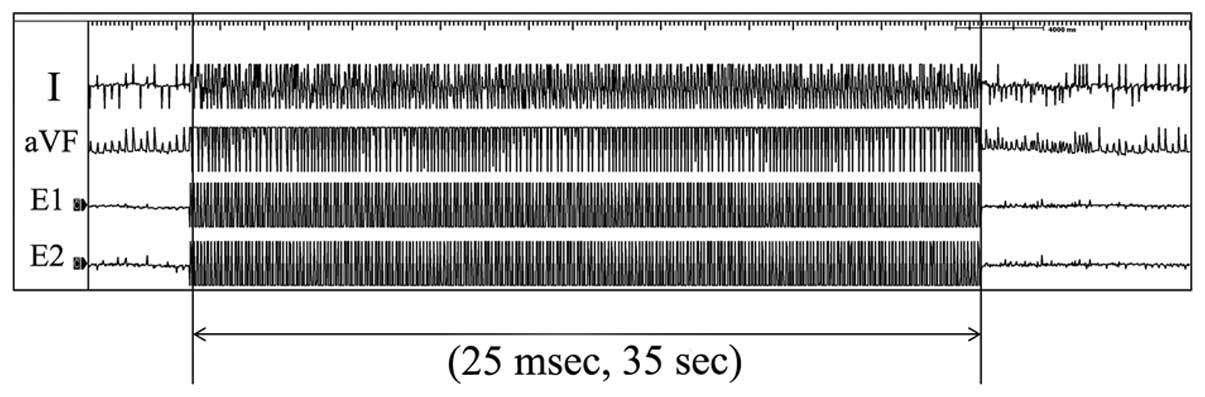
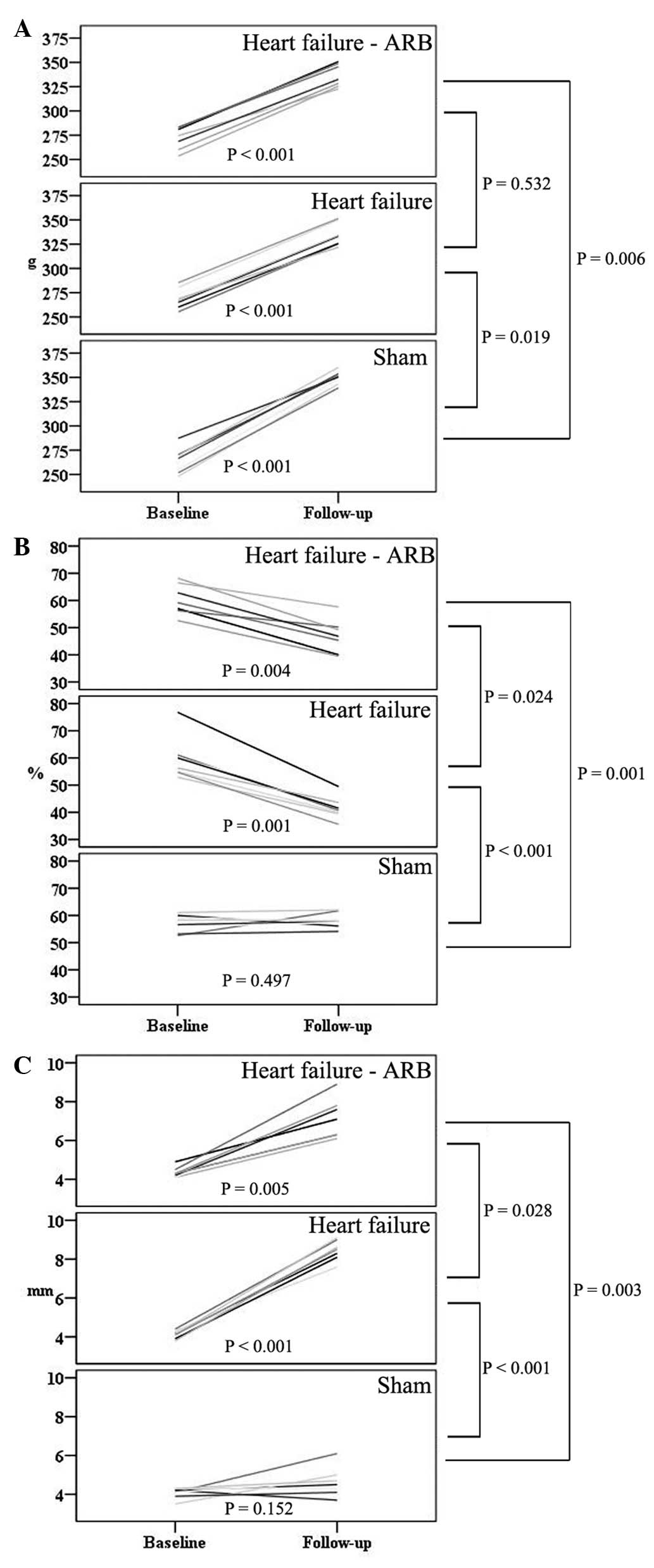
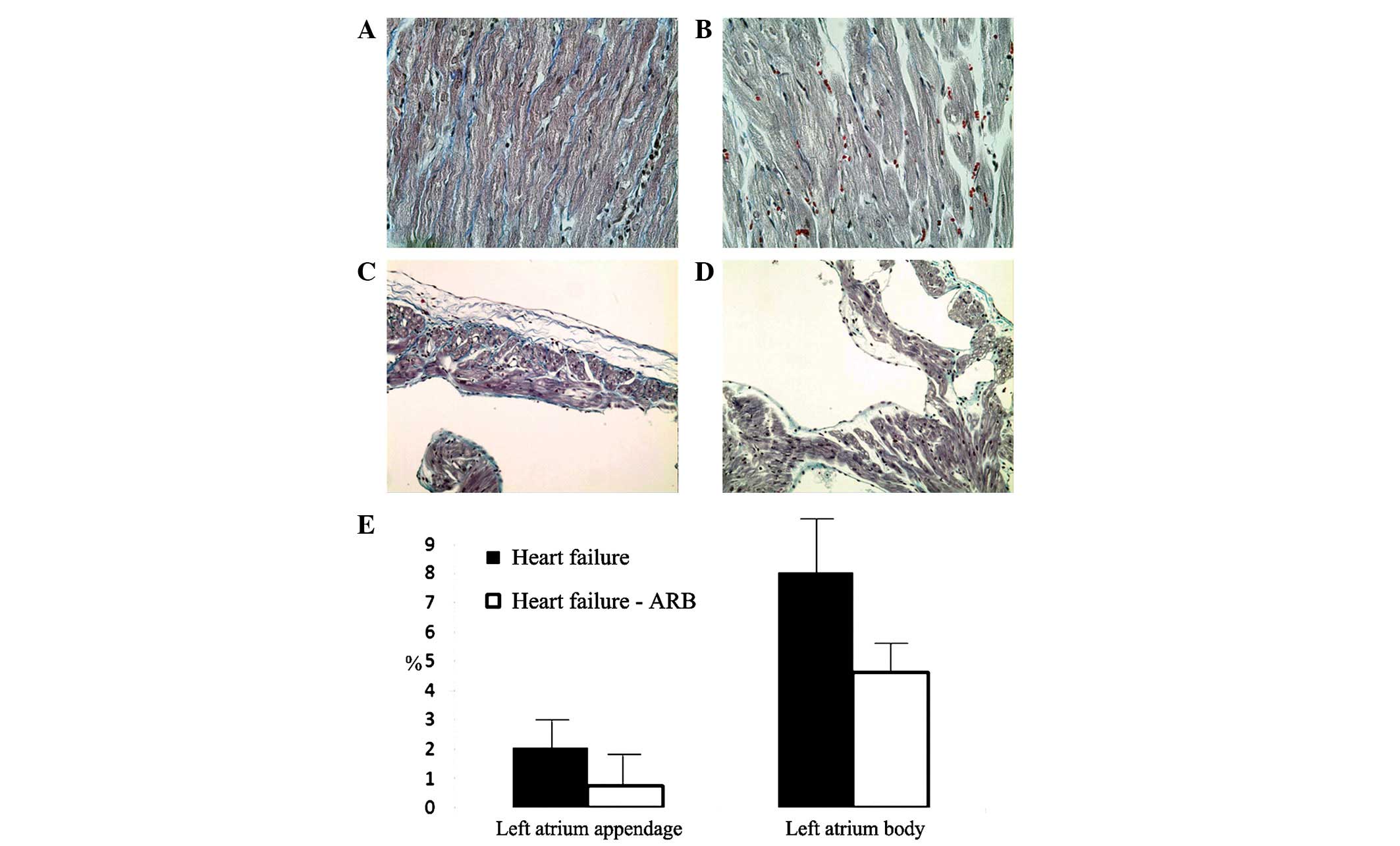
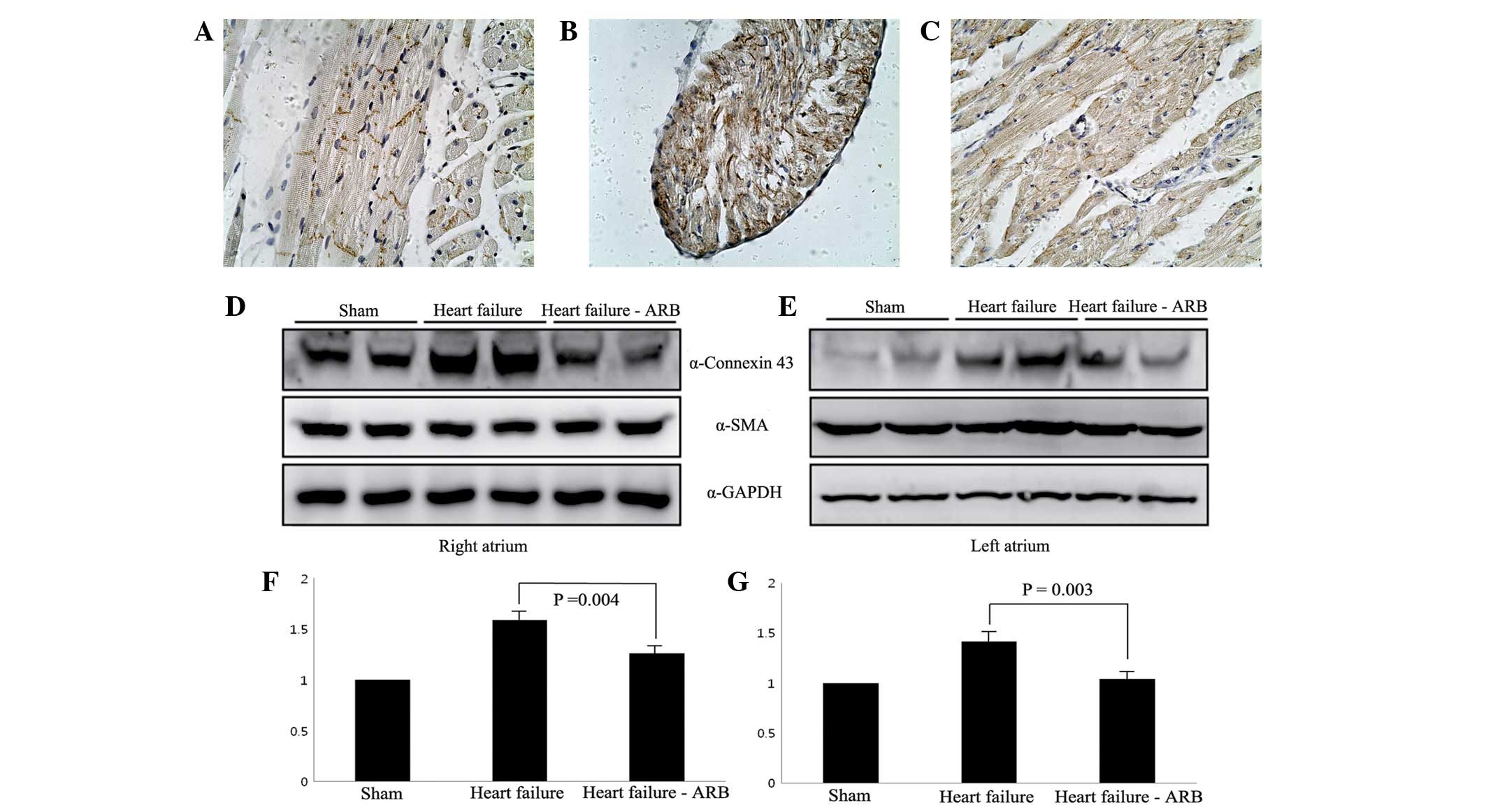
|
1
|
Kumagai K, Nakashima H, Urata H, Gondo N,
Arakawa K and Saku K: Effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor
antagonist on electrical and structural remodeling in atrial
fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 41:2197–2204. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wollert KC and Drexler H: The
kallikrein-kinin system in post-myocardial infarction cardiac
remodeling. Am J Cardiol. 80:158A–161A. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goette A, Staack T, Röcken C, et al:
Increased expression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and
angiotensin-converting enzyme in human atria during atrial
fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 35:1669–1677. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Novo G, Guttilla D, Fazio G, Cooper D and
Novo S: The role of the renin-angiotensin system in atrial
fibrillation and the therapeutic effects of ACE-Is and ARBS. Br J
Clin Pharmacol. 66:345–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boixel C, Fontaine V, Rücker-Martin C, et
al: Fibrosis of the left atria during progression of heart failure
is associated with increased matrix metalloproteinases in the rat.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 42:336–344. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ausma J, Wijffels M, Thoné F, Wouters L,
Allessie M and Borgers M: Structural changes of atrial myocardium
due to sustained atrial fibrillation in the goat. Circulation.
96:3157–3163. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li D, Fareh S, Leung TK and Nattel S:
Promotion of atrial fibrillation by heart failure in dogs: atrial
remodeling of a different sort. Circulation. 100:87–95. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dhein S: Role of connexins in atrial
fibrillation. Adv Cardiol. 42:161–174. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gollob MH: Cardiac connexins as candidate
genes for idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Curr Opin Cardiol.
21:155–158. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Daniëls MC, Keller RS and de Tombe PP:
Losartan prevents contractile dysfunction in rat myocardium after
left ventricular myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 281:H2150–H2158. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Johns TN and Olson BJ: Experimental
myocardial infarction. I. A method of coronary occlusion in small
animals. Ann Surg. 140:675–682. 1954. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jalife J: Experimental and clinical AF
mechanisms: bridging the divide. J Interv Card Electrophysiol.
9:85–92. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takeuchi S, Akita T, Takagishi Y, et al:
Disorganization of gap junction distribution in dilated atria of
patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Circ J. 70:575–582.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miyauchi Y, Zhou SM, Okuyama Y, et al:
Altered atrial electrical restitution and heterogeneous sympathetic
hyperinnervation in hearts with chronic left ventricular myocardial
infarction: implications for atrial fibrillation. Circulation.
108:360–366. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mitchell GF, Lamas GA, Vaughan DE and
Pfeffer MA: Left ventricular remodeling in the year after first
anterior myocardial infarction: a quantitative analysis of
contractile segment lengths and ventricular shape. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 19:1136–1144. 1992.
|
|
16
|
Thomas SA, Schuessler RB, Berul CI, et al:
Disparate effects of deficient expression of connexin43 on atrial
and ventricular conduction: evidence for chamber-specific molecular
determinants of conduction. Circulation. 97:686–691. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Solan JL and Lampe PD: Connexin
phosphorylation as a regulatory event linked to gap junction
channel assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1711:154–163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ai X and Pogwizd SM: Connexin 43
downregulation and dephosphorylation in nonischemic heart failure
is associated with enhanced colocalized protein phosphatase type
2A. Circ Res. 96:54–63. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Savelieva I and Camm AJ: Atrial
fibrillation and heart failure: natural history and pharmacological
treatment. Europace. 5(Suppl 1): S5–S19. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kato T, Iwasaki YK and Nattel S: Connexins
and atrial fibrillation: filling in the gaps. Circulation.
125:203–206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hoyano M, Ito M, Kimura S, et al:
Inducibility of atrial fibrillation depends not on inflammation but
on atrial structural remodeling in rat experimental autoimmune
myocarditis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 19:e149–157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reil JC, Hohl M, Selejan S, et al:
Aldosterone promotes atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J.
33:2098–2108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rucker-Martin C, Milliez P, Tan S, et al:
Chronic hemodynamic overload of the atria is an important factor
for gap junction remodeling in human and rat hearts. Cardiovasc
Res. 72:69–79. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nakashima H, Kumagai K, Urata H, Gondo N,
Ideishi M and Arakawa K: Angiotensin II antagonist prevents
electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Circulation.
101:2612–2617. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
European Heart Rhythm Association;
European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery; Camm AJ, Kirchhof
P, Lip GYH, et al: Guidelines for the management of atrial
fibrillation The Task Force for the Management of Atrial
Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Europace.
12:1360–1420. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Camm AJ, Lip GY, De Caterina R, et al:
2012 focused update of the ESC Guidelines for the management of
atrial fibrillation: an update of the 2010 ESC Guidelines for the
management of atrial fibrillation - developed with the special
contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association. Europace.
14:1385–1413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nicolosi GL, Latini R, Marino P, et al:
The prognostic value of predischarge quantitative two-dimensional
echocardiographic measurements and the effects of early lisinopril
treatment on left ventricular structure and function after acute
myocardial infarction in the GISSI-3 trial. Gruppo Italiano per lo
Studio della Sopravvivenza nell’Infarto Miocardico. Eur Heart J.
17:1646–1656. 1996.
|
|
28
|
St John Sutton M, Pfeffer MA, Plappert T,
et al: Quantitative two-dimensional echocardiographic measurements
are major predictors of adverse cardiovascular events after acute
myocardial infarction. The protective effects of captopril.
Circulation. 89:68–75. 1994.
|
|
29
|
Schieffer B, Wirger A, Meybrunn M, et al:
Comparative effects of chronic angiotensin-converting enzyme
inhibition and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on cardiac
remodeling after myocardial infarction in the rat. Circulation.
89:2273–2282. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|