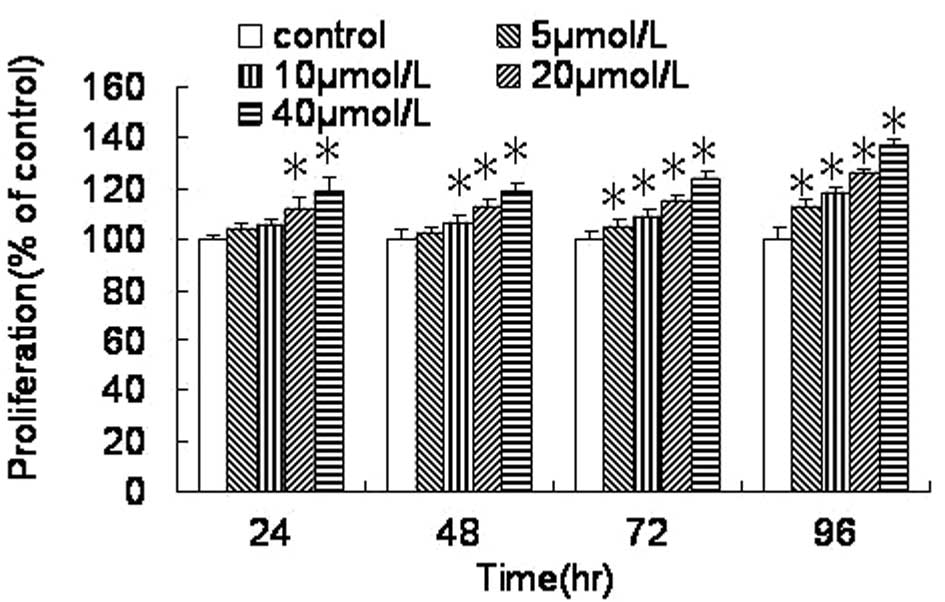
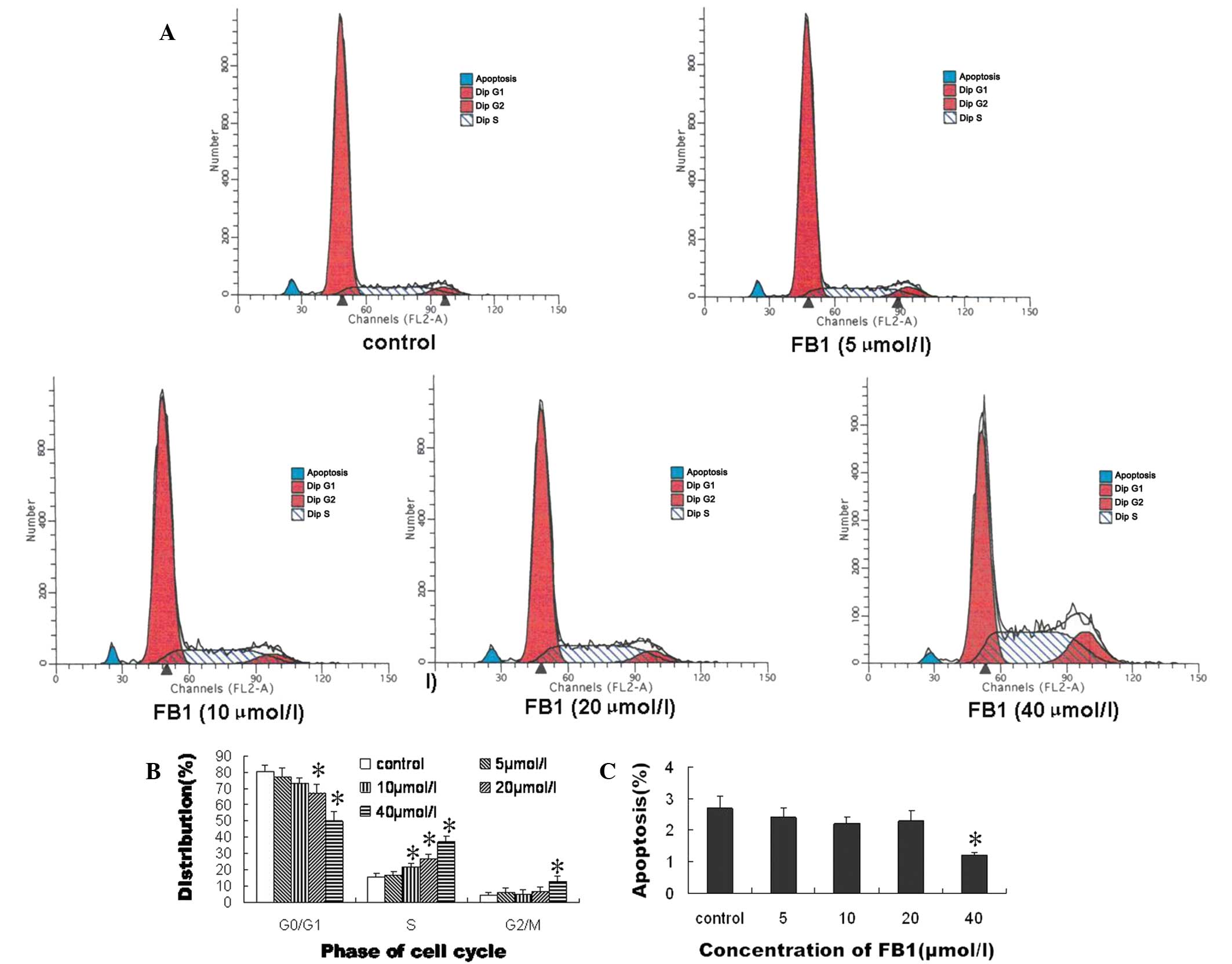
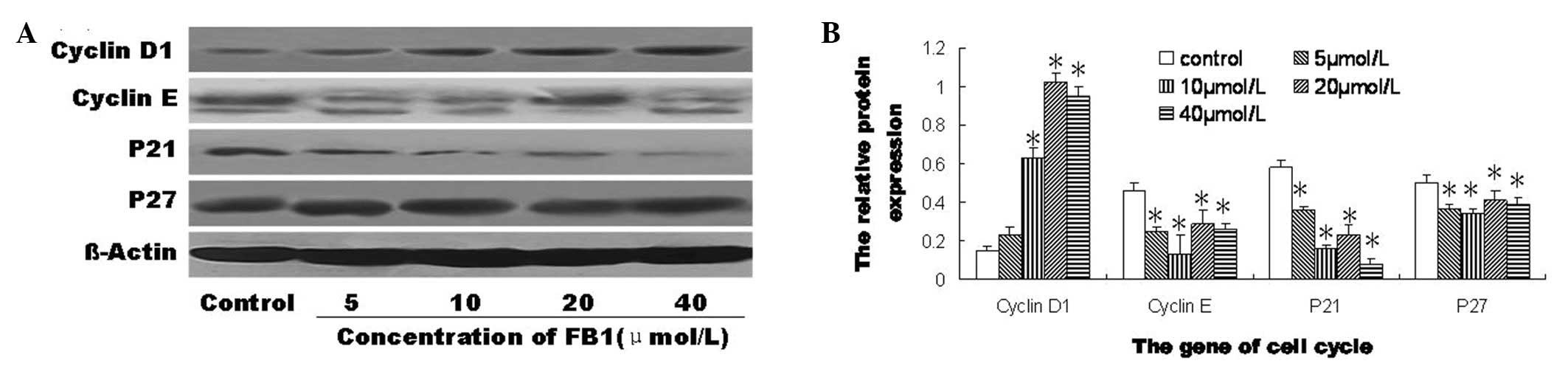
|
1
|
Theumer MG, Clop EM, Rubinstein HR and
Perillo MA: The lipid-mediated hypothesis of fumonisin B1
toxicodynamics tested in model membranes. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 64:22–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stockmann-Juvala H and Savolainen K: A
review of the toxic effects and mechanisms of action of fumonisin
B1. Hum Exp Toxicol. 27:799–809. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cano-Sancho G, Ramos AJ, Marin S and
Sanchis V: Occurrence of fumonisins in Catalonia (Spain) and an
exposure assessment of specific population groups. Food Addit
Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 29:799–808. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van der Westhuizen L, Shephard GS, Rheeder
JP and Burger HM: Individual fumonisin exposure and sphingoid base
levels in rural populations consuming maize in South Africa. Food
Chem Toxicol. 48:1698–1703. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alizadeh AM, Rohandel G, Roudbarmohammadi
S, et al: Fumonisin B1 contamination of cereals and risk of
esophageal cancer in a high risk area in northeastern Iran. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:2625–2628. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun G, Wang S, Hu X, et al: Fumonisin B1
contamination of home-grown corn in high-risk areas for esophageal
and liver cancer in China. Food Addit Contam. 24:181–185. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schwerdt G, Königs M, Holzinger H, Humpf
HU and Gekle M: Effects of the mycotoxin fumonisin B(1) on cell
death in human kidney cells and human lung fibroblasts in primary
culture. J Appl Toxicol. 29:174–182. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Galvano F, Russo A, Cardile V, Galvano G,
Vanella A and Renis M: DNA damage in human fibroblasts exposed to
fumonisin B(1). Food Chem Toxicol. 40:25–31. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Seefelder W, Humpf HU, Schwerdt G,
Freudinger R and Gekle M: Induction of apoptosis in cultured human
proximal tubule cells by fumonisins and fumonisin metabolites.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 192:146–153. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kouadio JH, Mobio TA, Baudrimont I, Moukha
S, Dano SD and Creppy EE: Comparative study of cytotoxicity and
oxidative stress induced by deoxynivalenol, zearalenone or
fumonisin B1 in human intestinal cell line Caco-2. Toxicology.
213:56–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bondy GS, Barker MG, Lombaert GA, et al: A
comparison of clinical, histopathological and cell-cycle markers in
rats receiving the fungal toxins fumonisin B1 or fumonisin B2 by
intraperitoneal injection. Food Chem Toxicol. 38:873–886. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang SK, Liu S, Yang LG, et al: Effect of
fumonisin B1 on the cell cycle of normal human liver cells. Mol Med
Rep. 7:1970–1976. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Czerednik A, Busscher M, Bielen BA,
Wolters-Arts M, de Maagd RA and Angenent GC: Regulation of tomato
fruit pericarp development by an interplay between CDKB and CDKA1
cell cycle genes. J Exp Bot. 63:2605–2617. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto S, Kohsaka S and Nakajima K: Role
of cell cycle-associated proteins in microglial proliferation in
the axotomized rat facial nucleus. Glia. 60:570–581. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moreira PR, Guimarães MM, Guimarães AL, et
al: Methylation of P16, P21, P27, RB1 and P53 genes in odontogenic
keratocysts. J Oral Pathol Med. 38:99–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
de Andrade BA, León JE, Carlos R,
Delgado-Azañero W, Mosqueda-Taylor A and de Almeida OP:
Immunohistochemical expression of p16, p21, p27 and cyclin D1 in
oral nevi and melanoma. Head Neck Pathol. 6:297–304.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Myburg RB, Dutton MF and Chuturgoon AA:
Cytotoxicity of fumonisin B1, diethylnitrosamine, and catechol on
the SNO esophageal cancer cell line. Environ Health Perspect.
110:813–815. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang H, Wei H, Ma J and Luo X: The
fumonisin B1 content in corn from North China, a high-risk area of
esophageal cancer. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 19:139–141.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Severino L, Russo R, Luongo D, De Luna R,
Ciarcia R and Rossi M: Immune effects of four Fusarium-toxins (FB1,
ZEA, NIV, DON) on the proliferation of Jurkat cells and porcine
lymphocytes: in vitro study. Vet Res Commun. 32(Suppl 1):
S311–S313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Taranu I, Marina DE, Burlacu R, Pinton P,
Damian V and Oswald IP: Comparative aspects of in vitro
proliferation of human and porcine lymphocytes exposed to
mycotoxins. Arch Anim Nutr. 64:383–393. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gelderblom WC, Galendo D, Abel S,
Swanevelder S, Marasas WF and Wild CP: Cancer initiation by
fumonisin B(1) in rat liver - role of cell proliferation. Cancer
Lett. 169:127–137. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McKean C, Tang L, Tang M, et al:
Comparative acute and combinative toxicity of aflatoxin B1 and
fumonisin B1 in animals and human cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
44:868–876. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marin DE, Gouze ME, Taranu I and Oswald
IP: Fumonisin B1 alters cell cycle progression and interleukin-2
synthesis in swine peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 51:1406–1412. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fornelli F, Minervini F and Mulè G:
Cytotoxicity induced by nivalenol, deoxynivalenol, and fumonisin B1
in the SF-9 insect cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
40:166–171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seegers JC, Joubert AM, Panzer A, et al:
Fumonisin B1 influenced the effects of arachidonic acid,
prostaglandins E2 and A2 on cell cycle progression, apoptosis
induction, tyrosine- and CDC2-kinase activity in oesophageal cancer
cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 62:75–84. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mobio TA, Anane R, Baudrimont I, et al:
Epigenetic properties of fumonisin B(1): cell cycle arrest and DNA
base modification in C6 glioma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
164:91–96. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ramljak D, Calvert RJ, Wiesenfeld PW, et
al: A potential mechanism for fumonisin B(1)-mediated
hepatocarcinogenesis: cyclin D1 stabilization associated with
activation of Akt and inhibition of GSK-3beta activity.
Carcinogenesis. 21:1537–1546. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Canavese M, Santo L and Raje N: Cyclin
dependent kinases in cancer: Potential for therapeutic
intervention. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:451–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Douville JM, Cheung DY, Herbert KL,
Moffatt T and Wigle JT: Mechanisms of MEOX1 and MEOX2 regulation of
the cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p16 in vascular
endothelial cells. PLoS One. 6:e290992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Canepa ET, Scassa ME, Ceruti JM, et al:
INK4 proteins, a family of mammalian CDK inhibitors with novel
biological functions. IUBMB Life. 59:419–426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ito Y, Yoshida H, Matsuzuka F, et al:
Expression of the components of the Cip/Kip family in malignant
lymphoma of the thyroid. Pathobiology. 71:164–170. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sugimoto M, Martin N, Wilks DP, et al:
Activation of cyclin D1-kinase in murine fibroblasts lacking both
p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1). Oncogene. 21:8067–8074. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Verlinden L, Verstuyf A, Convents R,
Marcelis S, Van Camp M and Bouillon R: Action of
1,25(OH)2D3 on the cell cycle genes, cyclin D1, p21 and
p27 in MCF-7 cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 142:57–65. 1998.
|
|
34
|
Hirai T, Kuwahara M, Yoshida K, Osaki A
and Toge T: The prognostic significance of p53, p21 (Waf1/Cip1),
and cyclin D1 protein expression in esophageal cancer patients.
Anticancer Res. 19:4587–4591. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Faria MH, Patrocinio RM, Moraes Filho MO
and Rabenhorst SH: Immunoexpression of tumor suppressor genes p53,
p21 WAF1/CIP1 and p27 KIP1 in human astrocystic tumors. Arq
Neuropsiquiatr. 65:1114–1122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang XP, Rong TH, Lin P, et al: Cyclin D1
overexpression in esophageal cancer from southern China and its
clinical significance. Cancer Lett. 231:94–101. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Anayama T, Furihata M, Takeuchi T, et al:
Insufficient effect of p27(KIP1) to inhibit cyclin D1 in human
esophageal cancer in vitro. Int J Oncol. 18:151–155.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|