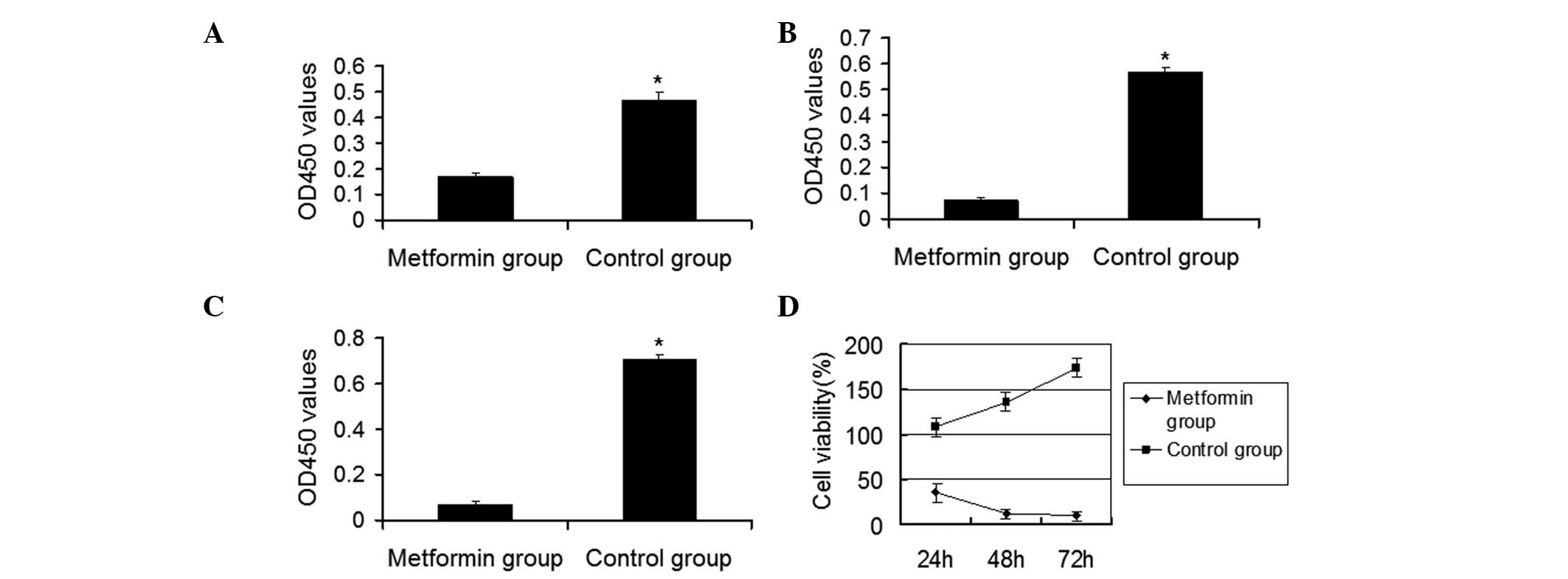
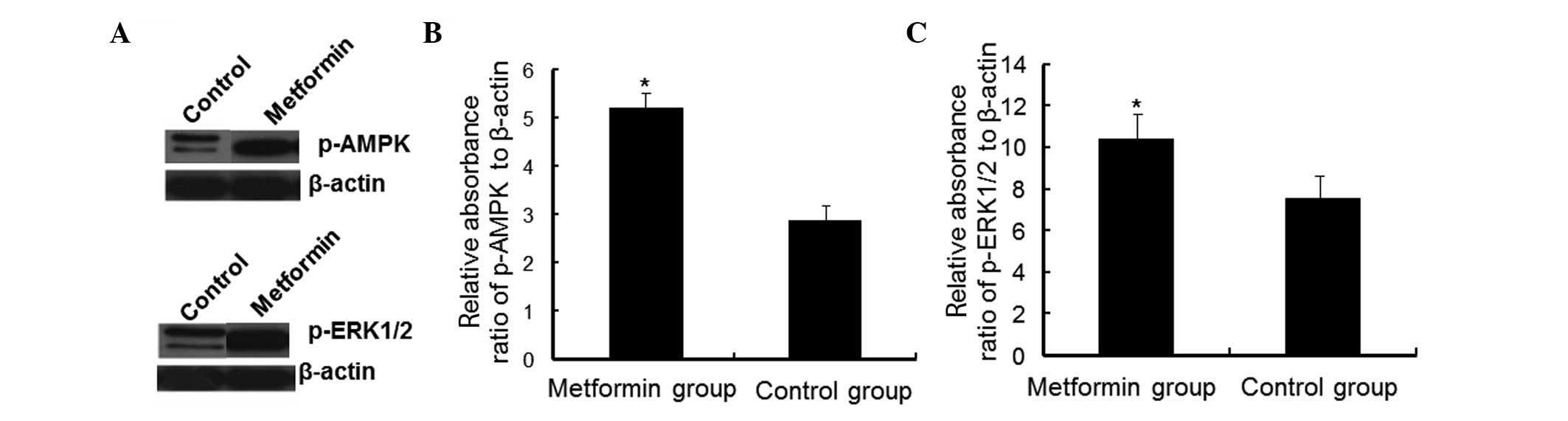
|
1
|
Vestergaard C, Deleuran M, Gesser B and
Grønhøj Larsen C: Expression of the T-helper 2-specific chemokine
receptor CCR4 on CCR10-positive lymphocytes in atopic dermatitis
skin but not in psoriasis skin. Br J Dermato1. 149:457–463. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bowcock AM and Krueger JG: Getting under
the skin: the immunogenetics of psoriasis. Nat Rev Immunol.
5:699–711. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bhalerao J and Bowcock AM: The genetics of
psoriasis: a complex disorder of the skin and immune system. Hum
Mol Genet. 7:1537–1545. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bowcock AM and Cookson WO: The genetics of
psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and atopic dermatitis. Hum Mol
Genet. 13:R43–R55. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Abdou AG and Hanout HM: Evaluation of
survivin and NF-kappaB in psoriasis, an immunohistochemical study.
J Cutan Pathol. 35:445–451. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rahman M, Alam K, Ahmad MZ, et al:
Classical to current approach for treatment of psoriasis: a review.
Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 12:287–302. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fusenig NE and Boukamp P: Multiple stages
and genetic alterations in immortalization, malignant
transformation, and tumor progression of human skin keratinocytes.
Mol Carcinog. 23:144–158. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stein M, Bernd A, Ramirez-Bosca A,
Kippenberger S and Holzmann H: Measurement of anti-inflammatory
effects of glucocorticoids on human keratinocytes in vitro.
Comparison of normal human keratinocytes with the keratinocyte cell
line HaCaT. Arzneimittelforschung. 47:1266–1270. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Müller K and Prinz H: Antipsoriatic
anthrones with modulated redox properties. 4. Synthesis and
biological activity of novel 9,
10-dihydro-1,8-dihydroxy-9-oxo-2-anthracenecarboxylic and
-hydroxamic acids. J Med Chem. 40:2780–2787. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Caning D and Hardie
DG: AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1:15–25.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Witters LA: The blooming of the French
lilac. J Clin Invest. 108:1105–1107. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang ZJ, Zheng ZJ, Shi R, Su Q, Jiang Q
and Kip KE: Metformin for liver cancer prevention in patients with
type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 97:2347–2353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Buzzai M, Jones RG, Amaravadi RK, Lum JJ,
DeBerardinis RJ, Zhao F, Viollet B and Thompson CB: Systemic
treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs
p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 67:6745–6752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ben Sahra I, Laurent K, Loubat A, et al:
The antidiabetic drug metformin exerts an antitumoral effect in
vitro and in vivo through a decrease of cyclin D1 level. Oncogene.
27:3576–3586. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dowling RJ, Zakikhani M, Fantus IG, Pollak
M and Sonenberg N: Metformin inhibits mammalian target of
rapamycin-dependent translation initiation in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 67:10804–10812. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Hattmann L and Shridhar
V: Metformin attenuates ovarian cancer cell growth in an AMP-kinase
dispensable manner. J Cell Mol Med. 15:166–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG,
Sonenberg N and Pollak M: Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent
growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:10269–10273. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bosch M, Gil J, Bachs O and Agell N:
Calmodulin inhibitor W13 induces sustained activation of ERK2 and
expression of p21(cip1). J Biol Chem. 273:22145–22150. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Zeng Y, Ji Y and Xing F: Two-sided
effect of ERK signal pathway on HaCaT cell proliferation induced by
EGF. Basic & Clinical Medicine. 26:471–475. 2006.(In
Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Pumiglia KM and Decker SJ: Cell cycle
arrest mediated by the MEK/mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:448–452. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Z, Zhang B, Wang M and Carr BI:
Persistent ERK phosphorylation negatively regulates cAMP response
element-binding (CREB) activity via recruitment of CREB-binding
protein to pp90RSK. J Biol Chem. 278:11138–11144. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, et al: ERK
activation mediates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA
damage independently of p53. J Biol Chem. 277:12710–12717. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|