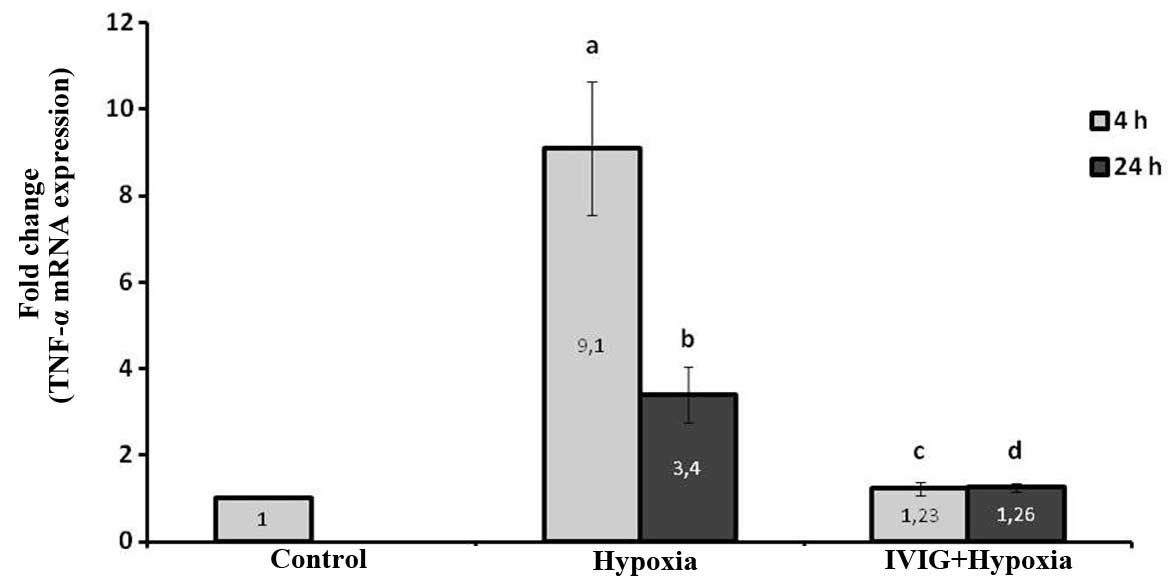
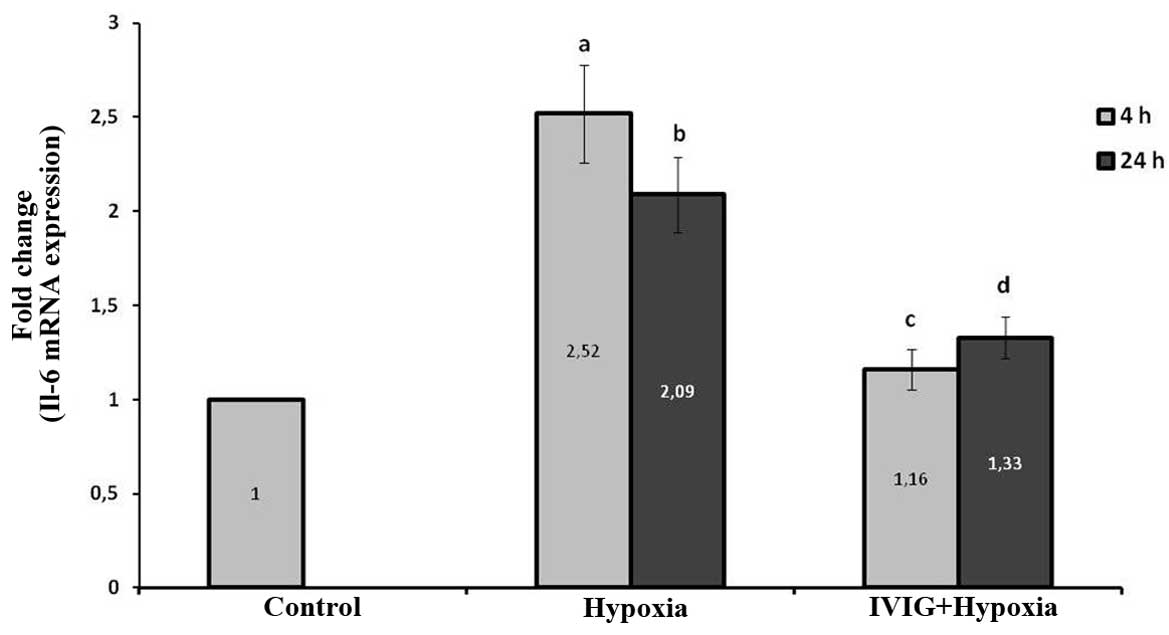
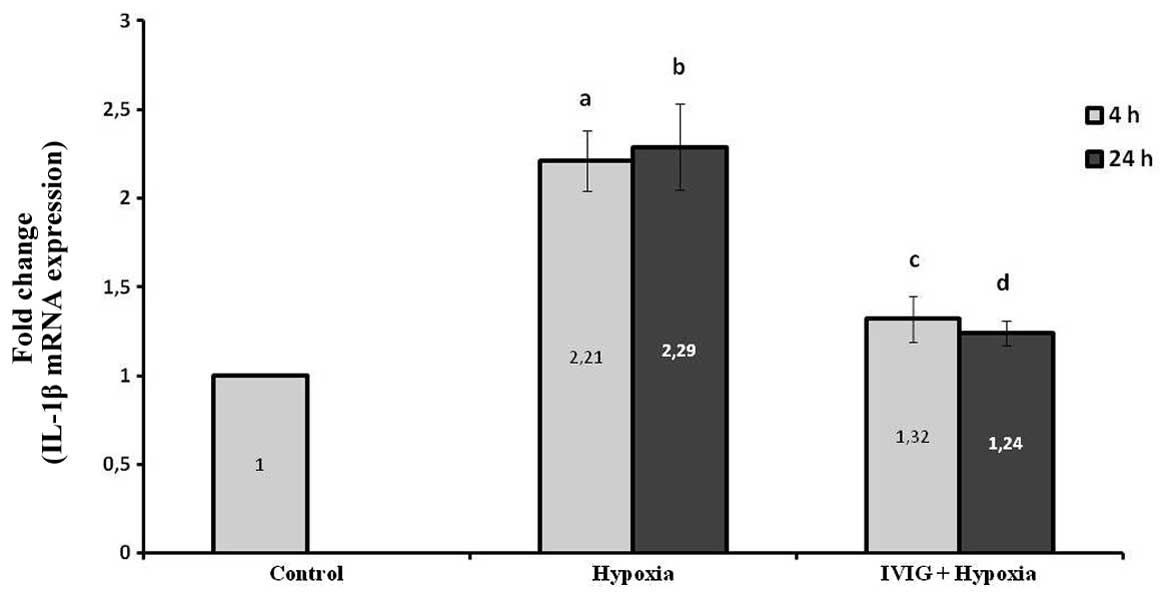
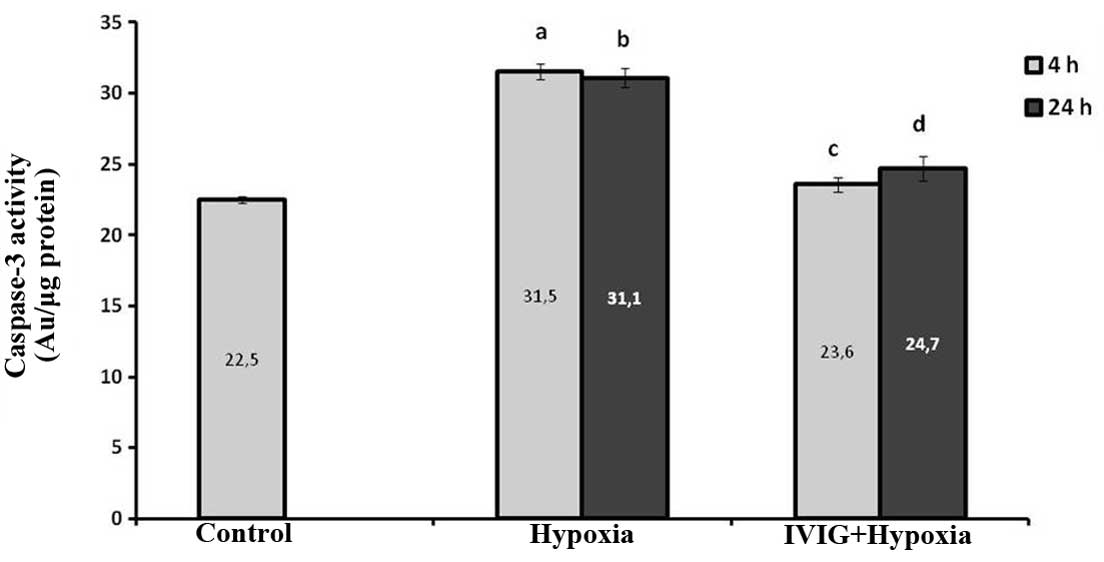
|
1
|
Volpe JJ: Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy:
clinical aspects. Neurology of the Newborn. 5th edition. WB
Saunders; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 400–480. 2008
|
|
2
|
Perlman JM: Pathogenesis of
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J Perinatol. 27:S39–S46. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kapetanakis A, Azzopardi D, Wyatt J and
Robertson NJ: Therapeutic hypothermia for neonatal encephalopathy:
a UK survey of opinion, practice and neuroinvestigation at the end
of 2007. Acta Paediatr. 98:631–635. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gluckman PD, Wyatt JS, Azzopardi D,
Ballard R, Edwards AD, Ferriero DM, et al: Selective head cooling
with mild systemic hypothermia after neonatal encephalopathy:
multicentre randomised trial. Lancet. 365:663–670. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
O'Brien FE, Iwata O, Thornton JS, De Vita
E, Sellwood MW, Iwata S, et al: Delayed whole-body cooling to 33 or
35 degrees C and the development of impaired energy generation
consequential to transient cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in the newborn
piglet. Pediatrics. 117:1549–1559. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Y, Barks JD, Xu G and Silverstein FS:
Topiramate extends the therapeutic window for hypothermia-mediated
neuroprotection after stroke in neonatal rats. Stroke.
35:1460–1465. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ma D, Hossain M, Chow A, Arshad M, Battson
RM, Sanders RD, et al: Xenon and hypothermia combine to provide
neuroprotection from neonatal asphyxia. Ann Neurol. 58:182–193.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jatana M, Singh I, Singh AK and Jenkins D:
Combination of systemic hypothermia and N-acetylcysteine attenuates
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats. Pediatr Res.
59:684–689. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kelen D and Robertson NJ: Experimental
treatments for hypoxic ischaemic encephalopathy. Early Hum Dev.
86:369–377. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Dammann O and O'Shea TM: Cytokines and
perinatal brain damage. Clin Perinatol. 35:643–663. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McAdams RM and Juul SE: The role of
cytokines and inflammatory cells in perinatal brain injury. Neurol
Res Int. 2012:5614942012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A and Hofer M:
Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches.
J Transl Med. 7:972009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Durandy A, Kaveri SV, Kuijpers TW, Basta
M, Miescher S, Ravetch JV and Rieben R: Intravenous immunoglobulins
- understanding properties and mechanisms. Clin Exp Immunol.
158(Suppl 1): 2–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Arumugam TV, Tang SC, Lathia JD, Cheng A,
Mughal MR, Chigurupati S, et al: Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
protects the brain against experimental stroke by preventing
complement-mediated neuronal cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:14104–14109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Arumugam TV, Woodruff TM, Lathia JD,
Selvaraj PK, Mattson MP and Taylor SM: Neuroprotection in stroke by
complement inhibition and immunoglobulin therapy. Neuroscience.
158:1074–1089. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kalay S, Oztekin O, Tezel G, et al: The
effects of intraperitoneal pentoxifylline treatment in rat pups
with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatr Neurol. 49:319–323.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rice JE III, Vannucci RC and Brierley JB:
The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the
rat. Ann Neurol. 9:131–141. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
VanGuilder HD, Vrana KE and Freeman WM:
Twenty-five years of quantitative PCR for gene expression analysis.
Biotechniques. 44:619–626. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Leonardo CC and Pennypacker KR:
Neuroinflammation and MMPs: potential therapeutic targets in
neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury. J Neuroinflammation. 6:132009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lai AY and Todd KG: Microglia in cerebral
ischemia: molecular actions and interactions. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 84:49–59. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yager JY: Animals models of
hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the newborn. Semin Pediatr Neurol.
11:31–46. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Northington FJ, Graham EM and Martin LJ:
Apoptosis in perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury: how important
is it and should it be inhibited? Brain Res Rev. 50:244–257. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Atici A, Bozlu G, Turhan AH, Polat A,
Nayci A, Okuyaz C and Taskinlar H: The role of trapidil on neuronal
apoptosis in neonatal rat model of hypoxic ischemic brain injury.
Early Hum Dev. 84:243–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bozlu G, Atici A, Turhan AH, Polat A,
Nayci A, Okuyaz C and Taskinlar H: Platelet-activating factor
antagonist (ABT-491) decreases neuronal apoptosis in neonatal rat
model of hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Brain Res. 1143:193–198.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Denker SP, Ji S, Dingman A, Lee SY,
Derugin N, Wendland MF and Vexler ZS: Macrophages are comprised of
resident brain microglia not infiltrating peripheral monocytes
acutely after neonatal stroke. J Neurochem. 100:893–904. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oygür N, Sönmez O, Saka O and Yeǧin O:
Predictive value of plasma and cerebrospinal fluid tumour necrosis
factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta concentrations on outcome of
full term infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Arch Dis
Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 79:F190–F193. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Foster-Barber A, Dickens B and Ferriero
DM: Human perinatal asphyxia: correlation of neonatal cytokines
with MRI and outcome. Dev Neurosci. 23:213–218. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kilpatrick L and Harris MC: Cytokines and
the inflammatory response. Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. Polin RA,
Fox WW and Fletcher J: 2nd edition. WB Saunders; Philadelphia, PA:
pp. 1967–79. 1998
|
|
29
|
Galasso JM, Wang P, Martin D and
Silverstein FS: Inhibition of TNF-alpha can attenuate or exacerbate
excitotoxic injury in neonatal rat brain. Neuroreport. 11:231–235.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen S, Yang X and Li CR: Immunoglobulin
therapy in neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Chin J
Pediatr. 3:38–42. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Dong YN, Zhang QY, Sui ZG, et al: Short
term effects of high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in
neonates with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Med J Qilu. 1:23–27.
2006.
|
|
32
|
Toungouz M, Denys CH, De Groote D and
Dupont E: In vitro inhibition of tumour necrosis factor-alpha and
interleukin-6 production by intravenous immunoglobulins. Br J
Haematol. 89:698–703. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Crow AR, Song S, Semple JW, Freedman J and
Lazarus AH: A role for IL-1 receptor antagonist or other cytokines
in the acute therapeutic effects of IVIg? Blood. 109:155–158. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|