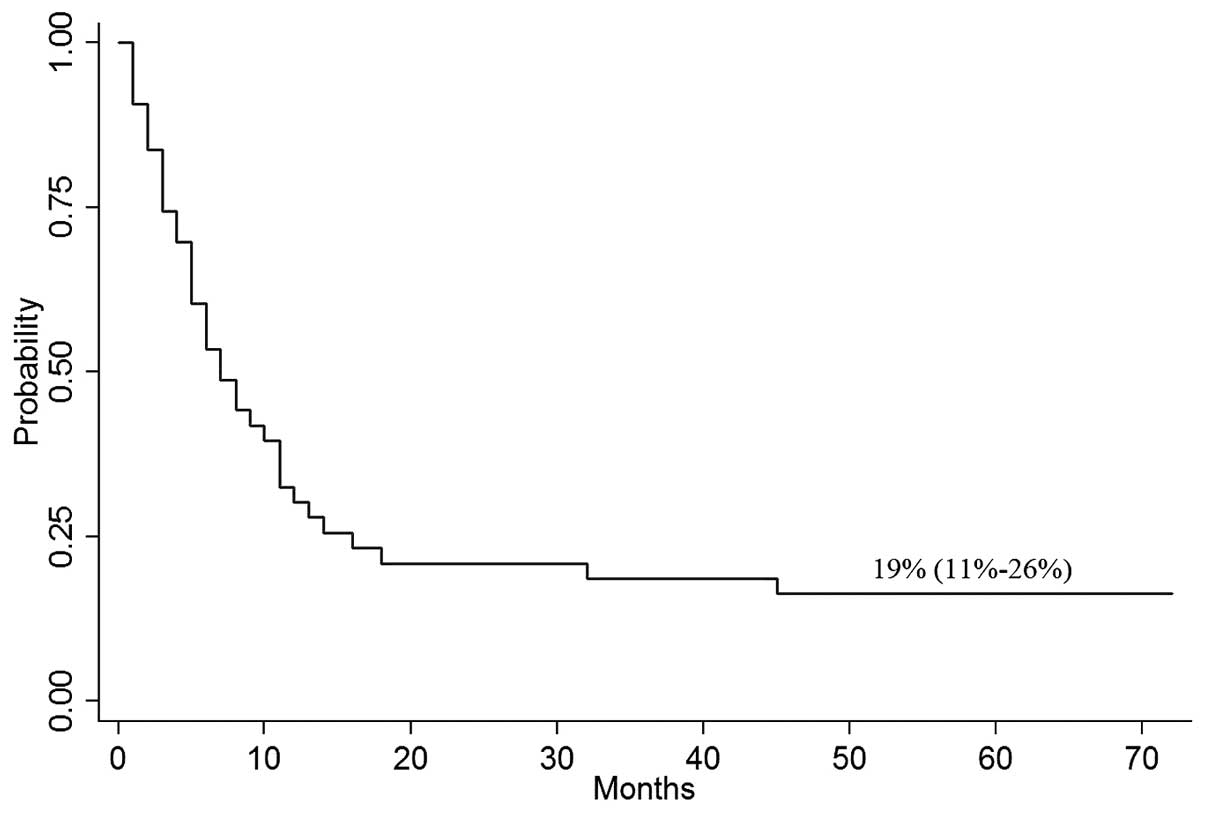
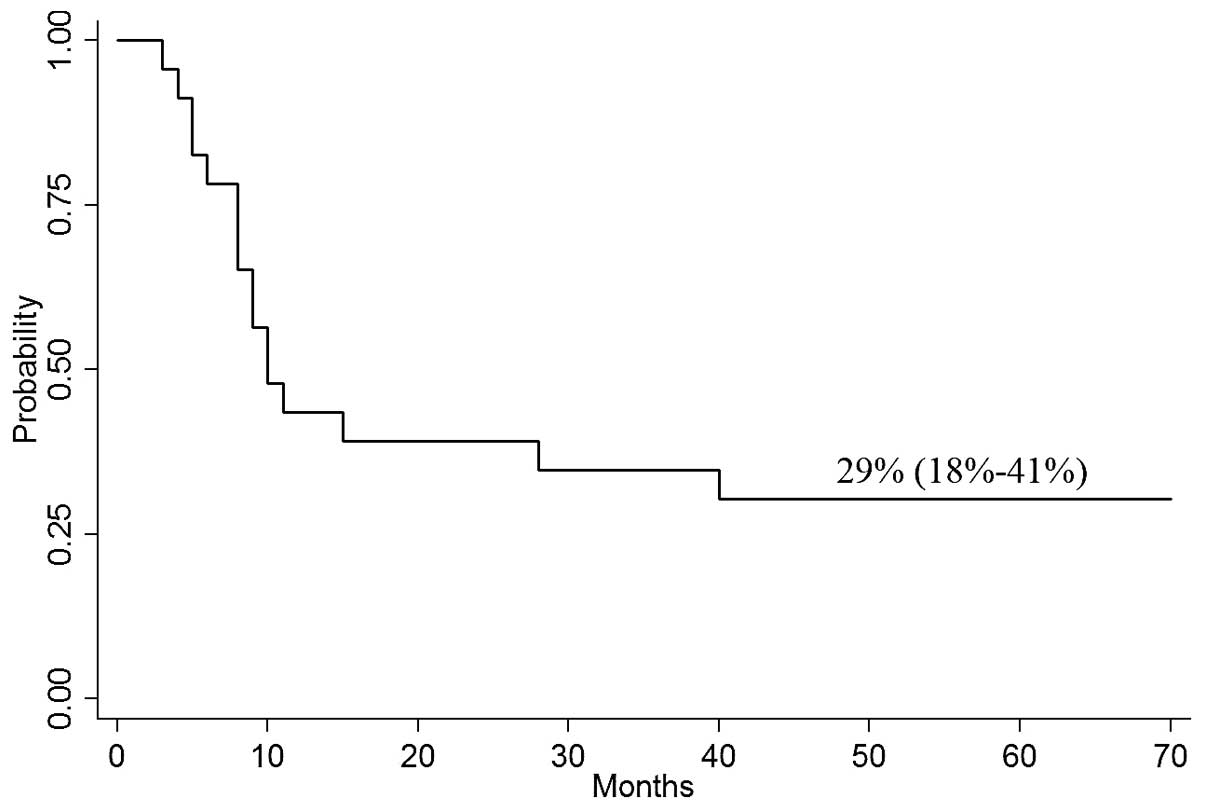
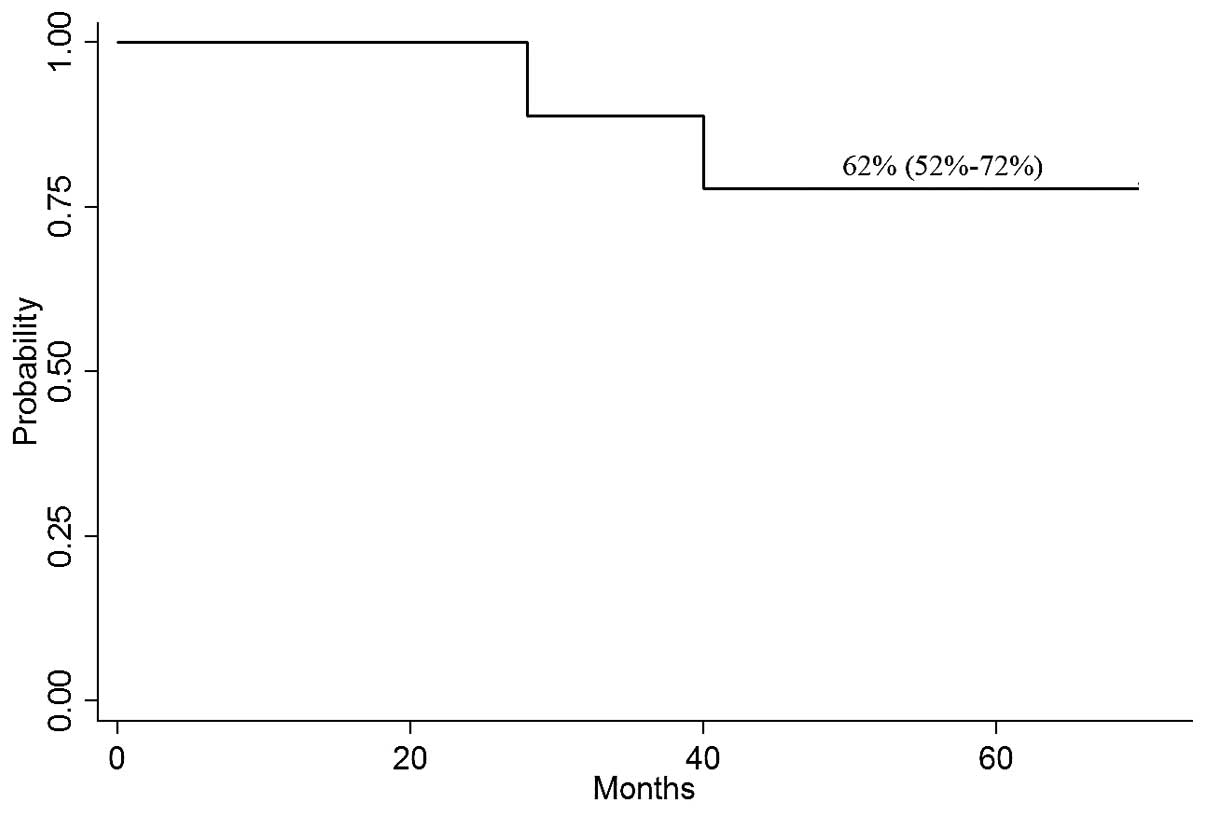
|
1.
|
Löwenberg B, Downing JR and Burnett A:
Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 341:1051–1062. 1999.
|
|
2.
|
Estey E and Döhner H: Acute myeloid
leukaemia. Lancet. 368:1894–1907. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Roboz GJ: Novel approaches to the
treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ
Program. 2011:43–50. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Gandhi V, Estey E, Keating MJ and Plunkett
W: Biochemical modulation of arabinosylcytosine for therapy of
leukemias. Leuk Lymphoma. 10:109–114. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Lee SR, Yang DH, Ahn JS, Kim YK, Lee JJ,
Choi YJ, Shin HJ, Chung JS, Cho YY, Chae YS, Kim JG, Sohn SK and
Kim HJ: The clinical outcome of FLAG chemotherapy without
idarubicin in patients with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid
leukemia. J Korean Med Sci. 24:498–503. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ferrara F, Palmieri S, Pocali B, Pollio F,
Viola A, Annunziata S, Sebastio L, Schiavone EM, Mele G,
Gianfaldoni G and Leoni F: De novo acute myeloid leukemia with
multilineage dysplasia: treatment results and prognostic evaluation
from a series of 44 patients treated with fludarabine, cytarabine
and G-CSF (FLAG). Eur J Haematol. 68:203–209. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Clavio M, Carrara P, Miglino M, Pierri I,
Canepa L, Balleari E, Gatti AM, Cerri R, Celesti L, Vallebella E,
Sessarego M, Patrone F, Ghio R, Damasio E and Gobbi M: High
efficacy of fludarabine-containing therapy (FLAG-FLANG) in poor
risk acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 81:513–520.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Hänel M, Friedrichsen K, Hänel A, Herbst
R, Morgner A, Neser S, Nicklisch M, Teich M, Ehninger G and Fiedler
F: Mito-flag as salvage therapy for relapsed and refractory acute
myeloid leukemia. Onkologie. 24:356–360. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT,
Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR and Sultan C: Proposed revised
criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report
of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med.
103:620–625. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Büchner
T, Willman CL, Estey EH, Schiffer CA, Doehner H, Tallman MS, Lister
TA, Lo-Coco F, Willemze R, Biondi A, Hiddemann W, Larson RA,
Löwenberg B, Sanz MA, Head DR, Ohno R and Bloomfield CD: Revised
recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis,
Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes and
Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid
Leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 21:4642–4649. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M and
Winkler A: Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer.
47:207–214. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Rustum YM, Slocum HK, Wang G, Bakshi D,
Kelly E, Buscaglia D, Wrzosek C, Early AP and Preisler H:
Relationship between plasma Ara-C and intracellular Ara-CTP pools
under conditions of continuous infusion and high-dose Ara-C
treatment. Med Pediatr Oncol. 10(Suppl 1): 33–43. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Kern W and Estey EH: High-dose cytosine
arabinoside in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: Review of
three randomized trials. Cancer. 107:116–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Gandhi V, Estey E, Keating MJ and Plunkett
W: Fludarabine potentiates metabolism of cytarabine in patients
with acute myelogenous leukemia during therapy. J Clin Oncol.
11:116–124. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Ossenkoppele GJ, Graveland WJ, Sonneveld
P, Daenen SM, Biesma DH, Verdonck LF, Schaafsma MR, Westveer PH,
Peters GJ, Noordhuis P, Muus P, Selleslag D, van der Holt B,
Delforge M, Löwenberg B and Verhoef GE: The value of fludarabine in
addition to ARA-C and G-CSF in the treatment of patients with
high-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and AML in elderly patients.
Blood. 103:2908–2913. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Hubeek I, Litvinova E, Peters GJ,
Broekhuizen R, Haarman EG, Huismans DR, Cloos J, Zwaan CM,
Fleischhack G, Creutzig U and Kaspers GJ: The effect of G-CSF on
the in vitro cytotoxicity of cytarabine and fludarabine in the FLAG
combination in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Oncol.
25:1823–1829. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Carella AM, Cascavilla N, Greco MM,
Melillo L, Sajeva MR, Ladogana S, D’Arena G, Perla G and Carotenuto
M: Treatment of “poor risk” acute myeloid leukemia with
fludarabine, cytarabine and G-CSF (flag regimen): a single center
study. Leuk Lymphoma. 40:295–303. 2001.
|
|
18.
|
Wang SH, Yu L, Wang QS, Li HH, Zhao Y and
Li F: Effects of FLAG protocol in treatment of the first time
induced non-remission acute myeloid leukemia. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue
Ye Xue Za Zhi. 15:1297–1299. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
19.
|
Yavuz S, Paydas S, Disel U and Sahin B:
IDA-FLAG regimen for the therapy of primary refractory and relapse
acute leukemia: a single-center experience. Am J Ther. 13:389–393.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Pastore D, Specchia G, Carluccio P, Liso
A, Mestice A, Rizzi R, Greco G, Buquicchio C and Liso V: FLAG-IDA
in the treatment of refractory/relapsed acute myeloid leukemia:
single-center experience. Ann Hematol. 82:231–235. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Feldman EJ, Seiter K, Damon L, Linker C,
Rugo H, Ries C, Case DC Jr, Beer M and Ahmed T: A randomized trial
of high- vs standard-dose mitoxantrone with cytarabine in elderly
patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 11:485–489. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Feldman EJ, Alberts DS, Arlin Z, Ahmed T,
Mittelman A, Baskind P, Peng YM, Baier M and Plezia P: Phase I
clinical and pharmacokinetic evaluation of high-dose mitoxantrone
in combination with cytarabine in patients with acute leukemia. J
Clin Oncol. 11:2002–2009. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|