da Xue Xue Bao. 26:534–536. 2001.(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Liang QH, Luo X, Chen CH, Wang AY, He JH,
Tan Y and Bao TC: A clinical observation on the effects of
Bizhongxiao Decoction on the interleulkin-1β level in the serum of
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hunan Zhong Yi Xue Yuan Xue
Bao. 6:43–45. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Tang TF, Liang QH, Luo X, Chen J and Li
XL: Effects of bizhongxiao decoction on serum matrix
metalloproteinase 3 and its tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase
1 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis at active phase. Zhongguo
Lin Chuang Kang. 9:114–116. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Liang QH, Chen J, He JH, Li XL, Zhang HX,
Wang AY and Tan Y: Correlation between plasma contents of tumor
necrosis factor-α and expressions of vascular endothelium growth
factor in collagen II-induced arthritis rats. Zhonghua Feng Shi
Bing Xue Za Zhi. 7:655–658. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Wang AY, Liang QH, Tang FQ, Li CY, Chen J,
Bao TC, Luo X and Yang B: Effect of bizhongxiao decoction on the
synovitis gene expression profiles of rats with collagen induced
arthritis: a study on the cDNA microarrays. Zhongguo Lin Chuang
Kang Fu. 9(11): 42–43. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Yang B, Liang QH, Cai Y, Xie W, He JH and
Liu XC: Effect of bizhongxiao decoction on protein in synovitis of
rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Zhongguo Lin Chuang Kang Fu.
10(15): 74–78. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Li WY, Huang SJ and Wang R: Advances in
research on pharmacological actions and quality control of Paeoniae
Radix Alba. Pharm Care Res. 12:118–122. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
State Pharmacopoeia Committee of the PRC.
Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China 2010. 1. China
Medical Science and Technology Press; Beijing: pp. 96–97. 2010, (In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Gao XR and Tian GY: Active principles of
Paeonia lactiflora Pall. Chinese Journal of New Drugs.
6:416–418. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Hu N, Xu HY, Chen ZW and Xing GH: The
pharmacology research progress of Paeoniflorin. Qiqihar Yi Xue Yuan
Yuan Bao. 28:1093–1095. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Wang XY, Wei W, Tang LQ, Wu Hong, Yang YQ
and Chen Y: Effect of paeoniflorin on peritoneal macrophage from
rats of adjuvant-induced arthritis. Anhui Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
42:189–192. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Zhang LL, Wei W, Wang NP, Wang QT, Chen
JY, Chen Y, Wu H and Hu XY: Paeoniflorin suppresses inflammatory
mediator production and regulates G protein-coupled signaling in
fibroblast-like synoviocytes of collagen induced arthritic rats.
Inflamm Res. 57:388–395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei W, Wu XM and Li YJ: Experimental
Methodology of Pharmacology. People’s Medical Publishing House;
Beijing: pp. 1698–1699. 2010, (In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Hang XF, Ma BL, Zhang JY, Bai J, Wang L
and Hao AM: Establishment of autoimmune experimental animal model
for rheumatoid arthritis. Shanghai Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 21:330–333.
2001.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Nguyen DT, Guillarme D, Heinisch S,
Barrioulet MP, Rocca JL, Rudaz S and Veuthey JL: High throughput
liquid chromatography with sub-2 microm particles at high pressure
and high temperature. J Chromatogr A. 1167:76–84. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nováková L, Matysová L and Solich P:
Advantages of application of UPLC in pharmaceutical analysis.
Talanta. 68:908–918. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wren SA and Tchelitcheff P: Use of
ultra-performance liquid chromatography in pharmaceutical
development. J Chromatogr A. 1119:140–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guillarme D, Nguyen DT, Rudaz S and
Veuthey JL: Method transfer for fast liquid chromatography in
pharmaceutical analysis: application to short columns packed with
small particle. Part II: gradient experiments. Eur J Pharm
Biopharm. 68:430–440. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Guan J, Lai CM and Li SP: A rapid method
for the simultaneous determination of 11 saponins in Panax
notoginseng using ultra performance liquid chromatography. J
Pharm Biomed Anal. 44:996–1000. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han LF, Wu B, Pan GX, Wang YF, Song XB and
Gao XM: UPLC-PDA analysis for simultaneous quantification of four
active compounds in crude and processed rhizome of Polygonum
multiflorum Thunb. Chromatographia. 70:657–659. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu T, Wang C, Wang X, Xiao HQ, Ma Q and
Zhang Q: Comparison of UPLC and HPLC for analysis of 12 phthalates.
Chromatographia. 68:803–806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lu XY, Chu C and Yan JZ: Simultaneous
determination of paeoniflorin and albiflorin in Radix Paeoniae Alba
by UPLC. Zhong Nan Yao Xue. 10:98–100. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Zhang C and Yang ZS: TCM syndrome
differentiation and experience in rheumatoid arthritis. Zhongguo
Lin Chuang Yi Sheng Za Zhi. 35:66–67. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Li JL, Sun L, Xi ZX, Li X and Sun LN:
Research development of traditional Chinese medicine monomer
composition on the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Zhong Yao
Cai. 35:1355–1360. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Huang Y: Advances in methods of quality
control in Chinese materia medica formula. Yao Xue Shi Jian Za Zhi.
26:11–13. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Sun R, Lv LL, Guo SD and Liu GQ: Study on
effects of paeoniflorin on blood brain barrier and pathological
changes during reperfusion of CMAO model in rats. Journal of Harbin
University of Commerce (Natural Sciences Edition). 4:405–410.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
29
|
Zheng SC, Li XY, Ou YB and Sun R: Research
development on pharmacological of paeoniflorin. Zhongguo Yao Wu
Jing Jie. 2:100–103. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Ma W, Ma WD, Miao ZH and Tian JY:
Protective effect of paeoniflorin on the Aβ1–40-induced
neurotoxicity in cultured PC12 cells. Journal of Ningxia Medical
University. 2:132–135. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Guo P, Wang JF and Wang SQ: Effects of
paeoniflorin on Epo and G-CSF gene expression in bone marrow of
irradiated blood deficiency mice. Journal of Shandong University of
TCM. 3:236–239. 2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Sun R, Zuo YF, Li XY and Ou YB: Progress
of paeoniflorin against neuronal injury pharmacological research.
Shangdong Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao. 36:454–456. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Hu ZY, Xu L, Yan R, Huang Y, Liu G, Zhou
WX and Zhang YX: Advance in studies on effect of paeoniflorin on
nervous system. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 38:297–301. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
34
|
Liu ZQ, Jiang ZH, Chan K, Zhou H, Wong YF,
Bian ZX, Xu HX and Liu L: Pharmacokinetic interaction of
paeoniflorin and sinomenine: pharmacokinetic parameters and tissue
distribution characteristics in rats and protein binding ability in
vitro. J Pharmacol Sci. 99:381–391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen LC, Chou MH, Lin MF and Yang LL:
Pharmacokinetics of paeoniflorin after oral administration of
Shao-yao Gan-chao Tang in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol. 88:250–255. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen X, Gu Q, Qiu F and Zhong D: Rapid
determination of metformin in human plasma by liquid
chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. J Chromatogr B
Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 802:377–381. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Strand V and Kavanaugh AF: The role of
interleukin-1 in bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 43(Suppl 3): iii10–iii16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zwerina J, Hayer S, Tohidast-Akrad M,
Bergmeister H, Redlich K, Feige U, Dunstan C, Kollias G, Steiner G,
Smolen J and Schett G: Single and combined inhibition of tumor
necrosis factor, interleukin-1, and RANKL pathways in tumor
necrosis factor-induced arthritis: effects on synovial
inflammation, bone erosion, and cartilage destruction. Arthritis
Rheum. 50:277–290. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Brennan FM and McInnes IB: Evidence that
cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest.
118:3537–3545. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|