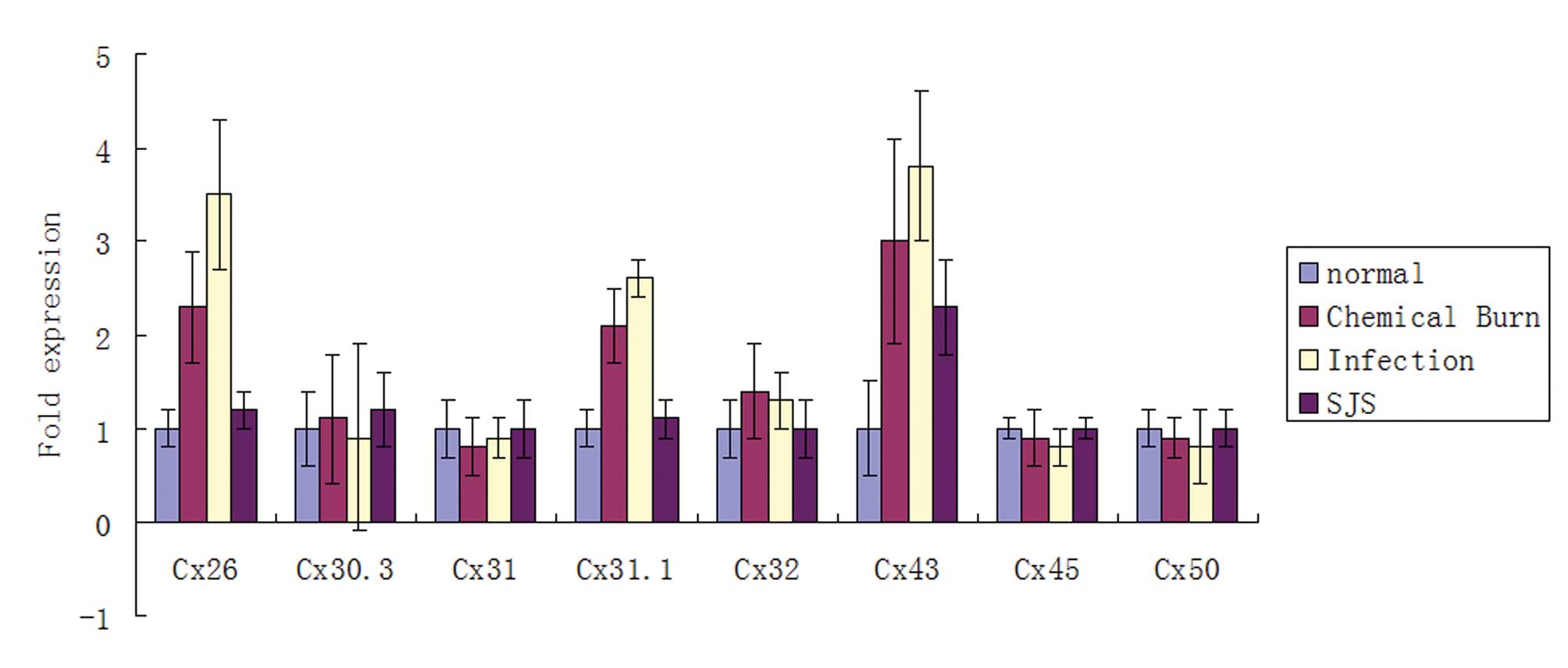
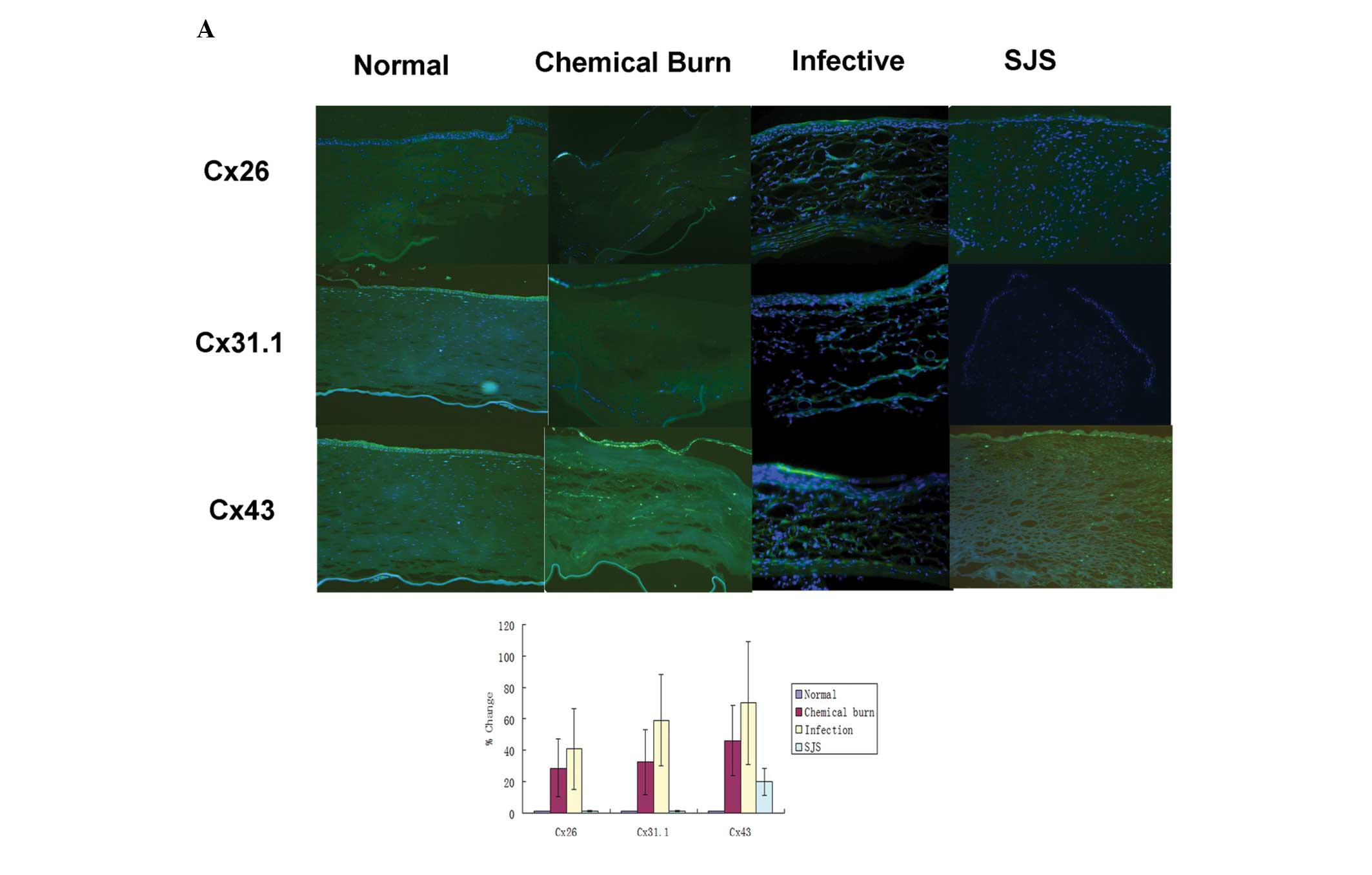
|
1
|
Cao F, Eckert R, Elfgang C, et al: A
quantitative analysis of connexin-specific permeability differences
of gap junctions expressed in HeLa transfectants and Xenopus
oocytes. J Cell Sci. 111:31–43. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kumar NM and Gilula NB: The gap junction
communication channel. Cell. 84:381–388. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yeager M and Nicholson BJ: Structure of
gap junction intercellular channels. Curr Opin Struct Biol.
6:183–192. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chin KY: Connexins, a new target in wound
treatment. J Wound Care. 20:386–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ormonde S, Chou CY, Goold L, et al:
Regulation of connexin43 gap junction protein triggers vascular
recovery and healing in human ocular persistent epithelial defect
wounds. J Membr Biol. 245:381–388. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chang CY, Laux-Fenton WT, Law LY, et al:
Antisense down regulation of connexin31.1 reduces apoptosis and
increases thickness of human and animal corneal epithelia. Cell
Biol Int. 33:376–385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hughes WF Jr: Alkali burns of the eye;
review of the literature and summary of present knowledge. Arch
Ophthal. 35:423–449. 1946. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
WF H: Alkali burns of the eye; clinical
and pathologic course. Arch Ophthal. 36:189–214. 1946. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wagoner MD: Chemical injuries of the eye:
current concepts in pathophysiology and therapy. Surv Ophthalmol.
41:275–313. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin A, Patel N, Yoo D, DeMartelaere S and
Bouchard C: Management of ocular conditions in the burn unit:
thermal and chemical burns and Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic
epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res. 32:547–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang YS, Huang FC, Tseng SH, et al:
Erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal
necrolysis: acute ocular manifestations, causes, and management.
Cornea. 26:123–129. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yip LW, Thong BY, Lim J, Tan AW, Wong HB,
Handa S and Heng WJ: Ocular manifestations and complications of
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: an Asian
series. Allergy. 62:527–531. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hynes AY, Kafkala C, Daoud YJ and Foster
CS: Controversy in the use of high-dose systemic steroids in the
acute care of patients with Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Int
Ophthalmol Clin. 45:25–48. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oliva MS, Schottman T and Gulati M:
Turning the tide of corneal blindness. Indian J Ophthalmol.
60:423–427. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kawakita T, Higa K, Shimmura S, et al:
Fate of corneal epithelial cells separated from limbus in vivo.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:8132–8137. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chan KY, Patton DL and Cosgrove YT:
Time-lapse videomicroscopic study of in vitro wound closure in
rabbit corneal cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 30:2488–2498.
1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matic M, Petrov IN, Rosenfeld T and
Wolosin JM: Alterations in connexin expression and cell
communication in healing corneal epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 38:600–609. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schlingmann B, Schadzek P, Busko S,
Heisterkamp A and Ngezahayo A: Cataract-associated D3Y mutation of
human connexin46 (hCx46) increases the dye coupling of gap junction
channels and suppresses the voltage sensitivity of hemichannels. J
Bioenerg Biomembr. 44:607–614. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Scherer SS and Kleopa KA: X-linked
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 17:9–13. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wangemann P: Supporting sensory
transduction: cochlear fluid homeostasis and the endocochlear
potential. J Physiol. 576:11–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
de Zwart-Storm EA, Rosa RF, Martin PE, et
al: Molecular analysis of connexin26 asparagine14 mutations
associated with syndromic skin phenotypes. Exp Dermatol.
20:408–412. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lorentz R, Shao Q, Huang T, Fishman GI and
Laird DW: Characterization of gap junction proteins in the bladder
of Cx43 mutant mouse models of oculodentodigital dysplasia. J Membr
Biol. 245:345–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gomes P, Srinivas SP, Van Driessche W,
Vereecke J and Himpens B: ATP release through connexin hemichannels
in corneal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
46:1208–1218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan X, Chen Z, Yang Z, et al: Expression
pattern of connexins in the corneal and limbal epithelium of a
primate. Cornea. 28:194–199. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Laux-Fenton WT, Donaldson PJ, Kistler J
and Green CR: Connexin expression patterns in the rat cornea:
molecular evidence for communication compartments. Cornea.
22:457–464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dong Y, Roos M, Gruijters T, et al:
Differential expression of two gap junction proteins in corneal
epithelium. Eur J Cell Biol. 64:95–100. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Spanakis SG, Petridou S and Masur SK:
Functional gap junctions in corneal fibroblasts and myofibroblasts.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 39:1320–1328. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matic M, Petrov IN, Chen S, et al: Stem
cells of the corneal epithelium lacks connexins and metabolite
transfer capacity. Differentiation. 61:251–260. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wolosin JM, Budak MT and Akinci MA: Ocular
surface epithelial and stem cell development. Int J Dev Biol.
48:981–991. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ratkay-Traub I, Hopp B, Bor Z, et al:
Regeneration of rabbit cornea following excimer laser
photorefractive keratectomy: a study on gap junctions, epithelial
junctions and epidermal growth factor receptor expression in
correlation with cell proliferation. Exp Eye Res. 73:291–302. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Laux-Fenton W: The role of connexins in
corneal homeostasis and repair: mastering the connections to
improve repair (PhD thesis). University of Auckland; Auckland, New
Zealand: 2003
|
|
32
|
Grupcheva CN, Laux WT, Rupenthal ID,
McGhee J, McGhee CN and Green CR: Improved corneal wound healing
through modulation of gap junction communication using
connexin43-specific antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:1130–1138. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Oviedo-Orta E and Howard Evans W: Gap
junctions and connexin-mediated communication in the immune system.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1662:102–112. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vera LS, Gueudry J, Delcampe A, et al: In
vivo confocal microscopic evaluation of corneal changes in chronic
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Cornea.
28:401–407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
No authors listed. Gap junction-mediated
intercellular signalling in health and disease. In: Proceedings of
a meeting; London, United Kingdom. 2–5 March 1998; Novartis Found
Symp. 219. pp. 1–284. 1999
|
|
36
|
Harris AL: Emerging issues of connexin
channels: biophysics fills the gap. Q Rev Biophys. 34:325–472.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Laux-Fenton WT, Donaldson PJ, Kistler J
and Green CR: Connexin expression patterns in the rat cornea:
molecular evidence for communication compartments. Cornea.
22:457–464. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Coutinho P, Qiu C, Frank S, Tamber K and
Becker D: Dynamic changes in connexin expression correlate with key
events in the wound healing process. Cell Biol Int. 27:525–541.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Goliger JA and Paul DL: Wounding alters
epidermal connexin expression and gap junction-mediated
intercellular communication. Mol Biol Cell. 6:1491–1501. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wilson SE: Corneal myofibroblast biology
and pathobiology: generation, persistence, and transparency. Exp
Eye Res. 99:78–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Coutinho P, Qiu C, Frank S, et al:
Limiting burn extension by transient inhibition of Connexin43
expression at the site of injury. Br J Plast Surg. 58:658–667.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Djalilian AR, McGaughey D, Patel S, Seo
EY, Yang C, Cheng J, Tomic M, Sinha S, Ishida-Yamamoto A and Segre
JA: Connexin 26 regulates epidermal barrier and wound remodeling
and promotes psoriasiform response. J Clin Invest. 116:1243–1253.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
de Zwart-Storm EA, Rosa RF, Martin PE,
Foelster-Holst R, Frank J, Bau AE, Zen PR, Graziadio C, Paskulin
GA, Kamps MA, van Geel M and van Steensel MA: Molecular analysis of
connexin26 asparagine14 mutations associated with syndromic skin
phenotypes. Exp Dermatol. 20:408–412. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|