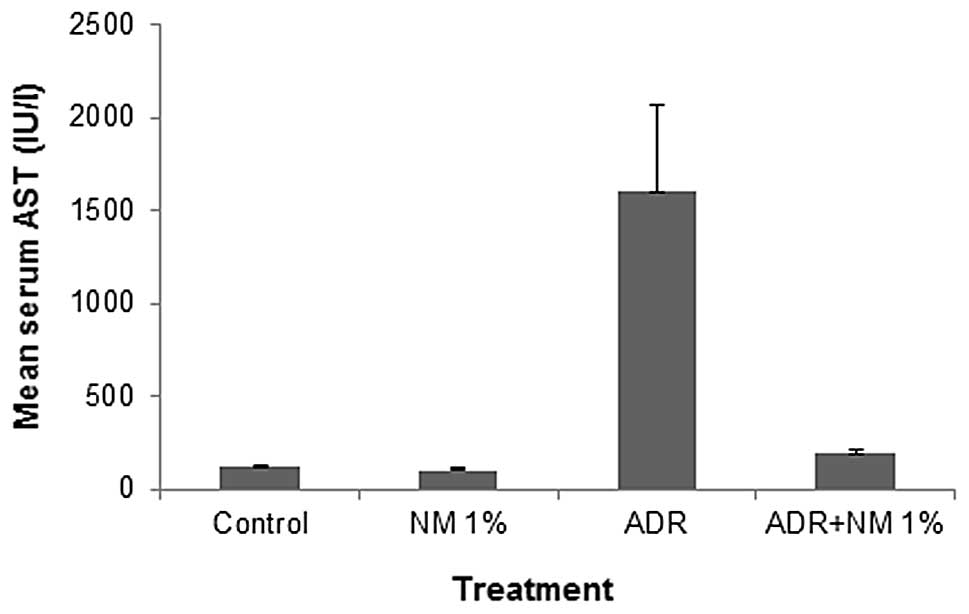
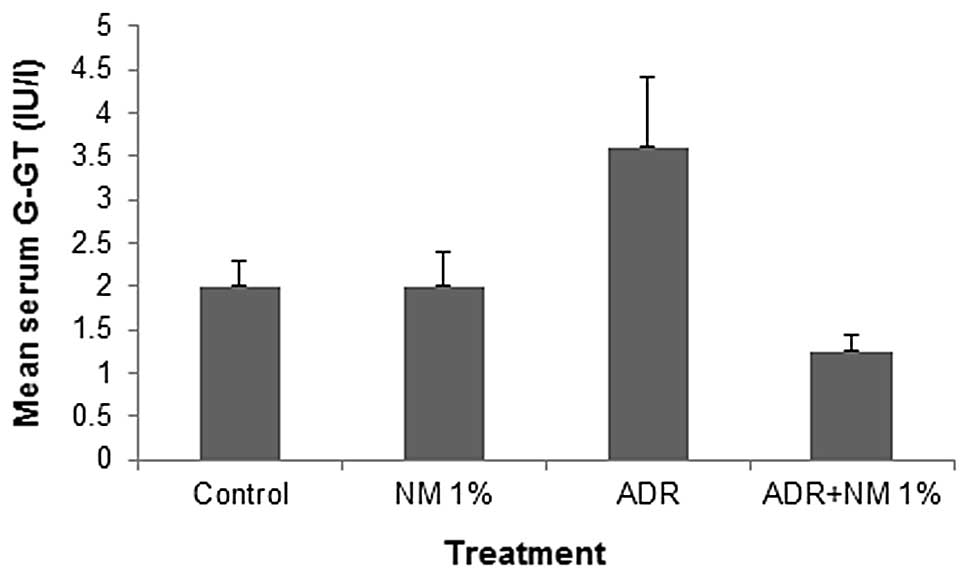
|
1
|
Saad SY, Najjar TA and Al-Rikabi AC: The
preventive role of deferoxamine against acute doxorubicin-induced
cardiac, renal and hepatic toxicity in rats. Pharmacol Res.
43:211–218. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeGraff W, Hahn SM, Mitchell JB and
Krishna MC: Free radical modes of cytotoxicity of adriamycin and
streptonigrin. Biochem Pharmacol. 48:1427–1435. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Poli G: Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis:
role of oxidative stress. Mol Aspects Med. 21:49–98. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Loguercio C and Federico A: Oxidative
stress in viral and alcoholic hepatitis. Free Radic Biol Med.
34:1–10. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen Y, Jungsuwadee P, Vore M, Butterfield
DA and St Clair DK: Collateral damage in cancer chemotherapy:
oxidative stress in nontargeted tissues. Mol Interv. 7:147–156.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Essick EE and Sam F: Oxidative stress and
autophagy in cardiac disease, neurological disorders, aging and
cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:168–177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feng YQ, Zuo XL, Li RF, Zhang KJ, Chen F
and Xiao H: Protection against doxorubicin-induced oxidative damage
in normal blood cells by naringenin. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za
Zhi. 16:790–793. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Kasapović J, Pejić S, Stojiljković V,
Todorović A, Radošević-Jelić L, Saičić ZS and Pajović SB:
Antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in the blood of breast
cancer patients of different ages after chemotherapy with
5-fluorouracil, doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide. Clin Biochem.
43:1287–1293. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bouayed J and Bohn T: Exogenous
antioxidants - double-edged swords in cellular redox state: Health
beneficial effects at physiologic doses versus deleterious effects
at high doses. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:228–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Alshabanah OA, Hafez MM, Al-Harbi MM,
Hassan ZK, Al Rejaie SS, Asiri YA and Sayed-Ahmed MM: Doxorubicin
toxicity can be ameliorated during antioxidant L-carnitine
supplementation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 3:428–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Venkatesan N, Punithavathi D and Arumugam
V: Curcumin prevents adriamycin nephrotoxicity in rats. Br J
Pharmacol. 129:231–234. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Niedzwiecki A, Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T and
Rath M: Micronutrient synergy – a new tool in effective control of
metastasis and other key mechanisms of cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 29:529–542. 2010.
|
|
13
|
Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Ivanov V, Rath M
and Niedzwiecki A: A nutrient mixture prevents acetaminophen
hepatic and renal toxicity in ICR mice. Hum Exp Toxicol.
27:223–230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Roomi M, Kalinovsky T, Roomi NW, Ivanov V,
Rath M and Niedzwiecki A: A nutrient mixture suppresses carbon
tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic toxicity in ICR mice. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 27:559–566. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Andreadou I, Sigala F, Iliodromitis EK,
Papaefthimiou M, Sigalas C, Aligiannis N, Savvari P, Gorgoulis V,
Papalabros E and Kremastinos DT: Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity
is successfully treated with the phytochemical oleuropein through
suppression of oxidative and nitrosative stress. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 42:549–558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Granados-Principal S, Quiles JL,
Ramirez-Tortosa CL, Sanchez-Rovira P and Ramirez-Tortosa MC: New
advances in molecular mechanisms and the prevention of adriamycin
toxicity by antioxidant nutrients. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:1425–1438.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shimpo K, Nagatsu T, Yamada K, Sato T,
Niimi H, Shamoto M, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H and Fujita K: Ascorbic
acid and adriamycin toxicity. Am J Clin Nutr. 54(6 Suppl):
1298S–1301S. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Doroshow JH, Locker GY, Ifrim I and Myers
CE: Prevention of doxorubicin cardiac toxicity in the mouse by
N-acetylcysteine. J Clin Invest. 68:1053–1064. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen JH, Tipoe GL, Liong EC, So HS, Leung
KM, Tom WM, Fung PC and Nanji AA: Green tea polyphenols prevent
toxin-induced hepatotoxicity in mice by down-regulating inducible
nitric oxide-derived prooxidants. Am J Clin Nutr. 80:742–751.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hasegawa R, Chujo T, Sai-Kato K, Umemura
T, Tanimura A and Kurokawa Y: Preventive effects of green tea
against liver oxidative DNA damage and hepatotoxicity in rats
treated with 2-nitropropane. Food Chem Toxicol. 33:961–970. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Patil LJ, Bothara SB and Balaraman R:
Effect of chronic administration of green tea extract on chemically
induced electrocardiographic and biochemical changes in rat heart.
Int J Green Pharm. 4:170–173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath
M and Niedzwiecki A: Comparative effects of EGCG, green tea and a
nutrient mixture on the patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in
cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 24:747–757. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|