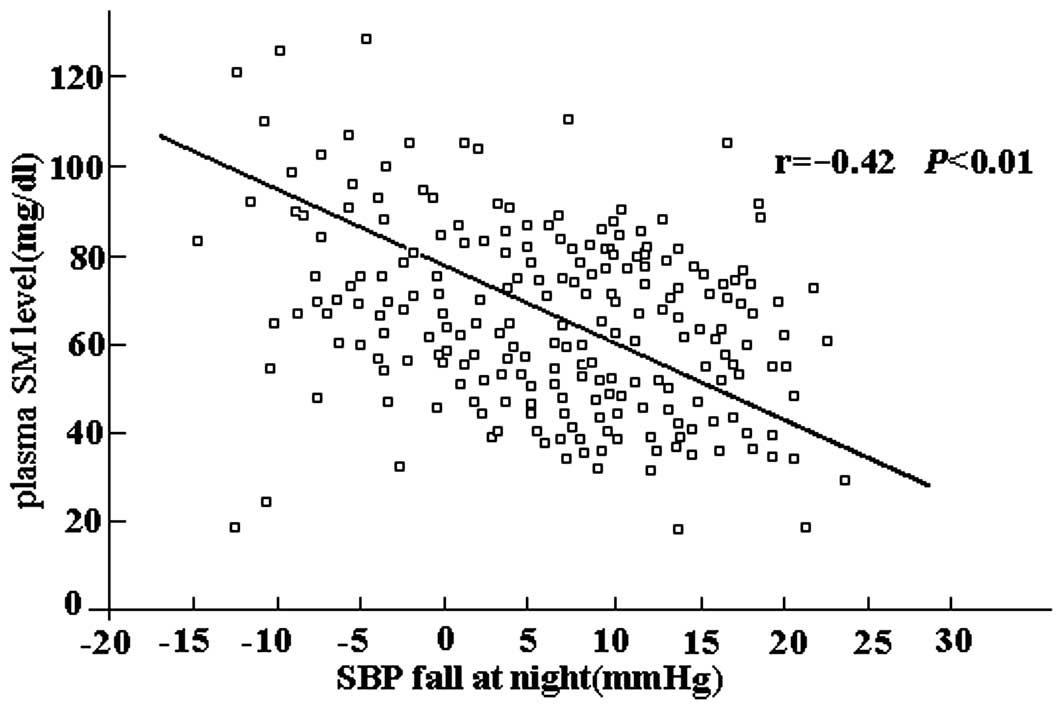
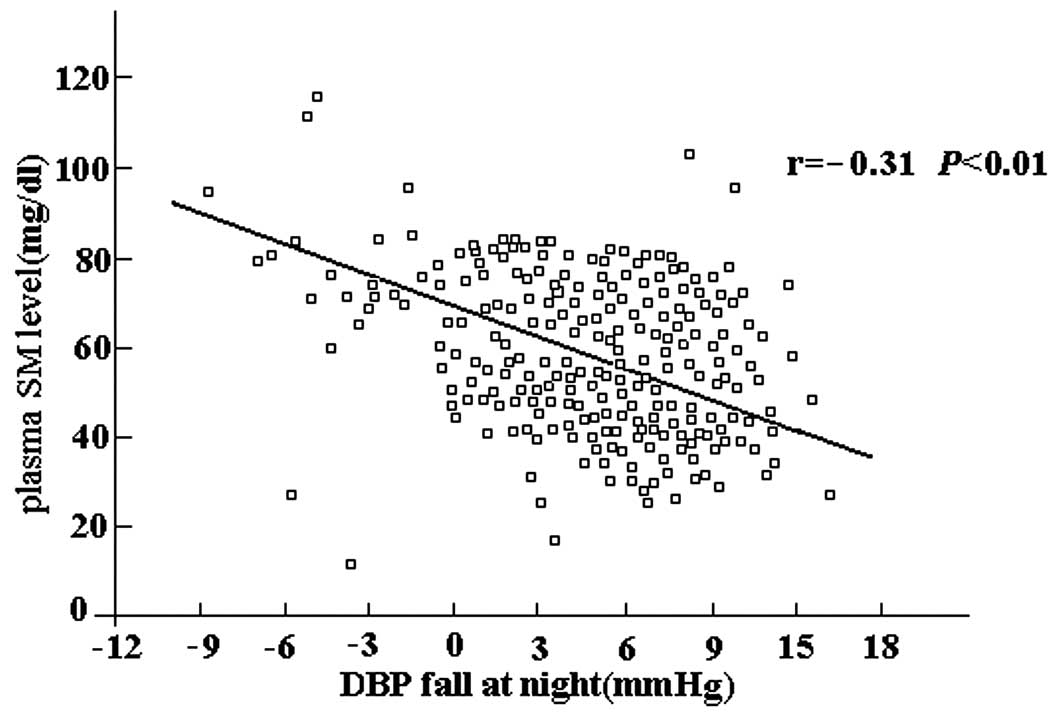
|
1
|
Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V and Deray G:
Abnormal blood pressure circadian rhythm: a target organ damage?
Int J Cardiol. 107:343–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Della Mea P, Lupia M, Bandolin V, et al:
Adiponectin, insulin resistance, and left ventricular structure in
dipper and nondipper essential hypertensive patients. Am J
Hypertens. 18:30–35. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kanbay M, Isik B, Akcay A, et al: Relation
between serum calcium, phosphate, parathyroid hormone and
‘nondipper’ circadian blood pressure variability profile in
patients with normal renal function. Am J Nephrol. 27:516–521.
2007.
|
|
4
|
Ordu S, Ozhan H, Alemdar R, et al:
Cystatin C levels in patients with dipper and nondipper
hypertension. J Investig Med. 60:676–679. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brown DA and London E: Structure and
function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J
Biol Chem. 275:17221–17224. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nelson JC, Jiang XC, Tabas I, Tall A and
Shea S: Plasma sphingomyelin and subclinical atherosclerosis:
findings from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. Am J
Epidemiol. 163:903–912. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang XC, Paultre F, Pearson TA, et al:
Plasma sphingomyelin level as a risk factor for coronary artery
disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:2614–2618. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kirkendall WM, Feinleib M, Freis ED and
Mark AL: Recommendations for human blood pressure determination by
sphygmomanometers. Subcommittee of the AHA Postgraduate Education
Committee. Circulation. 62:1146A–1155A. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mielke MM, Haughey NJ, Bandaru VV, et al:
Plasma sphingomyelins are associated with cognitive progression in
Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 27:259–269. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Devereux RB, Alonso DR, Lutas EM, et al:
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular hypertrophy:
comparison to necropsy findings. Am J Cardiol. 57:450–458. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Otterstad JE, Froeland G, St John Sutton M
and Holme I: Accuracy and reproducibility of biplane
two-dimensional echocardiographic measurements of left
ventriculardimensions and function. Eur Heart J. 18:507–513. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kario K, Pickering TG, Matsuo T, Hoshide
S, Schwartz JE and Shimada K: Stroke prognosis and abnormal
nocturnal blood pressure falls in older hypertensives.
Hypertension. 38:852–857. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oliveras A, Armario P, Martell-Clarós N,
Ruilope LM and de la Sierra A; Spanish Society of
Hypertension-Resistant Hypertension Registry. Urinary albumin
excretion is associated with nocturnal systolic blood pressure in
resistant hypertensives. Hypertension. 57:556–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tigen K, Karaahmet T, Fotbolcu H, et al:
The influence of dipper and nondipper blood pressure patterns on
left ventricular functions in hypertensive patients: a tissue
Doppler study. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars. 37:101–106. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kumak F and Gungor H: Comparison of the
left atrial appendage flow velocities between patients with dipper
versus nondipper hypertension. Echocardiography. 29:391–396. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rizzo V, Maio FD, Campbell SV, et al: Left
ventricular function, cardiac dysrhythmias, atrial activation, and
volumes in nondipper hypertensive individuals with left ventricular
hypertrophy. Am Heart J. 139:529–536. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mann S, Altman DG, Raftery EB and
Bannister R: Circadian variation of blood pressure in autonomic
failure. Circulation. 68:477–483. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sherwood A, Routledge FS, Wohlgemuth WK,
Hinderliter AL, Kuhn CM and Blumenthal JA: Blood pressure dipping:
ethnicity, sleep quality, and sympathetic nervous system activity.
Am J Hypertens. 24:982–988. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kaya MG, Yarlioglues M, Gunebakmaz O, et
al: Platelet activation and inflammatory response in patients with
non-dipper hypertension. Atherosclerosis. 209:278–282. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ermis N, Yagmur J, Acikgoz N, et al: Serum
gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels and inflammatory activity
in patients with non-dipper hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens.
34:311–315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maio R, Perticone M, Sciacqua A, et al:
Oxidative stress impairs endothelial function in nondipper
hypertensive patients. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:85–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Anan F, Takahashi N, Ooie T, Yufu K,
Saikawa T and Yoshimatsu H: Role of insulin resistance in nondipper
essential hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res. 26:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Demir M, Günay T, Özmen G and Melek M:
Relationship between vitamin D deficiency and nondipper
hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 35:45–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hla T and Dannenberg AJ: Sphingolipid
signaling in metabolic disorders. Cell Metab. 16:420–434. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang XC, Goldberg IJ and Park TS:
Sphingolipids and cardiovascular diseases: lipoprotein metabolism,
atherosclerosis and cardiomyopathy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 721:19–39.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|